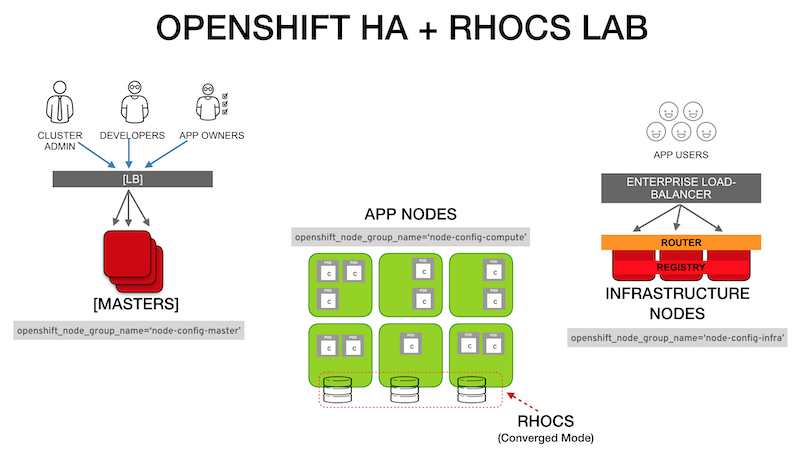
This repository is a prescriptive OpenShift inventory file I for my lab environment and some notes on the installation process. The inventory file is verbose to allow for quick adjustment during tests.
To customize the inventory file to your environment you may reference the official OpenShift documentation:
https://docs.openshift.com/container-platform/3.11/install/configuring_inventory_file.html
- The [LB] represents a dedicated RHEL minimal server OpenShift can configure to serve as the load balancer for the Master Nodes. In a production environment this may be replaced by load balancer configured in passthrough mode.
- Ensure DNS resolution of all nodes FQDN
- Register the FQDN for the cluster consoles like ocp-console.example.com (
openshift_master_cluster_hostname) - Register the wildcard subdomain for the apps like *.apps.example.com (
openshift_master_default_subdomain) - Ensure SELinux in
enforcingmode
NOTE 1: This is only a summary. For detailed information visit: https://docs.openshift.com/container-platform/latest/install/host_preparation.html
NOTE 2: The following instructions assume the use of a bastion node to deploy OpenShift
- Ensure bastion node has ssh access to all nodes
$ ssh-keygen
$ for host in master1.example.com \
master2.example.com \
master3.example.com \
infranode1.example.com \
infranode2.example.com \
node1.example.com \
node4.example.com \
node3.example.com \
ocs-node1.example.com \
ocs-node2.example.com \
ocs-node3.example.com; \
do ssh-copy-id -i ~/.ssh/id_rsa.pub $host; \
done
- Register the host
# register each host with RHSM
subscription-manager register --username=<user_name> --password=<password>
# pull subscriptions
subscription-manager refresh
# identify the available OpenShift subscriptions
subscription-manager list --available --matches '*OpenShift*'
# assign a subscription to the node
subscription-manager attach --pool=<pool_id>
- Assign subscription to the host
# Disable all RHSM repositories
subscription-manager repos --disable="*"
# Enable only repositories required by OpenShift
subscription-manager repos \
--enable="rhel-7-server-rpms" \
--enable="rhel-7-server-extras-rpms" \
--enable="rhel-7-server-ose-3.11-rpms" \
--enable="rhel-7-server-ansible-2.6-rpms"
- Make sure the systems have the latest patches
# Update RHEL
yum -y update
# Reboot with updated Kernel
reboot
- Install required installation tools at bastion node
$ yum -y install atomic-openshift-clients openshift-ansible
-
Prepare your custom inventory file. (See reference template in this repo)
-
Copy your OpenShift Ansible inventory file to the bastion node. Either using the bastion Ansible host file or maintaining a local inventory_file
/etc/ansible/hosts
_or_
~/inventory_file
- Inventory configuration details: https://docs.openshift.com/container-platform/3.11/install/configuring_inventory_file.html
- Validate bastion can reach all the nodes
ansible all -i inventory_file -m ping
- From bastion node run the installation of prerequisites (base packages & Docker) on all OpenShift nodes
ansible-playbook -f 20 -i inventory_file /usr/share/ansible/openshift-ansible/playbooks/prerequisites.yml
NOTE: In case of error indicating playbooks are not found, install the corresponding package in the bastion node executing: yum install openshift-ansible
NOTE: The -i <inventory_file> flag is not needed if using the default inventory path /etc/ansible/hosts
-
Once the previous step is completed WITHOUT any error, you may proceed with the deployment.
Deploy OpenShift using the
ansilbe-playbook
ansible-playbook -f 20 -i inventory_file /usr/share/ansible/openshift-ansible/playbooks/deploy_cluster.yml
NOTE: If the initial installation fails you need to uninstall OpenShift and start the installation from the prerequisites playbook.
# Uninstall OpenShift
ansible-playbook -i inventory_file /usr/share/ansible/openshift-ansible/playbooks/adhoc/uninstall.yml
# Remove leftover configs and certs from master and nodes
ansible nodes -i inventory_file -m file -a "dest=/etc/origin state=absent"
ansible nodes -i inventory_file -m file -a "dest=/etc/cni state=absent"
Under certain installation failure scenarios (specially with network plugins) there might be some iptables entries left behind. To reset these you should have a clean iptables backup.
NOTE: The following is a sample iptables.plain from VMs running in a RHV environment:
# filename: iptables.plain
# sample configuration for iptables service
*filter
:INPUT ACCEPT [0:0]
:FORWARD ACCEPT [0:0]
:OUTPUT ACCEPT [0:0]
-A INPUT -m state --state RELATED,ESTABLISHED -j ACCEPT
-A INPUT -p icmp -j ACCEPT
-A INPUT -i lo -j ACCEPT
-A INPUT -p udp -m multiport --dports 60001:60005 -j ACCEPT
-A INPUT -p tcp -m state --state NEW -m tcp --dport 22 -j ACCEPT
-A INPUT -j REJECT --reject-with icmp-host-prohibited
-A FORWARD -j REJECT --reject-with icmp-host-prohibited
COMMIT
To restore this iptables config to all the nodes use:
ansible nodes -i inventory_file -m copy -a "src=./iptables.plain dest=/etc/sysconfig/iptables"
Restart iptables service. Some CNI plugin installation failures might require a reboot of the node.
# Uninstall OCS
ansible-playbook -i <path_to_inventory_file> /usr/share/ansible/openshift-ansible/playbooks/openshift-glusterfs/uninstall.yml
# Uninstall OCS deleting data
ansible-playbook -i <path_to_inventory_file> -e "openshift_storage_glusterfs_wipe=true" /usr/share/ansible/openshift-ansible/playbooks/openshift-glusterfs/uninstall.yml
# Cleaning OCS leftovers
ansible -i inventory_file glusterfs -a "rm -rf /var/lib/heketi /etc/glusterfs /var/lib/glusterd /var/log/glusterfs"
# Clean partitions of OCS target disks
ansible -i inventory_file glusterfs -a "wipefs -a -f /dev/<path_to_disks>"
To use the bastion node for cluster administration, copy the .kube directory from master1 to your bastion
ansible -i inventory_file masters[0] -b -m fetch -a "src=/root/.kube/config dest=/root/.kube/config flat=yes"
Once the .kube directory is in your bastion node, validate you are system:admin
oc whoami
The following commands you be successful
oc get nodes --show-labels
oc get nodes -o wide
oc get pod --all-namespaces -o wide
oc login -u <ocp_user>
Login into the web console by accessing the name indicated in the openshift_master_cluster_hostname variable of the inventory_file (i.e. https://openshift-console.example.com)
Try some demo applications to test the environment.
I have some simple demo activities here: https://github.com/williamcaban/podcool-docs
Deploying custom certificates are not part of this lab documentation. If need to use custom certificates refer to the following documentation
-
Configuring Custom Certificates
https://docs.openshift.com/container-platform/3.11/install_config/certificate_customization.html
-
Redeploying Certificates
https://docs.openshift.com/container-platform/3.11/install_config/redeploying_certificates.html
-
To deploy OpenShift named certificates