- Dockerize https://github.com/swimlane/devops-practical
- MongoDB should also be deployed as a docker container
- Create a Helm chart for the application and use Helm (v3) to deploy it to a Kubernetes cluster
- You can use a hosted service like EKS/GKE/AKS or create your own cluster using Kubespray (https://github.com/kubernetes-sigs/kubespray ) or kURL ( https://kurl.sh/ )
- Use terraform to create as much of the Kubernetes cluster and required infrastructure as possible
Eliminate as many single points of failure for your Kubernetes cluster deployment as possible
Bonus points for the following:
- Security
- Scalability
- Using Ansible to ensure NTP is installed and running on the worker nodes
- As well any dependencies needed for Kubernetes if not using EKS/GKE/AKS prebuilt images
- Using Packer to create the worker node images and applying the Ansible playbook
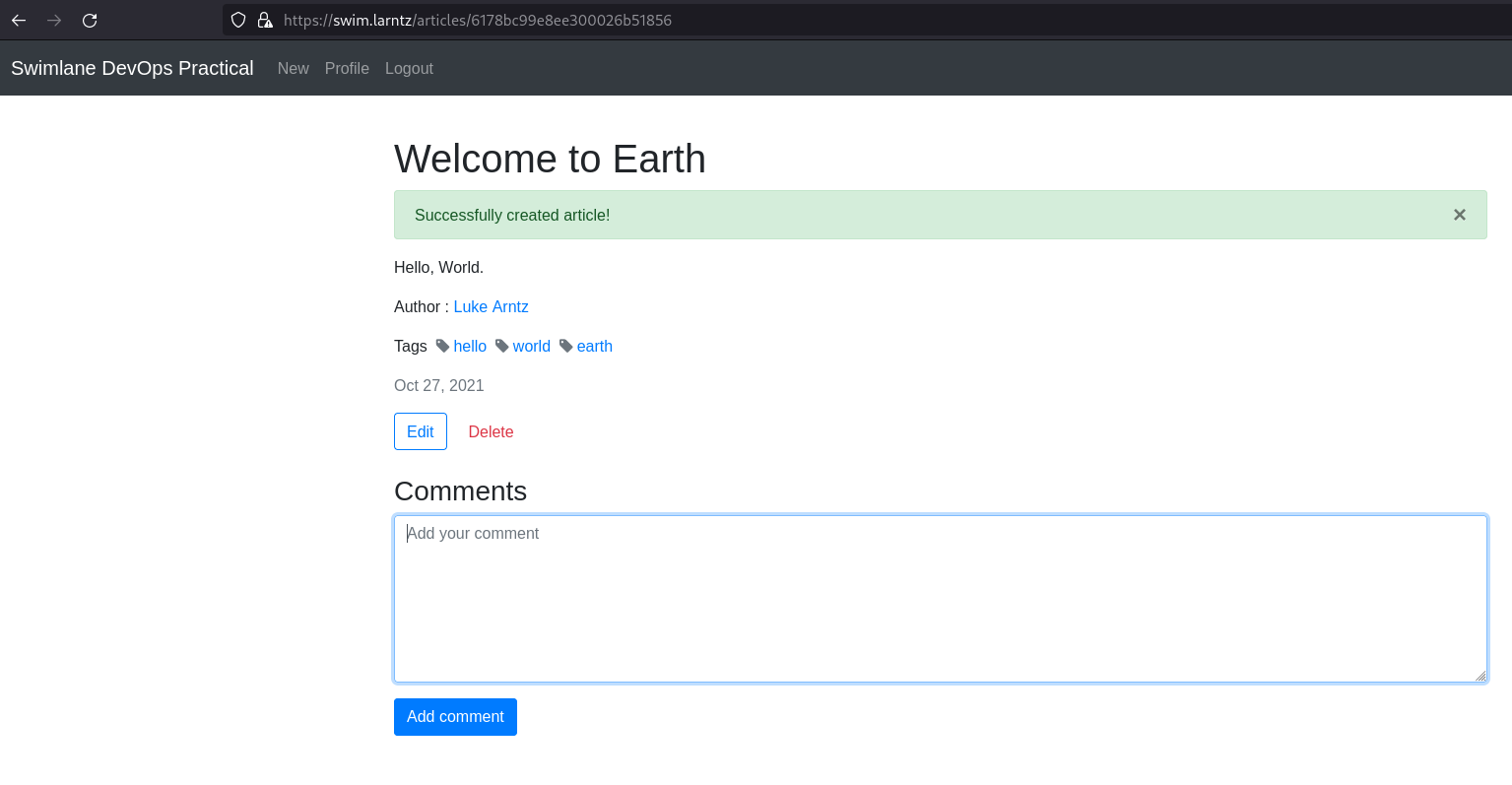
Access the app running in Kubernetes, register for an account, and add a record.
To deliver your work, create a public Github repository with the following (at a minimum):
- Readme with the commands used to deploy the Helm chart and Terraform
- Helm chart
- Terraform files
- Dockerfiles
- Screenshot of the running application with a new record added
If you don't make it through everything here we'd still like to see the progress you made and your thought process on the remaining work.
This solution will build an HA k8s cluster on libvirt/qemu using the following tools:
- packer
- terraform
- ansible
- helm (called from ansible)
We will build an haproxy loadbalancer, three contorl plane nodes, and between 2-7 worker nodes.
This was developed and tested on Debian 10. Other distros may have different requirements. Setting up libvirt, qemu, and user permissions is outside the scope of this document. Information to get started setting up KVM on Debian can be found here
These commands should be run from a user that can sudo without a password.
- Install initial debian packages on host system.
sudo apt install -y git python3 python3-venv build-essential software-properties-common mkisofs \ apt-transport-https ca-certificates curl - Clone this code repository.
git clone https://github.com/larntz/devops-practical.git devops-practical - Move into the
devops-practicaldirectory.cd devops-practical
NOTE: the remaining commands in this README should be executed from the repo's top level directory.
- Clone the kubespray repository into the
ansible-playbooksdirectory.git clone https://github.com/kubernetes-sigs/kubespray.git ansible-playbooks/kubespray - Create a python3 venv and activate it.
python3 -m venv ./venv # NOTE: you may need to source a different `activate` file if your shell isn't bash. source ./venv/bin/activate - Install required python packages with pip.
pip install -r ansible-playbooks/requirements/requirements.txt -r ansible-playbooks/kubespray/requirements.txt - Install required ansible-galaxy collections.
ansible-galaxy install -r ansible-playbooks/requirements/collections.yaml - Install
packer,terraform,helm, andkubectl.# add hashicorp repositories curl -fsSL https://apt.releases.hashicorp.com/gpg | sudo apt-key add - sudo apt-add-repository "deb [arch=amd64] https://apt.releases.hashicorp.com $(lsb_release -cs) main" # add helm repositories curl https://baltocdn.com/helm/signing.asc | sudo apt-key add - echo "deb https://baltocdn.com/helm/stable/debian/ all main" | sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/helm-stable-debian.list # add kubernetes repo sudo curl -fsSLo /usr/share/keyrings/kubernetes-archive-keyring.gpg https://packages.cloud.google.com/apt/doc/apt-key.gpg echo "deb [signed-by=/usr/share/keyrings/kubernetes-archive-keyring.gpg] https://apt.kubernetes.io/ kubernetes-xenial main" | sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/kubernetes.list sudo apt update && sudo apt -y install packer terraform helm kubectl
Once the prerequisites are met the entire system can be built using the commands below.
- create the vm image with packer.
packer build packer/debian.json - deploy vm infrastructure using terraform
terraform -chdir=terraform/ init terraform -chdir=terraform/ apply -auto-approve - use ansible to configure loadblancer, kubespray vars, and install cert-manager, ingress-nginx, mongodb, and our devops-practical swimapp.
ansible-playbook -i cluster-hosts ansible-playbooks/configure-cluster.yaml
After the cluster has been deployed and configured the admin kubeconfig file will be located at ansible-playbooks/kubespray/kubeconfig/admin.conf.
Access the cluster via kubectl after setting the KUBECONFIG environment variable.
export $PWD/ansible-playbooks/kubespray/kubeconfig/admin.conf
kubectl get nodes
Output:
NAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSION
kgnmyp-cp-00 Ready control-plane,master 75m v1.22.2
kgnmyp-cp-01 Ready control-plane,master 74m v1.22.2
kgnmyp-cp-02 Ready control-plane,master 74m v1.22.2
kgnmyp-wk-00 Ready <none> 73m v1.22.2
kgnmyp-wk-01 Ready <none> 73m v1.22.2
kgnmyp-wk-02 Ready <none> 39m v1.22.2
kgnmyp-wk-03 Ready <none> 39m v1.22.2
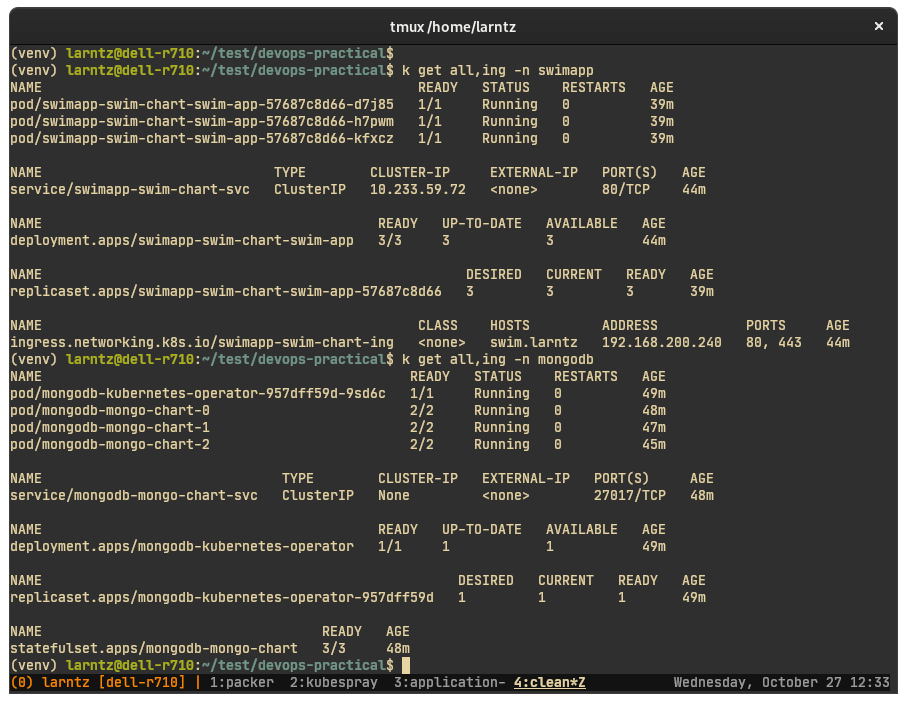
The ansible playbook will automatically deploy the helm charts included in this repository, but they can be installed manually with the commands below. The charts in the repo were left untarred to make them easier to browse on github.
NOTE: mongodb needs to be installed and ready before installing the application. If the database isn't ready the application will fail to start properly.
helm install:
helm install mongodb helm-charts/mongo-chart/ -n mongodb --create-namespace
helm install:
helm install swimapp helm-charts/swim-chart/ -f helm-charts/swim-values.yaml -n swimapp --create-namespace
These charts are from the project's repos.
We are deploying ingress-nginx with only one custom value. contorller.config.hsts=false. HSTS needs disabled because we are using self signed ceritifcates. In a production environment HSTS should be enabled.
helm repo add ingress-nginx https://kubernetes.github.io/ingress-nginx
helm repo update
helm install ingress-nginx ingress-nginx/ingress-nginx -n ingress-nginx --create-namespace --set controller.config.hsts=false
We install cert-manager with only one custom value, installCRDs=true.
helm repo add jetstack https://charts.jetstack.io
helm repo update
helm install cert-manager jetstack/cert-manager -n cert-manager --create-namespace --version v1.5.4 --set installCRDs=true
NOTE: after cert manager is installed we need to configure a clusterissuer. The ansible playbooks included in this repo will create the issuer, but to create it manually run:
kubectl apply -f helm-charts/cert-manager-clusterissuer.yaml
The docker/ directory contains the dockerfile to build the application.
The commands used to build and push the image are:
docker build -t larntz/swim:2021102700 -f Dockerfile.swimapp .
docker push larntz/swim/2021102700
- Mongodb is configured to require a login and only allows access to the specified database.
- The application is accessible over HTTPS only. Cert-manager automatically provisions self signed certificates, but in a production envirionment we would use an actually trusted isuser such as let's encrypt.
- When packer is creating the vm images it calls an ansible playbook that installs any available updates.
Security could be improved by requiring TLS to connect to the mongodb members. But, becuase I am using self signed certificates I would need to create a configMap that includes the CA certificate. Furthermore, there is no integration between the mongodb-community-operator and cert-manager at this time so this coniguration would require some additional glue to automate.
- cluster is deployed with 3 control plane nodes behind an haproxy loadbalancer.
- The mongodb-community-operator is used to deploy mongodb as a cluster. By default we are deployhing 3 members. This can be scaled up and down.
- The application is deployed with 3 replicas. This can be scaled up and down.
HA functionality could be improved using multiple ingress controllers, multiple load balancers with a vip coupled with a service like route53 that can do loadbalancing and health checks. Next steps from there could be a multi-cluster deployment.
The mongodb cluster can be scaled up and down by modifying the members field of the mongo-values.yaml file and running helm upgrade for the chart.
The application can be scaled up and down by modifying the replicas of the swim-values.yaml file and running helm upgrade for the charge.
To scale the cluster up, first run terraform with an updated worker_nodes var, and then run the scale.yaml playbook from kubespray.
Example:
terraform -chdir=terraform apply -auto-approve -var worker_nodes=5
ansible-playbook -i cluster-hosts ansible-playbooks/kubespray/scale.yml --become
To scale the cluster down, first run the remove-node.yaml playbook from kubespray and then run terraform again with a workder_nodes variable decreased appropriately.
Example (removing 1 node):
ansible-playbook -i cluster-hosts ansible-playbooks/kubespray/remove-node.yml --become -e node=kgnmyp-wk-04
terraform -chdir=terraform apply -auto-approve -var worker_nodes=4
NOTE: Nodes must be removed in reverse order (highest nubmered nodes first). You must run the remove-node.yaml playbook for each node you intend to remove before running the terraform command.
There are a few help scripts used during development. They are only intended for testing purposes, and not production quality.
bootstrap-project.sh: this script can be run after step 3 of the prebuild steps. It will clone the kubespray repo, install a python venv and all python requirements, and install terraform, packer, helm, and kubectl on the host system.create-cluster.sh: this script will run the remainig build steps. At completion the cluster will be provisioned and the application will be installed and running. NOTE: customize terraform variables and helm values before running this step.destroy-cluster.sh: this script will tear down the cluster vms, support libvirt resources, and delete configuration files created during deployment.