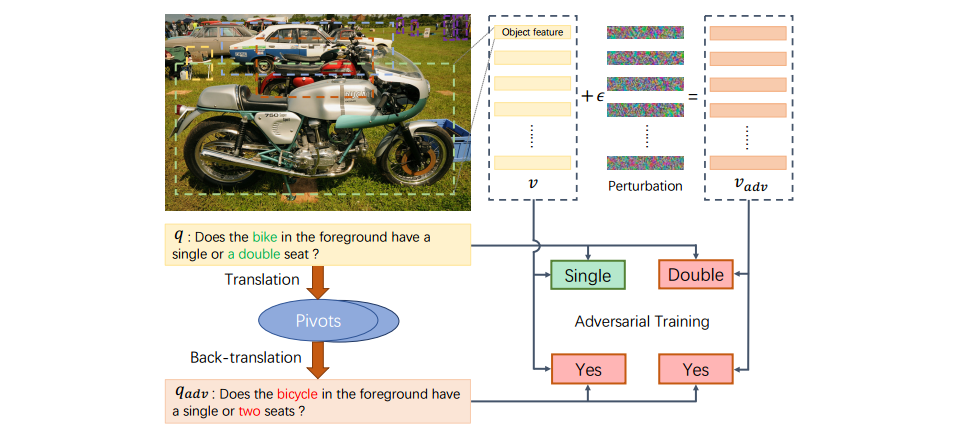
This repository corresponds to the ECCV 2020 paper Semantic Equivalent Adversarial Data Augmentation for Visual Question Answering.
You may need at least 1 GPU with 11GB memory for training, and 200GB free disk space for storing VQAv2 dataset. We strongly recommend to use a SSD drive to guarantee high-speed I/O.
- Python 3.6
- pytorch = 1.0
- torchvision 0.2
- h5py 2.7
- tqdm 4.19
-
git clone https://github.com/zaynmi/seada-vqa.git -
We recommend to install everything in an Anaconda environment.
conda create -n seada python=3.6 source activate seada -
Install Pytorch 1.0 and torchvision
conda install pytorch=1.0 torchvision cudatoolkit=10.0 -c pytorch -
Install other dependencies as follows:
pip install -r requirements.txt python -m spacy download en -
Install OpenNMT-py for generating paraphrases, it allows to install
onmtpackage in your environment:git clone https://github.com/zaynmi/OpenNMT-py.git cd OpenNMT-py python setup.py install cd .. -
Download and unpack the translation models into the
seada/sea/translation_modelsfolder. You'll get four.ptmodels.
Prepare Dataset (Follow Cyanogenoid/vqa-counting)
- In the
datadirectory, execute./download.shto download VQA v2 and the bottom-up-top-down features. - Prepare the data by running
python data/preprocess-features.py
python data/preprocess-vocab.py
This creates an h5py database (95 GiB) containing the object proposal features and a vocabulary for questions and answers at the locations specified in config.py. It is strongly recommended to put database in SSD.
python main.py --attack_only --attack_mode q --attack_al sea --attacked_checkpoint {your_trained_model}.pth --fliprate 0.3 --topk 2 --paraphrase_data train
This would generate paraphrases of train set with top-2 semantic similarity score and 30% flip rate considering {your_trained_model}.pth (A BUTD model), and store them in config.paraphrase_save_path. Similarly, by setting --paraphrase_data val, you can get paraphrases of val set. Don't forget to change config.paraphrase_save_path accordingly.
In our paper, we didn't specify the flip rate , topk and attacked_checkpoint (--fliprate 0, --topk 1), which means we simply use paraphrases with top-1 semantic similarity score.
There is another step left. We need to sort the generated paraphrases in the same order with annotations file. The script is in sort_para.py
-
Option-1. Use both visual adversarial examples and paraphrases to augment data.
python main.py --advtrain --attack_al ifgsm,sea --attack_mode vq --attacked_checkpoint {checkpoint_you_attack_when_eval}.pth --resume {your_partial_trained_model}.pth -
Option-2. Use visual adversarial examples to augment data.
python main.py --advtrain --attack_al ifgsm --attack_mode v --attacked_checkpoint {checkpoint_you_attack_when_eval}.pth --resume {your_partial_trained_model}.pth -
Option-3. Use paraphrases to augment data.
python main.py --advtrain --attack_al sea --attack_mode q --attacked_checkpoint {checkpoint_you_attack_when_eval}.pth --resume {your_partial_trained_model}.pth
--attacked_checkpoint is optional, which allows you to evaluate the performance of adversarially trained model defense against adversarial examples generated by {checkpoint_you_attack_when_eval}.pth
If you want to train with train and val set, add --advtrain_data trainval
- Generate
.jsonfile for you to upload to on-line evaluation server. The result file is specified inconfig.result_json_path.
python main.py --test_advtrain --checkpoint {your_trained_model}.pth
- Or you can evaluate on the val set.
--attacked_checkpointis optional and if it is declared, you would see the performance of defense.
python main.py --eval_advtrain --checkpoint {your_trained_model}.pth --attack_al ifgsm --attack_mode v --attacked_checkpoint {checkpoint_you_attack_when_eval}.pth
How our model behaves when attacked by the attackers is of great concern to us too. You can use
python main.py --attack_only --attack_mode v --attack_al pgd --alpha 0.5 --iteration 6 --epsilon 5 --attacked_checkpoint {checkpoint_being_attacked}.pth
All the attackers act as a white-box attacker.
The code is released under the MIT License
If this repository is helpful for your research, we'd really appreciate it if you could cite the following paper:
@inproceedings{tang2020semantic,
title={Semantic Equivalent Adversarial Data Augmentation for Visual Question Answering},
author={Tang, Ruixue and Ma,Chao and Zhang, Wei Emma and Wu, Qi and Yang, Xiaokang},
booktitle={European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV)},
year={2020}
}