CQS implementation using NodeJS, NestJS Typescript and Sequelize ORM.
The example implements a deposit and an withdraw command and a query to list all operations made in a given account.
- Clone the repository
- Copy .env.example and save a .env file with the correct values
- Enter each app folder (cd backend / cd frontend) and run:
npm installnpm run build(only backend)npm start
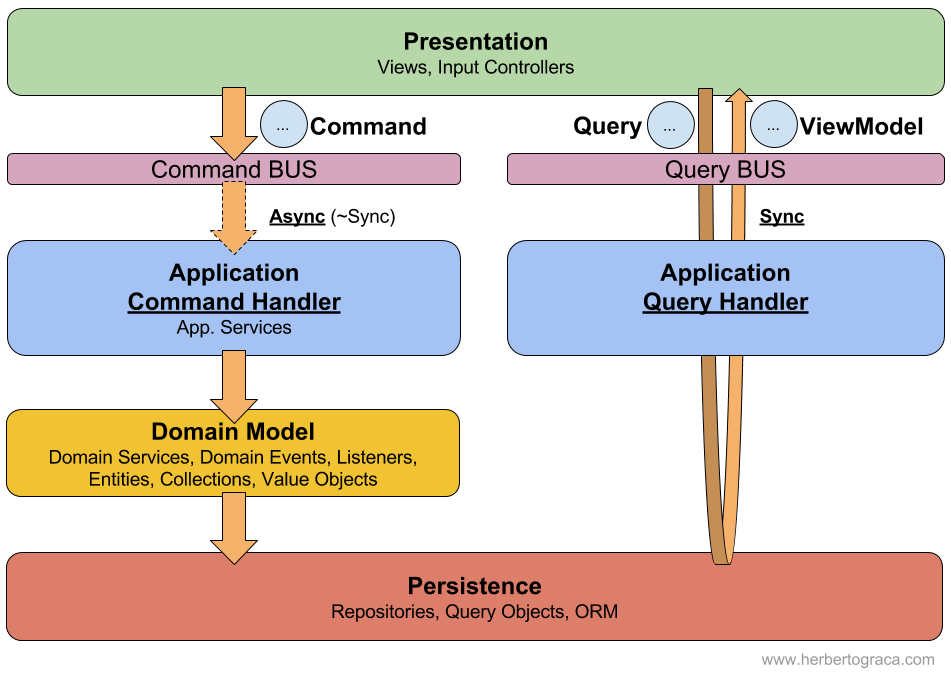
CQS - Command Query Separation (by Bertrand Meyer), is a programming pattern that separates the logic of a program into commands (change the state of the system) and queries (Return a result without making any changes to the system). The persistance remains the same for both write and reading, focusing the separations at a class level.
- Helps archiving the Single Responsibility Principle (Separation of Concerns)
- Code for mutating and reading data is separated, letting you focus on a single goal.
- Helps to break down complex business flows with events and event handlers
- It can be hard to organize, since you can have a lot of queries and commands in a big and complex application.
I will describe below the DepositCommand and the ListAccountOperationsQuery process flows
- Controller: Account Controller
- Aggregate: AccountOperation
- deposit()
- withdraw()
- creditBalance(amount: number)
- debitBalance(amount: number)
- Aggregate: Account
- Deposit Command
- Deposit Command Handler
- Deposited Event
- Deposited Event Handler
- AccountOperationRepository
Steps:
- The Request is received by the controller > controller calls the commandBus (new DepositCommand)
- The Deposit handler that subscribed to the (DepositCommand) starts its execution (new AccountOperation).
- The aggregate root executes its logic (accountOperation.deposit()) and define the Event that will be fired when its commited (new DepositedEvent).
- The aggregate root is saved using a repository (AccountOperationRepository.saveAccountOperation).
- the aggregate root is commited (accountOperation.commit) and the event is fired. The controller will now return its response.
- The event handlers observing the fired event will execute their logic (DepositedEventHandler).
- This happens asynchronously and doesn't return any value to the interface. Because of that, you must have compensating events to handle errors.
- Operation is completed.
- ListAccountOperationsQuery
- ListAccountOperationsQueryHandler
- ListAccountOperationsResult
Steps:
- The Request is received by the controller > controller calls the queryBus (new ListAccountOperationsQuery)
- The ListAccountOperationsQueryHandler that subscribed to the (ListAccountOperationsQuery) starts its execution.
- The data is queried form the persistance (accountOperationQuery.listAccountOperations).
- The data is returned to the user according to the type defined (ListAccountOperationsResult.Factory).
- Operation is completed.
CQS (Command Query Separation) is not CQRS (Command Query Responsibility Segregation). The CQRS is derived from CQS. You can read more about it here: https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/architecture/patterns/cqrs
Make the data validation before dispatching the command / query
The command handler can be sync if you need to wait all operations to take place before dispatching the event. Depending on your use-case, you can even call another commands. Commands can return error messages, exceptions or any other data necessary to the usercase (if the used data can be queried later, ex: an ID)
The event handler is asynchronous and you must have compensating events to handle errors.
The entity can validate domain rules (ex: user should have enough ballance to make a withdraw)
Its a practice focused application. Everything was done to simulate scenarios where i could use the technologies proposed.
Some objects only exists for this reason and they haven't receive a lot of love, since it would increase the complexity and time where it dosent matter for this training purpose.