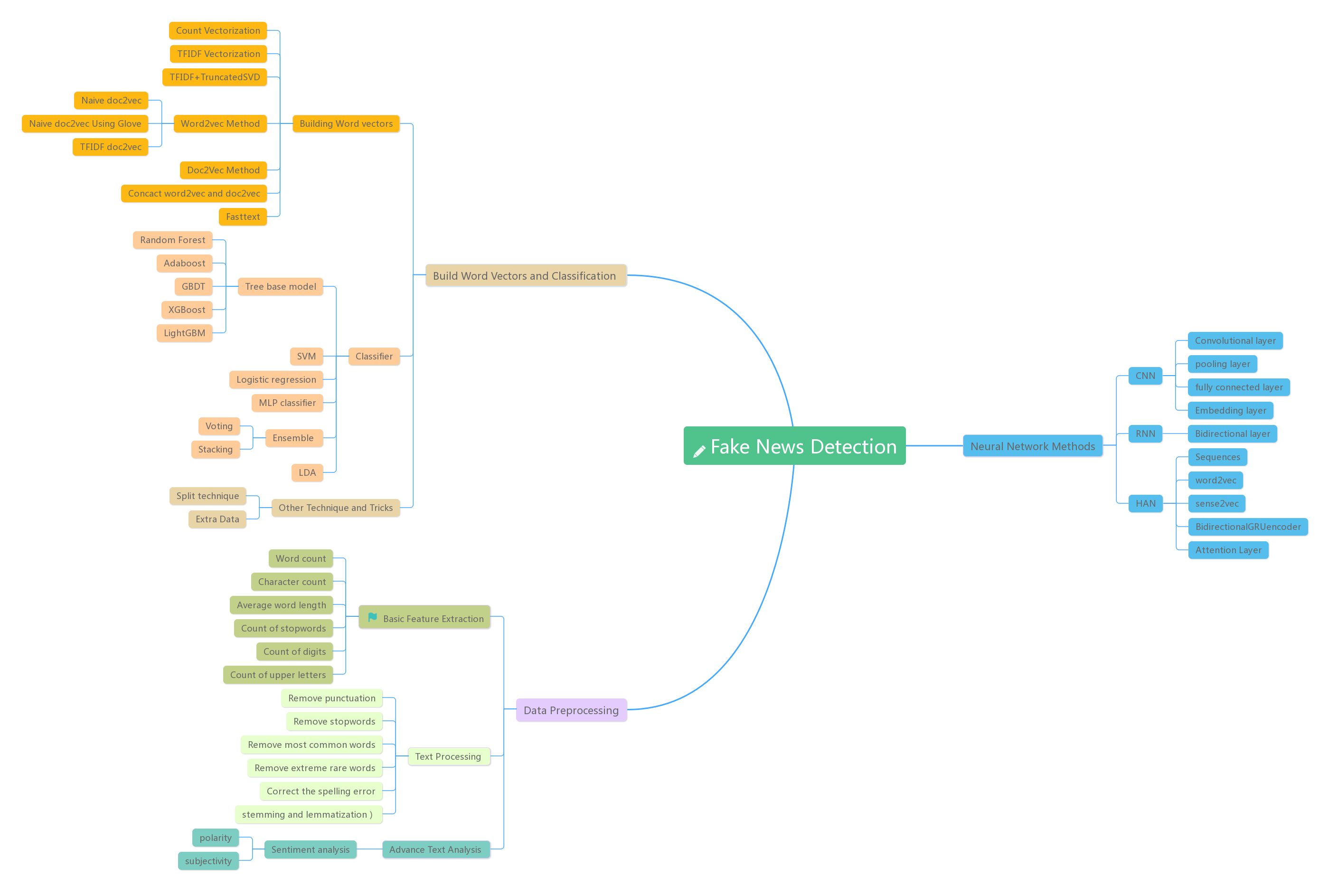
FakeNews-Detection
Fake news detection using both ensembled model and HAN nearal network
we can achieve 94.8% accuracy using the first model and higher than 98% using the second one.
Group4 Final Project
Yao Zonghai
Li Mingyang
Mei Longxiang
import pandas as pd
df = pd.read_csv('fake_or_real_news.csv')
df.tail()
#替换列名
df.rename(columns={"label":"fake"}, inplace=True)
label_map = {"FAKE": 1, "REAL": 0}
df['fake'] = df['fake'].map(label_map)
#丢掉无用的列
df = df.drop(['Unnamed: 0','title_vectors'],axis=1)
df = df.reset_index(drop=True)import re
#正则表达式去掉一些无用的形式
def execute(x):
temp=x
pat1 = "[a-zA-Z]+'t"
#substitude the ***'t' words with not ***
temp = re.sub(pat1, 'not', temp)
pat2 = "[a-zA-Z]+’t"
temp = re.sub(pat2, 'not', temp)
#邮箱地址
pat3="[\w!#$%&'*+/=?^_`{|}~-]+(?:\.[\w!#$%&'*+/=?^_`{|}~-]+)*@(?:[\w](?:[\w-]*[\w])?\.)+[\w](?:[\w-]*[\w])?"
temp = re.sub(pat3, 'email', temp)
#url网址
pat4="[a-zA-z]+://[^\s]*"
temp = re.sub(pat4, 'url', temp)
#日期
pat5="([0-9]{3}[1-9]|[0-9]{2}[1-9][0-9]{1}|[0-9]{1}[1-9][0-9]{2}|[1-9][0-9]{3})-(((0[13578]|1[02])-(0[1-9]|[12][0-9]|3[01]))|((0[469]|11)-(0[1-9]|[12][0-9]|30))|(02-(0[1-9]|[1][0-9]|2[0-8])))"
temp = re.sub(pat5, 'date', temp)
#电话号码 qq号码等 各种数字串
pat6="[0-9]+"
temp = re.sub(pat6, 'number', temp)
return temp
def text_execute(x):
return execute(x['text'])
def title_execute(x):
return execute(x['title'])
df['text'] = df.apply(text_execute,axis=1)TextBlob is a Python (2 and 3) library for processing textual data. It provides a simple API for diving into common natural language processing (NLP) tasks such as part-of-speech tagging, noun phrase extraction, sentiment analysis, classification, translation, and more. Here we use textblob for sentiment analysis, and the range of polarity is -1 to 1, the range of subjectivity is from 0 to 1.
from textblob import TextBlob
# df['text'].apply(lambda x: str(TextBlob(x).correct()))
df['sentiment_polarity'] = df['text'].apply(lambda x: TextBlob(x).sentiment[0] )
df['sentiment_subjectivity'] = df['text'].apply(lambda x: TextBlob(x).sentiment[1] )df.head().dataframe tbody tr th {
vertical-align: top;
}
.dataframe thead th {
text-align: right;
}
| title | text | fake | numerics | sentence_count | word_count | char_count | avg_word | stopwords | upper | hashtags | sentiment_polarity | sentiment_subjectivity | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | You Can Smell Hillary’s Fear | Daniel Greenfield, a Shillman Journalism Fello... | 1 | 0 | 87 | 1298 | 7513 | 5.788136 | 534 | 38 | 0 | 0.059595 | 0.562654 |
| 1 | Watch The Exact Moment Paul Ryan Committed Pol... | Google Pinterest Digg Linkedin Reddit Stumbleu... | 1 | 0 | 26 | 446 | 2641 | 5.921525 | 176 | 3 | 0 | 0.082652 | 0.518638 |
| 2 | Kerry to go to Paris in gesture of sympathy | U.S. Secretary of State John F. Kerry said Mon... | 0 | 0 | 16 | 423 | 2549 | 6.026005 | 173 | 6 | 0 | 0.102574 | 0.348775 |
| 3 | Bernie supporters on Twitter erupt in anger ag... | — Kaydee King (@KaydeeKing) November number, n... | 1 | 0 | 17 | 404 | 2715 | 6.720297 | 127 | 5 | 0 | 0.063645 | 0.503563 |
| 4 | The Battle of New York: Why This Primary Matters | It's primary day in New York and front-runners... | 0 | 0 | 21 | 307 | 1850 | 6.026059 | 120 | 3 | 0 | 0.251709 | 0.420109 |
import nltk
from itertools import chain
titles = df.title.values
texts = df.text.values
y = df.fake.valuestitle_text_word = []
for i in range(0, len(df)):
title_text_word.append(str(titles[i]) + " " + str(texts[i]))
tokenized = [nltk.word_tokenize(word) for word in title_text_word]Calculation of both the most frequent words before and after the data cleaning
from collections import Counter
token_counter = Counter(token.lower() for sentences in tokenized for token in sentences)
top10 = token_counter.most_common()[:10]
for index, tok in enumerate(top10):
print('{:>2}.{:>5} freq: {:>7}'.format(index+1, tok[0], tok[1])) 1. the freq: 292303
2. , freq: 261049
3. . freq: 204791
4. to freq: 140937
5. of freq: 130644
6. and freq: 119928
7. a freq: 108544
8. in freq: 99154
9. that freq: 72460
10.number freq: 57140
from nltk.corpus import stopwords
from string import punctuation
def clean_text(tokenized_list, stopwords, punctuation, lemmatize=False):
new_list = []
for doc in tokenized_list:
new_list.append([token.lower() for token in doc
if token.lower() not in chain(stopwords, punctuation)
and token.lower() != "'s" and token.lower() != "''"
and token.lower() != "``" and token.lower() != "—"])
# delete the expression like "'s"
return new_list
stop_word = stopwords.words('english')
punct = punctuation + '’' + '‘' + '”' + '“'
cleaned_list = clean_text(tokenized, stop_word, punct)
# re-counter the token and list the new top10 most common words.
new_token_counter = Counter(token.lower() for sentences in cleaned_list for token in sentences)
new_top20 = new_token_counter.most_common()[:20]
for index, tok in enumerate(new_top20):
print('{:>2}.{:>5} freq: {:>7}'.format(index+1, tok[0], tok[1])) 1.number freq: 57140
2.trump freq: 22985
3. said freq: 21176
4.clinton freq: 17946
5.would freq: 12751
6.people freq: 11668
7. one freq: 11381
8. new freq: 9542
9.state freq: 8874
10.president freq: 8615
11.obama freq: 8496
12. also freq: 8216
13.campaign freq: 7806
14. us freq: 7732
15.hillary freq: 7707
16. like freq: 7095
17.could freq: 6657
18. time freq: 6487
19. even freq: 6454
20.states freq: 6184
Build Gensim Doc2Vec (300 dimension)
from gensim.models.doc2vec import TaggedDocument
from gensim.models import Doc2Vec
class TagDocIterator:
def __init__(self, doc_list, idx_list):
self.doc_list = doc_list
self.idx_list = idx_list
def __iter__(self):
for doc, idx, in zip(self.doc_list, self.idx_list):
tag = [idx]
yield TaggedDocument(words=doc, tags=tag)
doc2vec_model = Doc2Vec(size=300, epoch=5, window=7,hs=1,dbow_words=1,dm=1,workers=4)
doc2vec_model.build_vocab(TagDocIterator(cleaned_list, df.index))
doc2vec_model.train(TagDocIterator(cleaned_list, df.index), epochs=10, total_examples=doc2vec_model.corpus_count)
final_feature_text = []
for i in range(len(doc2vec_model.docvecs)):
final_feature_text.append(doc2vec_model.docvecs[i])
final_feature_title_1 = pd.DataFrame(final_feature_text)C:\Anaconda3\lib\site-packages\gensim\models\doc2vec.py:570: UserWarning: The parameter `size` is deprecated, will be removed in 4.0.0, use `vector_size` instead.
warnings.warn("The parameter `size` is deprecated, will be removed in 4.0.0, use `vector_size` instead.")
Adding the extra feature Vectors into the Trained Vector
final_feature_title_1['sentence_count']=df['sentence_count'].values
final_feature_title_1['word_count']=df['word_count']
final_feature_title_1['char_count']=df['char_count']
final_feature_title_1['avg_word']=df['avg_word']
final_feature_title_1['hashtags']=df['hashtags']
final_feature_title_1['stopwords']=df['stopwords']
final_feature_title_1['upper']=df['upper']
final_feature_title_1['numerics']=df['numerics']
final_feature_title_1['sentiment_polarity']=df['sentiment_polarity']
final_feature_title_1['sentiment_subjectivity']=df['sentiment_subjectivity']Use sklearn to Nomarlize the vector, making sure they are in the same range
final_feature_title_1.tail()
from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler
ss = StandardScaler()
standard_text=ss.fit_transform(final_feature_title_1.values)
final_feature = pd.DataFrame(standard_text)import sklearn.metrics as metrics
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
train_1 = pd.concat([final_feature], axis=1)
Y_1 = df['fake'].as_matrix()
train_x_1, test_x_1, train_y_1, test_y_1 = train_test_split(train_1, Y_1, test_size=0.3, random_state=1)
train_x_1.shape, test_x_1.shape, train_y_1.shape, test_y_1.shapeC:\Anaconda3\lib\site-packages\ipykernel_launcher.py:4: FutureWarning: Method .as_matrix will be removed in a future version. Use .values instead.
after removing the cwd from sys.path.
((4434, 310), (1901, 310), (4434,), (1901,))
Building the Naive Doc2Vec
After building the Doc2vec, we did some experienments to judge which strategy we should choose when we are processin the data: These stratagy include : Whether we should remove the stop rare word , whether we should remove punctuations,Whether adding the new features help with accuracy. and ways to deal with the titles ,we canconcatenate titles with the text, and we can also build an indivisual title text. Also, we
We also used the word2vec to build the naive doc2vec File "<ipython-input-144-5aae0c41ae82>", line 1
We also used the word2vec to build the naive doc2vec
^
SyntaxError: invalid syntax
from nltk.corpus import gutenberg
from gensim import models
# Training word2vec model on Gutenberg corpus. This may take a few minutes.
model = models.Word2Vec(cleaned_list,
size = 300,
window = 9,
min_count = 1,
sg = 1,
alpha = 0.025,
iter=10,
batch_words = 10000,
)import numpy as np
np.seterr(divide='ignore', invalid='ignore')
new_title_vectors_1 = np.zeros((len(df), 300))
for i in range(0, len(df)):
# I find that a line has no title after we cleaned the punctuation and stopwords, so the length maybe 0
if len(cleaned_list[i]) != 0:
for word in cleaned_list[i]:
new_title_vectors_1[i] += model.wv[word]
# calculate the average of the word vector
new_title_vectors_1[i] = new_title_vectors_1[i] / len(cleaned_list[i])
new_title_vectors_1.shapeimport sklearn.metrics as metrics
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
final_feature_w2v = pd.DataFrame(new_title_vectors_1)
train_1 = pd.concat([final_feature_w2v], axis=1)
Y_1 = df['fake'].as_matrix()
train_x_1, test_x_1, train_y_1, test_y_1 = train_test_split(train_1, Y_1, test_size=0.3, random_state=1)
train_x_1.shape, test_x_1.shape, train_y_1.shape, test_y_1.shapeConcatenate the two(Gensim Doc2Vec, Naive Doc2Vec together)
If we concatenate the two vectors into a larger vector with more than 600 dimensions the result will get better.
final_feature_w2v.head()final_feature.head()final_feature_concat1 = pd.concat([final_feature_w2v,final_feature],axis=1)
final_feature_concat = pd.DataFrame(final_feature_concat1.values)final_feature_concat.head()import nltk
from nltk.corpus import stopwords
def splitSentence(paragraph):
tokenizer = nltk.data.load('tokenizers/punkt/english.pickle')
sentences = tokenizer.tokenize(paragraph)
return len(sentences)
df['numerics']=df['text'].apply(lambda sen:len([x for x in sen.split() if x.isdigit()]))
df['text'] = df.apply(text_execute,axis=1)
df['sentence_count']=df['text'].apply(splitSentence)
df['word_count']=df['text'].apply(lambda x:len(str(x).split(" ")))
df['char_count']=df['text'].str.len()
df['avg_word']=df.apply(lambda x:x['char_count']/x['word_count'],axis=1)
#df['avg_sentence']=df.apply(lambda x:x['word_count']/x['sentence_count'],axis=1)
stop=stopwords.words('english')
df['stopwords']=df['text'].apply(lambda sen:len([x for x in sen.split() if x in stop]))
df['upper']=df['text'].apply(lambda sen:len([x for x in sen.split() if x.isupper()]))
df['hashtags']=df['text'].apply(lambda sen:len([x for x in sen.split() if x.startswith("#") or x.startswith("$") or x.startswith("&")]))import sklearn.metrics as metrics
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
train_1 = pd.concat([final_feature_concat], axis=1)
Y_1 = df['fake'].as_matrix()
train_x_1, test_x_1, train_y_1, test_y_1 = train_test_split(train_1, Y_1, test_size=0.3, random_state=1)
train_x_1.shape, test_x_1.shape, train_y_1.shape, test_y_1.shapefrom sklearn.metrics import classification_report
import os
os.environ['KMP_DUPLICATE_LIB_OK']='True'
from xgboost import XGBClassifier
XGmodel = XGBClassifier(max_depth=7,
learning_rate=0.2,
n_estimators=1000,
silent=True,
objective='binary:logistic',
nthread=-1,
gamma=0,
min_child_weight=1,
max_delta_step=0,
subsample=1,
colsample_bytree=1,
colsample_bylevel=1,
reg_alpha=0,
reg_lambda=1,
scale_pos_weight=1,
base_score=0.5,
seed=0,
missing=None)
XGmodel.fit(train_x_1, train_y_1)
y_pred = XGmodel.predict(test_x_1)
y_pred= (y_pred>0.5)
print(metrics.accuracy_score(test_y_1, y_pred),'\n')
matrix = metrics.confusion_matrix(test_y_1,y_pred)
print(matrix,'\n')
print(classification_report(test_y_1, y_pred)) import time
from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression
start = time.time()
lr_model_1 = LogisticRegression(max_iter=60)
lr_model_1.fit(train_x_1, train_y_1)
training_time = time.time() - start
predict_y_1 = lr_model_1.predict(test_x_1)
accuracy_1 = metrics.accuracy_score(test_y_1.ravel(), predict_y_1.ravel())
precision_1 = metrics.precision_score(test_y_1.ravel(), predict_y_1.ravel())
recall_1 = metrics.recall_score(test_y_1.ravel(), predict_y_1.ravel())
f1_1 = metrics.f1_score(test_y_1.ravel(), predict_y_1.ravel())
print('Accuracy: {:.2f} | Precision: {:.2f} | Recall: {:.2f} | F1-measure: {:.2f} | Training time: {:.2f}s'
.format(accuracy_1, precision_1, recall_1, f1_1, training_time))from sklearn.neural_network import MLPClassifier
x_train=train_x_1
x_test=test_x_1
y_train=train_y_1
y_test=test_y_1
mlp=MLPClassifier()
y_pred = mlp.fit(x_train, y_train).predict(x_test)
accuracy = metrics.accuracy_score(y_test.ravel(), y_pred.ravel())
matrix = metrics.confusion_matrix(y_test,y_pred)
print('Accuracy= {:.4f}'.format(accuracy))
print('\nconfusion_matrix:\n',matrix)
print('report:\n',classification_report(y_test, y_pred))
# print('Accuracy= {:.4f} | Precision= {:.4f} | Recall= {:.4f} | f1 score= {:.4f}'.format(accuracy,precision,recall,f1,))from sklearn.ensemble import VotingClassifier
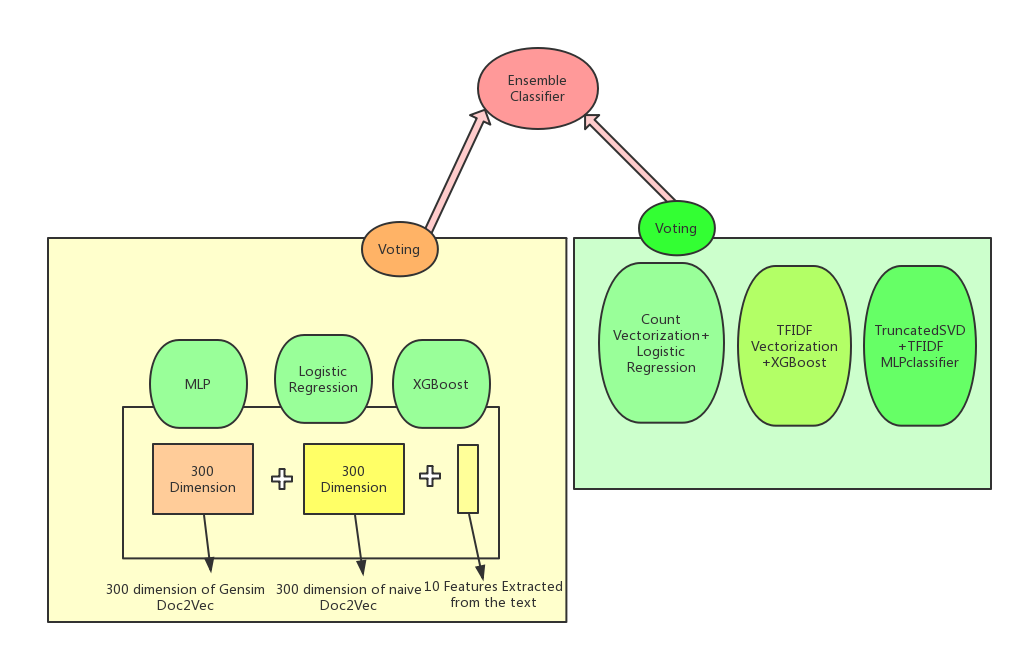
eclf = VotingClassifier(estimators=[('xgb', XGmodel), ('lr_model_1', lr_model_1),('mlp',mlp)],weights=[3,1,1])
pre=eclf.fit(x_train, y_train)
y_pred = eclf.predict(x_test)
y_pred= (y_pred>0.5)
print(metrics.accuracy_score(y_test, y_pred),'\n')
matrix = metrics.confusion_matrix(y_test,y_pred)
print(matrix,'\n')
print(classification_report(y_test, y_pred)) from sklearn.feature_extraction.text import TfidfVectorizer
from sklearn.feature_extraction.text import CountVectorizer
from sklearn.decomposition import TruncatedSVD
from sklearn.feature_extraction.stop_words import ENGLISH_STOP_WORDS
from sklearn.metrics import f1_score, accuracy_score , recall_score , precision_score
from sklearn.cross_validation import cross_val_score
tfidf = TfidfVectorizer(stop_words=ENGLISH_STOP_WORDS,ngram_range=(1,2),max_df= 0.85, min_df= 0.01,sublinear_tf=True, use_idf=True)
count = CountVectorizer(stop_words=ENGLISH_STOP_WORDS,ngram_range=(1,2),max_df= 0.85, min_df= 0.01)
svd = TruncatedSVD(2)X_body_text=texts
X_headline_text=titles
X_body_tfidf = tfidf.fit_transform(X_body_text)
X_headline_tfidf = tfidf.fit_transform (X_headline_text)
X_body_count = count.fit_transform(X_body_text)
X_headline_count = count.fit_transform (X_headline_text)
X_SVDtransformed = svd.fit_transform(X_body_tfidf)X_body_tfidf_train, X_body_tfidf_test, y_body_train, y_body_test = train_test_split(X_body_tfidf,y, test_size = 0.3, random_state=1234)X_body_count_train, X_body_count_test, y_body_train, y_body_test = train_test_split(X_body_count,y, test_size = 0.3, random_state=1234)X_svd_train, X_svd_test, y_svd_train, y_svd_test = train_test_split(X_body_tfidf,y, test_size = 0.3, random_state=1234)lr_count = LogisticRegression(penalty='l1')
# train model
lr_count.fit(X_body_count_train, y_body_train)
# get predictions for article section
y_body_pred = lr_count.predict(X_body_count_test)
# print metrics
print ("Logistig Regression F1 and Accuracy Scores : \n")
print ( "F1 score {:.4}%".format( f1_score(y_body_test, y_body_pred, average='macro')*100 ) )
print ( "Accuracy score {:.4}%".format(accuracy_score(y_body_test, y_body_pred)*100) )
cros_val_list = cross_val_score(lr_count, X_body_count,y,cv=7)
print (cros_val_list)
print (cros_val_list.mean())Logistic Regression + raw count
lr_count = LogisticRegression(penalty='l1')
# train model
lr_count.fit(X_body_count_train, y_body_train)
# get predictions for article section
y_body_pred = lr_count.predict(X_body_count_test)
# print metrics
print ("Logistig Regression F1 and Accuracy Scores : \n")
print ( "F1 score {:.4}%".format( f1_score(y_body_test, y_body_pred, average='macro')*100 ) )
print ( "Accuracy score {:.4}%".format(accuracy_score(y_body_test, y_body_pred)*100) )
cros_val_list = cross_val_score(lr_count, X_body_count,y,cv=7)
print (cros_val_list)
print (cros_val_list.mean())XgBoost + tfidf count
xgb_tfidf = XGBClassifier(max_depth=5,
learning_rate=0.2,
n_estimators=1000,
silent=True,
objective='binary:logistic',
nthread=-1,
gamma=0,
min_child_weight=1,
max_delta_step=0,
subsample=1,
colsample_bytree=1,
colsample_bylevel=1,
reg_alpha=0,
reg_lambda=1,
scale_pos_weight=1,
base_score=0.5,
seed=0,
missing=None)
xgb_tfidf.fit(X_body_tfidf_train, y_body_train)
y_xgb_body_pred = xgb_tfidf.predict(X_body_tfidf_test)
# print metrics
print ("XGBoost F1 and Accuracy Scores : \n")
print ( "F1 score {:.4}%``".format( f1_score(y_body_test, y_xgb_body_pred, average='macro')*100 ) )
print ( "Accuracy score {:.4}%".format(accuracy_score(y_body_test, y_xgb_body_pred)*100) )
MLPClassifier + svd+tfidf count
from sklearn.metrics import classification_report
from sklearn import metrics
from sklearn.neural_network import MLPClassifier
mlp_svd=MLPClassifier()
y_pred = mlp_svd.fit(X_svd_train, y_body_train).predict(X_svd_test)
accuracy = metrics.accuracy_score(y_body_test.ravel(), y_pred.ravel())
matrix = metrics.confusion_matrix(y_body_test,y_pred)
print('Accuracy= {:.4f}'.format(accuracy))
print('\nconfusion_matrix:\n',matrix)
print('report:\n',classification_report(y_body_test, y_pred))
# print('Accuracy= {:.4f} | Precision= {:.4f} | Recall= {:.4f} | f1 score= {:.4f}'.format(accuracy,precision,recall,f1,))from sklearn.ensemble import VotingClassifier
eclf2 = VotingClassifier(estimators=[('xgb_tfidf', xgb_tfidf), ('lr_count', lr_count),('mlp_svd',mlp_svd)],weights=[1,1,2])
pre=eclf2.fit(x_train, y_train)
y_pred = eclf2.predict(x_test)
y_pred= (y_pred>0.5)
print(metrics.accuracy_score(y_test, y_pred),'\n')
matrix = metrics.confusion_matrix(y_test,y_pred)
print(matrix,'\n')
print(classification_report(y_test, y_pred)) Fasttext Model
from gensim.test.utils import common_texts
from gensim.models import FastText
model_fasttext = FastText(cleaned_list, size=300, window=7, min_count=1, iter=10)import numpy as np
np.seterr(divide='ignore', invalid='ignore')
fasttext_vectors = np.zeros((len(df),300))
for i in range(0, len(df)):
# I find that a line has no title after we cleaned the punctuation and stopwords, so the length maybe 0
if len(cleaned_list[i]) != 0:
for word in cleaned_list[i]:
fasttext_vectors[i] += model_fasttext.wv[word]
# calculate the average of the word vector
fasttext_vectors[i] = fasttext_vectors[i] / len(cleaned_list[i])
fasttext_vectors.shapeimport sklearn.metrics as metrics
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
train_fast = pd.DataFrame(fasttext_vectors)
Y_1 = df['fake'].as_matrix()
train_x_fast, test_x_fast, train_y_fast, test_y_fast = train_test_split(train_fast, Y_1, test_size=0.3, random_state=1)
train_x_fast.shape, test_x_fast.shape, train_y_fast.shape, test_y_fast.shapeimport time
from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression
start = time.time()
lr_model_fast = LogisticRegression(max_iter=60)
lr_model_fast.fit(train_x_fast, train_y_fast)
training_time = time.time() - start
predict_y_1 = lr_model_fast.predict(test_x_fast)
accuracy_1 = metrics.accuracy_score(test_y_fast.ravel(), predict_y_1.ravel())
precision_1 = metrics.precision_score(test_y_fast.ravel(), predict_y_1.ravel())
recall_1 = metrics.recall_score(test_y_fast.ravel(), predict_y_1.ravel())
f1_1 = metrics.f1_score(test_y_fast.ravel(), predict_y_1.ravel())
print('Accuracy: {:.2f} | Precision: {:.2f} | Recall: {:.2f} | F1-measure: {:.2f} | Training time: {:.2f}s'
.format(accuracy_1, precision_1, recall_1, f1_1, training_time))from sklearn.metrics import classification_report
from sklearn import metrics
from sklearn.neural_network import MLPClassifier
mlp_fasttext=MLPClassifier()
y_pred = mlp_fasttext.fit(train_x_fast, train_y_fast).predict(test_x_fast)
accuracy = metrics.accuracy_score(test_y_fast.ravel(), y_pred.ravel())
matrix = metrics.confusion_matrix(test_y_fast,y_pred)
print('Accuracy= {:.4f}'.format(accuracy))
print('\nconfusion_matrix:\n',matrix)
print('report:\n',classification_report(test_y_fast, y_pred))
# print('Accuracy= {:.4f} | Precision= {:.4f} | Recall= {:.4f} | f1 score= {:.4f}'.format(accuracy,precision,recall,f1,))from sklearn.metrics import classification_report
import os
os.environ['KMP_DUPLICATE_LIB_OK']='True'
from xgboost import XGBClassifier
xg_test = XGBClassifier(max_depth=7,
learning_rate=0.2,
n_estimators=1000,
silent=True,
objective='binary:logistic',
nthread=-1,
gamma=0,
min_child_weight=1,
max_delta_step=0,
subsample=1,
colsample_bytree=1,
colsample_bylevel=1,
reg_alpha=0,
reg_lambda=1,
scale_pos_weight=1,
base_score=0.5,
seed=0,
missing=None)
xg_test.fit(train_x_fast, train_y_fast)
y_pred = xg_test.predict(test_x_fast)
y_pred= (y_pred>0.5)
print(metrics.accuracy_score(test_y_fast, y_pred),'\n')
matrix = metrics.confusion_matrix(test_y_fast,y_pred)
print(matrix,'\n')
print(classification_report(test_y_fast, y_pred)) Putting all together
from sklearn.ensemble import VotingClassifier
eclf_final = VotingClassifier(estimators=[('eclf', eclf), ('eclf2', eclf2)],weights=[2,1])
pre=eclf_final.fit(x_train, y_train)
y_pred = eclf_final.predict(x_test)
y_pred= (y_pred>0.5)
print(metrics.accuracy_score(y_test, y_pred),'\n')
matrix = metrics.confusion_matrix(y_test,y_pred)
print(matrix,'\n')
print(classification_report(y_test, y_pred)) 0.9484481851657023
[[871 43]
[ 55 932]]
precision recall f1-score support
0 0.94 0.95 0.95 914
1 0.96 0.94 0.95 987
avg / total 0.95 0.95 0.95 1901
C:\Anaconda3\lib\site-packages\sklearn\preprocessing\label.py:151: DeprecationWarning: The truth value of an empty array is ambiguous. Returning False, but in future this will result in an error. Use `array.size > 0` to check that an array is not empty.
if diff:
C:\Anaconda3\lib\site-packages\sklearn\preprocessing\label.py:151: DeprecationWarning: The truth value of an empty array is ambiguous. Returning False, but in future this will result in an error. Use `array.size > 0` to check that an array is not empty.
if diff:
C:\Anaconda3\lib\site-packages\sklearn\preprocessing\label.py:151: DeprecationWarning: The truth value of an empty array is ambiguous. Returning False, but in future this will result in an error. Use `array.size > 0` to check that an array is not empty.
if diff:
C:\Anaconda3\lib\site-packages\sklearn\preprocessing\label.py:151: DeprecationWarning: The truth value of an empty array is ambiguous. Returning False, but in future this will result in an error. Use `array.size > 0` to check that an array is not empty.
if diff:
C:\Anaconda3\lib\site-packages\sklearn\preprocessing\label.py:151: DeprecationWarning: The truth value of an empty array is ambiguous. Returning False, but in future this will result in an error. Use `array.size > 0` to check that an array is not empty.
if diff: