Version: 7.9.0
MODEST stands for: Multi OS Deployment Engine Server Tool
WARNING: This is a somewhat significant clean up of the previous tool (mode) - it is currently not working for everything
Known to be working:
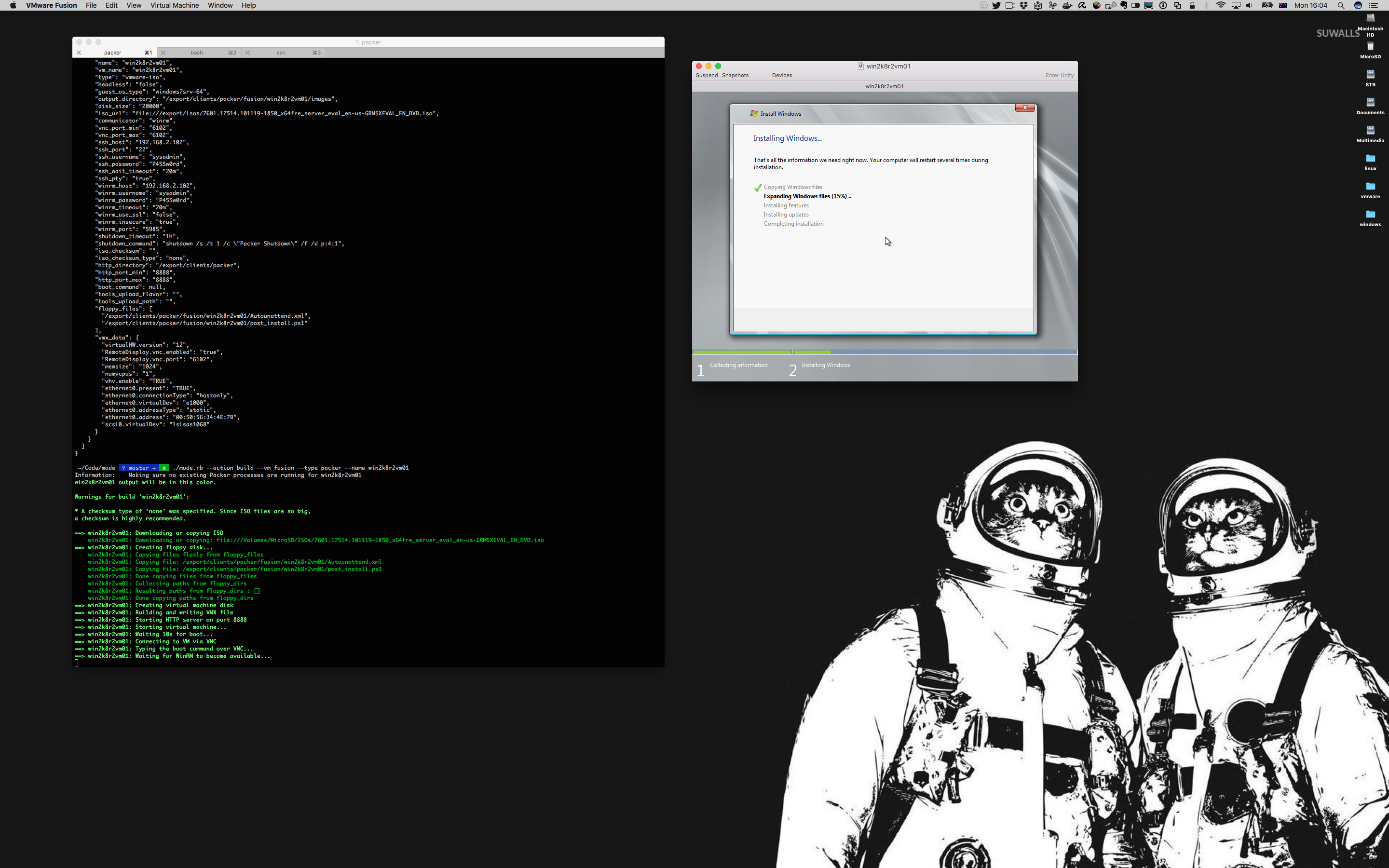
- Packer (Windows, CentOS, RHEL, Ubuntu, ESXi, SLES 12.x, Solaris 11 x86)
- PXE Server (vSphere/ESXi, Ubuntu, etc)
- VMware Fusion/Workstation and VirtualBox VM creation
- Solaris 11 AI
- Solaris 10 Jumpstart
Issues:
- Packer Windows installs do not work for host-only network configs (Packer issue)
- set vmnetwork to NAT
This tool is designed to greatly simplify the creation of VMs for testing purposes.
With a single command line command you can create and manage VMware Fusion and VirtualBox VMs.
MODEST is a Ruby script to configure server and client configuration for Packer, PXE/DHCP, BOOTP and HTTP based install services, eg:
- Solaris 11 Automated Installer (AI) service
- Solaris 10 (and earlier) Jumpstart services
- Centos, Scientific, OEL, Fedora, and RHEL Kickstart services
- Ubuntu Linux Preseed and Subiquity services
- SuSE Enterprise Linux AutoYast services
- ESXi Kickstart services
- PXE boot install services for Linux and ESXi
- Simplify creation, deletion, snapshot, import and export of VirtualBox VMs
- Simplify creation, deletion, snapshot, import and export of Parallels VMs
- Simplify creation, deletion, snapshot, import and export of VMware Fusion VMs
- Simpllfy creation of Solaris Zones
- Simplify creation of Solaris VM Server for SPARC Control Domains
- Simplify creation of Solaris VM Server for SPARC Guest Domains
- Linux Containers (Currently Ubuntu support only)
- OpenBSD PXE boot service
- Initial CoreOS PXE boot support
- Provide completely headless VM support
- Simplify creation of Packer images
- Deploy Virtual Center Server Appliance
- Simplify creation and build of VMs with Packer
- Linux (RHEL, OEL, SuSE, Ubuntu, CentOS, Fedora, Scientific)
- Solaris 10 & 11
- Windows Server 2008 R2, 2012 R2, 2016, 2019, 2022
- ESXi
- Create AMIs
- AWS support
- List, stop, start, create, and delete instances
- List and delete AMIs
- List, create and delete buckets
- List bucket ACLs
- Upload and download files to/from buckets
- List, create, and delete CloudFormation stacks
- List, create and delete EC2 security groups and rules
- Initial Docker support
- Initial Ansible support
- Create AWS EC2 instances
Currently supported host Operating Systems:
- Linux
- Mac OS
- Solaris
- Windows (in development)
Currently supported virtualisation software:
- VirtualBox
- VMware Workstation / Fusion
- KVM (Requires Packer 1.4.3 or later)
- Docker (in development)
- Multipass
Less supported (have not been recently tested)
- Parallels
- Zones
- Solaris OVM
Currently supported deployment software:
- Packer (1.4.3 or later recommended - required for KVM support)
Currently supported deployment targets with packer:
- VirtualBox
- VMware Fusion
- AWS
Some example screen captures:
RedHat Linux Kickstart Client Examples
Ubuntu Linux Preseed Client Examples
Why another OS/VM deployment tool?
Most of the other tools Packer, Vagrant, etc, concentrated on NAT based configurations. If they did have host-only network support, it didn't always work correctly (e.g. Packer and VirtualBox). Also I wanted a tool which I could use to build configurations for physical or virtual machines.
In most cases I was using PXE to boot and install physical machines, or virtual machines. I was also using a number of different OSes, e.g. Solaris, Windows, Linux, etc. I was also having issues with earlier versions of Packer and deploying Solaris and vSphere, where the install would stall part way through. This has since been fixed, and I've added Packer support.
The script will try to install the required modules, therefore I would recommend like with any other Ruby development environment you run your own version under rbenv or similar.
The script will make system changes, therefore I recommend you run in on a development machine, or in a VM.
This software is licensed as CC-BA (Creative Commons By Attrbution)
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/legalcode
Mode is designed to be used in a number of scenarios:
- Testing vendor OS deployment technologies (e.g. Kickstart, Jumpstart etc)
- PXE boot
- Pre and post install scripts
- A environment for quickly deploying VMs for testing purposes
- In a similar fashion to veewee or vagrant
- An environment for quickly deploying servers in a Datacenter or testlab via cross-over cable
Linux
- Where possible I've used biosdevnames as part of installation to reduce network device renaming
Packer support
- Simplify creation of Packer images for VirtualBox and VMware Fusion
- Currently supports Solaris 10, Solaris 11, Linux (RHEL, OEL, SuSE, Ubuntu, CentOS, Fedorac, Scientific), Windows Server 2008 R2, 2012 R2, 2016, 2019, 202 ESXi
Linux Container Creation
- Installs required packages and sets up network for public facing containers that can be connected to via ssh (Currently Ubuntu support only)
- Creates containers and sets up network (Currently Ubuntu support only)
Oracle VM Server for SPARC
- Setup Control Domain based on a set of questions
- Cleate Guest Domains based on a set of questions
VirtualBox and VMware Fusion VM creation
- Can create VMs to speed up the automation of testing new images
- Can run VMs headless and connect via serial allowing remote installation
Parallels VM creation
- Can create and delete VMs
- Can boot/stop VMs
Solaris Zone Creation
- Asks a set of questions to generate a template and then install a zone
Solaris 11 AI
- If a local repository exists it is used to configure installation services
- If a local repository is not present it mounts the repository ISO and configures it
- Changes the default install service manifest to reboot servers after installation
- Changes the default install service to use the local repository rather than the default Oracle one
- Changes the default grub configuration default to an autamated install rather than an interactive one
- Disables the default range based DHCP configuration and adds clients on an
individual basis
- Reduces the chances of conflicts with existing DHCP services, and
- Resolves the issue of DHCP licenses running out
- Creates an individual configuration profile for each client
- Configures network and other services
- Includes code to optionally create alternate package repository
- Automatically builds packages for facter, hiera, and puppet
- Adds packages to base installation manifest
- Post installation script capability (work in progress)
CentOS, Scientific Linux, Fedora, and RedHat Linux Kickstart
- Creates an Apache directory and alias for a HTTP based installation
- Creates PXE configuration that jumps straight into an installation and pulls kickstart file from server
- Includes code for optionally installing additional packages
- Automatically downloads Puppet packages
- Add packages to post installation
Ubuntu Linux Preseed
- Adds required append statement to PXE configuration so install is fully automated
- Currently only basic client support (auto partitions disk)
OpenSuSE Linux and SLES (SuSE Enterprise Linux) AutoYast
- Creates AutoYast XML file based on answers to questions
Solaris 10 (and earlier) Jumpstart:
- Automatically tries to determine boot and mirror disk ids based on modestl
- Automatically tires to determine kernel architecture (e.g. sun4u / sun4v) based on modestl
- Ability to quickly deploy flar based installs by answering a few questions
ESXi Kickstart:
- Automatically created PXE boot and jumpstart configuration files
- Automatically adds post install commands to turn on ESXi services such as SSH
All:
- Asks a set of default questions to produce a consistent error checked profile for each client
- Makes sure clients are added and deleted correctly removing the chance of installing the wrong thing to the wrong machine
- Installs and configures (and uninstalls and unconfigures if needed) server services (DHCP etc)
- Post installation scripting to perform tasks such as patching and security
The architecture of modestst is made up of the following layers:
- Host machine
- Can be a laptop or a server
- Manages VMs (including Deployment Server)
- Provides hostonly or bridged networking for VMs
- Can provide boot services for external machines via cross-over cable or switch
- Can be used to provide installation media (ISOs) to deployment server via shared filesystem
- Deployment Server
- Manages OS installation media (ISOs) and repositories
- Manages PXE boot configurations
- The VMs on the host you wish an OS to be installed to
- External machines you may wish to install and OS to (e.g. Testlab or DC)
- Manages client VM configurations
- The VMs on the host you wish an OS to be installed to
- External machines you may wish to install and OS to (e.g. Testlab or DC)
- Manages post installation scripts
I'll go into more detail and an actual example of the process in the getting started section, but basically the process of deploying a VM is as follows:
- Create a blank VM on the host machine
- Configure the VM installation template/configuration on the Deployment Server
- Boot the VM on the host machine and let it PXE boot and install
By default the script uses a hostonly network, 130.194.2.0 for VMware Fusion, and 130.194.56.0 for VirtualBox. As such the script will try to configure port forwarding.
Hostonly networks and IP forwarding is used as it's far more reliable for consistent deployments.
An example host-only network layout For VMware Fusion with vmnet interfaces is as follows:
__ External network __ External Interface (e.g. en0)
e.g. 192.168.1.0 e.g. 192.168.1.100
|
|
VM Host
|
|
Host-only Interface (e.g. vmnet1) __ Host-only network
e.g. 192.168.52.1 e.g. 192.168.52.0
|
|
____________________________________|
|
____________________|____________________
| | |
| | |
Deployment Server Test Server 1
e.g. 192.168.52.100 e.g 192.168.52.101
An example host-only network layout For VMware Fusion with bridge interfaces (MacOS BigSur) is as follows:
__ External network __ External Interface (e.g. en0)
e.g. 192.168.1.0 e.g. 192.168.1.100
|
|
VM Host
|
|
Host-only Interface (e.g. bridge100) __ Host-only network
e.g. 192.168.104.1 e.g. 192.168.104.0
|
|
____________________________________|
|
____________________|____________________
| | |
| | |
Deployment Server Test Server 1
e.g. 192.168.104.100 e.g 192.168.104.101
An example host-only network for VirtualBox is as follows:
__ External network __ External Interface (e.g. en0)
e.g. 192.168.1.0 e.g. 192.168.1.100
|
|
VM Host
|
|
Host-only Interface (e.g. vboxnet0) __ Host-only network
e.g. 192.168.56.1 e.g. 192.168.56.0
|
|
_____________________________________|
|
____________________|____________________
| | |
| | |
Deployment Server Test Server 1
e.g. 192.168.56.100 e.g 192.168.56.101
An example of host-only network for KVM is as follows:
__ External network __ External Interface (e.g. en0)
e.g. 192.168.1.0 e.g. 192.168.1.100
|
|
VM Host
|
|
Host-only Interface (e.g. virbr0) __ Host-only network
e.g. 192.168.122.1 e.g. 192.168.122.0
|
|
___________________________________|
|
____________________|____________________
| | |
| | |
Deployment Server Test Server 1
e.g. 192.168.122.100 e.g 192.168.122.101
All:
- Socat
- Ruby
- Version 1.8 or greater
- Although it's been coded with 2.x I've avoided using 2.x features
- Version 1.8 or greater
- Packer (if using Packer)
- Ansible (if using ansible)
- boto python module
- Docker (if using Docker)
- docker
- docker-machine
- docker-compose
- Required Gems
- rubygems
- getopt/long
- builder
- socket
- parseconfig
- unix_crypt
- pathname
- netaddr
- ipaddr
- json
- yaml
- pp
- aws-sdk
- ssh-config
- open-uri
- net/ssh
- nokogiri
- mechanize
- uri
- socket
- net/http
- net/scp
Required Packages for Linux:
- git
- gcc
- ruby-devel
- xz-devel
- zlib-devel
- libxml2-devel
- libgpg-error-devel
- libgcrypt-devel
- libxslt-devel
- libstdc++-devel
- gcc-c++
- libgnome-keyring
- perl-Error
- perl-TermReadKey
- git
- Perl-git
- libapr
- libapr-util
- mail-cap
- httpd-tools
- httpd
- xinetd
- tftp-server
- dhcp
- winlib (for building Windows VMs with Packer)
Required packages for Mac OS:
- winlib (for building Windows VMs with Packer)
Required packages for Windows:
- cygwin
- ruby
- git
- curl
Kickstart, AutoYast, and Preseed Services:
- Solaris 11, Linux, or OS X
AI Services:
- Solaris 11
Jumpstart Services:
- Solaris 11 or OS X (Linux to be added)
Linux Containers:
- Linux (Currently only Ubuntu supported)
Solaris Containers:
- Solaris 10 or 11 (Some branded container support on Solaris 11)
VM Client Services:
- VMware Fusion or VirtualBox
Prior to VirtualBox 5.x, bridged networking on OS X has been severely broken, therefore it is recommended to use VirtualBox 5.x or VMware Fusion if available.
If using OS X and a installation platform for Jumpstart it is recommended to use flar based installs as the performance of the OS X NFS is poor
- Parallels
There is initial Parallels support for creating VMs
Some of the things I'd like to add support for:
- Vagrant and Veewee
- VMware API
- OpenStack