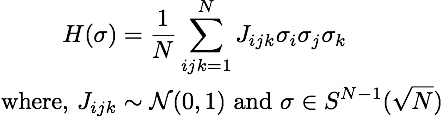GD and SGD on the spherical 3-spin glass Hamiltonian
For a given number of variables, first fix coefficients sampling from a mean zero variance one distribution, and form the surface of a degree three homogeneous polynomial with the spherical constraint. Then run basic optimization algorithms on this surface starting from a random initial point.
Make sure to specify correct paths. Also, one can easily convert between GPU and CPU by switching between torch.Tensor vs torch.CudaTensor, and modifying libraries nn to cunn.
Papers that use the results of this code:
[1] Levent Sagun, V. Ugur Guney, Gerard Ben Arous, Yann LeCun, Explorations on high dimensional landscapes
[2] Anna Choromanska, Mikael Henaff, Michael Mathieu, Gerard Ben Arous, Yann LeCun, The Loss Surfaces of Multilayer Networks
[3] Levent Sagun, Thomas Trogdon, Yann LeCun, Universal halting times in optimization and machine learning
[4] Andrew J. Ballard, Ritankar Das, Stefano Martiniani, Dhagash Mehta, Levent Sagun, Jacob D. Stevenson, David J. Wales, Perspective: Energy Landscapes for Machine Learning