Mingyu Ding, Yuqi Huo, Haoyu Lu, Linjie Yang, Zhe Wang, Zhiwu Lu, Jingdong Wang, Ping Luo
This work includes:
(1) NAS-Bench-MR, a NAS benchmark built on four challenging datasets under practical training settings for learning task-transferable architectures.
(2) An efficient predictor-based algorithm Network Coding Propagation (NCP), which back-propagates the gradients of neural predictors to directly update architecture codes along desired gradient directions for various objectives.
This framework is implemented and tested with Ubuntu/Mac OS, CUDA 9.0/10.0, Python 3, Pytorch 1.3-1.6, NVIDIA Tesla V100/CPU.
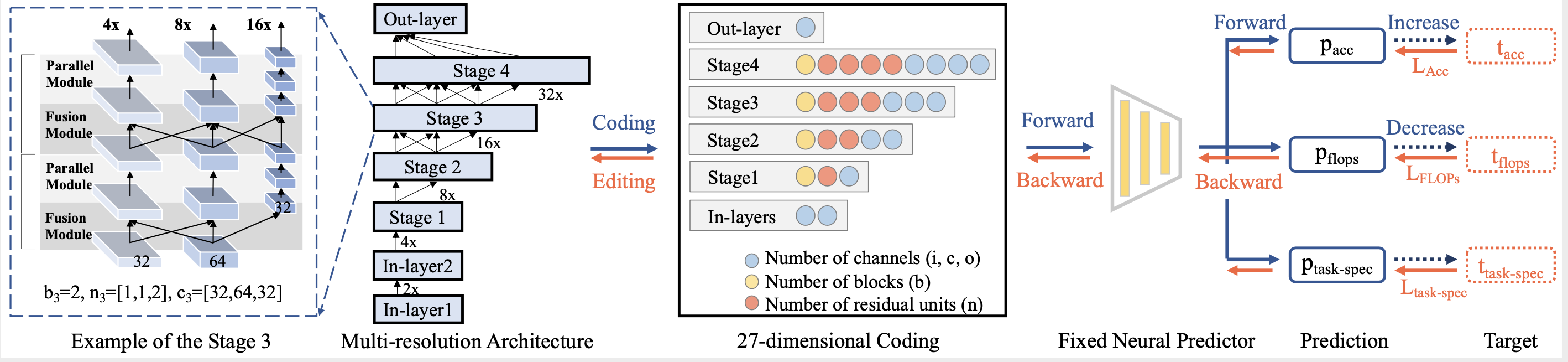
We build our benchmark on four computer vision tasks, i.e., image classification (ImageNet), semantic segmentation (CityScapes), 3D detection (KITTI), and video recognition (HMDB51).
Totally 9 different settings are included, as shown in the data/*/trainval.pkl folders.
Note that each .pkl file contains more than 2500 architectures, and their corresponding evaluation results under multiple metrics.
The original training logs and checkpoints (including model weights and optimizer data) will be uploaded to Google drive (more than 4T). We will share the download link once the upload is complete.
python3 tools/train_predictor.py # --cfg configs/seg.yamlpython3 tools/ncp.py # --cfg configs/seg.yaml- An example in NAS-Bench-MR (Seg):
{'mIoU': 70.57,
'mAcc': 80.07,
'aAcc': 95.29,
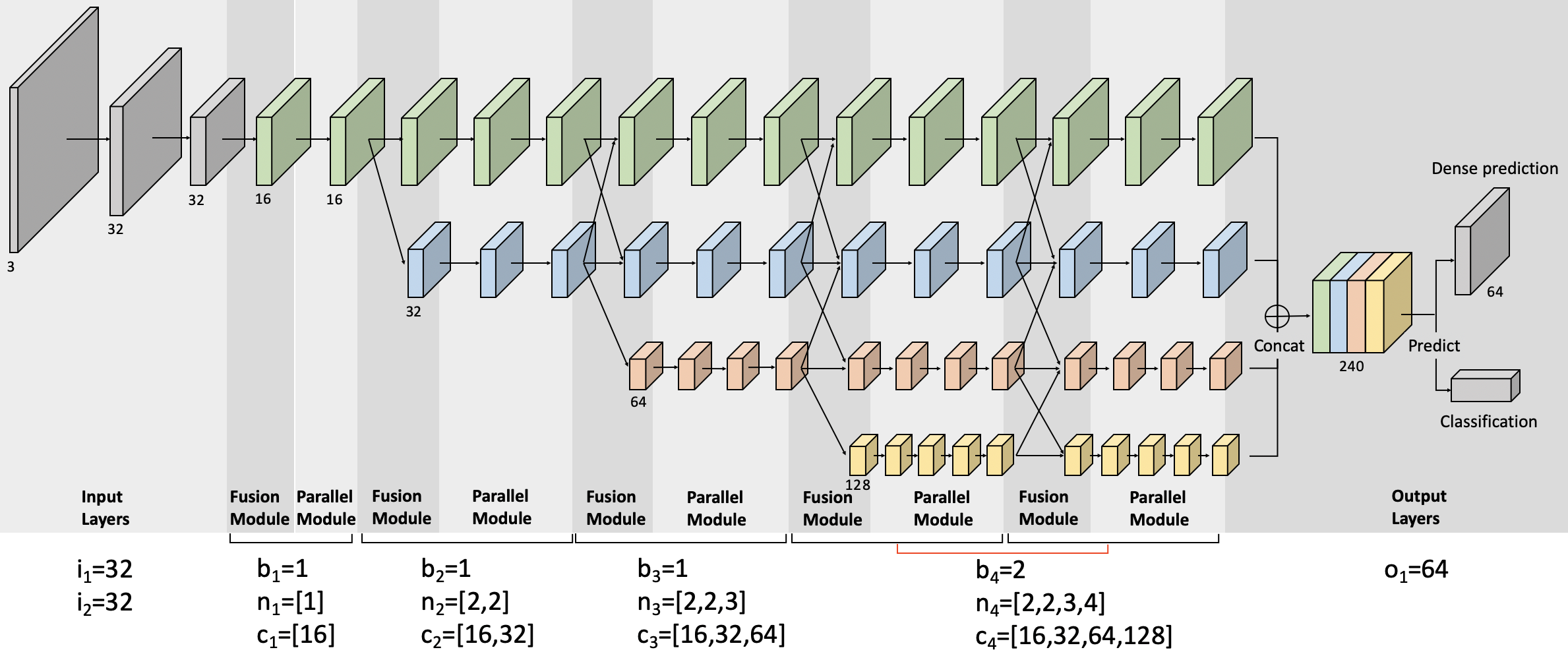
'input_channel': [16, 64],
# [num_branches, [num_convs], [num_channels]]
'network_setting': [[1, [3], [128]],
[2, [3, 3], [32, 48]],
[2, [3, 3], [32, 48]],
[2, [3, 3], [32, 48]],
[3, [2, 3, 2], [16, 32, 16]],
[3, [2, 3, 2], [16, 32, 16]],
[4, [2, 4, 1, 1], [96, 112, 48, 80]]],
'last_channel': 112,
# [num_branches, num_block1, num_convs1, num_channels1, ..., num_block4, num_convs4, num_channels4, last_channel]
'embedding': [16, 64, 1, 3, 128, 3, 3, 3, 32, 48, 2, 2, 3, 2, 16, 32, 16, 1, 2, 4, 1, 1, 96, 112, 48, 80]
}- Load Datasets:
import pickle
exps = pickle.load(open('data/seg/trainval.pkl', 'rb'))
# Then process each item in exps- Load Model / Get Params and Flops (based on the thop library):
import torch
from thop import profile
from models.supernet import MultiResolutionNet
# Get model using input_channel & network_setting & last_channel
model = MultiResolutionNet(input_channel=[16, 64],
network_setting=[[1, [3], [128]],
[2, [3, 3], [32, 48]],
[2, [3, 3], [32, 48]],
[2, [3, 3], [32, 48]],
[3, [2, 3, 2], [16, 32, 16]],
[3, [2, 3, 2], [16, 32, 16]],
[4, [2, 4, 1, 1], [96, 112, 48, 80]]],
last_channel=112)
# Get Flops and Parameters
input = torch.randn(1, 3, 224, 224)
macs, params = profile(model, inputs=(input, )) Each code in data/search_list.txt denotes an architecture. It can be load in our supernet as follows:
- Code2Setting
params = '96_128-1_1_1_48-1_2_1_1_128_8-1_3_1_1_1_128_128_120-4_4_4_4_4_4_128_128_128_128-64'
embedding = [int(item) for item in params.replace('-', '_').split('_')]
embedding = [ 96, 128, 1, 1, 48, 1, 1, 1, 128, 8, 1, 1,
1, 1, 128, 128, 120, 4, 4, 4, 4, 4, 128, 128,
128, 128, 64]
input_channels = embedding[0:2]
block_1 = embedding[2:3] + [1] + embedding[3:5]
block_2 = embedding[5:6] + [2] + embedding[6:10]
block_3 = embedding[10:11] + [3] + embedding[11:17]
block_4 = embedding[17:18] + [4] + embedding[18:26]
last_channels = embedding[26:27]
network_setting = []
for item in [block_1, block_2, block_3, block_4]:
for _ in range(item[0]):
network_setting.append([item[1], item[2:-int(len(item) / 2 - 1)], item[-int(len(item) / 2 - 1):]])
# network_setting = [[1, [1], [48]],
# [2, [1, 1], [128, 8]],
# [3, [1, 1, 1], [128, 128, 120]],
# [4, [4, 4, 4, 4], [128, 128, 128, 128]],
# [4, [4, 4, 4, 4], [128, 128, 128, 128]],
# [4, [4, 4, 4, 4], [128, 128, 128, 128]],
# [4, [4, 4, 4, 4], [128, 128, 128, 128]]]
# input_channels = [96, 128]
# last_channels = [64]- Setting2Code
input_channels = [str(item) for item in input_channels]
block_1 = [str(item) for item in block_1]
block_2 = [str(item) for item in block_2]
block_3 = [str(item) for item in block_3]
block_4 = [str(item) for item in block_4]
last_channels = [str(item) for item in last_channels]
params = [input_channels, block_1, block_2, block_3, block_4, last_channels]
params = ['_'.join(item) for item in params]
params = '-'.join(params)
# params
# 96_128-1_1_1_48-1_2_1_1_128_8-1_3_1_1_1_128_128_120-4_4_4_4_4_4_128_128_128_128-64'For academic use, this project is licensed under the 2-clause BSD License. For commercial use, please contact the author.