Identify Fraud from Enron Email
Project Overview
This project is about using machine learning techniques to indetify persons of interest (POIs) in the Enron dataset. "In 2000, Enron was one of the largest companies in the United States. By 2002, it had collapsed into bankruptcy due to widespread corporate fraud. In the resulting Federal investigation, a significant amount of typically confidential information entered into the public record, including tens of thousands of emails and detailed financial data for top executives." This data will be used in this project to build a person of interest indentifier.
Dataset Exploration
General
The dataset provided by Udacity contains 144 rows (persons) and 21 columns (features). We got dataset that includes way more non-POI's than POI's (12,5% or 18 POIs), which needs to be considered when evaluating the classification algos. If an algo such as POI = False would be deployed the accuracy would already be at 87.5%, but precision at 0%.
Missing Data
Another important note about the dataset is the amount of missing data points which make some of those features not usable in the classifier. Most extreme is loan advanves with 96% of values missing:
| feature | missing values | % missing |
|---|---|---|
| loan_advances | 139 | 0.965278 |
| director_fees | 128 | 0.888889 |
| restricted_stock_deferred | 127 | 0.881944 |
| deferral_payments | 105 | 0.729167 |
| deferred_income | 94 | 0.652778 |
| long_term_incentive | 77 | 0.534722 |
| bonus | 61 | 0.423611 |
| to_messages | 58 | 0.402778 |
| shared_receipt_with_poi | 58 | 0.402778 |
| from_this_person_to_poi | 58 | 0.402778 |
| from_poi_to_this_person | 58 | 0.402778 |
| from_messages | 58 | 0.402778 |
| other | 52 | 0.361111 |
| expenses | 48 | 0.333333 |
| salary | 48 | 0.333333 |
| exercised_stock_options | 43 | 0.298611 |
| restricted_stock | 34 | 0.236111 |
| total_payments | 21 | 0.145833 |
| total_stock_value | 18 | 0.125000 |
Outliers
There were a four outliers of which two are still included in this dataset. The ones removed were TOTAL and TRAVEL AGENCY IN THE PARK, which are both no natural persons. The ones still inclueded are SKILLING JEFFREY K as well as LAY KENNETH L which have very high payments but were in the center of the fraud and should be included. Also there were two parsing mistakes that needed to be fixed.
Feature selection
Feature engineering
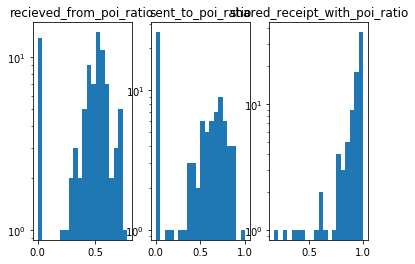
The first hypothesis that came into my mind when thinking about POI identification was: People that interacted a lot with POIs might be POIs as well. There are three measurable interactions with POIs in the dataset: sending, recieving emails as well as sharing a reciept with a POI. So I translated those interactions into ratios of total emails/receipts to know the relative amount of interactions that were done with POIs. While the email ratios are normal distributed the reciept ratio is skewed:
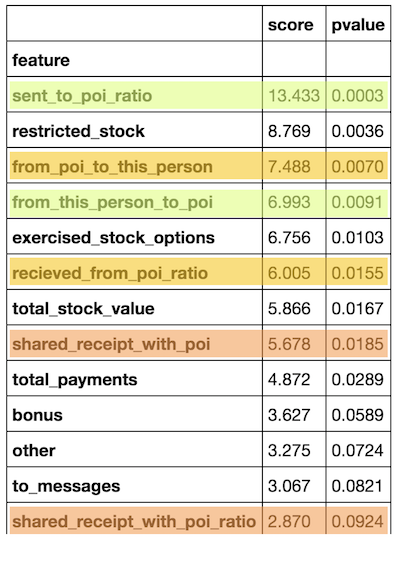
When analysing the impact of those new features compared to their original ones using K-best, sent_to_poi_ratio turned out to have the highest impact of all (score: 13.4, p-value 0%), but all other features performed worse:
Feature benchmarking
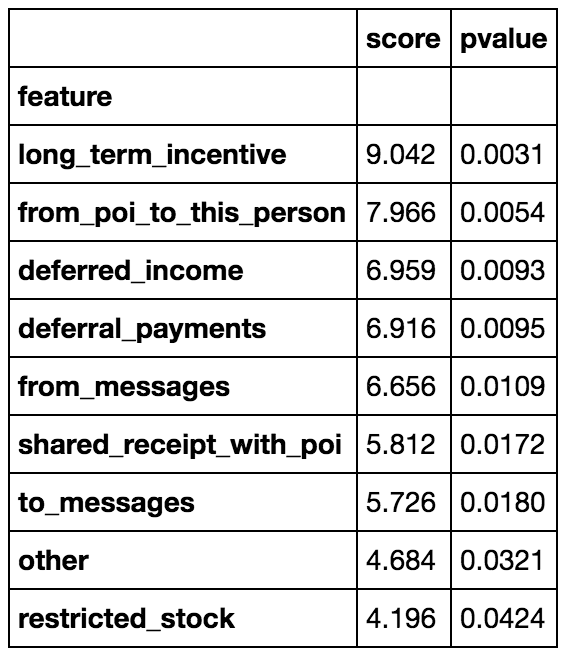
I ended up using all features exept the ones I did in the identifier. I started with a set of features selected using the common univariate statistical FPR test for each feature using the standard α = 0.05 cutoff.
That feature selection performed worse than including all features as seen in the table below. I played around with different combinations but ended up using all of the features included in the original dataset as I did not achive higher precision and recall values.
| Algorithm | precision | recall | precision selected features | recall selected features |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| KMeans | 0.034 | 0.203 | 0.058 | 0.243 |
| SVC | 0.313 | 0.625 | 0.228 | 0.494 |
| RandomForestClassifier | 0.269 | 0.123 | 0.189 | 0.093 |
Algorithm selection
When running the three selected algorithms on the new features vs. the old ones the old dataset achieved higher precision recall values for KMeans and SVC. As seen below SVC had the highest precision revall values, and performed better on the old dataset which is why I picked that combination.
| Algorithm | precision | recall | precision new features | recall new features | △ precision | △ recall |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| KMeans | 0.034 | 0.203 | 0.029 | 0.163 | 0.005 | 0.04 |
| SVC | 0.313 | 0.625 | 0.272 | 0.615 | 0.041 | 0.01 |
| RandomForestClassifier | 0.269 | 0.123 | 0.309 | 0.157 | -0.04 | -0.034 |
I ended up using a Support Vector Machine Classifier after trying K-means Clustering and Random Forest as well. I chose those algorithms as they come from three different approaches to identify patterns which I wanted to try on the dataset.
| Algorithm | precision | recall |
|---|---|---|
| KMeans | 0.025 | 0.147 |
| SVC | 0.265 | 0.609 |
| Random Forest | 0.312 | 0.160 |
Feature scaling
Log scaling
While plotting the histograms of the features the highly skewed distribution of most of the features could be observed. This is very handy given the amount of missing data. Imputation using the median is appropiate given normal distribtions while it's no good fit for highly skewed data as it will change the distribution curve a lot. Also some models perform better or even require a normal distribution I applied log scaling to the features. Finally the log scaling can easily be reverted using the exponential function no information is lost.
Impute missing values
As mentioned above the missing data was relplaced using the mean, after log scaling the features.
Parameter Tuning
Parameter tuning is about choosing a set of optimal parameters for a learning algorithm. If the parameters are not tuned well the algortihm risks overfitting. After chosing SVC as the algorithm to further tune I first played around with the features selected leading to include all original features in the model as those had the highest natural precision & recall. Then I moved on to optimise parameters gamma (Kernel coefficient) and C (penalty). After reading about them and moving them around to find the optimum I eneded up achiving a precision & recall of over 0.3.
Model Validation
General
"In machine learning, model validation is referred to as the process where a trained model is evaluated with a testing data set. The testing data set is a separate portion of the same data set from which the training set is derived. The main purpose of using the testing data set is to test the generalization ability of a trained model (Alpaydin 2010)." In this dataset validation was done by quantifying the performance of the SVC algorithm based on confusion matrix metrics: precision and recall. The most common mistake done is to overfit the data by choosing a bad validation metric. In this case I chose to ignore accuracy as the enron dataset is highly skewed and accuracy could be achieved by biasing towards non-pois. Given we guess all people being non pois the accuracy would already be at 86%, but precision at 0%.
First I chose the algorithm based on the highest precision and recall values and after that I tweaked the parameters, benchmarking the precison&recall differences by changing one parameter as long as there would be a negative difference to then move on to the next parameter.
Validation Metrics
The algorithms had the following mean precision and recall values of 1000 iterations:
| Algorithm | precision | recall |
|---|---|---|
| KMeans | 0.025 | 0.147 |
| SVC | 0.265 | 0.609 |
| Random Forest | 0.312 | 0.160 |
When optimising the performance of the SVC algorithm I chose C=2000 and gamma=0.0001 which lead to the following:
| Algorithm | precision | recall |
|---|---|---|
| SVC | 0.314 | 0.630 |
Precision: How many selected items are relevant?
Of all indentified POIs there are 31% which actually are POIs while 69% are non-pois.
Recall: How many relevant items are selected? The model identified 63% of all POIs in the dataset.
Outlook
Given the bad precision of only 31% this identifier is mostly wrong in identifying POIs from the Enron dataset. Still with a recall of 69% it is better than guessing. It turnes out that identifying Fraud or Spamm which is based on highly skewed data is very hard. To increase the performance of identification I'd suggest to look for patterns in the text of the emails. Maybe there are certain word combinations that are mostly used by POIs. The documentation on Spamm classification which is available could be of great help there as it handles a similar problem: identifying behavioural patterns of a small group of people.
References
Articles
- A look at those involved in the Enron scandal, USA Today - http://usatoday30.usatoday.com/money/industries/energy/2005-12-28-enron-participants_x.htm
- The Immortal Life of the Enron E-mails, MIT Technology Review - https://www.technologyreview.com/s/515801/the-immortal-life-of-the-enron-e-mails/
- Implementing a Weighted Majority Rule Ensemble Classifier in scikit-learn, Sebastian Raschka - http://sebastianraschka.com/Articles/2014_ensemble_classifier.html
- Color Palettes in Seaborn, Chris Albon - http://chrisalbon.com/python/seaborn_color_palettes.html
- Random Forests, Leo Breiman and Adele Cutler - http://www.stat.berkeley.edu/~breiman/RandomForests/cc_home.htm
- Python sklearn.feature_selection.f_classif Examples - http://www.programcreek.com/python/example/85917/sklearn.feature_selection.f_classif
- Handle missing data python - https://machinelearningmastery.com/handle-missing-data-python/
- Exponents Logarithms - https://www.mathsisfun.com/algebra/exponents-logarithms.html
- how-to-build-a-simple-spam-detecting-machine-learning-classifier - https://hackernoon.com/how-to-build-a-simple-spam-detecting-machine-learning-classifier-4471fe6b816e
- Model Validation, Machine Learning - https://link.springer.com/referenceworkentry/10.1007%2F978-1-4419-9863-7_233
Cheatsheets
- Markdown - https://github.com/adam-p/markdown-here/wiki/Markdown-Cheatsheet
- Pandas - https://github.com/pandas-dev/pandas/blob/master/doc/cheatsheet/Pandas_Cheat_Sheet.pdf
- Numpy - https://s3.amazonaws.com/assets.datacamp.com/blog_assets/Numpy_Python_Cheat_Sheet.pdf
Documentation
- Pipelining: chaining a PCA and a logistic regression, scikit learn - http://scikit-learn.org/stable/auto_examples/plot_digits_pipe.html
- matplotlib.axes, matplotlib - http://matplotlib.org/api/axes_api.html
- DataFrame quantiles, pandas - http://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/version/0.17.0/generated/pandas.DataFrame.quantile.html
- Visualization, pandas - https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/visualization.html
- pyplot, matplotlib - https://matplotlib.org/devdocs/api/_as_gen/matplotlib.pyplot.hist.html
- sort values, pandas - https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/generated/pandas.DataFrame.sort_values.html
- Working with missing data, pandas - https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/missing_data.html
- sklearn.feature_selection.SelectFpr - http://scikit-learn.org/stable/modules/generated/sklearn.feature_selection.SelectFpr.html
- ipython notebook - http://ipython.org/ipython-doc/dev/notebook/index.html
- python data structures - https://docs.python.org/2/tutorial/datastructures.html
- scipy iqr - https://docs.scipy.org/doc/scipy-0.19.1/reference/generated/scipy.stats.iqr.html
- seaborn heatmaps - https://seaborn.pydata.org/generated/seaborn.heatmap.html
- sklearn univariate-feature-selection - http://scikit-learn.org/stable/modules/feature_selection.html#univariate-feature-selection
- sklearn.decomposition.PCA - http://scikit-learn.org/stable/modules/generated/sklearn.decomposition.PCA.htm
- pandas dropna - https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/generated/pandas.DataFrame.dropna.html
- pandas Indexing and Selecting Data - https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/indexing.html
GitHub Repositories
- EnsembleVoteClassifier, Sebastian Raschka - http://rasbt.github.io/mlxtend/user_guide/classifier/EnsembleVoteClassifier/
- Grace Pehl: Identifying Persons of Interest from the Enron Corpus - https://github.com/grace-pehl/enron
- brandjamie: Marchine Learning with the enron emails dataset - https://github.com/brandjamie/udacity_enron
- Daria ALekseeva: Enron Dataset - https://github.com/DariaAlekseeva/Enron_Dataset
- watanabe8760: uda-da-p5-enron-fraud-detection - https://github.com/watanabe8760/uda-da-p5-enron-fraud-detection
- Mayukh Sobo: Enron Fraud https://github.com/MayukhSobo/EnronFraud
Q&A pages
- Pandas Replacement for .ix, Stack Overflow - https://stackoverflow.com/questions/43838999/pandas-replacement-for-ix
- Sci-kit and Regression Summary, Stack Overflow - http://stackoverflow.com/questions/26319259/sci-kit-and-regression-summary
- How to obtain True Positive, True Negative, False Positive and False Negative, Stack Overflow - https://stackoverflow.com/questions/31324218/scikit-learn-how-to-obtain-true-positive-true-negative-false-positive-and-fal
- Why do we need to normalize data before analysis, Cross Validated - http://stats.stackexchange.com/questions/69157/why-do-we-need-to-normalize-data-before-analysis
- Perform feature normalization before or within model validation?, Cross Validated - http://stats.stackexchange.com/questions/77350/perform-feature-normalization-before-or-within-model-validation
- How should the interquartile range be calculated in Python?, Stack Overflow - http://stackoverflow.com/questions/27472330/how-should-the-interquartile-range-be-calculated-in-python
- scikit learn svc coef0 parameter range, Stack Overflow - http://stackoverflow.com/questions/21390570/scikit-learn-svc-coef0-parameter-range
- What is a good range of values for the svm.SVC() hyperparameters to be explored via GridSearchCV()?, Stack Overflow - http://stackoverflow.com/questions/26337403/what-is-a-good-range-of-values-for-the-svm-svc-hyperparameters-to-be-explored
- Imputation before or after splitting into train and test?, Cross Validated - http://stats.stackexchange.com/questions/95083/imputation-before-or-after-splitting-into-train-and-test
- Is there a rule-of-thumb for how to divide a dataset into training and validation sets?, Stack Overflow - http://stackoverflow.com/questions/13610074/is-there-a-rule-of-thumb-for-how-to-divide-a-dataset-into-training-and-validatio
- What is the difference between test set and validation set?, Cross Validated - http://stats.stackexchange.com/questions/19048/what-is-the-difference-between-test-set-and-validation-set
- Python - What is exactly sklearn.pipeline.Pipeline?, Stack Overflow - http://stackoverflow.com/questions/33091376/python-what-is-exactly-sklearn-pipeline-pipeline
- How can I use a custom feature selection function in scikit-learn's pipeline, Stack Overflow - http://stackoverflow.com/questions/25250654/how-can-i-use-a-custom-feature-selection-function-in-scikit-learns-pipeline
- Seaborn distplot y-axis normalisation wrong ticklabels, Stack Overflow - http://stackoverflow.com/questions/32274865/seaborn-distplot-y-axis-normalisation-wrong-ticklabels
- How to save a Seaborn plot into a file, Stack Overflow - http://stackoverflow.com/questions/32244753/how-to-save-a-seaborn-plot-into-a-file
- Seaborn plots not showing up, Stack Overflow - https://stackoverflow.com/questions/26597116/seaborn-plots-not-showing-up
- Select rows from a dataframe, Stack Overflow - https://stackoverflow.com/questions/17071871/select-rows-from-a-dataframe-based-on-values-in-a-column-in-pandas
- make-the-size-of-a-heatmap-bigger-with-seaborn - https://stackoverflow.com/questions/38913965/make-the-size-of-a-heatmap-bigger-with-seaborn
- pandas-sort-column-by-correlation-to-first-column - https://stackoverflow.com/questions/41340023/pandas-sort-column-by-correlation-to-first-column
- sklearn-error-valueerror - https://stackoverflow.com/questions/31323499/sklearn-error-valueerror-input-contains-nan-infinity-or-a-value-too-large-for
- how-to-ignore-deprecation-warnings-in-python - https://stackoverflow.com/questions/879173/how-to-ignore-deprecation-warnings-in-python
Tools
- Markdown Tables Generator - http://www.tablesgenerator.com/markdown_tables
- JSON pretty print - http://jsonprettyprint.com
Wikipedia
- Enron scandal - https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Enron_scandal
- Boxplots - https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Box_plot
- Interquartile range - https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Interquartile_range
- False positive rate - https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/False_positive_rate
- False discovery rate - https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/False_discovery_rate
- Precision and recall - https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Precision_and_recall
- Independent component analysis - https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Independent_component_analysis