#SafeScroll
Chrome extension offering content screening. Available for download from the Chrome Web Store.
SafeScroll is a Chrome extension that gives users the power of content screening. Intended for trauma survivors, SafeScroll reads your webpage before you do and will throw up a removable block between you and the content you don't want to see.
All content screens are easily removed by clicking the lock icon in the top-right corner. SafeScroll can act as a preemptive warning for possibly triggering material, but you always have the ability to dismiss the warning. If you decide you actually didn't want to see what was beneath, simply click the lock icon again to put the screen back in place.
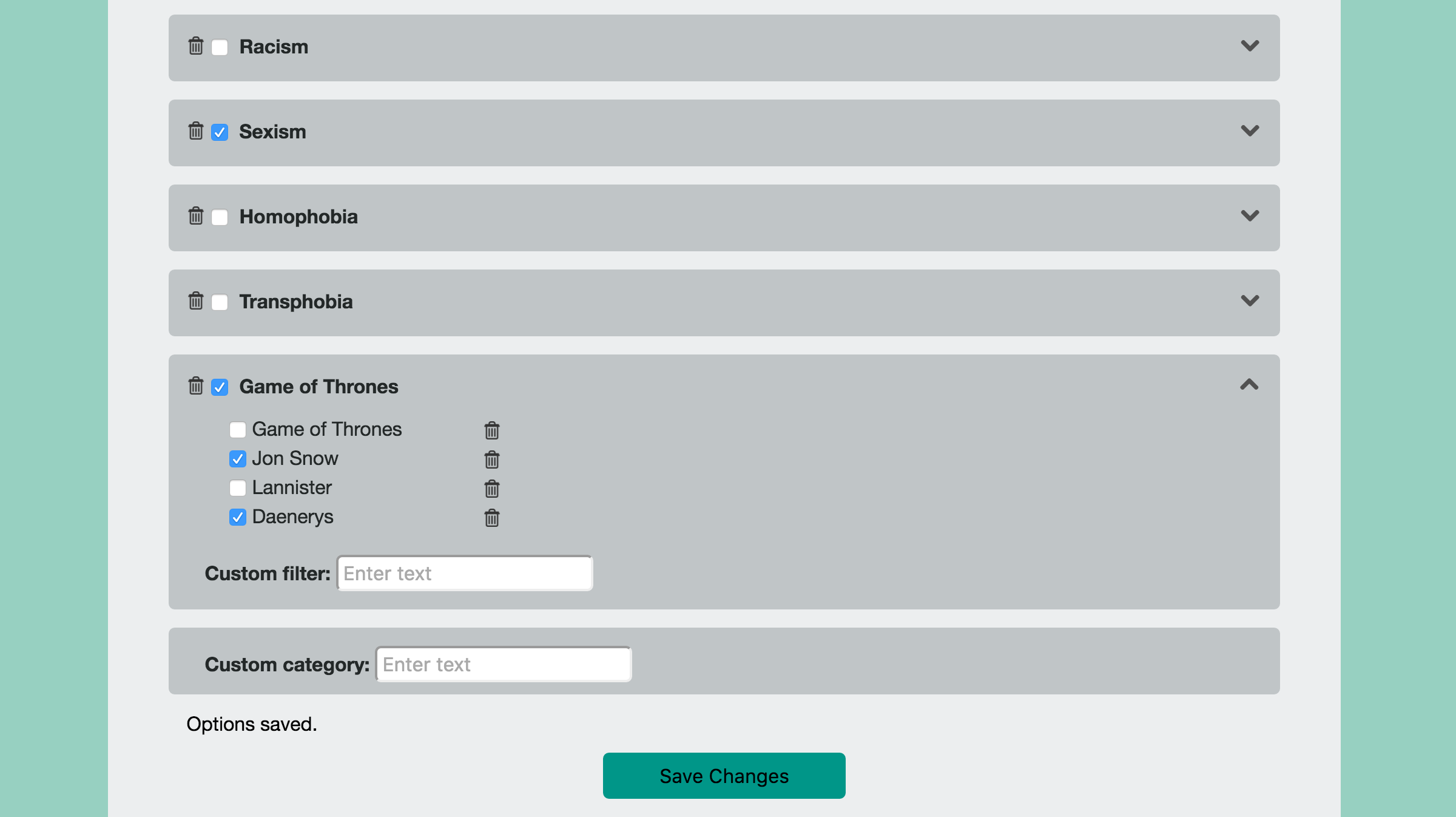
SafeScroll screening is fully customizable -- use default settings or dive into the details to block exactly what you need to.
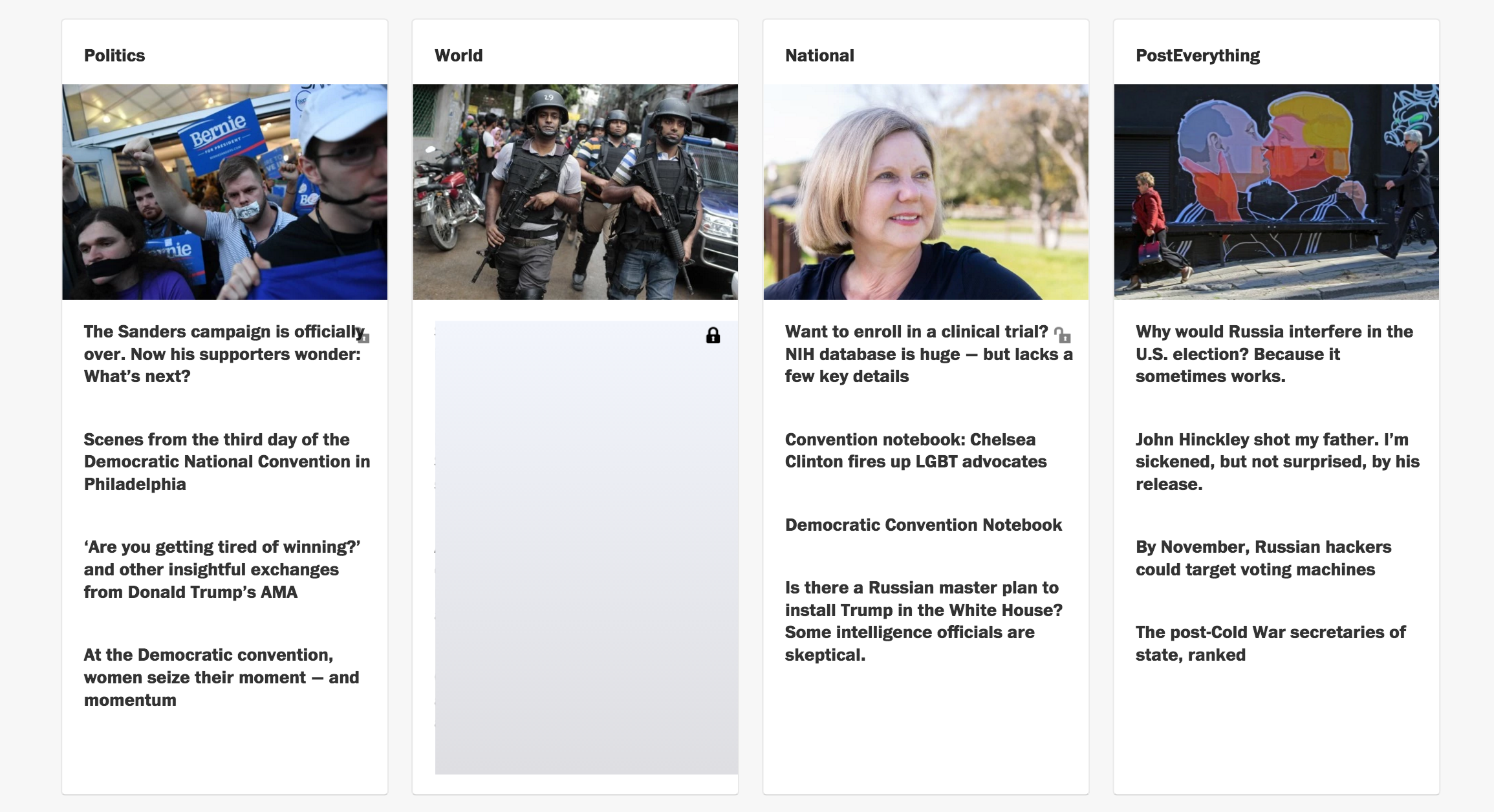
Use SafeScroll to broadly block out news stories of gun violence, or narrow it down to particularly relevant events by entering custom settings.
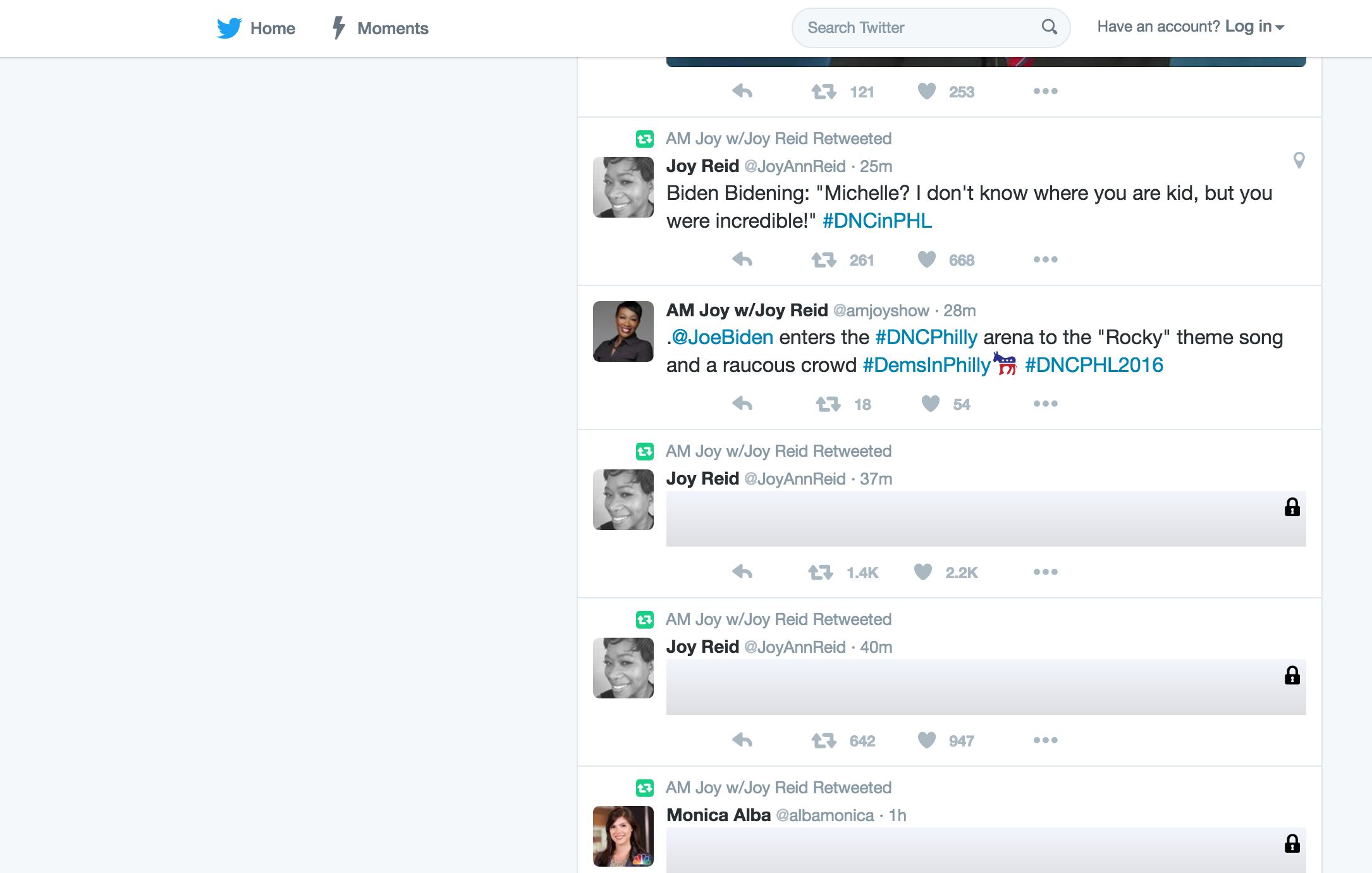
Screen out hate speech from social media.
Users can create new categories and sub-fields and remove existing ones to customize what content is blocked.
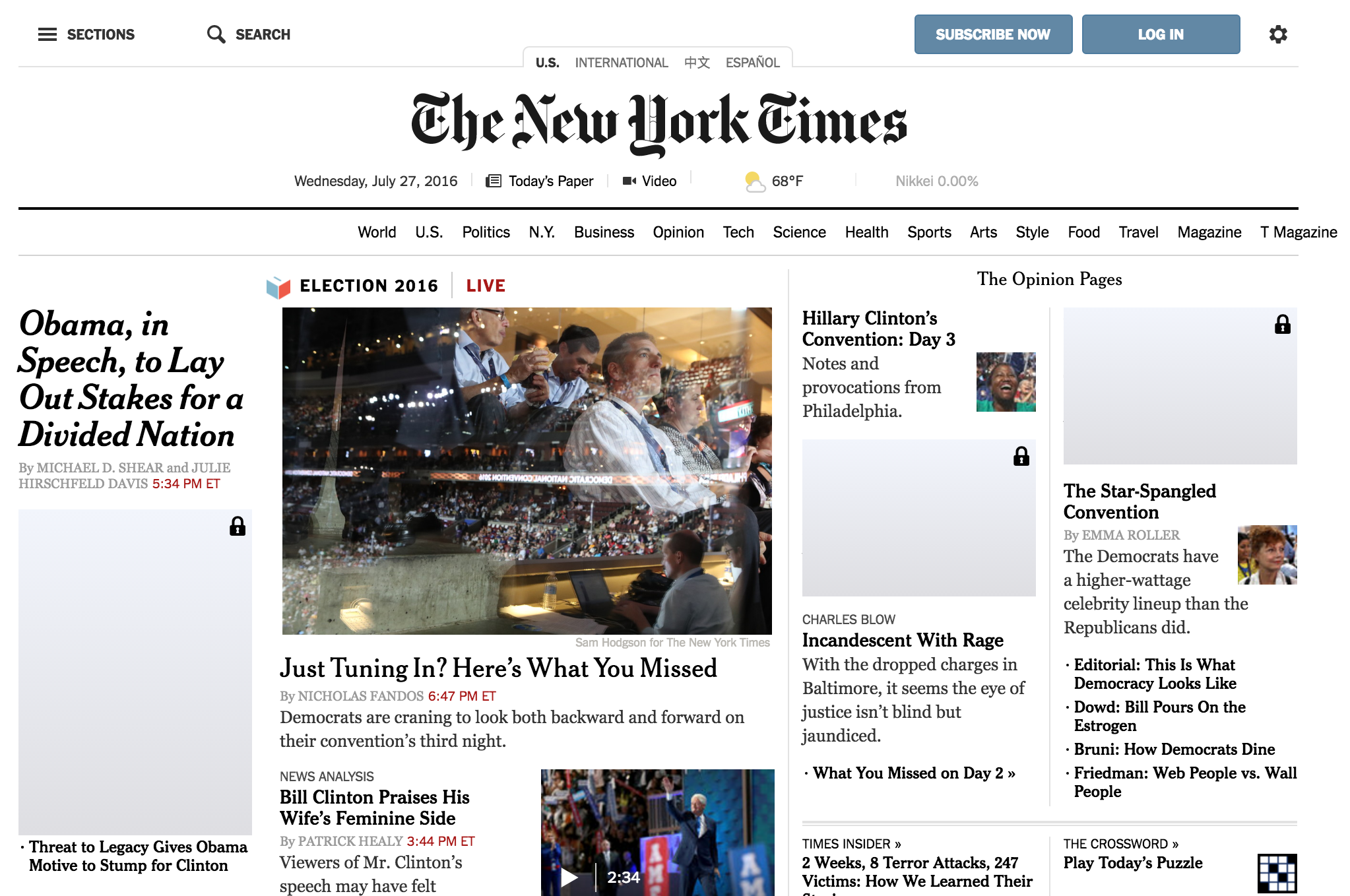
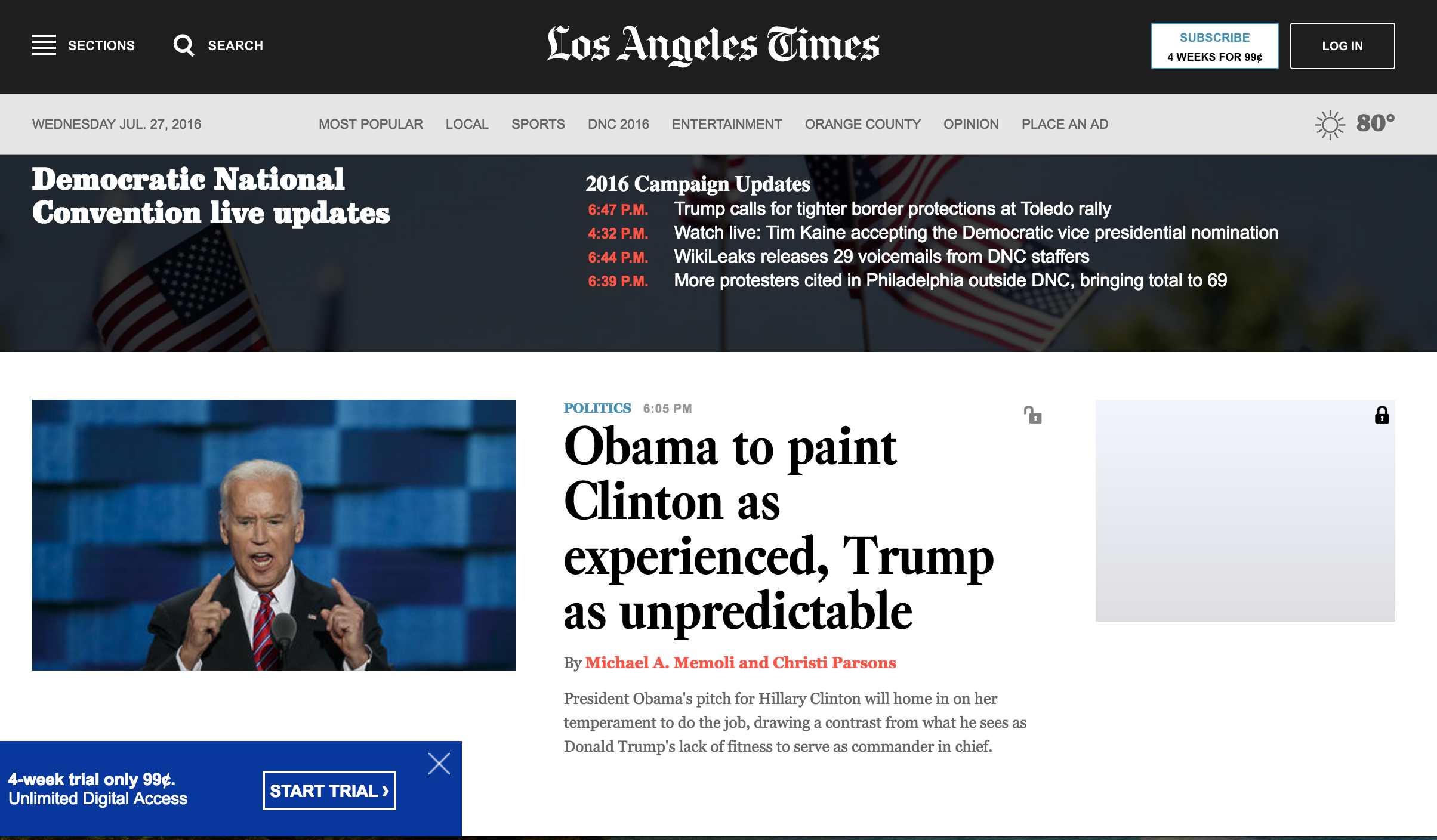
SafeScroll is a powerful tool for screening out unwanted material, whether it's a relatively rare term or a name that's over the news. Here we're blocking all stories related to Donald Trump on the New York Times, and unhidden a Trump-related article on the LATimes that we decided we wanted to peek at (notice the toggle-able unlock symbol in the top-right corner of the article heading).
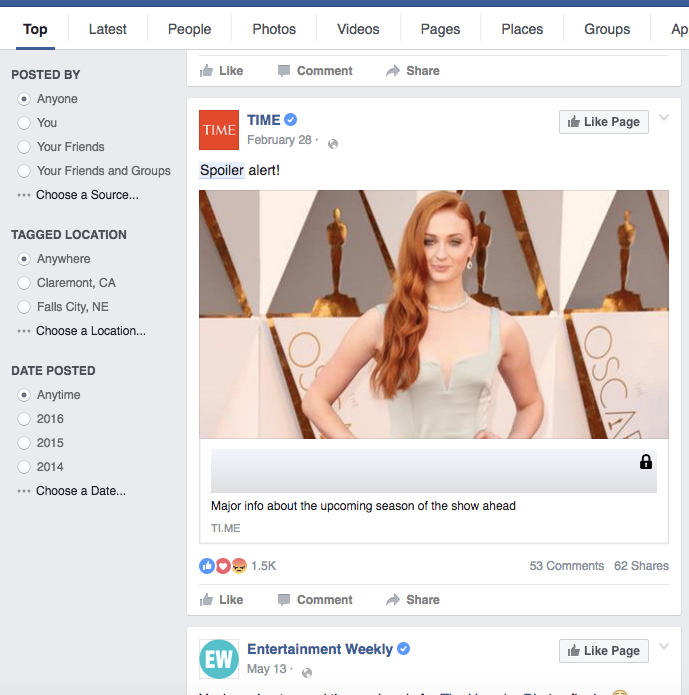
While SafeScroll was built to address very serious issues, the same technology is just as adept handling more frivolous applications. Haven't gotten to the latest episode of Game of Thrones? Afraid of spoilers? Block out all mentions of Game of Thrones and related words until you get caught up!
Screening is achieved by traversing the DOM tree and comparing each text node to regular expressions generated through users' input on the options page. Each time a filtered word or phrase is caught, SafeScroll retraces its steps back up the DOM tree until it finds a non-text parent container whose CSS display property is set to block, and inserts a div of the same size overtop to hide the content underneath.
function findParentContainer(elementNode) {
const texts = ["p", "h1", "h2", "h3", "h4", "h5", "h6", "span", "a"];
let node = elementNode.parentNode;
while (node) {
if (($(node).css('display') === 'block') && (
!texts.includes(node.localName))) {
return node;
} else {
node = node.parentNode;
}
}
}
function generateWarning(parentNode) {
let warning = $('<div></div>').addClass("extension-warning");
let lock = $('<div class="lock locked"></div>');
$(parentNode).append(lock);
$('.lock').off().on('click', function(e) {
e.preventDefault();
e.stopPropagation();
toggleLock(this);
});
return warning;
}Each screen is equipped with a lock icon to control its display properties. Upon creation of a screen, a lock element is attached to the parent container that's being blocked. The lock is outfitted with a jQuery click listener that toggles the class of the inserted screen to hide or reveal the content beneath.
function toggleLock(element) {
let classes = $(element).attr('class').split(' ');
if (classes.includes('locked')) {
$(element).removeClass('locked');
$(element).addClass('unlocked');
$(element.parentNode).children('.extension-warning').css("display", "none");
} else if (classes.includes('unlocked')) {
$(element).removeClass('unlocked');
$(element).addClass('locked');
$(element.parentNode).children('.extension-warning').css("display", "block");
}
}Users control and customize the extension through interaction with the options page and integration with Chrome Storage API. Input fields create DOM elements through jQuery and insert them directly onto the page.
function createItem(category, check, value) {
const parent = $(`#${category}`);
let input;
if (value) {
input = value;
} else {
input = $(`#${category}-input`).val();
}
if (check === "true") {
check = true;
} else {
check = false;
}
const label = $(`<label class="content-label ${input}">${input}</label>`);
const newItem = $('<input/>', {
"class": "content-item",
type: "checkbox",
value: `${input}`,
checked: check
});
const deleteDiv = $('<div class="delete-content-item"></div>');
deleteDiv.on('click', e => {
deleteContentItem(e);
});
$(parent).append(label.prepend(newItem).append(deleteDiv));
$('.custom-content').val('');
}Upon saving, all page content is read and stored alongside its checked/unchecked status and category. This is all saved through Chrome Storage, rendering it accessible by the web page script and upon revisiting the options page.
In future releases we are looking to include the following features:
- Color-coded screens to indicate category of underlying content
- Customizable styling of screens
- Crowd-sourced flagging of content that belongs to a commonly blocked category but isn't easily flagged by our algorithm, such as images and videos