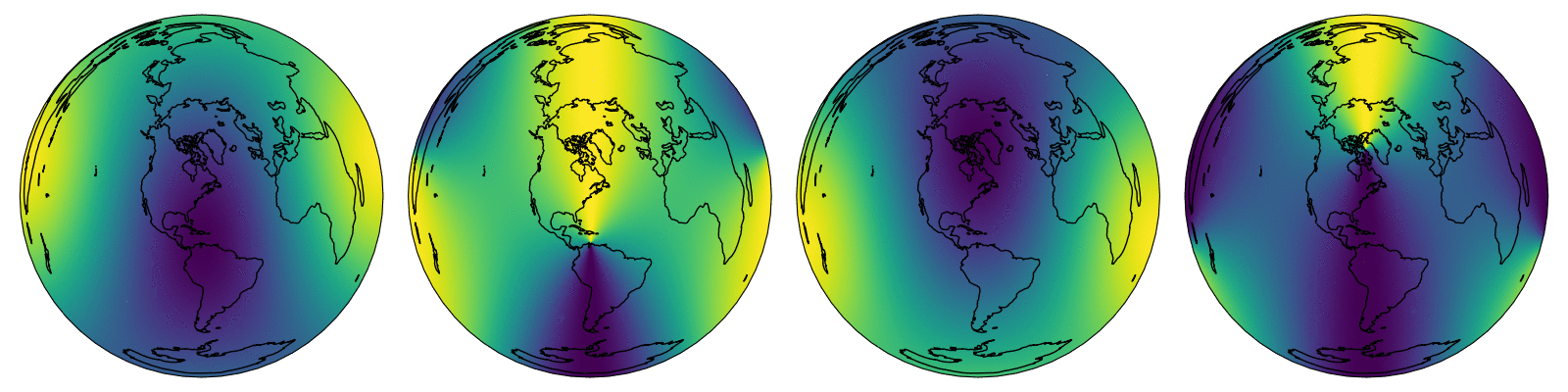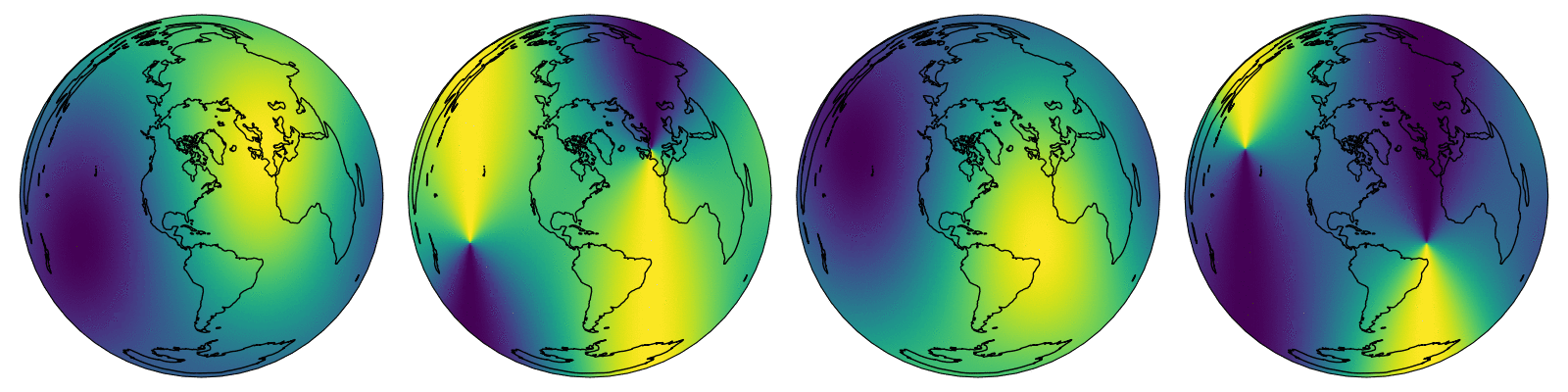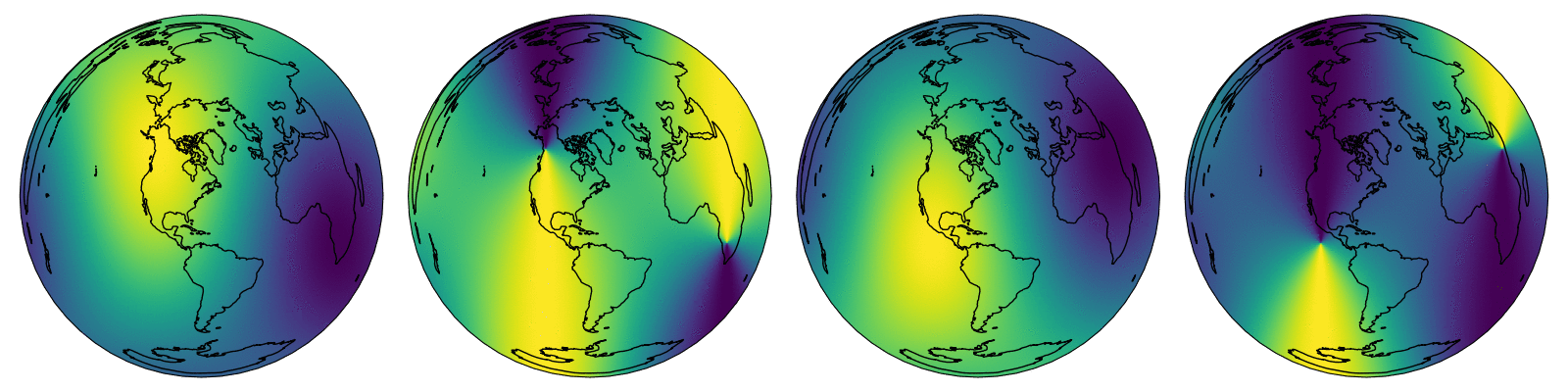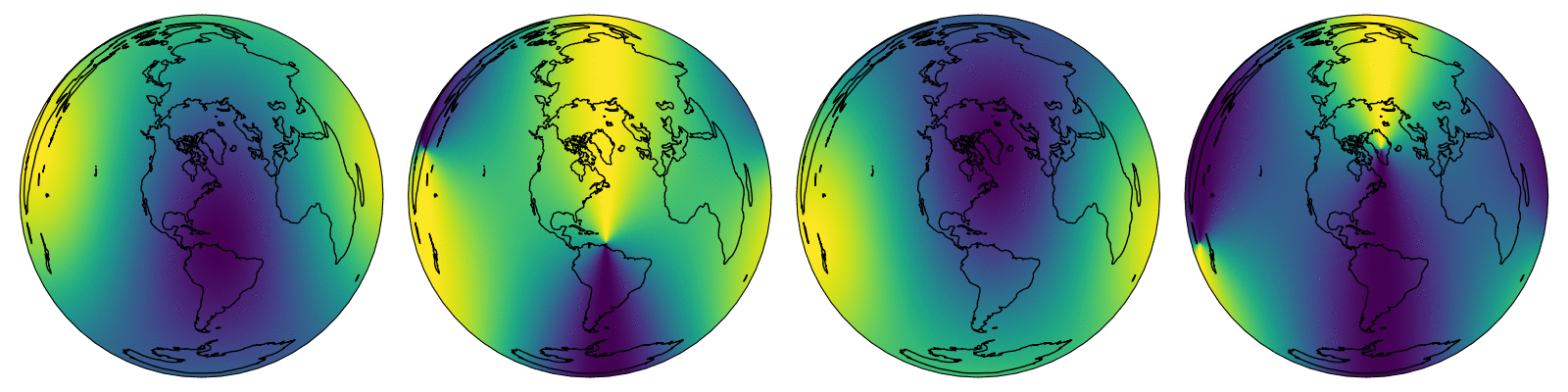
This is a Cython implementation of the NREL Solar Position Algorithm for Solar Radiation Applications. Designed for calculating solar zenith and azimuth across a temporal and spatial dimension.
git clone ...
python3 -m venv .venv && source .venv/bin/activate
pip install .import numpy as np
import fast_spa
# 200x200km area
lats = np.linspace(30, 31, 100)
lons = np.linspace(-80, -79, 100)
lats, lons = np.meshgrid(lats, lons)
datetime_obj = (
np.arange("2023-01-01", "2023-01-02", dtype="datetime64[h]")
.astype("datetime64[ns]")
.astype(str)
.tolist()
)
%timeit fast_spa.fast_spa(datetime_obj, lats, lons)
29.1 ms ± 299 µs per loop (mean ± std. dev. of 7 runs, 10 loops each)There is also integration with the ETOPO2022 dataset for elevation data.
import numpy as np
from numpy.typing import ArrayLike
import cartopy.crs as ccrs
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import fast_spa
ZENITH_ANGLE = 0
AZIMUTH_ANGLE = 1
def contourf(
ax: GeoAxes,
data: ArrayLike,
lons: ArrayLike,
lats: ArrayLike,
title="",
**kwargs,
) -> GeoAxes:
ax.title.set_text(title)
ax.coastlines()
ax.add_feature(cfeature.STATES)
ax.contourf(
lons,
lats,
data,
transform=ccrs.PlateCarree(),
**kwargs,
)
return ax
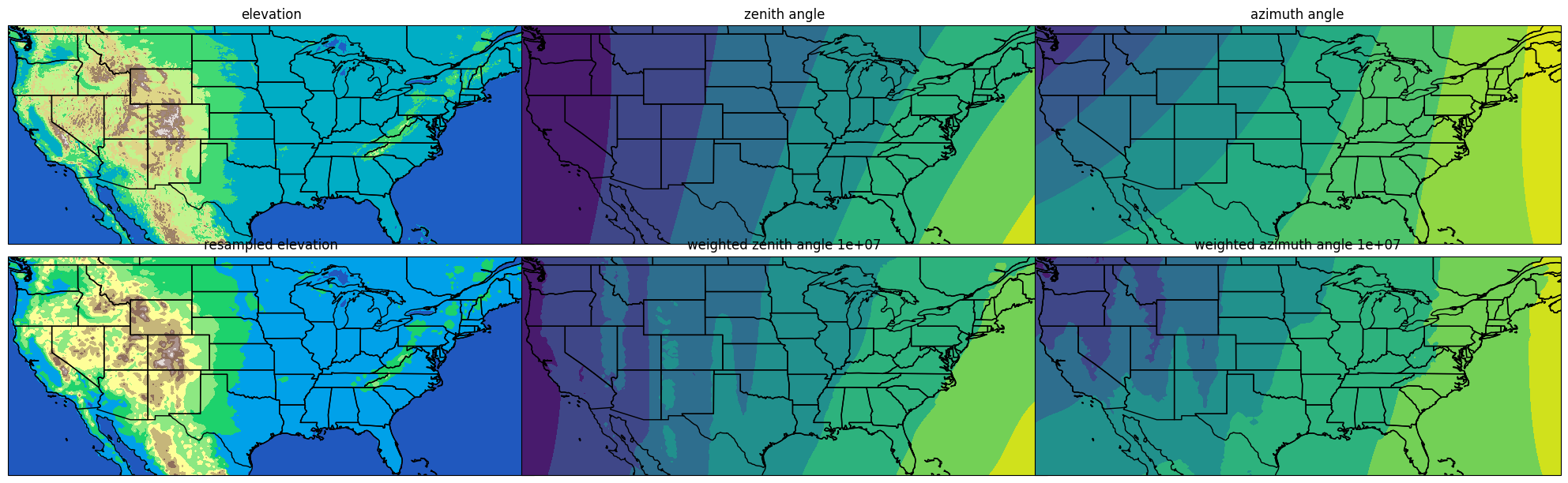
def main(
etopo: fast_spa.ETOPO2022 = fast_spa.ETOPO2022(),
lons=np.linspace(-125, -65, 200),
lats=np.linspace(25, 50, 100),
weight: float = 1e7,
):
fig, axes = plt.subplots(
2, 3, figsize=(20, 6), subplot_kw={"projection": ccrs.PlateCarree()}
)
# - plot the non-resampled elevation data
lons, lats = np.meshgrid(lons, lats)
y_mask = np.logical_and(etopo.lat >= lats.min(), etopo.lat <= lats.max())
x_mask = np.logical_and(etopo.lon >= lons.min(), etopo.lon <= lons.max())
fig.tight_layout()
e = etopo[y_mask, x_mask]
e[e < -100] = -100 # set the ocean to -100m
contourf(
axes[0, 0],
e,
etopo.lon[x_mask],
etopo.lat[y_mask],
"elevation",
cmap="terrain",
)
# - resample the elevation data to fit the lon, lat grid
e = etopo.resample(lons, lats)
e[e < -100] = -100 # set the ocean to -100m
spa_data = fast_spa.fast_spa(datetime_obj, lats, lons, e)
# - apply a weight to the elevation data for SPA calculation
weighted = fast_spa.fast_spa(datetime_obj, lats, lons, e * weight)
weighted = np.radians(weighted)
contourf(
axes[1, 0],
e,
lons,
lats,
"resampled elevation",
cmap="terrain",
)
contourf(
axes[0, 1],
spa_data[ZENITH_ANGLE, 0, :, :],
lons,
lats,
"zenith angle",
)
contourf(
axes[1, 1],
weighted[ZENITH_ANGLE, 0, :, :],
lons,
lats,
f"weighted zenith angle {weight:.0e}",
)
contourf(
axes[0, 2],
spa_data[AZIMUTH_ANGLE, 0, :, :],
lons,
lats,
"azimuth angle",
)
contourf(
axes[1, 2],
weighted[AZIMUTH_ANGLE, 0, :, :],
lons,
lats,
f"weighted azimuth angle {weight:.0e}",
)
plt.show()
main()