Overview
The program should support the entire ActiveTwo series of amplifiers by BioSemi (http://www.biosemi.com/), including Mark 1 and Mark 2 amplifiers, analog input boxes, and so on. Daisy-chained multi-amp setups should work but have not yet been tested. While the application has a variety of customizable settings using it is as simple as clicking one button to get data collected.
Downloading
Please first check the Releases page to see if there is a release there for you. If not then you may find and old version on the sccn ( https://sccn.ucsd.edu/download/software/LSL/Apps/)
You may also build the application from source though the project hasn't been updated in a while and will require some manual configuration.
Usage
-
It is essential that you have the correct drivers installed. There is an old set of drivers from 2006 which are known to not work with this program. You find more recent drivers that have been tested in the drivers-win32_64.zip file.
-
Plug the BioSemi USB box into the computer and connect it via the fiber-optic cable to the amplifier (note that the cable must go into the "out" socket of the amp as the label indicates the direction of the data flow). Plug the amp into the battery box and turn it on.
-
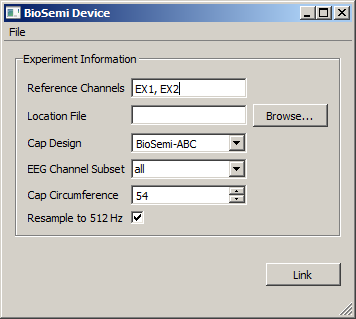
Start the BioSemi app. You should see a window like the following.
-
First-time test: The amplifier should work out of the box without having to change any settings: try to press the "Link" button to confirm that it works (you will get an error message if not). If not you are most likely using an incompatible driver. Note also that ActiView cannot be reading from the device at the same time as this app. If these considerations do not help, you might try to first test just a single amp with its speed mode set to 4 (all channels, 2KHz).
-
For practical use you will likely want to customize at least the channel subset and resampling settings before you link. Note that changes to settings while data is "in flight", i.e. while the application is linked, will have no effect and should generally be avoided to prevent confusion. The changes will however be accounted for when you unlink and then (re-)link again.
-
Note that settings that are changed while the program is linked will have no effect (you can in general not change the properties of a stream while it is online).
== Optional ==
It is possible to record only a subset of channels (see EEG Channel Subset), or at a different sampling rate. Note that the EX channels are always recorded (even if they are blank). If you uncheck "Resample to 512 Hz" the app will stream out data at the native rate of the amp, which is 2Khz or more (depending on the speed mode setting); if you check it a resampling filter will be applied, which has characteristics very similar to MATLAB's built-in resample() function in terms of pre/post-ringing and antialiasing.
The remaining settings allow to assign certain types of meta-data to the recorded stream:
- The reference channels that were used can be labeled; this is purely informational and the data is not in fact re-referenced.
- An .sfp electrode location file can be loaded and embedded in the per-channel meta-data (for example Zebris digitizer systems produce such files).
- The Cap Design can be labeled (if multiple designs are in use within the lab; to add a new design to the list, type it in and confirm by pressing enter.
- The cap circumference can be assigned, as well.
The configuration settings can be saved to a .cfg file (see File / Save Configuration) and subsequently loaded from such a file (via File / Load Configuration). Importantly, the BioSemi program can be started with a command-line argument of the form "BioSemi.exe -c myconfig.cfg", which allows to load the config automatically at start-up. The recommended procedure to use the BioSemi app in production experiments is to make a shortcut on the experimenter's desktop which points to a previously saved configuration customized to the study being recorded to minimize the chance of operator error.
== Rebuilding ==
Pre-requisites:
- Build environment (e.g., Visual Studio, Xcode, gcc+make)
- Qt
- Boost (v > 1.47.0)
- LSL (v1.02 or later, probably found in the same source tree as this application)
- BioSemi driver
- For MacOS and Win64, this is already provided in the DLL folder.
- For Linux, download here and follow the instructions.
Build instructions:
- With CMake (Windows/Mac/Linux):
mkdir build && cd build- Call
cmake ..with optional arguments Qt5_DIR and BOOST_ROOT- e.g., on my Mac:
cmake .. -DBOOST_ROOT=$(brew --prefix boost@1.60) - e.g., on my Win box:
cmake .. -G "Visual Studio 14 2015 Win64"
- e.g., on my Mac:
- Build and install the application
make && make install- If using VS2015, open the project, switch the target to Release, then build the INSTALL target.
- With Visual Studio 2008 project files:
- Customize the QtSDK location (default is C:\DEVEL\QtSDK)
- Set the environment variable BOOST_ROOT to point to the location of your boost_v_vv_v directory (otherwise you will have to change project settings)
- The following settings likely have to be customized for the project:
- In Project|Properties:
- under Configuration Properties|C/C++|Additional Include Directories, change the location of your QtSDK headers
- under Configuration Properties|Linker|General|Additional Library Directories, change the location of your QtSDK libraries
- under Configuration Properties|Linker|Input|Additional Dependencies, adapt the list of your QtSDK libraries
- If you are switching to debug build, you need to apply the same setting for this configuration, too
- With QtCreator
- Use the attached .pro file. It probably has to be modified for your environment.
Old notes from Wiki
-
Channel Subset: For a typical recording session you should select the correct channel subset (typical values are 32, 64, 128, 160 or all, either with AUX channels or without), although it does not hurt to record blank channels. You cannot disable the EX channels since some of them will normally be used to record a reference signal. The channel subsets cover the desired number of banks starting from A. If you have daisy-chained multiple amplifiers you will record the selected number of channels from each amp (e.g., 2x128 for two amps and 128 channels selected).
-
Resampling: You might want to uncheck the "Resample to 512 Hz" checkbox in order to record at the native rate of the amplifier (which depends on the speed mode and can be between 2KHz and 16KHz). If resampling is enabled, a linear-phase FIR anti-aliasing filter will be used that has essentially the same coefficients as MATLAB's resample() function. The real-time output will have an extra latency of 10ms, but for the purposes of time synchronization between streams this extra lag is being accounted for. The filter introduces 10ms of ringing (ripples) before and after any peak event of the data. It is enabled by default because the recorded files can easily grow very large otherwise and 2KHz is often overkill for EEG analysis.
-
With all settings made, you can now click "Link" to link the app to the LSL. This will give you a stream named BioSemi with type EEG. The channel labels will generally conform to the BioSemi naming scheme (A1-A32, B1-B32, ..., EX1-EX8, AUX1, AUX2, etc.) and are also found in the stream's meta-data. For multi-amp setups the channels will be labelled A1_Box1, ..., B16_Box2, and so on. The first channel is the trigger channel and is named Trig1 (it contains the bitmask of the active triggers).
-
For subsequent uses you can save the desired settings from the GUI via File / Save Configuration. If the app is frequently used with different settings you might make a shortcut on the desktop that points to the app and appends to the Target field of the shortcut the snippet
-c name_of_config.cfgto denote the name of the config file that should be loaded at startup.
-
Further Settings
All other settings are meta-data that are attached to the stream without affecting the signal but which can help making sense of the data during later analysis. They are primarily for record-keeping by the experimenters.
-
Reference Channels: In particular, the "reference channels" setting can be used to denote which channels were used to record the reference signal. Due to the way in which BioSemi records the signal, the data should always be re-referenced prior to analysis. Note that this app does not perform the re-referencing itself.
-
Location File: It is possible to load measured channel locations from a file and attach the channel locations directly to the meta-data to keep all information together. Currently the program supports Zebris .sfp files (although other formats might work, too).
-
Cap Design: This is a user-assigned label of the cap design or cap layout that was used to record. A new cap design label can be typed in and added to the list by pressing Enter.
-
Cap Circumference: This is the circumference of the cap/head that was used for the recording, in cm.
Other Notes
A time synchronization measurement between the BioSemi amplifier with analog input box and the AudioCaptureWin app has shown a signal alignment within 5ms. More precisely, the BioSemi signal was lagging by ca. 4ms, which could be due to driver or USB overhead -- if you make your own sync measurements, please let us know of the outcome.