Deep neural networks have gained great success recently for sentiment classification. However, these approaches do not fully exploit the linguistic knowledge or rely heavily on expensive phrase-level annotation.. In this paper, we propose a novel sentiment lexicon enhanced attention-based LSTM (SLEA-LSTM) model to improve the performance of sentence-level sentiment classification. Our method successfully integrates sentiment lexicon into deep neural networks via single-head or multi-head attention mechanisms. We conduct extensive experiments on MR and SST datasets. The experimental results show that our model achieved comparable or better performance than the state-of-the-art methods.
In general, sentiment classification is the problem of classifying the sentiment polarity of a text as positive, negative or neutral. It has attracted increasing attention recently due to its broad applications. Most existing work establishes sentiment classifiers using supervised machine learning approaches, such as support vector machine (SVM), convolutional neural network (CNN), long short-term memory (LSTM).
Despite the effectiveness of previous studies, sentiment classification still remains a challenge in real-world. A comprehensive and high quality sentiment lexicon plays a crucial role in traditional sentiment classification approaches. Despite its usefulness, to date, the sentiment lexicon has received little attention in recent neural network models (e.g., CNN and LSTM) that achieve the state-of-the-art in generic sentiment classification.
To address the aforementioned limitation, in this paper, we propose a novel sentiment lexicon enhanced attention-based LSTM (SLEA-LSTM) model, which aims to leverage the high quality sentiment lexicon to further improve the classification accuracy. More specifically, our model consists two independent LSTM networks with additional attention layers on the top. The two LSTM networks are used to learn the hidden representations of context and sentiment words of input respectively. In addition, we explore two types of attention mechanisms: single-head and multi-head attention methods. The single-head attention computes attention weights of different word locations according to their intent importance associated with sentiment lexicon, which usually only focuses on specific parts of the input. While the multi-head attention allows the model to jointly attend to information from different representation subspaces at different positions. The experiment results show that our model is efficient and achieves state-of-the-art results.
The main contributions of our work can be summarized as follows:
First, we propose a novel sentiment lexicon enhanced attention-based LSTM (SLEA-LSTM) model for sentence-level sentiment classification. The model integrates sentiment lexicon into neural networks, which fully employs previous linguistic knowledge to improve the performance of sentiment classification.
Second, instead of (Qian et al., 2017) which imposes linguistic roles into neural networks by applying linguistic regularization on intermediate outputs with KL divergence, we adopt attention mechanism to integrate sentiment lexicon into deep neural networks. At the same time, we perform single-head and multi-head attention mechanisms respectively. To the best of our knowledge, our work is the first one that explores incorporating sentiment lexicon with neural networks via attention mechanism for sentence-level sentiment classification.
We conduct experiments on MR and SST datasets to verify the effectiveness of our model. The experimental results show that our model achieved comparable or better performance than the state-of-the-art methods.
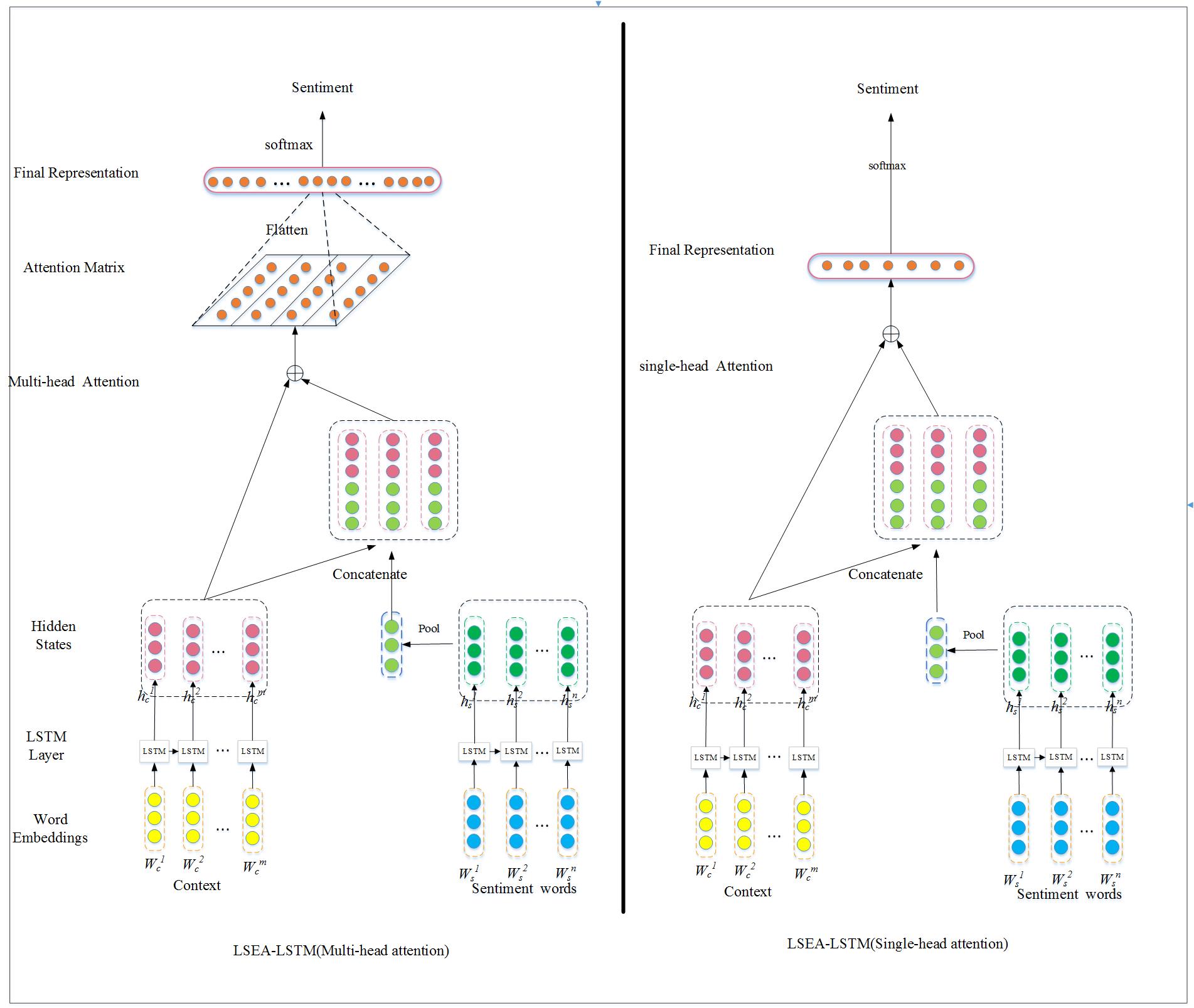 Figure 1: The overall architecture of SLEA-LSTM.
Figure 1: The overall architecture of SLEA-LSTM.
Our model mainly consists of three parts. The first part uses two independent LSTM layers to convert the sequence of input word embeddings into two sequences of hidden states for context words and sentiment words respectively. The second part mainly computes attention scores using single-head or multi-head attention mechanisms. The third part predicts the sentiment label with the final sentence representation. The overall architecture of SLEA-LSTM model is shown in Figure1.