-
What is Operating System ?
Operating system is an interface between user and the computer hardware. The hardware of the computer cannot understand the human readable language as it works on binaries i.e. 0's and 1's. Also it is very tough for humans to understand the binary language, in such case we need an interface which can translate human language to hardware and vice-versa for effective communication. -
Types of Operating System:
- Single User - Single Tasking Operating System
- Single User - Multitasking Operating System
- Multi User - Multitasking Operating System
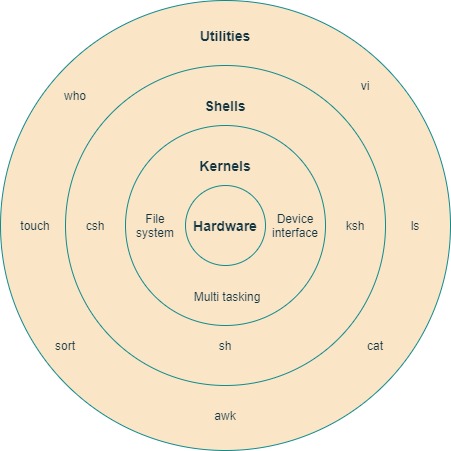
- The architecture of UNIX can be divided into Four levels of functionality, as shown in Figure .
-
Hardware
Hardware consists of all physical devices attached to the System.
Example:- Hard disk drive, RAM, Motherboard, CPU etc. -
Kernel
kernel is the core component for any (Linux) operating system which directly interacts with the hardware. it schedules tasks, manages resources, and controls security.- Different types of the kernel are:
- Monolithic Kernel
- Hybrid kernels
- Exo kernels
- Micro kernels
- Different types of the kernel are:
-
Shell
Shell is the interface which takes input from users and sends instructions to the Kernel, Also takes the output from Kernel and send the result back to output user and starting applications.- Types of shells are classified into four:
- Korn shell
- Bourne shell
- C shell
- Types of shells are classified into four:
-
Utilities
Utilities provides the functionalities of an operating system to the users.
| Path | Description |
|---|---|
| / | It is parent directory for all other directories.(root directory) |
| /root | It is home directory for root user and it provides working environment for root user |
| /home | It is home directory for other users and it provide working environment for other users |
| /boot | It contains bootable files for Linux. Like GRUB (GRand Unified Boot loader) boot.ini, ntldr |
| /etc | It contains all configuration files. Like User info /etc/passwd |
| /usr | By default softwares are installed in /usr directory |
| /opt | It is optional directory for /usr and it contains third party softwares. |
| /bin | It contains commands used by all users(Binary files) |
| /sbin | It contains commands used by only Super User (root) |
| /dev | It contains device file like hard disk /dev/hda |
| /proc | It contain process files and data are not permanent, they keep changing like information of CPU /proc/cpuinfo |
| /var | It is containing variable data like mails, log files |
| /mnt | It is default mount point for any partition. It is empty by default |
| /media | It contains all of removable media like CD-ROM, pen drive |
| /lib | It contains library files which are used by OS. Library files in Linux are shared object files |
-
Basic Commands
-
LS Command
-
Filter Commands
-
GREP Command
-
Find Command
-
File Permissions
-
Changing Ownership and Group
-
VI Editor
-
Linux Links
-
Managing Process
-
Signals In Linux
-
Top Command
-
User Administration
-
Group Administration