(Left) Front view of the multi-modal data acquisition system. (Right) Samples of map data form different dataset sequences. From left to right and top to down, we display maps generated from a forest, an urban area, an open road and a large indoors hall, respectively.
Our dataset was captured by a rich suite of sensors. Subsets of the data from the Indoor04 sequence are visualized here. The leftmost column shows the lidar data from Livox Avia and Horizon; the second column shows the lidar data from Ouster OS1 and OS0; the third column shows the data from the VLP-16 and depth image from L515. The rightmost column shows the RGB image from L515 and range images from 0S1 and OS0.
| Indoor data(Calibrate Sequence) | OpenRoad SLAM example(Road02 Sequence) |
|---|---|
 |
 |
| Forest SLAM example(Forest01 Sequence) | Hall SLAM example(Indoor04 Sequence) |
 |
 |
The dataset is available at the University of Turku servers. Specific links for each sequence and for the ground truth data are available in Section 3.1 of this file.
We present a novel multi-modal lidar dataset with sensors showcasing different scanning modalities (spinning and solid-state), sensing technologies, and lidar cameras. The focus of the dataset is on low-drift odometry, with ground truth data available in both indoors and outdoors environments with sub-millimeter accuracy from a motion capture (MOCAP) system. For comparison in longer distances, we also include data recorded in larger spaces indoors and outdoors.The dataset contains point cloud data from spinning lidars and solid-state lidars. Also, it provides range images from high resolution spinning lidars, RGB and depth images from a lidar camera, and inertial data from built-in IMUs.
Keywords: Lidar, Dataset, Multi-modal, Multi-scenario, SLAM, Solid-state lidars
-
A dataset with data from 5 different lidar sensors and one lidar camera in a variety of environments. This is, to our knowledge, the most diverse dataset in terms of lidar sensors for these environments. The dataset includes spinning lidars with 16 (Velodyne VLP-16), 64 (Ouster OS1-64) and 128 (Ouster OS1-128) channels and different vertical FoVs. Two different solid-state lidars (Livox Horizon and Livox Avia) with different scanning patterns and FoVs are also included. A lidar camera (RealSense L515) provides RGB images and lidar-aided depth images. Low-resolution images with depth, near-infrared and laser reflectivity data from the Ouster sensors complete the dataset.
-
The dataset includes sequences with MOCAP-based ground truth in both indoors and outdoors environments. This is, to the best of our knowledge, the first lidar dataset to provide such accurate ground truth in forest environments in addition to indoor areas, albeit the limited trajectory length.
-
In addition to the MOCAP-labeled data, the dataset includes other sequences in large indoor halls, roads, and forest paths. The wide variety of sensors enables comparison between lidar odometry and mapping algorithms to an extent that was not possible before, with both general-purpose and sensor-specific approaches.
-
Based on the presented dataset, we provide a baseline comparison of the state-of-the-art in lidar odometry, localization and mapping. We compare the odometry lift as well as the quality of the maps obtained with different sensors and different algorithms.
2022.03.01 Initial dataset upload
This work is licensed under the MIT license and is provided for academic purpose. Please contact us at qingqli@utu.fi for further information.
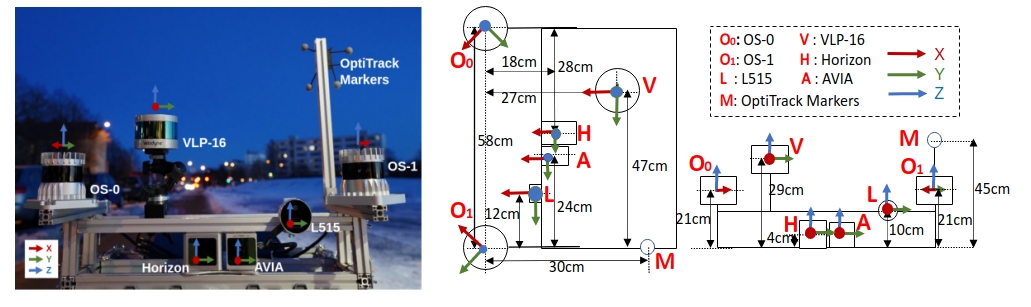
Physical drawings and schematics of the sensor suite is given below. The unit of the figures is centimeter.
Our data collecting platform, front view RGB (left), top view (middle) and front view (right).
Sensor specification for the presented dataset. Angular resolution is configurable in the OS1-64 (varying the vertical FoV). Livox lidars have a non-repetitive scan pattern that delivers higher angular resolution with longer integration times. Range is based on manufacturerinformation, with values corresponding to 80% Lambertian reflectivity and 100 klx sunlight, except for the L515 lidar camera.
The rostopics of our rosbag sequences are listed as follows:
-
VLP-16 LIDAR :
/velodyne_points sensor_msgs/PointCloud2 -
OS0 LIDAR :
/os_cloud_node/imu : sensor_msgs/Imu,
/os_cloud_node/points : sensor_msgs/PointCloud2,
/img_node/nearir_image : sensor_msgs/Image,
/img_node/range_image : sensor_msgs/Image,
/img_node/reflec_image : sensor_msgs/Image, -
OS1 LIDAR :
/os_cloud_nodee/imu : sensor_msgs/Imu,
/os_cloud_nodee/points : sensor_msgs/PointCloud2,
/img_nodee/nearir_image : sensor_msgs/Image,
/img_nodee/range_image : sensor_msgs/Image,
/img_nodee/reflec_image : sensor_msgs/Image,
/img_nodee/signal_image : sensor_msgs/Image, -
Horizon LIDAR :
/livox/imu : sensor_msgs/Imu,
/livox/lidar : livox_ros_driver/CustomMsg -
AVIA LIDAR :
/avia/livox/imu : sensor_msgs/Imu,
/avia/livox/lidar : livox_ros_driver/CustomMsg, -
L515 LIDAR CAMERA:
/cam_1/color/image_raw : sensor_msgs/Image,
/cam_1/depth/image_rect_raw : sensor_msgs/Image, -
MOCAP SYSTEM:
/vrpn_client_node/optitest/pose : geometry_msgs/PoseStamped
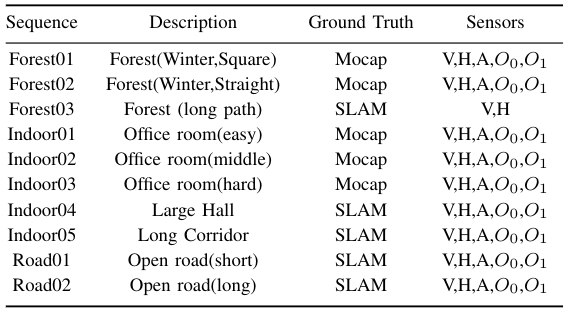
List of data sequences in our dataset
(V: Velodyne VLP-16, H:Livox Horizon, A:Livox Avia, O_0: Ouster OS0, O_1: Ouster OS1.
| Sequence Name | Collection Date | Total Size | Duration | Features | Rosbag | GroundTruth |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Forest01 | 2022-02-08 | 21.9g | 62s | Winter,night,Square | Rosbag | MOCAP link |
| Forest02 | 2022-02-08 | 22.4g | 73s | Winter,night,Straight | Rosbag | MOCAP link |
| Forest03 | 2021-09-28 | 7.3g | 717s | Autumn,forest.long | Rosbag | - |
| Indoor01(easy) | 2022-04-27 | 49.3g | 114s | day,indoor,office | Rosbag | MOCAP link |
| Indoor02(medium) | 2022-02-21 | 16.7g | 42.3s | day, indoor,office | Rosbag | MOCAP link |
| Indoor03(diffcult) | 2021-02-21 | 19.2g | 46.7s | day,indoor,office | Rosbag | MOCAP link |
| Indoor04(Hall) | 2022-02-09 | 92.8g | 248s | day,indoor,Hall | Rosbag | SLAM link |
| Indoor05(Corridor) | 2022-02-09 | 141.5g | 551s | day,indoor,corridor | Rosbag | SLAM link |
| Road01 | 2022-02-20 | 47.6g | 110s | day,short road | Rosbag | - |
| Road02 | 2022-02-20 | 212.7g | 487s | day,long road | Rosbag* | SLAM link |
- Note: For sequence Road02, please decompress the rosbag first
rosbag decompress road02.bag - Note: For sequence Forest03 and Road01, the SLAM results are not provided, therefore end users can generate SLAM results. Other sequences that in MoCAP system unavailable environment, SLAM result are generated from FAST_LIO with OS0 (128 Channels) lidar.
The meaning of each column in ground truth files is as follows:
timestamp, pose.position.x, pose.position.y, pose.position.z, roll, pitch, yaw, pose.orientation.x, pose.orientation.y, pose.orientation.z, pose.orientation.w.
In the MOCAP system available environment, the ground truth data from the MOCAP system are recorded in rosbag. The user can generate the ground truth file by himself. A Script named 'result_sub_ros.py' is provided in the scripts folder to record the result and save it into a CSV file.
python2 result_sub_ros.py
| Sequence Name | Collection Date | Total Size | Duration | Features | Rosbag |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LidarsCali | 2022-02-11 | 21.9g | 19.1s | room | Rosbag |
We teseted some well-known lidar SLAM methods, which are listed below:

Qualitative comparison of the mapping quality. Top row showm the rgb image, map LIOL Horizon, FLIO OS0. Bottom row shows a parking signs in rgb image, and mapping result from Horizon-based LIOL, Horizon, Avia, OS0, and OS1-based FLIO, and Velodyne's LeGo-LOAM maps, respectively.

Estimated trajectories. Top row: Indoor01, Indoor02, Indoor03, Forest02. Bottom row: Forest01, Road02, Indoor04, Indoor05.
Rosbag recoreds message with their raw frame_id. If user need to show or run multiple lidar same time, we use srv_tools to change frame_id of each topics. To install srv_tools, please follow srv_tools installation.
Then follow the commands below:
cd ./scripts/ # Go to scripts folder
python2 change_frameid.py [inbag_path] [outbag_path] # Specify bag path
Note: This script will transform the raw frame_id to new one(right) as based on topic(left) follows:
"/avia/livox/lidar" -> "avia_frame"
"/avia/livox/imu" -> "avia_frame"
"/livox/imu" -> "horizon_frame"
"/livox/lidar" -> "horizon_frame"
"/os_cloud_node/points" -> "os0_sensor"
"/os_cloud_node/imu" -> "os0_imu"
"/os_cloud_nodee/points"-> "os1_sensor"
"/os_cloud_nodee/imu" -> "os1_imu"
Ubuntu 64-bit 16.04 or 18.04. ROS Kinetic or Melodic. ROS Installation and its additional ROS pacakge:
sudo apt-get install ros-${ROS_DISTRO}-cv-bridge ros-${ROS_DISTRO}-tf ros-${ROS_DISTRO}-message-filters ros-${ROS_DISTRO}-image-transport
NOTE You need to source your ROS installation for the $ROS_DISTRO env variable to be defined. For example, if your use ROS-melodic, the command should be:
sudo apt-get install ros-melodic-cv-bridge ros-melodic-tf ros-melodic-message-filters ros-melodic-image-transport
Follow PCL Installation.
To visualize data, we need install the Livox LiDAR SDK. Follow instructions Livox-ros-driver installation
cd ~/catkin_ws/src
git clone git@github.com:TIERS/multi-lidar-dataset.git
cd ..
catkin_make -DCATKIN_WHITELIST_PACKAGES="dataset_tools"
source /devel/setup.bash
Finally, we can visulize all data by
roslaunch dataset_tools data_show.launch
We use open-source tool evo for evalutation.
To evaluate LIDAR SLAM, you can run:
evo_ape tum optk.txt {SLAM_result}.txt -a -p
We provide a tool for extrinsic parameters between lidars that can calculate the extrinsic parameter based on GICP methods. As the OS0 has the highest FOV, we first rotate the coordinate of OS0 sensor 45 degrees to align its X-axis with Horizon, Avia and Velodyne. Then the rotated coordinate is treated as "base_link". All clouds from other lidar are matched with the "base_link" coordinate. For Avia, Horizon, we integrated the first five frames to increase point cloud density and reduce its low FOV impact.
To use this tools, first play one rosbag from our dataset:
rosbag play ICT_OUT_2022-02-20-17-34-49.bag --clock
Then run our calibration launch file:
roslaunch dataset_tools lidars_extri_comp.launch
Then you can find the calculated parameter, and its transformed cloud;
OS0 -> base_link 0 0 0 0.785398 -0 0 /os0_sensor /base_link 10
OS1 -> base_link 0.0100882 0.581502 -0.0210581 2.34826 3.12619 -3.13066 /os1_sensor /base_link 10
velo -> base_link -0.164831 0.173188 0.117624 3.07795 3.09161 3.12807 /velo_sensor /base_link 10
Avia -> base_link -0.0608374 0.29663 -0.122276 0.00549421 0.000246092 -0.011555 /avia_frame /base_link 10
hori -> base_link 0.00345477 0.145195 -0.134907 3.12905 3.14022 3.12706 /hori_frame /base_link 10
The RVIZ window will be opened and show the aligned point cloud.

For IMU intrinsics, visit Imu_utils
For extrinsics between cameras and LIVOX Lidar, visit livox_camera_lidar_calibration
Avia: https://www.livoxtech.com/avia,
Horizon:https://www.livoxtech.com/horizon,
OS0:https://ouster.com/products/scanning-lidar/os0-sensor/,
OS1:https://ouster.com/products/scanning-lidar/os1-sensor/,
Vlp-16:https://velodynelidar.com/products/puck/,
Realsense L515:https://www.intelrealsense.com/lidar-camera-l515/.
This research work is supported by the Academy of Finland's AeroPolis project (Grant 348480) and the Finnish Foundation for Technology Promotion (Grants 7817 and 8089).
Please cite our Dataset paper if the code or data in this repo helps your work:
@article{li2022dataset,
title={Multi-Modal Lidar Dataset for Benchmarking General-Purpose Localization and Mapping Algorithms},
author={ Li, Qingqing and Yu, Xianjia and Pe{\~n}a Queralta, Jorge and Westerlund, Tomi},
journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:2203.03454},
year={2022}
}