Comparison of mean cumulative count curves via the area under the curve (AUC)
Zachary R. McCaw
Updated: 2022-05-19
Description
This package provides functions for inference on the difference and ratio in AUCs comparing two mean cumulative count (MCC) curves. The MCC curves are estimated using an approach based on the method of Ghosh and Lin (2000), which accounts for the presence of terminal competing risks. Also see:
- CICs for comparing cumulative incidence curves.
Installation
devtools::install_github(repo = 'zrmacc/MCC')Methods
Estimation of the mean cumulative count curve
For each study arm, the MCC is estimated as follows. Define
Here
Data
The function GenData simulates example data in the format expected by this package. The recurrent event times are generated from a Poisson process that continues until censoring or death, whichever occurs first. Optionally, a gamma frailty_variance may be specified such that the patient-specific event and death rates are correlated. The example data includes 100 patients in each of the treatment and control arms. The maximum duration of follow-up is tau = 4 (e.g. years). The rate of recurrent events for patients in the treatment arm is 80% the rate for patients in the control arm.
library(MCC)
covariates <- data.frame(
arm = c(rep(1, 100), rep(0, 100))
)
data <- MCC::GenData(
beta_event = c(log(0.8)),
covariates = covariates,
frailty_variance = 0.2,
tau = 4
)
head(data)## idx status time arm cens_rate death_rate event_rate frailty
## 1 1 1 0.08845737 1 0.25 0.1888051 0.6041762 0.7552202
## 2 1 2 0.23565323 1 0.25 0.1888051 0.6041762 0.7552202
## 3 2 1 0.16410134 1 0.25 0.1884027 0.6028886 0.7536108
## 4 2 1 0.66910083 1 0.25 0.1884027 0.6028886 0.7536108
## 5 2 2 0.87297407 1 0.25 0.1884027 0.6028886 0.7536108
## 6 3 2 0.02295830 1 0.25 0.3140817 1.0050614 1.2563267
The essential data are:
idx, the subject index.time, the observation time.status, coded 0 for censoring, 1 for an event, 2 for death (or any competing terminal event).arm, coded as 1 for treatment, 0 for reference.
For analyzing other data sets, arm and status should have the same coding. Each subject should experience an observation-terminating event, i.e. either death or censoring.
The example data also include:
true_death_rate, the patient-specific terminal event rate, calculated asfrailtyxbase_death_ratexexp(covariates %*% beta_death). If omitted,beta_deathis set to zero.true_event_rate, the patient-specific recurrent event rate, calculated asfrailtyxbase_event_ratexexp(covariates %*% beta_event). If omitted,beta_eventis set to zero.frailty,the patient-specific frailty drawn from a gamma distribution with mean 1 and the specified variance.
Observation-terminating events
In contrast to the time to first event setting, in the multiple or recurrent events setting, a subject may remain at risk after experiencing an event of interest. An observation-terminating event, either censoring or the occurrence of a competing risk, is therefore necessary to remove a subject from the risk set. Conversely, a subject who lacks an observation-terminating event is implicitly assumed to remain at risk indefinitely. If a subject lacks an observation-terminating event, then by default CompareAUCs will add a censoring time immediately after their last event of interest. For example, if the data for subject 1 were:
## idx time status
## 1 1 2 1
## 2 1 3 1
## 3 1 5 1
then, for analysis, the subject is assumed to have been censored after the last event, as in the following:
## idx time status
## 1 1 2 1
## 2 1 3 1
## 3 1 5 1
## 4 1 5 0
If a subject who lacks an observation-terminating event should, in fact, remain at risk indefinitely, set cens_after_last = FALSE.
Terminal events of interest
Suppose the endpoint of interest includes a fatal event. One such endpoint is heart failure hospitalization (HFH) or cardiovascular (CV)-death. In this setting, it becomes necessary to distinguish non-fatal events of interest (e.g. HFH), after which the subject remains in the risk set, from fatal events of interest (e.g. CV-death), after which the subject is removed from the risk set. To achieve this, a fatal event of interest should be recorded using two records. The first, with status = 1, indicates that an event of interest has occurred. The second, with status = 2, indicates that the event was terminal. For example, the following data indicate that subject 1 had 3 events of interest, and that the 3rd event, occurring at time = 5, was terminal.
## idx time status
## 1 1 2 1
## 2 1 3 1
## 3 1 5 1
## 4 1 5 2
By contrast, the following data indicate that subject 2 had 3 events of interest, none of which was terminal:
## idx time status
## 1 2 2 1
## 2 2 3 1
## 3 2 5 1
Note that, by default, subject 2 is assumed to have been censored after their 3rd event of interest, as in the following:
## idx time status
## 1 2 2 1
## 2 2 3 1
## 3 2 5 1
## 4 2 5 0
Although censoring (status = 0) and a terminal event (status = 2) both remove a subject from the risk set, there is an important distinction. Censoring leaves open the possibility that the subject experienced more events of interest in the future, whereas a terminal event precludes the possibility of any future events of interest.
Analyses
AUCs
To compare the areas under the mean cumulative count curves up to time
aucs <- MCC::CompareAUCs(
data,
tau = 4,
boot = TRUE,
perm = TRUE,
reps = 200,
alpha = 0.05
)
show(aucs)## Marginal Areas:
## arm n area se tau
## 1 0 100 6.29 0.568 4
## 2 1 100 4.31 0.476 4
##
##
## CIs:
## method contrast observed se lower upper
## 1 asymptotic A1-A0 -1.980 0.7410 -3.430 -0.530
## 3 bootstrap A1-A0 -1.980 0.7480 -3.400 -0.616
## 2 asymptotic A1/A0 0.685 0.0978 0.518 0.906
## 4 bootstrap A1/A0 0.685 0.0994 0.508 0.890
##
##
## P-values:
## method contrast observed p
## 1 asymptotic A1-A0 -1.980 0.00748
## 3 bootstrap A1-A0 -1.980 0.00995
## 5 permutation A1-A0 -1.980 0.00995
## 2 asymptotic A1/A0 0.685 0.00801
## 4 bootstrap A1/A0 0.685 0.00995
## 6 permutation A1/A0 0.685 0.00995
Here:
tauis the truncation time, or the time up to which the AUC is calculated.bootindicates to construct bootstrap confidence intervals.permindicates to perform permutation tests for the difference and ratio of AUCs.repsis the number of simulation replicates.- The bootstrap is grouped by
idx, and stratified bystrata, if applicable.
- The bootstrap is grouped by
alphais 1 minus the desired coverage for confidence intervals.
Stratified Analysis
CompareAUCs also allows for stratified analysis. Consider a data set, similar to that described previously, but with the additional of a binary stratification factor. The event rate for individuals in stratum 1 is increased by 20%.
# Generate data with strata.
covariates <- data.frame(
arm = c(rep(1, 100), rep(0, 100)),
strata = stats::rbinom(200, 1, 0.25)
)
data <- MCC::GenData(
beta_event = c(log(0.8), log(1.2)),
covariates = covariates,
frailty_variance = 0.2,
tau = 4
)
# Stratified AUC analysis.
aucs <- MCC::CompareAUCs(
data,
strata = data$strata,
tau = 4,
boot = TRUE,
perm = TRUE,
reps = 200,
alpha = 0.05
)
show(aucs)## Marginal Areas:
## arm n area se tau
## 1 0 100 5.85 0.608 4
## 2 1 100 5.51 0.597 4
##
##
## CIs:
## method contrast observed se lower upper
## 1 asymptotic A1-A0 -0.338 0.852 -2.010 1.33
## 3 bootstrap A1-A0 -0.338 0.867 -1.860 1.21
## 2 asymptotic A1/A0 0.942 0.141 0.702 1.26
## 4 bootstrap A1/A0 0.942 0.146 0.720 1.24
##
##
## P-values:
## method contrast observed p
## 1 asymptotic A1-A0 -0.338 0.692
## 3 bootstrap A1-A0 -0.338 0.697
## 5 permutation A1-A0 -0.338 0.846
## 2 asymptotic A1/A0 0.942 0.692
## 4 bootstrap A1/A0 0.942 0.697
## 6 permutation A1/A0 0.942 0.846
Outputs
The output of CompareAUCs is an object with these slots.
@StratumAreascontaining the stratum-specific AUCs for each arm.
aucs@StratumAreas## arm strata n tau area var_area se_area weight
## 1 0 0 76 4 5.045419 34.65885 0.6753055 0.74
## 2 0 1 24 4 8.145358 42.53490 1.3312729 0.26
## 3 1 0 72 4 5.029110 31.44486 0.6608587 0.74
## 4 1 1 28 4 6.892973 48.72342 1.3191369 0.26
@MargAreascontaining the AUCs for each arm, marginalized over any strata.
aucs@MargAreas## arm n area se tau
## 1 0 100 5.851403 0.6078921 4
## 2 1 100 5.513715 0.5973172 4
@CIscontaining confindence intervals for the difference and ratio of AUCs.
aucs@CIs## method contrast observed se lower upper
## 1 asymptotic A1-A0 -0.3376884 0.8522445 -2.0080569 1.332680
## 3 bootstrap A1-A0 -0.3376884 0.8672591 -1.8618497 1.214607
## 2 asymptotic A1/A0 0.9422893 0.1414339 0.7021378 1.264580
## 4 bootstrap A1/A0 0.9422893 0.1456046 0.7199988 1.236457
@MCFcontaining the per arm mean cumulative count curve, averaged across strata.
head(aucs@MCF)## time mcf var_mcf se_mcf arm
## 1 0.004363264 0.009285714 0.002328061 0.04824999 1
## 2 0.016617209 0.019563492 0.009827984 0.09913619 1
## 3 0.023142688 0.028849206 0.011983596 0.10946961 1
## 4 0.024007674 0.039126984 0.019272254 0.13882454 1
## 5 0.037141490 0.048412698 0.021255417 0.14579238 1
## 6 0.039660038 0.057698413 0.023066131 0.15187538 1
@Pvalscontaining the bootstrap and permutation p-values.
aucs@Pvals## method contrast observed p
## 1 asymptotic A1-A0 -0.3376884 0.6919322
## 3 bootstrap A1-A0 -0.3376884 0.6965174
## 5 permutation A1-A0 -0.3376884 0.8457711
## 2 asymptotic A1/A0 0.9422893 0.6920809
## 4 bootstrap A1/A0 0.9422893 0.6965174
## 6 permutation A1/A0 0.9422893 0.8457711
@Repsis a list containing the bootstrap and permutation test statistics.
Adjusted AUCs
The previous estimator allows for stratification, but a different approach is needed to accommodate continuous covariates. If covariates are provided, then CompareAUCs uses an augmentation estimator to adjust for differences between the treatment groups. Note that strata and covariates should not both be provided. If adjustment for both is needed, use model.matrix to generate a design matrix including both covariates and stratum indicators, e.g. model.matrix(~ 0 + covar + strata, data = data), then supply the design matrix covar argument.
# Generate data with a continuous covariate.
covariates <- data.frame(
arm = c(rep(1, 100), rep(0, 100)),
covar = stats::rnorm(200)
)
data <- MCC::GenData(
beta_event = c(log(0.8), log(1.2)),
covariates = covariates,
frailty_variance = 0.2,
tau = 4
)
aucs <- MCC::CompareAUCs(
data,
tau = 4,
boot = TRUE,
perm = TRUE,
reps = 200,
alpha = 0.05
)
show(aucs)## Marginal Areas:
## arm n area se tau
## 1 0 100 5.74 0.579 4
## 2 1 100 5.28 0.612 4
##
##
## CIs:
## method contrast observed se lower upper
## 1 asymptotic A1-A0 -0.467 0.843 -2.12 1.18
## 3 bootstrap A1-A0 -0.467 0.877 -2.11 1.35
## 2 asymptotic A1/A0 0.919 0.141 0.68 1.24
## 4 bootstrap A1/A0 0.919 0.147 0.68 1.25
##
##
## P-values:
## method contrast observed p
## 1 asymptotic A1-A0 -0.467 0.579
## 3 bootstrap A1-A0 -0.467 0.607
## 5 permutation A1-A0 -0.467 0.577
## 2 asymptotic A1/A0 0.919 0.581
## 4 bootstrap A1/A0 0.919 0.607
## 6 permutation A1/A0 0.919 0.577
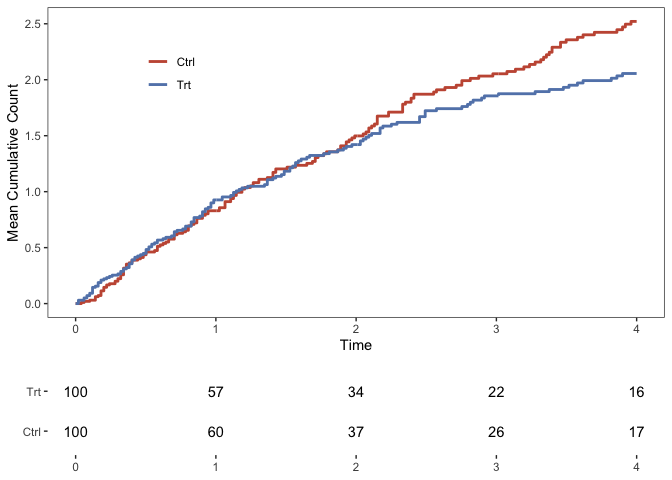
Plotting
The function PlotMCFs plots the mean cumulative count curves, comparing two treatment arms. Note that data must contain the column arm.
q <- MCC::PlotMCFs(data)
q_nar <- MCC::PlotNARs(
data = data,
x_breaks = seq(from = 0, to = 4)
)
q_main <- cowplot::plot_grid(
plotlist = list(q, q_nar),
nrow = 2,
align = "v",
axis = "l",
rel_heights = c(3, 1)
)
show(q_main)