In Dolores Park, 'neath the sun's bright array,
I feasted on a sandwich, in the midday.
While Waldo, donned in cap, hid in plain sight,
Like a needle in a haystack, out of the light,
Unseen by me, focus led astray, I missed the play
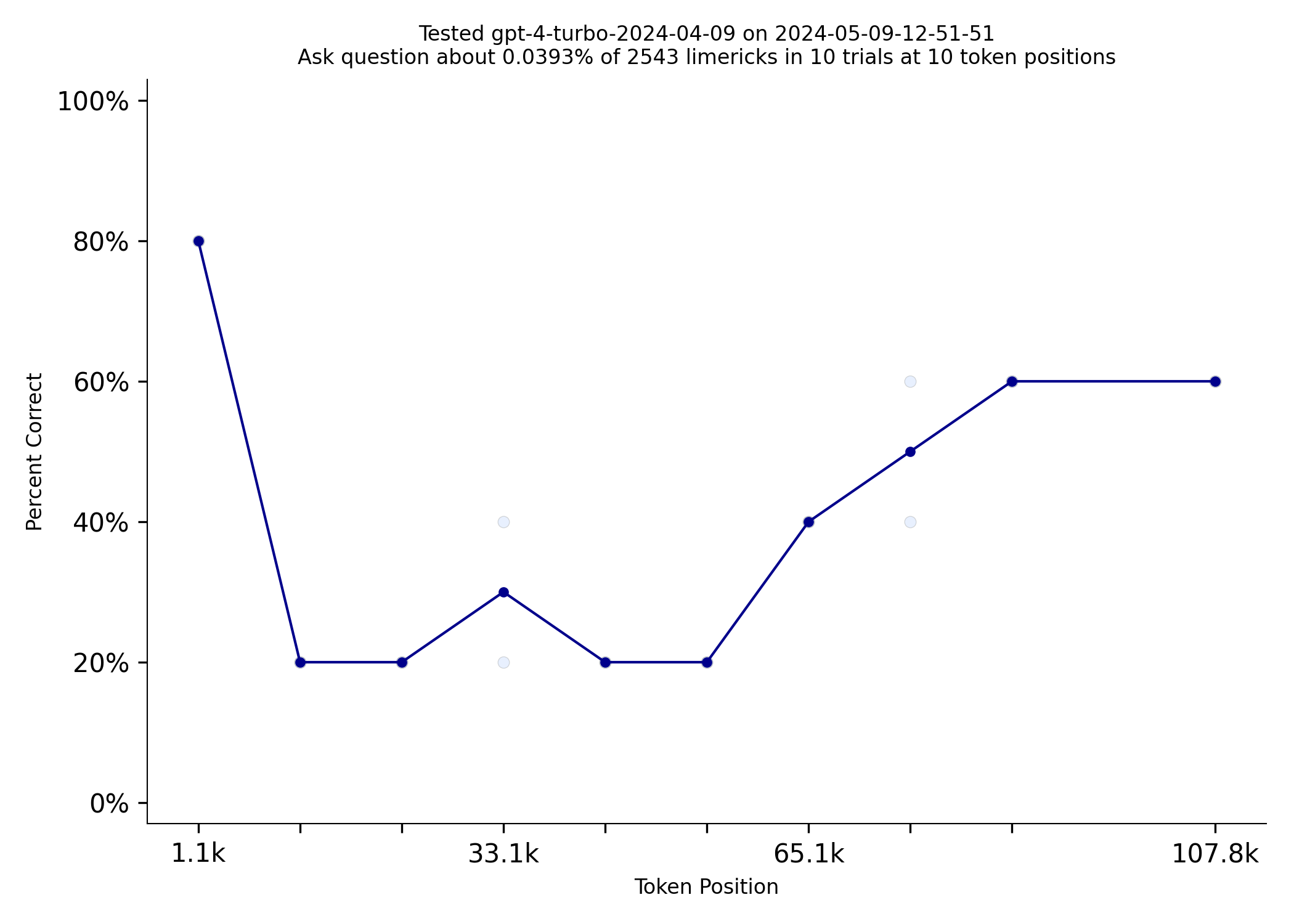
Needle in a haystack (NIAH) has been a wildly popular test for evaluating how effectively LLMs can pay attention to the content in their context window. As LLMs have improved NIAH has become too easy. Needle in a Needlestack (NIAN) is a new, more challenging benchmark. Even GPT-4-turbo struggles with this benchmark:
You can see more results on the [NIAN website](https://nian.llmonpy.ai).
NIAN creates a list of limericks from a large [database of limericks](https://zenodo.org/records/5722527) and asks a question about a specific limerick that has been placed at a test location. Each test will typically use 5 to 10 test limericks placed at 5 to 10 locations in the prompt. Each test is repeated 2-10 times. It is amazing that an LLM can answer these questions at all! Here is a [link to an example prompt](artifacts/sample_prompt.txt). The question is "Does Mr. Thistle follow our rules?" and the associated limerick is in the middle of the prompt:
Mr. Thistle, what's this all about?
All our rules you dismiss — baldly flout.
I have read your epistle;
It made my hairs bristle.
I'm blowing the whistle — you're out!
Evaluating the LLM responses is always challenging and NIAN is worthless without accurate evaluation. To get more accurate evaluation, NIAN uses 5 LLMs to evaluate the responses and pass/fail is determined by majority vote. NIAN includes tools to evaluate the evaluators and improve them with few shot prompting.
Given the number of trials and the 5 LLM calls per trial, it is important that NIAN make many LLM calls in parallel. It uses a rate limiter to manage the rate of LLM calls. NIAN can finish a 125 trial test in about 35 seconds.
NIAN supports the LLMs I have access to -- OpenAI, Anthropic and Mistral. Adding new LLMs is easy, and it will be covered later in this document. You can set the rate limits for each LLM, but you will want generous rate limits to run the tests. My development was done with OpenAI Tier 4, Anthropic Tier 4 and Mistral Tier 2. NIAN looks for the standard API keys -- OPENAI_API_KEY, ANTHROPIC_API_KEY, and MISTRAL_API_KEY. It looks first for these keys prefixed with "NIAN_" if you want to use NIAN specific keys.
You configure a test by setting the CURRENT_TEST_CONFIG or by changing DEFAULT_TEST_CONFIG. A TestConfig looks like this:
DEFAULT_TEST_CONFIG = TestConfig(model_list=[MISTRAL_7B, GPT3_5],
test_thread_count=100,
evaluator_model_list=EVALUATOR_MODEL_LIST,
default_evaluator=DefaultEvaluator(EVALUATOR_MODEL_LIST),
number_of_questions_per_trial=5,
repeat_question_limerick_count=100,
trial_count=5,
location_count=10)
Most of the settings are self-explanatory. The model_list is the list of LLMs to use for the test. The test_thread_count is the number of threads to used to generate answers etc. Repeat_question_limerick_count is the is least obvious. It controls how many times the limerick that the prompt asks a question about is repeated. When it is repeated, it is repeated in the prompt at the same location. This is a way to test if repeating information in the prompt helps the LLM answer the question. The trial_count is the number of trials to run for each question and each location. The total number of times a prompt will be sent to each model tested is:
number_of_questions_per_trial * trial_count * location_count
Adding a new LLM is easy. You need to create a new class that extends LLMClient. You need to implement the constructor and the do_prompt method. The client will look something like this.
class OpenAIModel(LlmClient):
def __init__(self, model_name, max_input, rate_limiter, thead_pool=None):
super().__init__(model_name, max_input, rate_limiter, thead_pool)
key = get_api_key("OPENAI_API_KEY")
self.client = OpenAI(api_key=key)
def do_prompt(self, prompt_text, system_prompt="You are an expert at analyzing text."):
completion = self.client.chat.completions.create(
model=self.model_name,
messages=[
{"role": "system", "content": system_prompt},
{"role": "user", "content": prompt_text}
],
temperature=0.0
)
result = completion.choices[0].message.content
return result
You will also need to create a global variable in llm_clients.py to make the model accessible. The client will need a rate limiter and a thread_pool to use for evaluation. The rate limiter is a RateLimiter object that will be used to manage the rate of LLM calls:
MISTRAL_RATE_LIMITER = RateLlmiter(*spread_requests(1000)) #used minute spread to seconds because tokens are TPM not TPS
MISTRAL_8X22B = MistralLlmClient("open-mixtral-8x22b", 24000, MISTRAL_RATE_LIMITER, MISTRAL_EXECUTOR)
NIAN includes tools to generate questions and answers for limericks, vet that LLMs can answer the questions, identify unique passing and failing answers to questions, report on dissent among LLMs on answer evaluation, report on variation in LLM answers when it is asked the same question multiple times at the same location, a tool to create plots from existing tests and a tool to run tests. All the scripts are in bin and set the venv for you.
nian runs the tests as configured in test_config.py. It presents progress bars for the model tests and evalutors. It stores it results in a date based directory in the "tests" directory.
dissent reports on the number of times the LLMs disagree on the evaluation of an answer. "Dissent" means that the LLM evaluated the answer differently than the majority of the LLMs. It writes the results to the console and the test directory. It runs on the most recent test unless you provide a test directory as an argument. This test is useful to determine if an LLM is an effective evaluator. GPT-3.5 was wrong very often in my tests, so I had to double up on mistral models.
question_variance reports on the variation in LLM answers when the same question is asked multiple times at the same location. It writes the results to the console and the test directory. It runs on the most recent test unless you provide a test directory as an argument. There is significant variation in LLMs on this test. It helps to determine if more trials per question are worthwhile.
answers reports on the unique answers to questions that passed and failed. It writes the result to answer_anlysis.json. The information can be used to if the evaluation is done correctly and help provide examples for few-shot prompting. It runs on the most recent test unless you provide a test directory as an argument.
reevaluate is a tool to reevaluate the answers to questions to support refinement of the evaluators. Typically, you would run tests, then use "answers" to analyze the answers, then add "alternate_answers" to the questions in full_questions.json to change the few-shot evaluation prompt. Then run reevaluate to get new evaluations. It only evaluates the answers, so it is quite fast. I reevaluated 1200 answers in about 2 minutes. It writes the results to the test directory with "reeval_" prefixed to the file name. It runs on the most recent test unless you provide a test directory as an argument.
plot is used to tweak the plots generated by the test. The code to generate the plots is in test_results.py. It runs on the most recent test unless you provide a test directory as an argument.
generate_questions is a tool to generate questions for limericks. It picks 5 limericks at random and asks you to provide a question about the limerick and also provide an answer. It does not pick limericks that are in full_questions.json. It writes the results to questions.json. You can add the questions you like to full_questions.json.
vet is a tool to test if the LLMs can answer the questions in full_questions.json. It gives every LLM in CURRENT_TEST_CONFIG.model_list this prompt:
This is a limerick:
$limerick_text
This is a question to test your understanding of the limerick:
$question_text
Please answer the question as concisely as possible. Do not explain your answer.
for each question in full_questions.json 5 times. For a question to pass, every LLM must answer correctly every time. This point of this tool is to make sure that NIAN is not testing the LLMs ability to answer a question about the limerick. It is testing the LLMs ability to pay attention to the limerick in the prompt. It writes the results to the vetter_results directory.