This repository describes how to customize AWS CodePipeline to deploy AWS CDK application. Specifically, this repository describes how to implement a deployment pipeline optimized for AWS CDK Project Template for DevOps in the simplest way with the least amount of effort. That is, if you specify only a name of source repository and the names of AWS CDK Stack you want to deploy selectively, a pipeline is automatically created for this.
-
1.1 How to work
1.2 Prerequisite
-
2.1 Multiple Target Deployment
2.2 Cross-Account Target Deployment
2.3 PrePost Build Commands Injection
2.6 Role Customizing
Configuring CDK application deployment pipeline is just as important as configuring AWS cloud resources with AWS CDK. To solve this purpose, an official pipeline-CDK Pipelines is being provided, and it fundamentally utilizes AWS CloudFormation Action in AWS CodePipeline's Deploy. As explained in the official documentation, this is not easy to customize as it is purpose-built.
This repository introduces a new CDK deployment pipeline for minimal effort and maximum customization without changes to existing CDK applications. By default, AWS CodeBuild is used so that you can insert any build scripts or AWS CLI commands with AWS CDK CLI commands you want as if you were running in your local development environment. In particular, this is abstracted so that it can be conveniently deployed in a stack unit without writing cdk deploy command in BuildSpec of AWS CodeBuild by yourself. If you simply list the names of the stacks you want to deploy, a AWS CodeBuild's BuildSpec document tailored to the AWS CDK deployment is created internally.
This new pipeline opimized for AWS CDK deployment covers the following AWS CDK Application deployment cases.
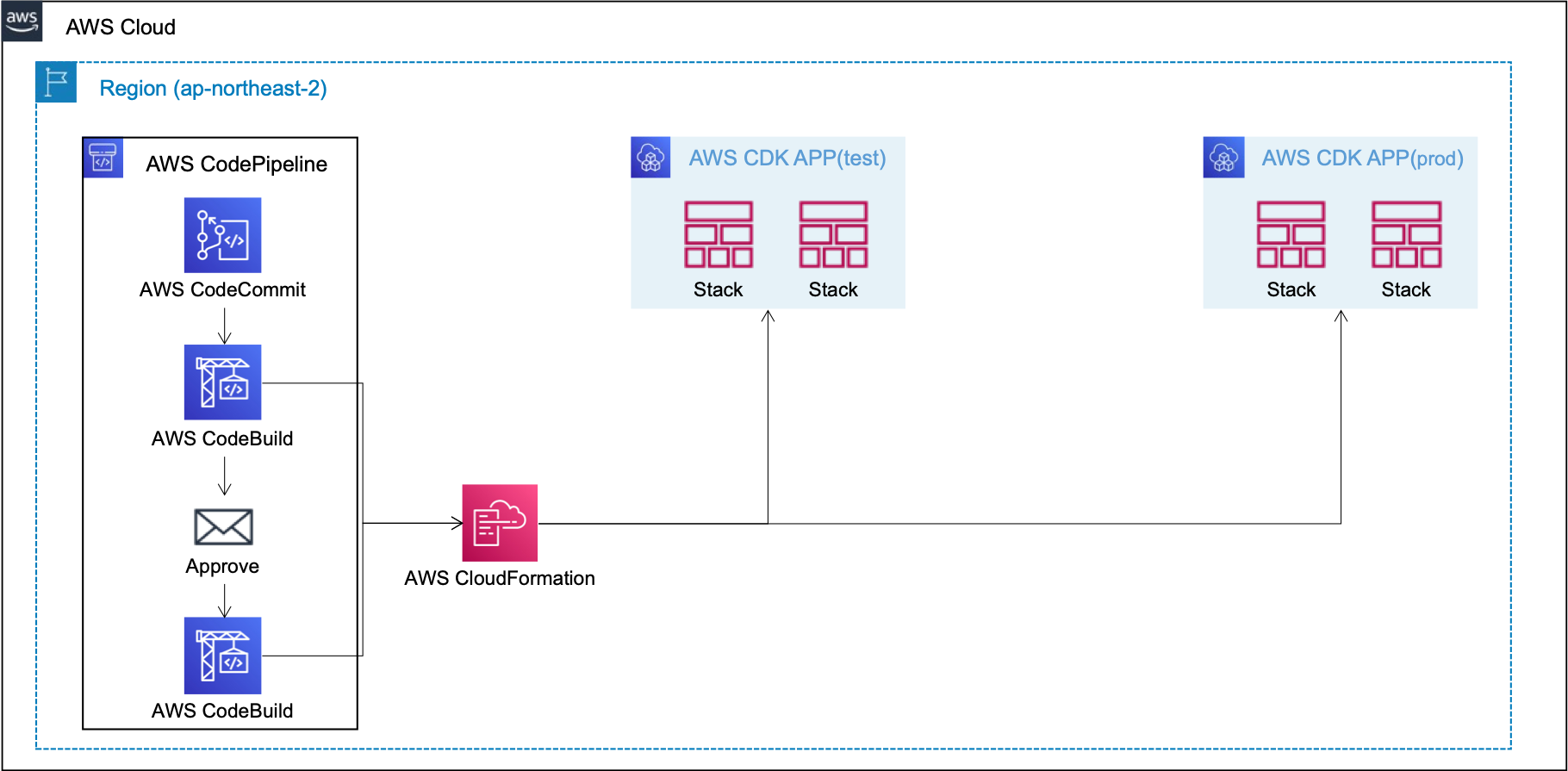
[Usecase 1] Test and Prod deployments in the same account & region
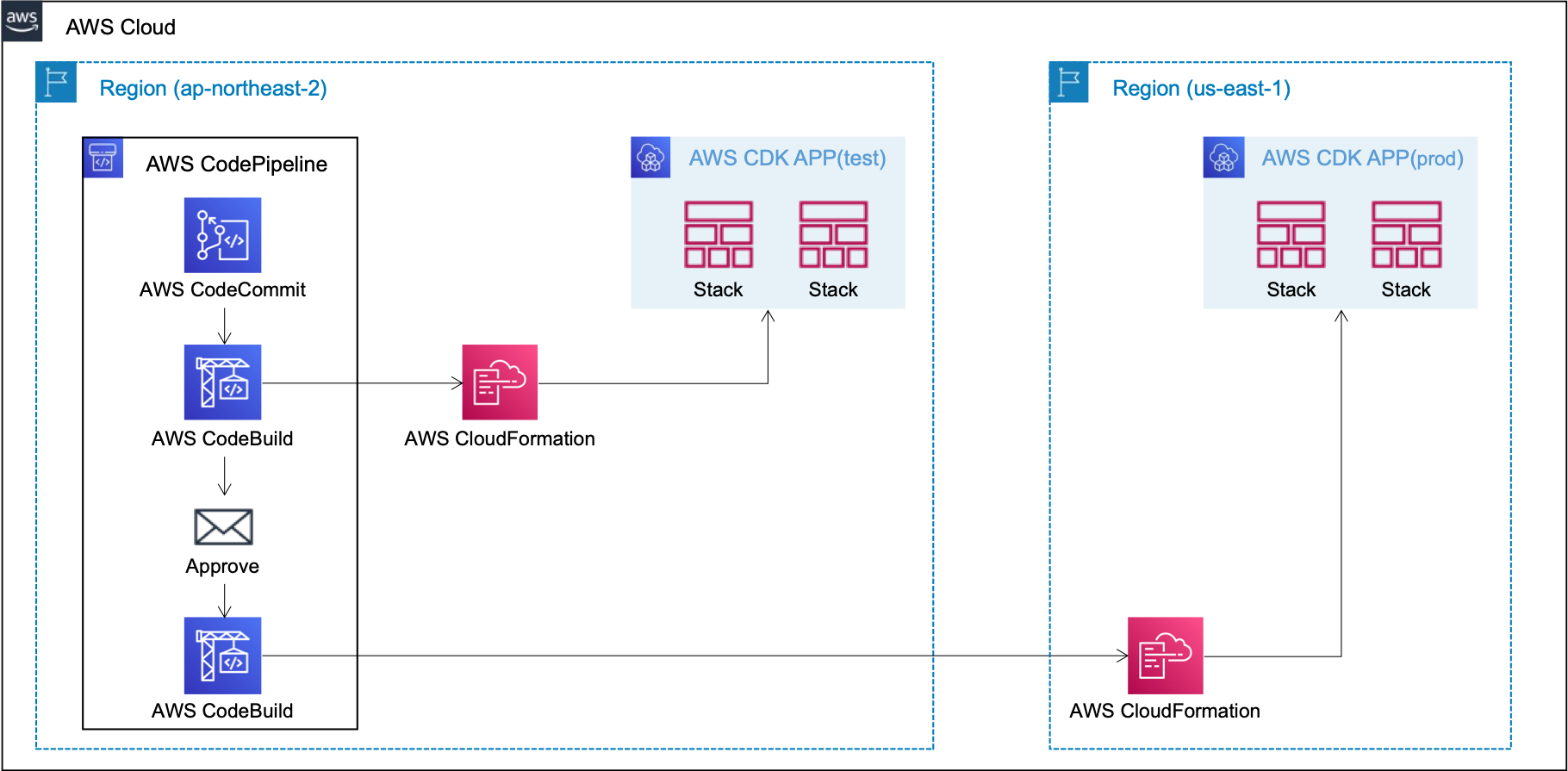
[Usecase 2] Test and Prod deployments in the same account & different region
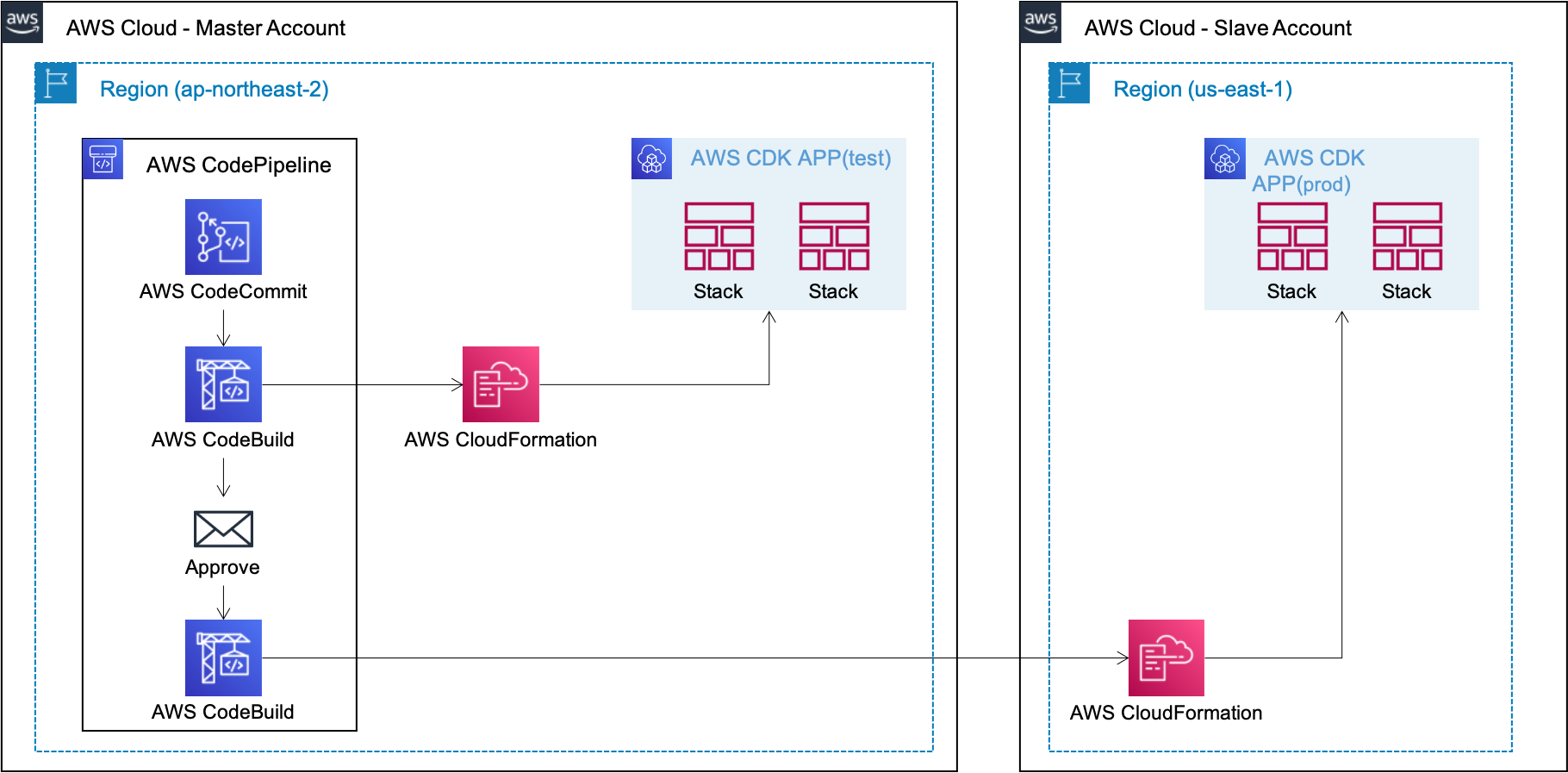
[Usecase 3] Test and Prod deployments in the different account & region
- It must have been cdk-bootstrapped in the target account/region beforehand.
StageandActionterminologies are same as AWS CodePipeline.- A AWS CodeCommit Repository named
sample-repoand branch namedrelease_cicdshould be prepared in advance for the practice. - The basic configuration concept(Stack dependency management, configuration-based stack deployment) was implemented on AWS CDK Project Template for DevOps project. We recommend that you read this project first.
- Because template framework is in AWS CDK Project Template for DevOps, please prepare the source code like this. Specifically these repositories provide both CDK v1 and v2 through branch, please append branch name to identify them!
git clone https://github.com/aws-samples/aws-cdk-project-template-for-devops.git -b release_cdk_v1 or release_cdk_v2
git clone https://github.com/aws-samples/aws-cdk-deploy-pipeline-using-aws-codepipeline.git -b release_cdk_v1 or release_cdk_v2
cp -r aws-cdk-project-template-for-devops/lib aws-cdk-deploy-pipeline-using-aws-codepipeline- Caution: You may be charged a small fee if you deploy through hands-on practice. For hands-on practice, account in
config/app-config-xxxx.jsonfile must be updated according to your environment.
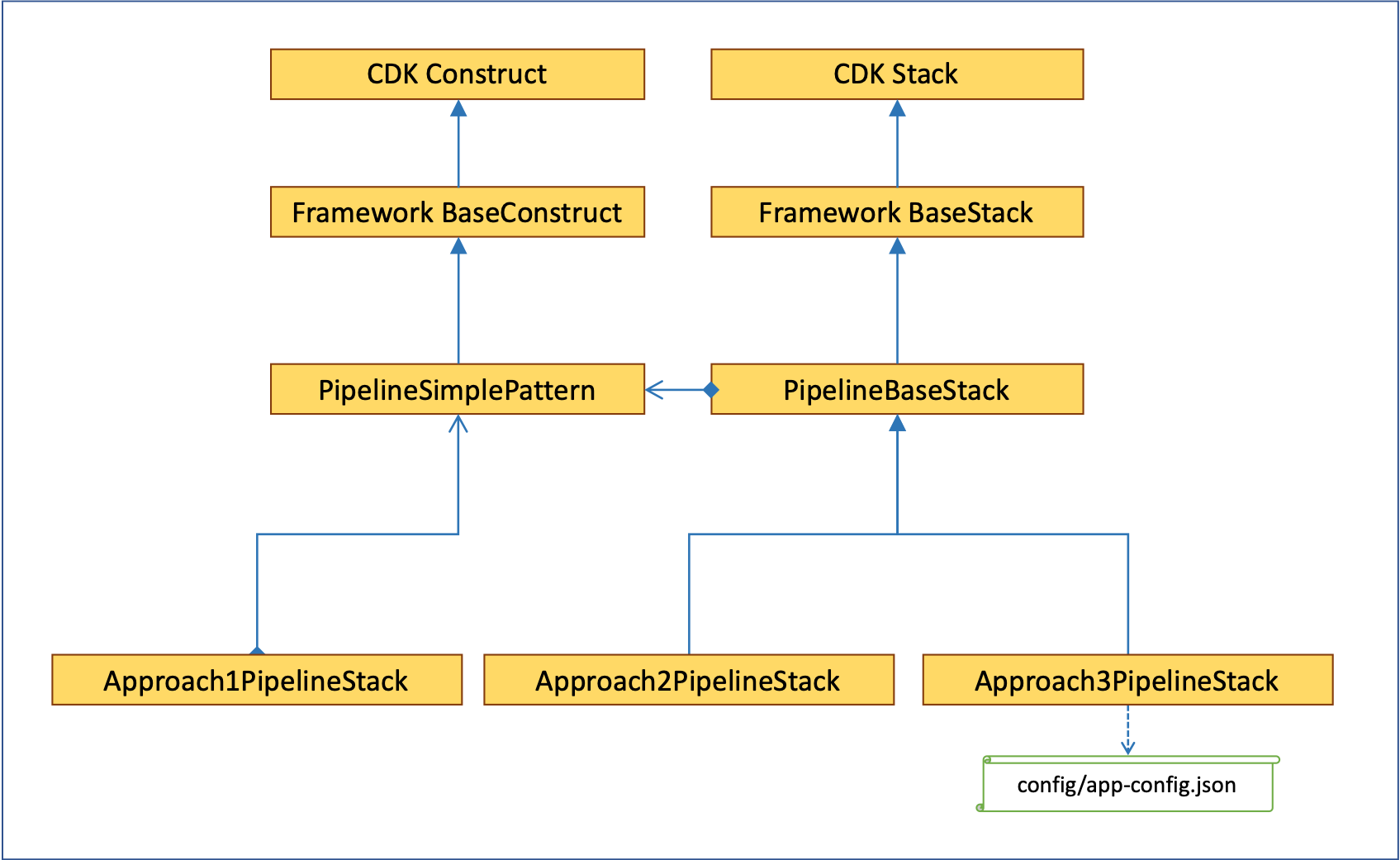
Basically, this provides a pipeline CDK Construct optimized for CDK deployment, and provides 3 approaches to make it convenient to use.
For now, don't worry about the detailed configuration, just understand the approach to how to use it. Detailed configuration will be described below. The example codes below are saved in the following infra/stack/sample1, and you can deploy it right away by specifying a config file as follows.
export APP_CONFIG=config/app-config-sample1.json
cdk list
PipelineSample1-Approach1PipelineStack
PipelineSample1-Approach2PipelineStack
PipelineSample1-Approach3PipelineStack
PipelineSample1-Sample1Service1StackApproach 1: Use PipelineSimplePattern construct class directly
In any your Stack, use this construct class directly with specific options. In this case, you have to care all options by yourself. ActionFlow option is the most important, and you'll set it the same for any other approach.
import * as base from '../../../lib/template/stack/base/base-stack';
import { AppContext } from '../../../lib/template/app-context';
import * as pipeline from '../../../lib/template/construct/pattern/pipeline-simple-pattern';
export class Approach1PipelineStack extends base.BaseStack {
constructor(appContext: AppContext, stackConfig: any) {
super(appContext, stackConfig);
new pipeline.PipelineSimplePattern(this, 'Approach1', {
projectPrefix: this.projectPrefix,
stackConfig: this.stackConfig,
stackName: this.stackName,
env: this.commonProps.env!,
pipelineName: 'Approach1Pipeline',
actionFlow: [
{
Name: 'GitClone',
Stage: 'SourceStage',
Kind: pipeline.ActionKind.SourceCodeCommit,
Enable: true,
Detail: {
RepositoryName: 'sample-repo',
BranchName: 'release_cicd'
}
},
{
Name: 'DeployAllStacks',
Stage: "DevDeployStage",
Kind: pipeline.ActionKind.BuildCodeBuild,
Enable: true,
Detail: {
AppConfigFile: "config/app-config-sample1.json",
BuildDeployStacks: {
StackNameList: ['Sample1Service1Stack'],
}
}
}
]
});
}
}Approach 2: Generalize PipelineBaseStack base class
Create a new Stack, where this stack have to generalize PipelineBaseStack base class. Becase this class is a abstract class, we have to override some methods. Template Method Pattern in OOP is applied for guiding pipeline configuration. This approach only requires passing in a minimal set of options, as the base class knows all of the default options. If you want to create additional resources, you can start with onPostConstructor() method instead of constructor() method.
import * as base from '../../../lib/template/stack/devops/pipeline-base-stack';
import { AppContext } from '../../../lib/template/app-context';
import { Override } from '../../../lib/template/stack/base/base-stack';
import * as pipeline from '../../../lib/template/construct/pattern/pipeline-simple-pattern';
export class Approach2PipelineStack extends base.PipelineBaseStack {
private pipeline: pipeline.PipelineSimplePattern;
constructor(appContext: AppContext, stackConfig: any) {
super(appContext, stackConfig);
}
@Override
onPostConstructor(pipeline: pipeline.PipelineSimplePattern): void {
this.pipeline = pipeline;
}
@Override
onPipelineName(): string {
return 'Approach2Pipeline';
}
@Override
onActionFlow(): pipeline.ActionProps[] {
return [
{
Name: 'GitClone',
Stage: 'SourceStage',
Kind: pipeline.ActionKind.SourceCodeCommit,
Enable: true,
Detail: {
RepositoryName: 'sample-repo',
BranchName: 'release_cicd'
}
},
{
Name: 'DeployAllStacks',
Stage: "DevDeployStage",
Kind: pipeline.ActionKind.BuildCodeBuild,
Enable: true,
Detail: {
AppConfigFile: "config/app-config-sample1.json",
BuildDeployStacks: {
StackNameList: ['Sample1Service1Stack'],
}
}
}
];
}
}Approach 3: Generalize PipelineBaseStack base class and inject pipeline configuration using config file
This approach is same to approach 2, but in here we don't configure pipeline options directly in a Stack class. All options are configured in an external json file such as config/app-config-xxx.json.
import * as base from '../../../lib/template/stack/devops/pipeline-base-stack';
import { AppContext } from '../../../lib/template/app-context';
import { Override } from '../../../lib/template/stack/base/base-stack';
import * as cicd from '../../../lib/template/construct/pattern/pipeline-simple-pattern';
export class Approach3PipelineStack extends base.PipelineBaseStack {
private pipeline: cicd.PipelineSimplePattern;
constructor(appContext: AppContext, stackConfig: any) {
super(appContext, stackConfig);
}
@Override
onPostConstructor(pipeline: cicd.PipelineSimplePattern): void {
this.pipeline = pipeline;
}
@Override
onPipelineName(): string {
return this.stackConfig.PipelineName;
}
@Override
onActionFlow(): cicd.ActionProps[] {
return this.stackConfig.ActionFlow;
}
}Stack class implementation is very simple, and it can be reused by changing the config file only externally. The json shown below is an example of a config file that is set externally and injected.
"Approach3Pipeline": {
"Name": "Approach3PipelineStack",
"PipelineName": "Approach3Pipeline",
"ActionFlow": [
{
"Name": "GitClone",
"Stage": "SourceStage",
"Kind": "SourceCodeCommit",
"Enable": true,
"Detail": {
"RepositoryName": "sample-repo",
"BranchName": "release_cicd"
}
},
{
"Name": "DeployAllStacks",
"Stage": "DevDeployStage",
"Kind": "BuildCodeBuild",
"Enable": true,
"Detail": {
"AppConfigFile": "config/app-config-sample1.json",
"BuildDeployStacks": {
"StackNameList": ["Sample1Service1Stack"]
}
}
}
]
}The configuration shown above is injected from app-main.ts like this:
new Approach3PipelineStack(appContext, appContext.appConfig.Stack.Approach3Pipeline);A pipeline can be defined as a AcionFlow option, and which is a sequence of Actions. ActionFlow option must adhere to the following rules:
- The first item of the
ActionFlowmust be aSourcekind such asSourceCodeCommitorSourceS3Bucket - The
ActionFlowmust contain at least two items, that means Source Action kind + Other Action kinds
For detailed explanation, suppose we have 3 MSA service stacks and 1 pipeline stack like this:
export APP_CONFIG=config/app-config-sample2.json
cdk list
PipelineSample2-Sample2Service1Stack
PipelineSample2-Sample2Service2Stack
PipelineSample2-Sample2Service3Stack
PipelineSample2-Sample2PipelineStackDepending on the dependencies of the stacks and the deployment strategy, we can think of a pipeline configuration by dividing it into four cases as follows. Full source code is ready in infra/stack/sample2/sample2-pipeline-stack.ts.
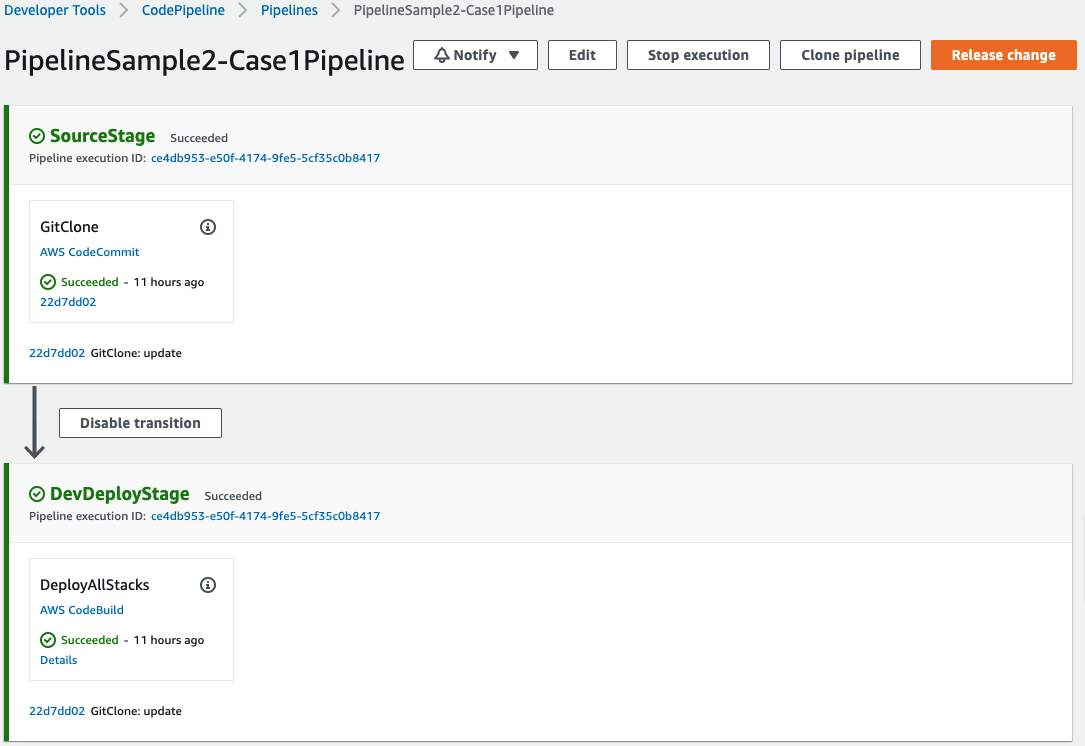
Case 1: Deploy all stacks in a single AWS CodeBuild project within a Stage
If the stacks are tightly dependent on each other and of cource deployment lifecycle is same, this approach is suitable. The following settings will deploy three stacks sequentially in one AWS CodeBuild project in one Stage.
private createCase1Pipeline() {
new pipeline.PipelineSimplePattern(this, 'case1', {
projectPrefix: this.projectPrefix,
stackConfig: this.stackConfig,
stackName: this.stackName,
env: this.commonProps.env!,
pipelineName: 'Case1Pipeline',
actionFlow: [
{
Name: 'GitClone',
Stage: 'SourceStage',
Kind: pipeline.ActionKind.SourceCodeCommit,
Enable: true,
Detail: {
RepositoryName: 'sample-repo',
BranchName: 'release_cicd'
}
},
{
Name: 'DeployAllStacks',
Stage: "DevDeployStage",
Kind: pipeline.ActionKind.BuildCodeBuild,
Enable: true,
Detail: {
AppConfigFile: "config/app-config-sample2.json",
BuildDeployStacks: {
StackNameList: ['Sample2Service1Stack', 'Sample2Service2Stack', 'Sample2Service3Stack'],
}
}
}
]
})
}The configuration shown above will automatically generate the following BuildSpec file. Internally, it sets up creates AWS CDK environment and deployment commands. Particularly, StackNameList: ['Sample2Service1Stack', 'Sample2Service2Stack', 'Sample2Service3Stack'] option will generate cdk deploy *StackName* --require-approval never command list.
{
"version": "0.2",
"phases": {
"install": {
"runtime-versions": {
"nodejs": 14
},
"commands": [
"npm install -g aws-cdk@1",
"npm install"
]
},
"pre_build": {},
"build": {
"commands": [
"cdk deploy *Sample2Service1Stack* --require-approval never",
"cdk deploy *Sample2Service2Stack* --require-approval never",
"cdk deploy *Sample2Service3Stack* --require-approval never"
]
},
"post_build": {}
},
"artifacts": {
"files": [
"**/*"
],
"exclude-paths": [
"cdk.out/",
"node_modules/",
".git/"
]
}
}Here's the final deployed pipeline:
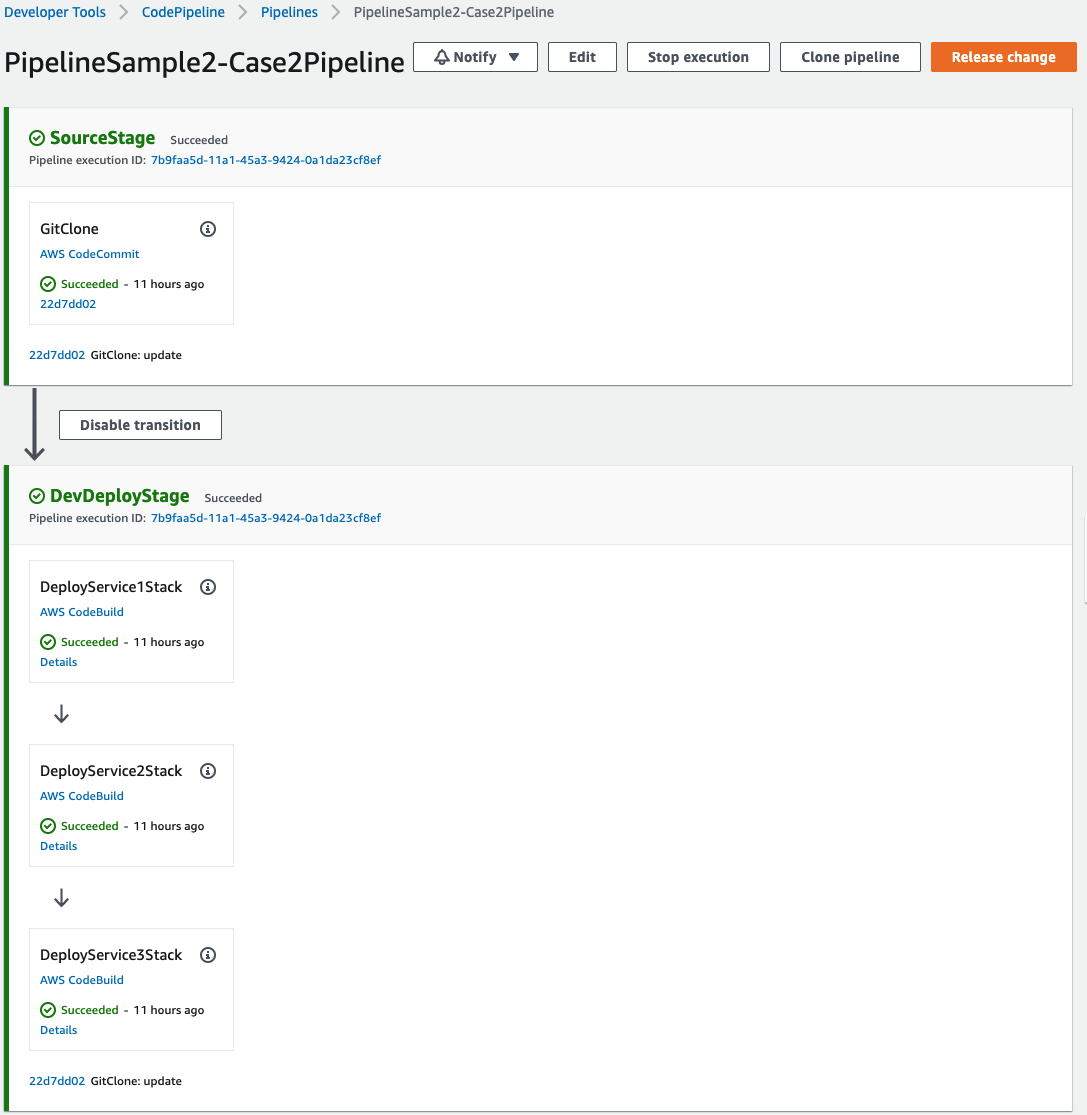
Case2: Deploy each stack in each AWS CodeBuild project in one Stage.
If the stacks are loosely coupled on each other and deployment lifecycle is same, this approach is suitable. The following settings will deploy three stacks sequentially in each AWS CodeBuild project in one Stage.
private createCase2Pipeline() {
new pipeline.PipelineSimplePattern(this, 'case2', {
projectPrefix: this.projectPrefix,
stackConfig: this.stackConfig,
stackName: this.stackName,
env: this.commonProps.env!,
pipelineName: 'Case2Pipeline',
actionFlow: [
{
Name: 'GitClone',
Stage: 'SourceStage',
Kind: pipeline.ActionKind.SourceCodeCommit,
Enable: true,
Detail: {
RepositoryName: 'sample-repo',
BranchName: 'release_cicd'
}
},
{
Name: 'DeployService1Stack',
Stage: "DevDeployStage",
Kind: pipeline.ActionKind.BuildCodeBuild,
Enable: true,
Order: 1,
Detail: {
AppConfigFile: "config/app-config-sample2.json",
BuildDeployStacks: {
StackNameList: ['Sample2Service1Stack'],
}
}
},
{
Name: 'DeployService2Stack',
Stage: "DevDeployStage",
Kind: pipeline.ActionKind.BuildCodeBuild,
Enable: true,
Order: 2,
Detail: {
AppConfigFile: "config/app-config-sample2.json",
BuildDeployStacks: {
StackNameList: ['Sample2Service2Stack'],
}
}
},
{
Name: 'DeployService3Stack',
Stage: "DevDeployStage",
Kind: pipeline.ActionKind.BuildCodeBuild,
Enable: true,
Order: 3,
Detail: {
AppConfigFile: "config/app-config-sample2.json",
BuildDeployStacks: {
StackNameList: ['Sample2Service3Stack'],
}
}
}
]
})
}It is important here that the stage names are all the same. Bacause all stage names are same with different action name, this will result in the following commands internally in each AWS CodeBuild project.
1st Build Project
cdk deploy *Sample2Service1Stack*2nd Build Project
cdk deploy *Sample2Service1Stack*3rd Build Project
cdk deploy *Sample3Service1Stack*Here's the final deployed pipeline:
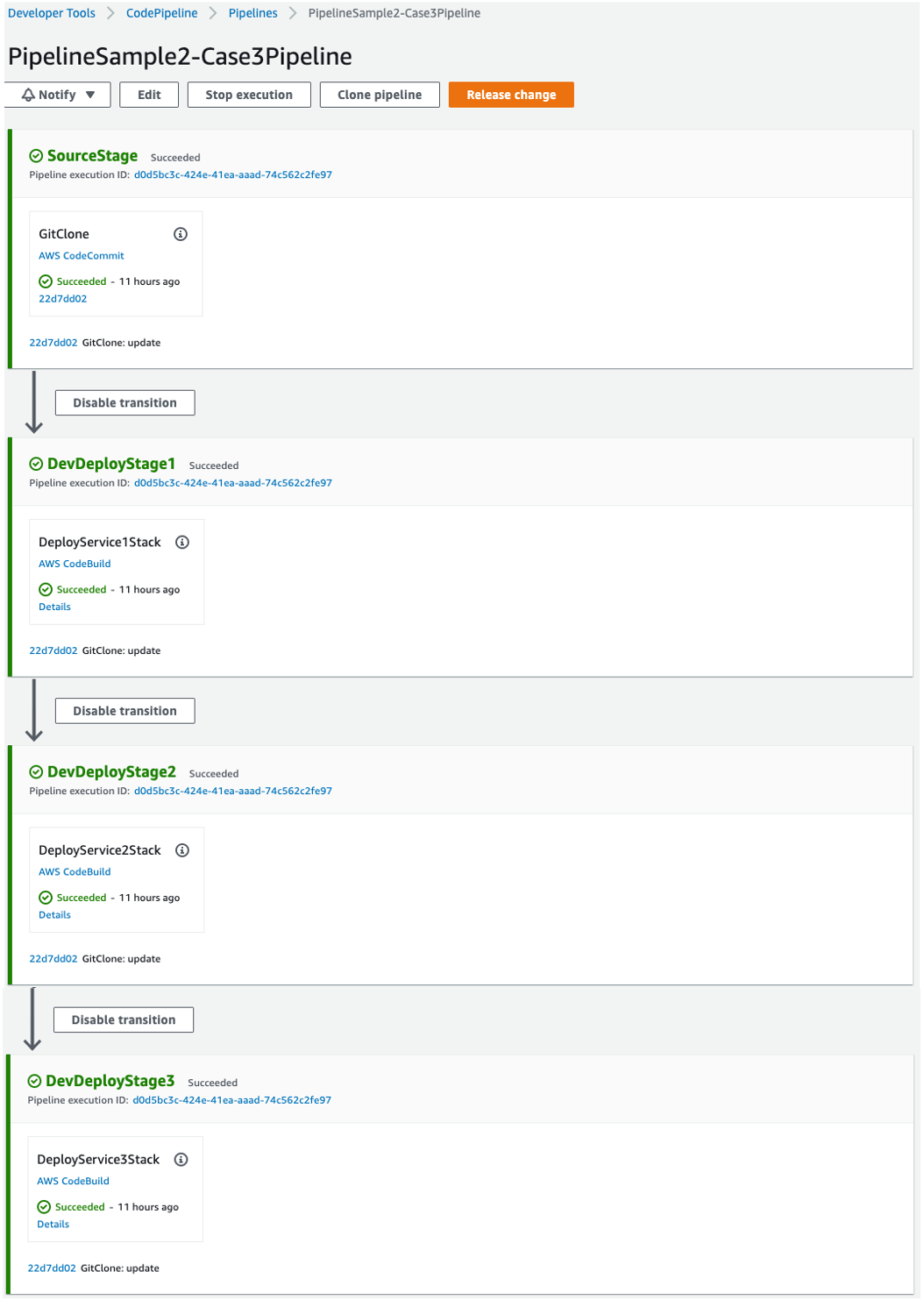
Case3: Deploy each stack in each AWS CodeBuild project of each Stage
If the stacks are to be deployed sequentially, each in an independent environment, this approach is suitable. The following settings will deploy three stacks sequentially in each AWS CodeBuild project in different Stages.
private createCase3Pipeline() {
new pipeline.PipelineSimplePattern(this, 'case3', {
projectPrefix: this.projectPrefix,
stackConfig: this.stackConfig,
stackName: this.stackName,
env: this.commonProps.env!,
pipelineName: 'Case3Pipeline',
actionFlow: [
{
Name: 'GitClone',
Stage: 'SourceStage',
Kind: pipeline.ActionKind.SourceCodeCommit,
Enable: true,
Detail: {
RepositoryName: 'sample-repo',
BranchName: 'release_cicd'
}
},
{
Name: 'DeployService1Stack',
Stage: "DevDeployStage1",
Kind: pipeline.ActionKind.BuildCodeBuild,
Enable: true,
Detail: {
AppConfigFile: "config/app-config-sample2.json",
BuildDeployStacks: {
StackNameList: ['Sample2Service1Stack'],
}
}
},
{
Name: 'DeployService2Stack',
Stage: "DevDeployStage2",
Kind: pipeline.ActionKind.BuildCodeBuild,
Enable: true,
Detail: {
AppConfigFile: "config/app-config-sample2.json",
BuildDeployStacks: {
StackNameList: ['Sample2Service2Stack'],
}
}
},
{
Name: 'DeployService3Stack',
Stage: "DevDeployStage3",
Kind: pipeline.ActionKind.BuildCodeBuild,
Enable: true,
Detail: {
AppConfigFile: "config/app-config-sample2.json",
BuildDeployStacks: {
StackNameList: ['Sample2Service3Stack'],
}
}
}
]
})
}Note that both Action name and Stage name are different. Here's the final deployed pipeline:
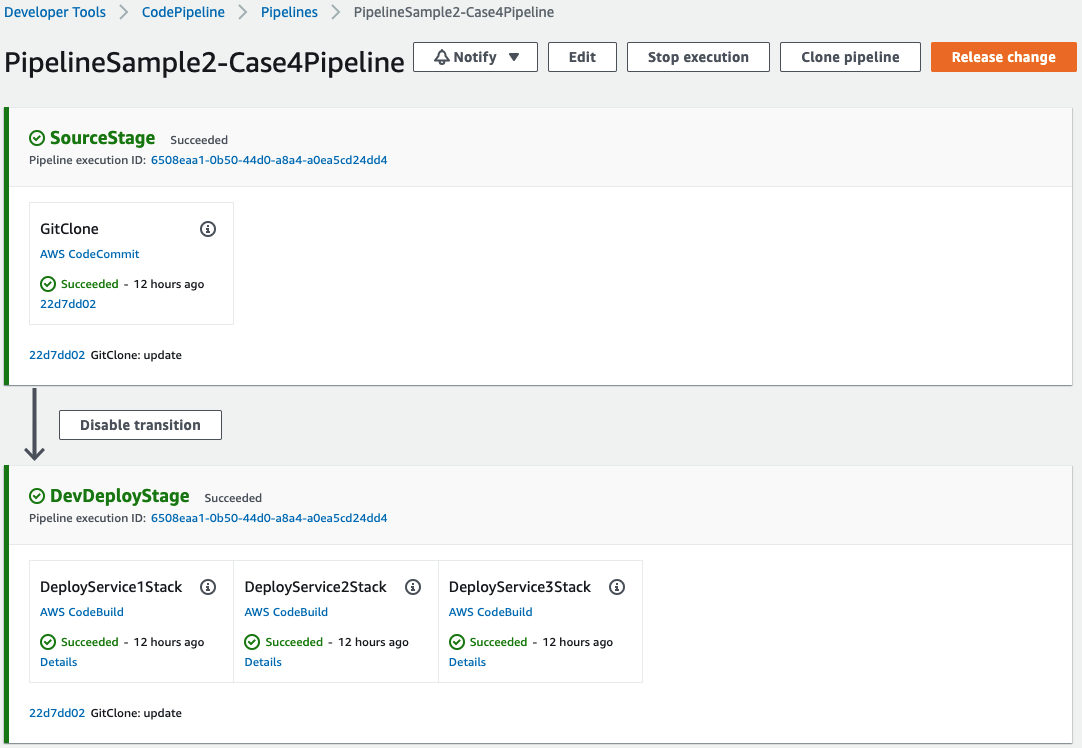
Case4: Deploy all stacks simultaneously in each AWS CodeBuild project of a single Stage
If the stacks are completely independent on each other and deployment lifecycle is same, this approach is suitable. The following settings will deploy three stacks at the same time in each AWS CodeBuild project within one Stage.
private createCase4Pipeline() {
new pipeline.PipelineSimplePattern(this, 'case4', {
projectPrefix: this.projectPrefix,
stackConfig: this.stackConfig,
stackName: this.stackName,
env: this.commonProps.env!,
pipelineName: 'Case4Pipeline',
actionFlow: [
{
Name: 'GitClone',
Stage: 'SourceStage',
Kind: pipeline.ActionKind.SourceCodeCommit,
Enable: true,
Detail: {
RepositoryName: 'sample-repo',
BranchName: 'release_cicd'
}
},
{
Name: 'DeployService1Stack',
Stage: "DevDeployStage",
Kind: pipeline.ActionKind.BuildCodeBuild,
Enable: true,
Order: 1,
Detail: {
AppConfigFile: "config/app-config-sample2.json",
BuildDeployStacks: {
StackNameList: ['Sample2Service1Stack'],
}
}
},
{
Name: 'DeployService2Stack',
Stage: "DevDeployStage",
Kind: pipeline.ActionKind.BuildCodeBuild,
Enable: true,
Order: 1,
Detail: {
AppConfigFile: "config/app-config-sample2.json",
BuildDeployStacks: {
StackNameList: ['Sample2Service2Stack'],
}
}
},
{
Name: 'DeployService3Stack',
Stage: "DevDeployStage",
Kind: pipeline.ActionKind.BuildCodeBuild,
Enable: true,
Order: 1,
Detail: {
AppConfigFile: "config/app-config-sample2.json",
BuildDeployStacks: {
StackNameList: ['Sample2Service3Stack'],
}
}
}
]
})
}Because Stage name is the same, they are grouped into one stage, and because Order is the same, they are deployed at the same time.
Here's the final deployed pipeline:
The following environment variables are provided to the build project. You can use these when you write a customized build commands.
The example values were written based on app-config-sample2.json config file.
| Variable Name | Example Value |
|---|---|
| ACCOUNT | 12345678901 |
| REGION | us-east-2 |
| PROJECT_NAME | Pipeline |
| PROJECT_STAGE | Sample2 |
| PROJECT_PREFIX | PipelineSample2 |
| APP_CONFIG | config/app-config-sample2.json |
| ON_PIPELINE | YES |
Full source code is ready in infra/stack/sample3.
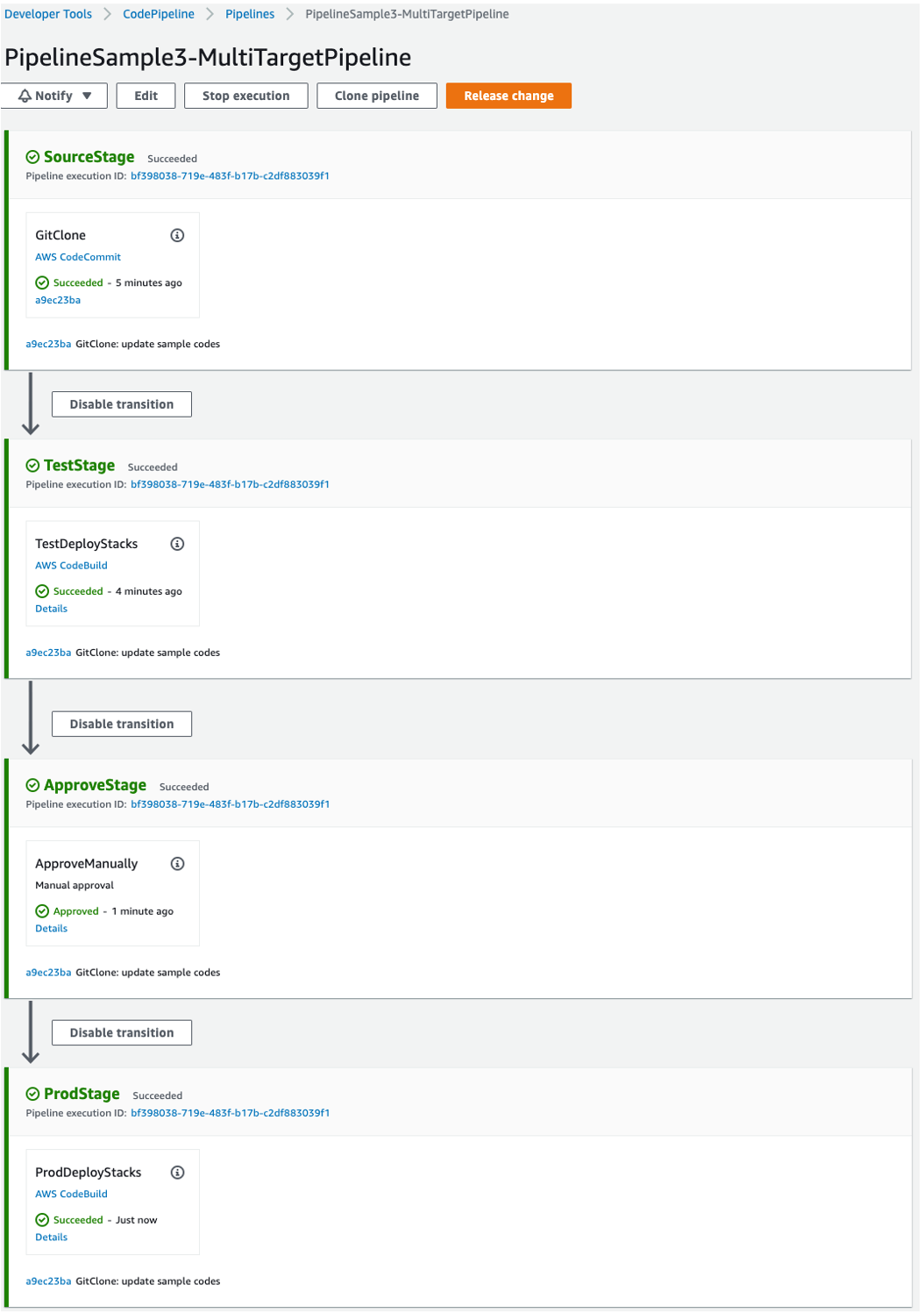
You can deploy test/prod stages step by step by using the config files that have the target environment, and you can put an approval step in the middle.
{
Name: "TestDeployStacks",
Stage: "TestStage",
Kind: pipeline.ActionKind.BuildCodeBuild,
Enable: true,
Detail: {
AppConfigFile: "config/app-config-sample3-test.json",
BuildDeployStacks: {
StackNameList: ["Sample3Service1Stack"],
}
}
},
{
Name: "ApproveManually",
Stage: "ApproveStage",
Kind: pipeline.ActionKind.ApproveManual,
Enable: true,
Detail: {
Description: "Must check stacks before prod"
}
},
{
Name: "ProdDeployStacks",
Stage: "ProdStage",
Kind: pipeline.ActionKind.BuildCodeBuild,
Enable: true,
Detail: {
AppConfigFile: "config/app-config-sample3-prod.json",
BuildDeployStacks: {
StackNameList: ["Sample3Service1Stack"],
}
}
}In here, app-config-sample3-test.json's destination is us-east-2, app-config-sample3-prod.json's destination is us-east-1. That is, Test-Stage deploy the stacks to us-east-2 and Prod-Stage deploy the stacks to us-east-1. This is a example case for cross-region distribution.
For deployment, execute the following command.
export APP_CONFIG=config/app-config-sample3.json
cdk list
...
...
PipelineSample3-Sample3PipelineStack
cdk deploy *Sample3PipelineStack
...
...
git push [remote repo name] [branch name]Here's the final deployed pipeline:
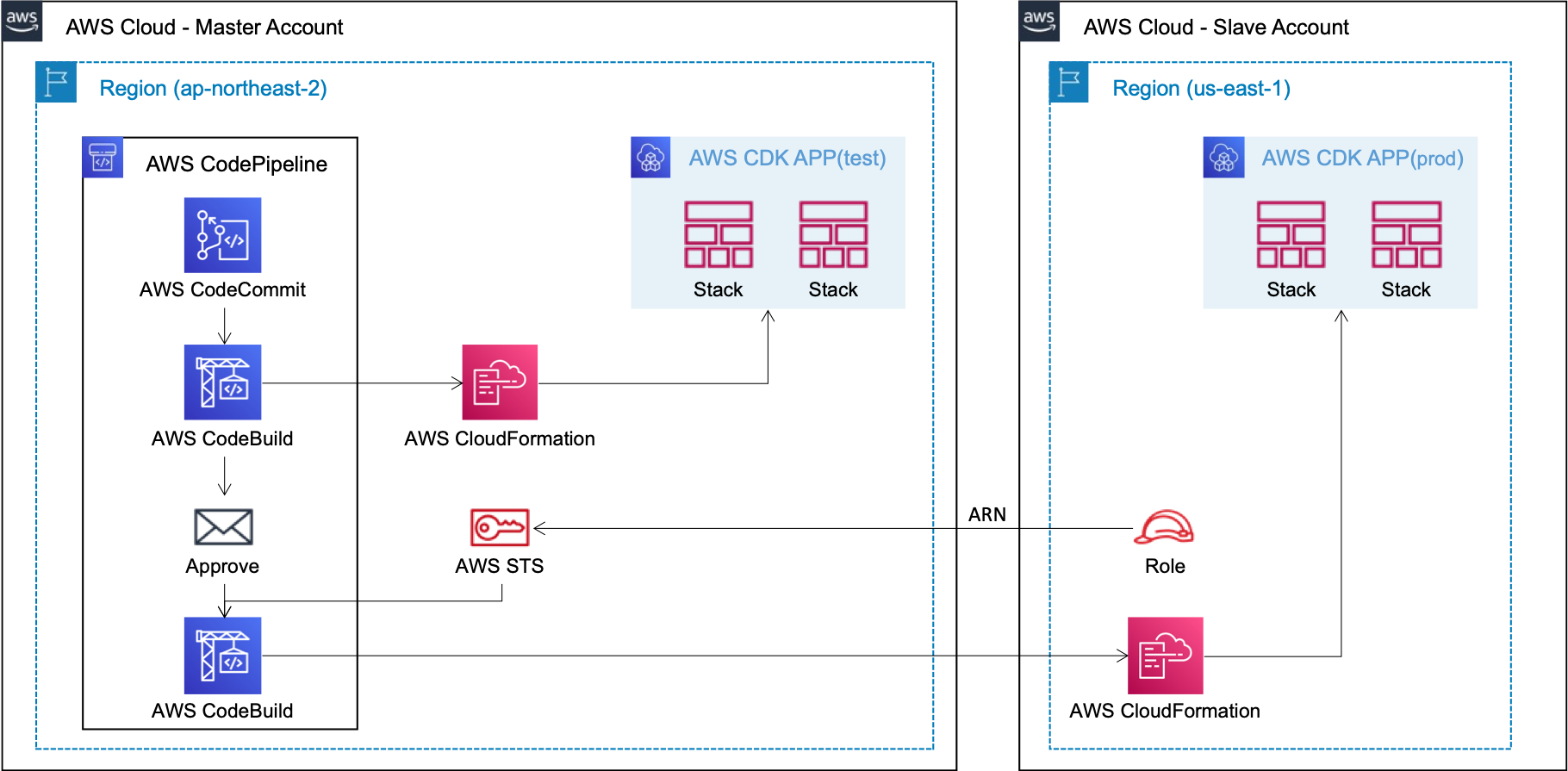
You can deploy each test/prod stage to the difference account/region. Mostly the same as Multiple Target Deployment above, the only difference is that you have to specify the difference accoun in config json file and prepare assume-role.
{
Name: 'TestDeployStacks',
Stage: "TestStage",
Kind: pipeline.ActionKind.BuildCodeBuild,
Enable: true,
Detail: {
AppConfigFile: "config/app-config-sample3-test.json",
BuildDeployStacks: {
PreCommands: ['aws sts get-caller-identity'],
StackNameList: ['Sample3Service1Stack'],
}
}
},
{
Name: 'ApproveManually',
Stage: 'ApproveStage',
Kind: pipeline.ActionKind.ApproveManual,
Enable: true,
Detail: {
Description: 'Must check stacks before prod'
}
},
{
Name: 'ProdDeployStacks',
Stage: "ProdStage",
Kind: pipeline.ActionKind.BuildCodeBuild,
Enable: true,
Detail: {
AppConfigFile: "config/app-config-sample3-prod-cross.json",
BuildDeployStacks: {
PreCommands: ['aws sts get-caller-identity'],
StackNameList: ['Sample3Service1Stack'],
},
BuildAssumeRoleArn: 'arn:aws:iam::[your account number]:role/[your assume-role name]'
}
}In here, app-config-sample3-test.json's destination is A-account, config/app-config-sample3-prod-cross.json's destination is B-account. And BuildAssumeRoleArn option is added, where the assume-role must have a minimu policy for a target Stack deployment, and the role must be set to trust the account where the pipeline is ready.
As shown in the following figure, temporary credentials are internally created using AWS STS to access the account.
You can inject build commands before and after deploying the stacks. This allows you to set up the environment, build some modules, perform unit tests, and so on.
{
Name: 'DeployStack1',
Stage: "DevDeployStage",
Kind: pipeline.ActionKind.BuildCodeBuild,
Enable: false,
Detail: {
AppConfigFile: "config/app-config-sample1.json",
BuildDeployStacks: {
PreCommands: [
'npm install --prefix code/lambda/api',
'pytest code/lambda/api/test'
],
StackNameList: ['Sample1Service1Stack'],
PostCommands: [
'aws s3 sync code/lambda/api/report s3://aaa/bb/cc'
]
}
}
}If you specify a lambda function as follows, the event is delivered at the time of each action change and the lambda is automatically called.
{
Name: 'DeployStack1',
Stage: "DevDeployStage",
Kind: pipeline.ActionKind.BuildCodeBuild,
Enable: false,
EventStateLambda: {
CodePath: 'code/lambda/cicd-event-state',
Handler: 'handler.handle',
Runtime: 'python3.7'
},
Detail: {
AppConfigFile: "config/app-config-sample1.json",
BuildDeployStacks: {
StackNameList: ['Sample1Service1Stack'],
}
}
}The disable option allows you to temporarily disable certain Actions without removing the complex options.
{
Name: 'DeployStack1',
Stage: "DevDeployStage",
Kind: pipeline.ActionKind.BuildCodeBuild,
Enable: false,
Detail: {
AppConfigFile: "config/app-config-sample1.json",
BuildDeployStacks: {
StackNameList: ['Sample1Service1Stack'],
}
}
},
{
Name: 'DeployStack2',
Stage: "DevDeployStage",
Kind: pipeline.ActionKind.BuildCodeBuild,
Enable: true,
Detail: {
AppConfigFile: "config/app-config-sample1.json",
BuildDeployStacks: {
StackNameList: ['Sample2Service1Stack'],
}
}
}If IAM Policies are not specified through the following method, AdministratorAccess permission is automatically granted.
const pipeline = new cicd.PipelineSimplePattern(this, 'Approach1', {
projectPrefix: this.projectPrefix,
stackConfig: this.stackConfig,
stackName: this.stackName,
env: this.commonProps.env!,
pipelineName: 'Approach1Pipeline',
actionFlow: [
],
buildPolicies: this.createCustomPolicies()
});
private createCustomPolicies(): iam.PolicyStatement[] {
const statement = new iam.PolicyStatement();
statement.addActions(
"cognito:*",
"dynamodb:*",
"application-autoscaling:*",
"elasticloadbalancingv2:*",
"elasticloadbalancing:*",
);
statement.addResources("*");
return [statement];
}@Override
protected onBuildPolicies(): iam.PolicyStatement[] | undefined {
const statement = new iam.PolicyStatement();
statement.addActions(
"cognito:*",
"dynamodb:*",
"application-autoscaling:*",
"elasticloadbalancingv2:*",
"elasticloadbalancing:*",
);
statement.addResources("*");
return [statement];
}Because we provide the other options to execute AWS CodeBuild project, you can customize the build project through the following two options.
{
Name: 'DeployAllStacks',
Stage: "DevDeployStage",
Kind: pipeline.ActionKind.BuildCodeBuild,
Enable: true,
Detail: {
AppConfigFile: 'config/app-config-sample1.json',
BuildSpecFile: 'script/cicd/buildspec_cdk_deploy.yaml'
}
}{
Name: 'DeployAllStacks',
Stage: "DevDeployStage",
Kind: pipeline.ActionKind.BuildCodeBuild,
Enable: true,
Detail: {
AppConfigFile: 'config/app-config-sample1.json',
BuildCommands: [
'pwd',
'ls -l',
'script/cicd/install_dependencies.sh',
'script/cicd/unit_test.sh',
'script/cicd/deploy_stacks.sh',
]
}
}Because we provide CodePipeline instance as a public member variable, you can customize anything using this object.
const pipeline = new cicd.PipelineSimplePattern(this, 'Approach1', {
projectPrefix: this.projectPrefix,
stackConfig: this.stackConfig,
stackName: this.stackName,
env: this.commonProps.env!,
pipelineName: 'Approach1Pipeline',
actionFlow: [
]
})
const codePipeline = pipeline.codePipeline;
codePipeline.addStage(.....);@Override
onPostConstructor(pipeline: pipeline.PipelineSimplePattern): void {
this.pipeline = pipeline;
const codePipeline = pipeline.codePipeline;
codePipeline.addStage(.....);
}Currently, the following limitations exist and will be improved soon.
- cross-account Deployments: completed
- AWS CodeBuild environment settings
- self-mutating
See CONTRIBUTING for more information.
This library is licensed under the MIT-0 License. See the LICENSE file.