The goal of our course project is to use the Q-Learning algorithm for UAV path planning, detecting and recording the signal strength value of each wireless router when the UAV is right above it. We achieve intelligent route planning for the UAV by implementing maximum data rate transmission with the router while avoiding obstacles. We also make use of the basic object-oriented features of the C++ language taught in this course for practice. In the code part, we adopted object-oriented programming concepts. In the research of the UAV route planning framework structure, a UAV class is defined, including flight radius, level flight speed, vertical flight speed, maximum and minimum flight altitude, etc., which embodies the concept of class and object; in the discussion of static global planning and dynamic local planning methods, two types of environment classes, obstacle class and router class, are defined as the simulation environment of the algorithm, realizing inheritance and polymorphism.
In this experiment, the main tools we use are:
- Visual Studio 2019 We mainly use Visual Studio 2019 for code writing, with the IDE version 16.8.6. Using the ISO C++ 17 standard, the operating system is Windows 10 x64, and the compiler is msvc.
- Unreal Engine 4 We use the UE 4 engine to perform 3D modeling of the UAV operating environment. UE 4 is a game development engine developed by Epic. UE 4 is a complete set of integrated tools for building games, simulations, and visualizations that can satisfy the vision of artists while also having enough flexibility to meet the needs of different scales of development teams.
- Airsim We use the Airsim API for controlling the UAV in the UE 4 engine. Airsim is an open-source platform for building drone, car, and other simulators based on the Unreal Engine and can be used for cross-platform simulation control through the PX4 flight controller. Its realistic physics and visual simulation environment make it a great platform. Not only does it simulate the dynamics of vehicles like cars and drones, but it also does an excellent job of simulating weather effects and lighting control.
- Fastor Tensor Library We imported a C++ tensor library called Fastor in our code. Fastor is a high-performance, stack-based tensor (fixed multi-dimensional array) library for modern C++ for manipulating multi-dimensional arrays in C++.
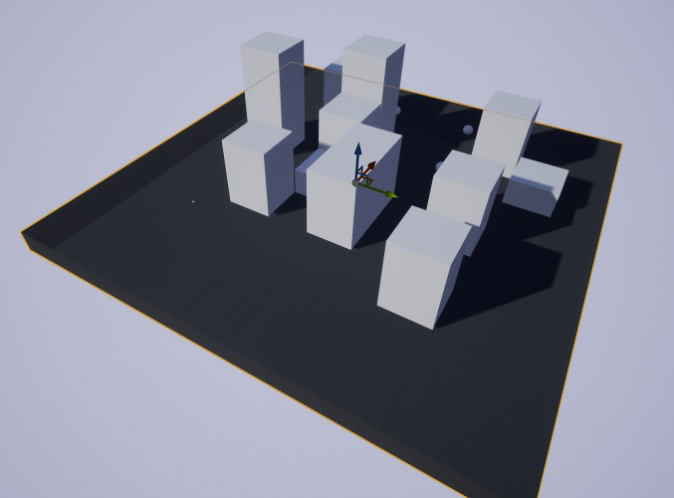
First, we created an environment for the UAV in Unreal Engine, initializing it as a 7x7 grid with each grid cell measuring 10m. Next, we set different buildings as obstacles in this environment. We divide the altitudes of the buildings into three levels: 60m, 150m, and 250m. There are two 60m obstacles, eight 150m obstacles, and two 250m obstacles. Finally, we set up five routers in the environment, represented by white spheres in the scene. The UAV's route must pass through all five routers while avoiding obstacles to achieve the optimal path. The positions of the buildings and routers are random.
In this experiment, we defined a UAV. We used fuel to define the UAV's flight radius. Then we initialized the UAV's flight speed and level flight speed to be 3 meters/second and the vertical flight speed to be 3 m/s. At the same time, we set three flight altitudes for the UAV: 50m, 125m, and 200m. Finally, we set the UAV to perform six actions: moving forward, backward, left, right, up, and down.
To optimize the UAV's path, we used the Q-learning algorithm. The Q-learning algorithm uses future rewards to influence the current action of a given state, so we used it as an algorithm for maximizing rewards. First, we used the UAV's takeoff position as the origin of the Airsim coordinate system, called the AirsimAPI to obtain the origin coordinates of each obstacle and router in the Airsim coordinate system. Then we set different rewards or penalties in the reward matrix according to the different environments. Next, we set five routers as the UAV's flight targets and trained 2000 times for each target router, with a total of 10000 training iterations for the entire program. According to the Q-learning algorithm, we initialized the Q-table, setting all Q-values to 0, selecting an action, executing the action, measuring the reward, and updating the Q-table after each test.
After training, we used the obtained Q-Table and the Q-learning algorithm for UAV path planning. We used the Airsim API to control the UAV in the UE 4 engine for demonstration, achieving good results.
Next, we changed the positions of the obstacles, retrained, and revalidated. The results show that the UAV can accurately traverse all routers in different environments, indicating that the model has good robustness.
- More complex environments: The current experiment was performed in a relatively simple environment with a small number of obstacles. To make the UAV more adaptable, the model can be tested and trained in more complex environments with a higher number of obstacles, different weather conditions, and varying topography.
- Other reinforcement learning algorithms: While Q-Learning was effective in this project, it may be beneficial to explore other reinforcement learning algorithms, such as Deep Q-Learning, Policy Gradient, or Actor-Critic methods, to compare their performance and effectiveness in UAV path planning.
- Multi-agent systems: The current project focuses on a single UAV. However, in practical scenarios, multiple UAVs may need to collaborate to accomplish a task. Extending the model to handle multi-agent systems can provide more realistic and practical solutions.
- Dynamic obstacles: In real-world situations, UAVs may encounter dynamic obstacles, such as moving vehicles or birds. Adapting the model to account for dynamic obstacles will improve the UAV's ability to navigate complex environments.
- Energy efficiency: The current model does not take energy efficiency into account when planning the UAV's path. Incorporating energy efficiency metrics could result in more efficient UAV trajectories, extending flight times, and reducing energy consumption.
- Real-world testing: While simulation environments like UE4 and Airsim provide a good starting point for testing the model, real-world testing is essential to evaluate the model's performance and robustness in practical scenarios. This will help identify any limitations of the model and provide valuable feedback for further improvements.
By addressing these potential improvements and expanding the scope of the project, the UAV's path planning capabilities can be further enhanced, making it more applicable and useful in various real-world applications, such as search and rescue missions, infrastructure inspection, or environmental monitoring.
[1] Practical Reinforcement Learning — 02 Getting started with Q-learning
[2] Communication basics: The relationship between baud rate, data transmission rate, and bandwidth
[3] Epic Games Unreal Engine 4 Documentation
[4] Microsoft Airsim Documentation
[5] Fastor-wiki
[6] Optimizing-UAV-trajectory-for-maximum-data-rate-via-Q-Learning
[8] Airsim series (Five) - Controlling quadcopter flight (core API)
[9] Q learning - epsilon greedy update
[10] How to Set Up a Grid for Level and Game Design Metrics
[11] 6.9 — Sharing global constants across multiple files (using inline variables)