- Introduction
- What is GitOps?
- What is Flux?
- Components Of Flux
- System Requirements
- Setup development cluster using KIND (Kubernetes in docker)
- Install & Configure Flux in Kubernetes Cluster
- GitOps In Action
- Setup Git repository "app-flux-infra"
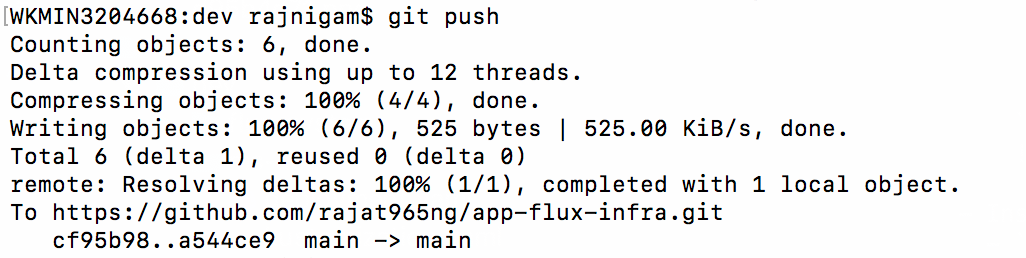
- Apply Kubernetes manifests (YAMLs)
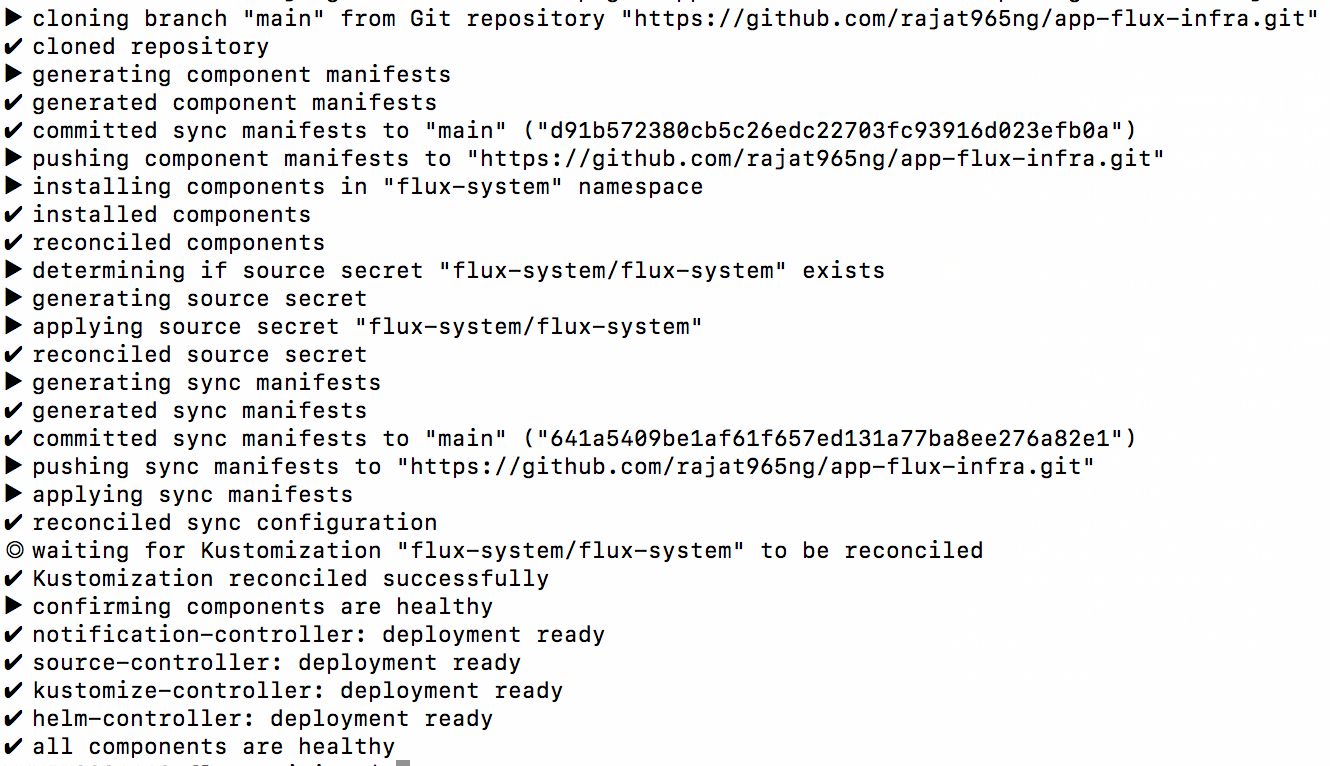
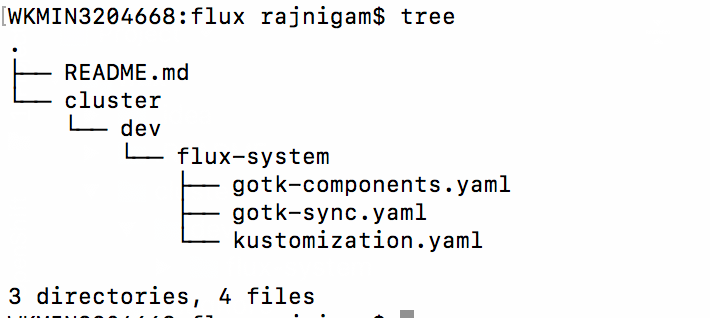
- Bootstrap Git repository in flux
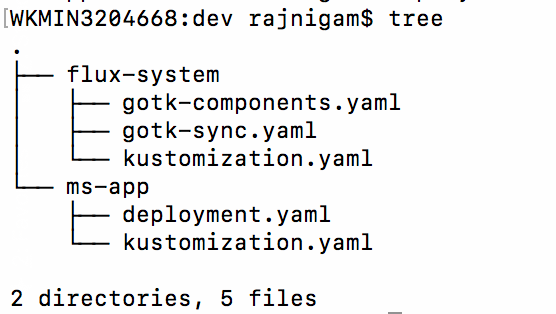
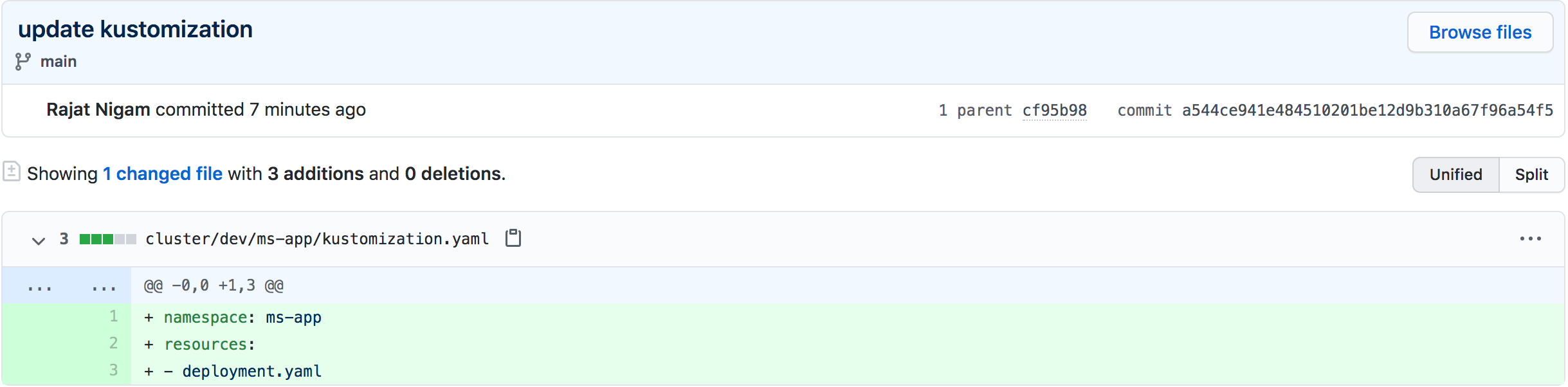
- Create an Nginx deployment under cluster/dev
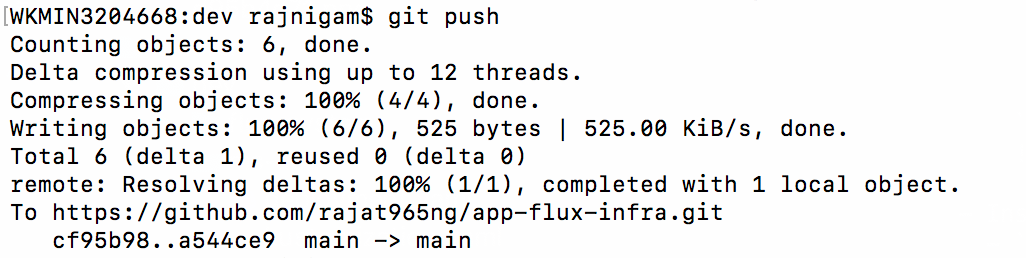
- Observe the deployments rolling on git push and Query Flux to view the currently deployed revision
- Trace applied revision to match with Git SHA
- Apply Helm Chart
- Create a Helm Chart "ms-template"
- Package Helm Chart
- How to convert Github repo into Helm repository?
- Configure Helm Repository in Flux
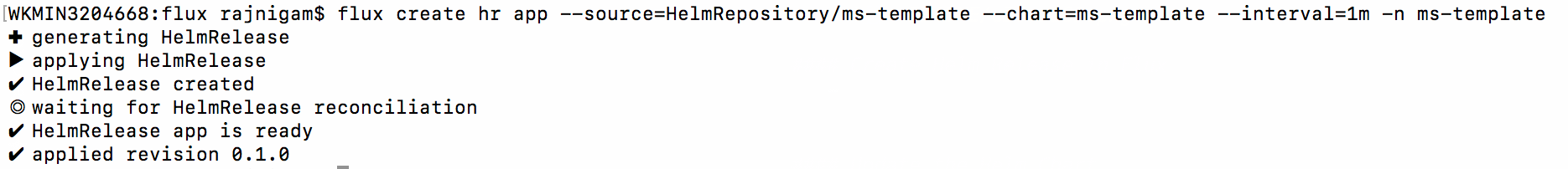
- Create Helm Release in Flux
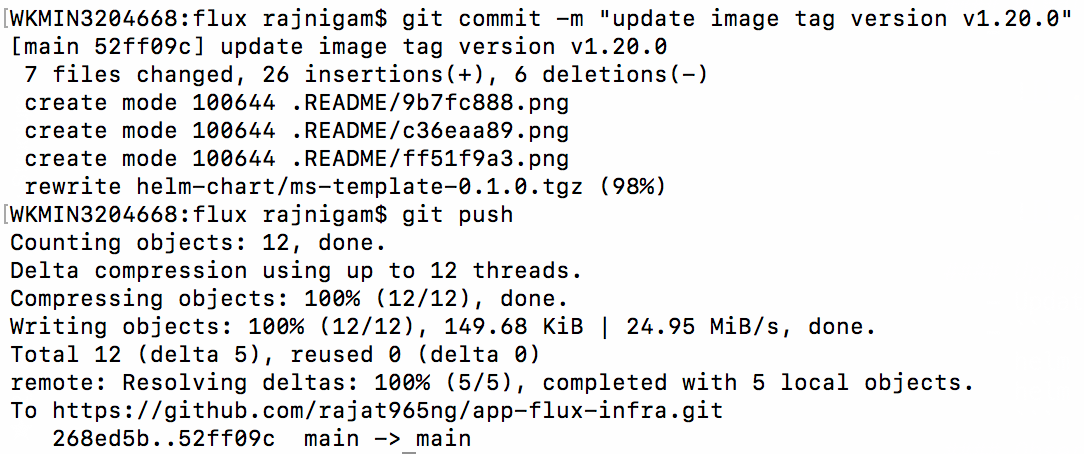
- Update the Helm Chart
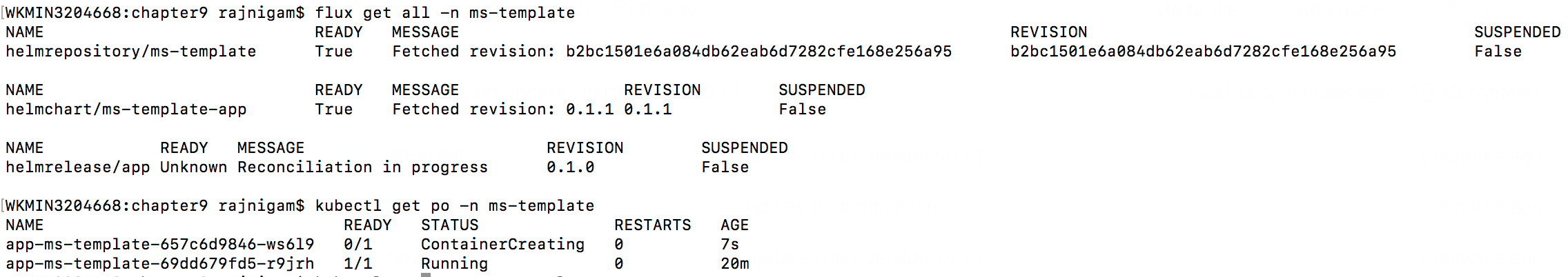
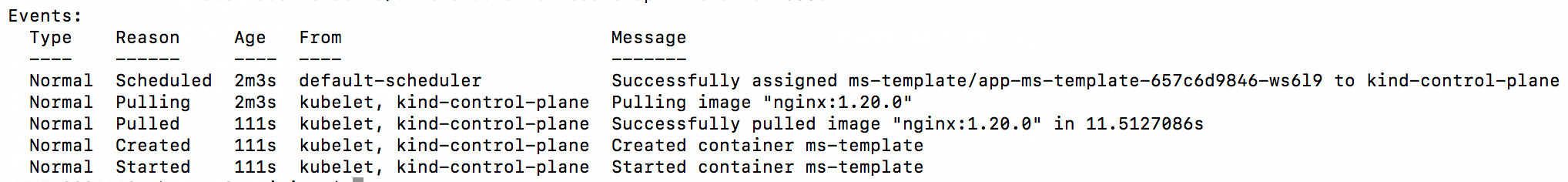
- Observe the helm update rolling
- Benefits of using Flux
- References
- The term GitOps was coined in August 2017 in a series of blogs by Alexis Richardson, cofounder and CEO of Weaveworks.
- GitOps is a set of procedures that uses the power of Git to provide both revision and change control within the Kubernetes platform.
- GitOps brings the core benefits of Infrastructure as Code and immutable infrastructure to the deployment, monitoring, and life-cycle management of Kubernetes applications in an intuitive, accessible way.
- A developer-centric experience for managing applications, with fully automated pipelines/workflows using Git for development and operations.
- Use of the Git revision control system to track and approve changes to the infrastructure and run-time environment of applications.
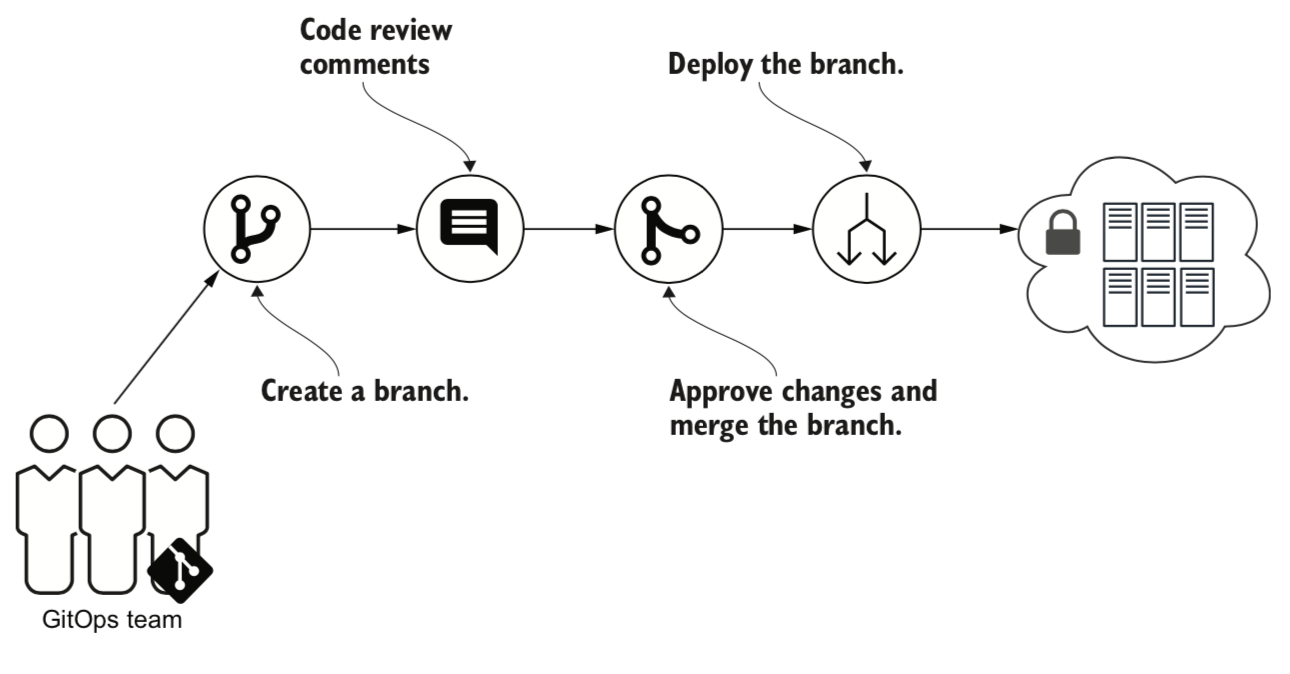
- The GitOps release workflow starts with creating a branch of the repository containing changes to the definition of the system’s desired state.
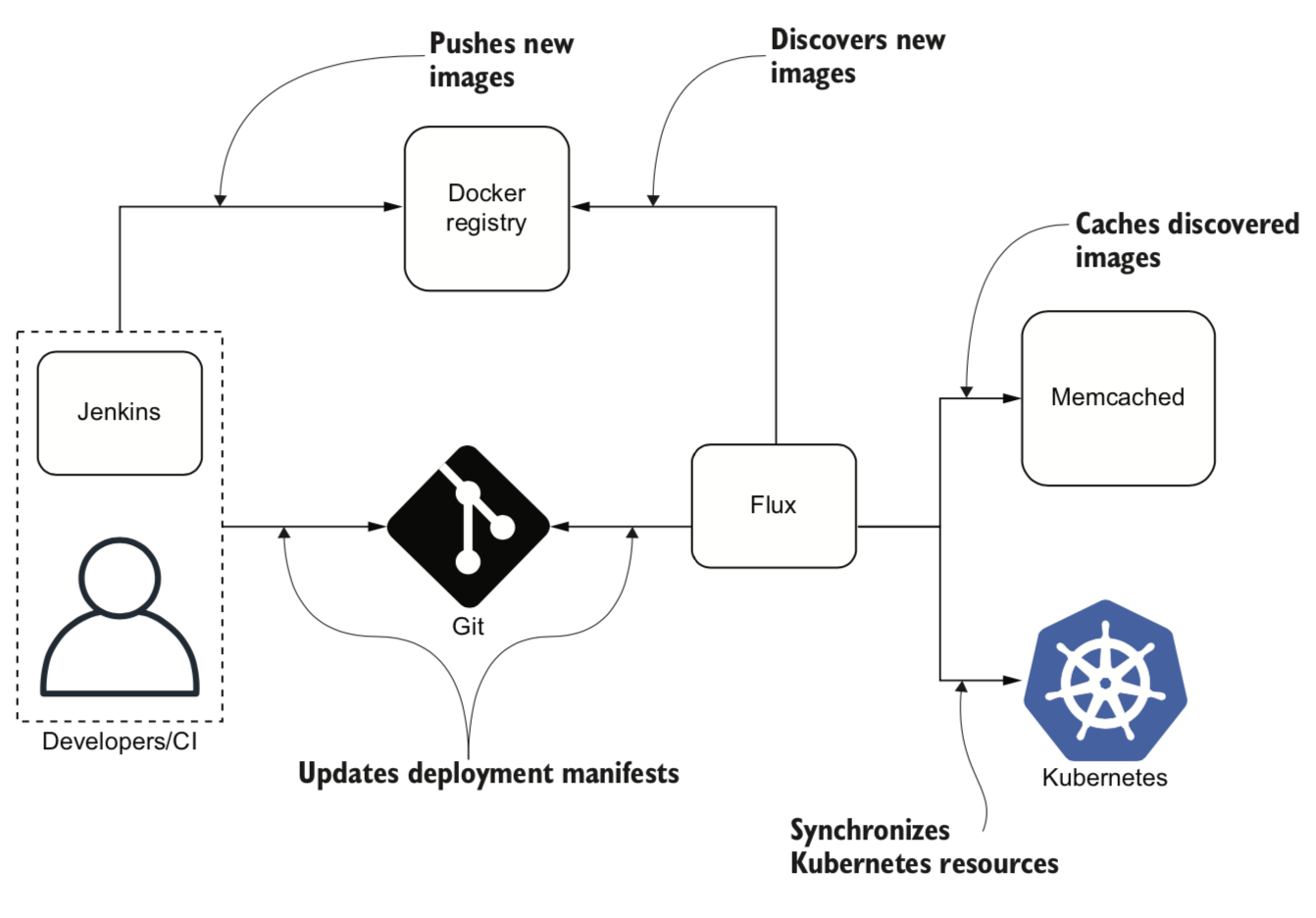
- Command line utility for assembling Kubernetes CD pipelines the GitOps way.
- The project was started in 2016 at Weaveworks and joined the CNCF Sandbox three years later.
- Flux does not introduce any additional layers on top of Kubernetes, such as applications or its own access control system.
- A single Flux instance manages one Kubernetes cluster and requires the user to maintain one Git repository that represents the cluster state.
- Flux typically runs inside of the managed cluster and relies on Kubernetes RBAC. This approach significantly simplifies the Flux configuration and helps flatten the learning curve.
- In the multitenant environment, each team can install an instance of Flux with limited access and use it to manage a single Namespace. That fully empowers the team to manage resources in the application Namespace and is still 100% secure because Flux access is managed by Kubernetes RBAC.
- Flux consists of only two components:
- The Flux daemon
- The key-value store Memcached (open source, high-performance, distributed memory object-caching system).
- There must be only one replica of the Flux daemon running at any time. Even if the daemon crashes in the middle of a deployment, it restarts quickly and idempotently resumes the deployment process.
- The main purpose of Memcached is to support Docker registry scanning. Flux uses it to store a list of available image versions of each Docker image.
-
wget https://github.com/kubernetes-sigs/kind/releases/download/v0.10.0/kind-darwin-amd64 mv kind-darwin-amd64 kind chmod +x kind mv kind /usr/local/bin/ kind version kind create cluster kubectl get ns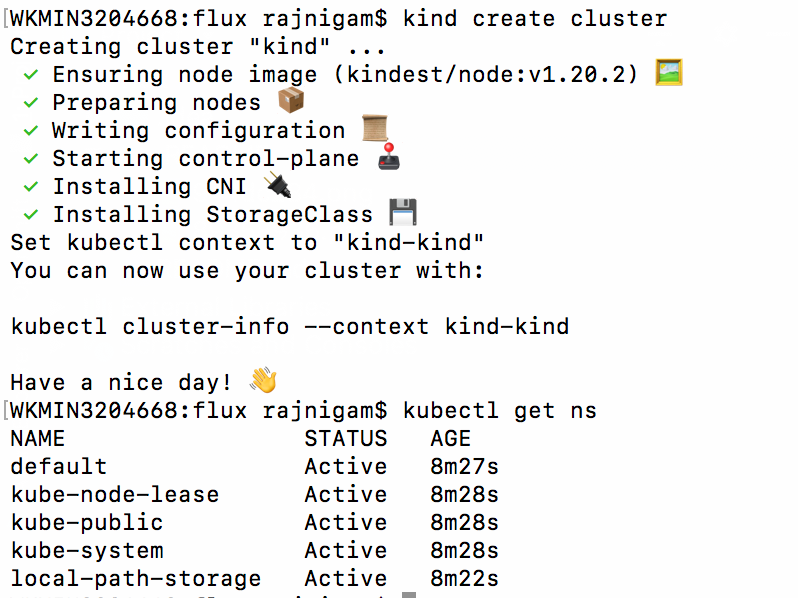
-
wget https://github.com/fluxcd/flux2/releases/download/v0.13.3/flux_0.13.3_darwin_amd64.tar.gz tar -xvf flux_0.13.3_darwin_amd64.tar.gz mv flux /usr/local/bin/ flux --version flux check --pre flux install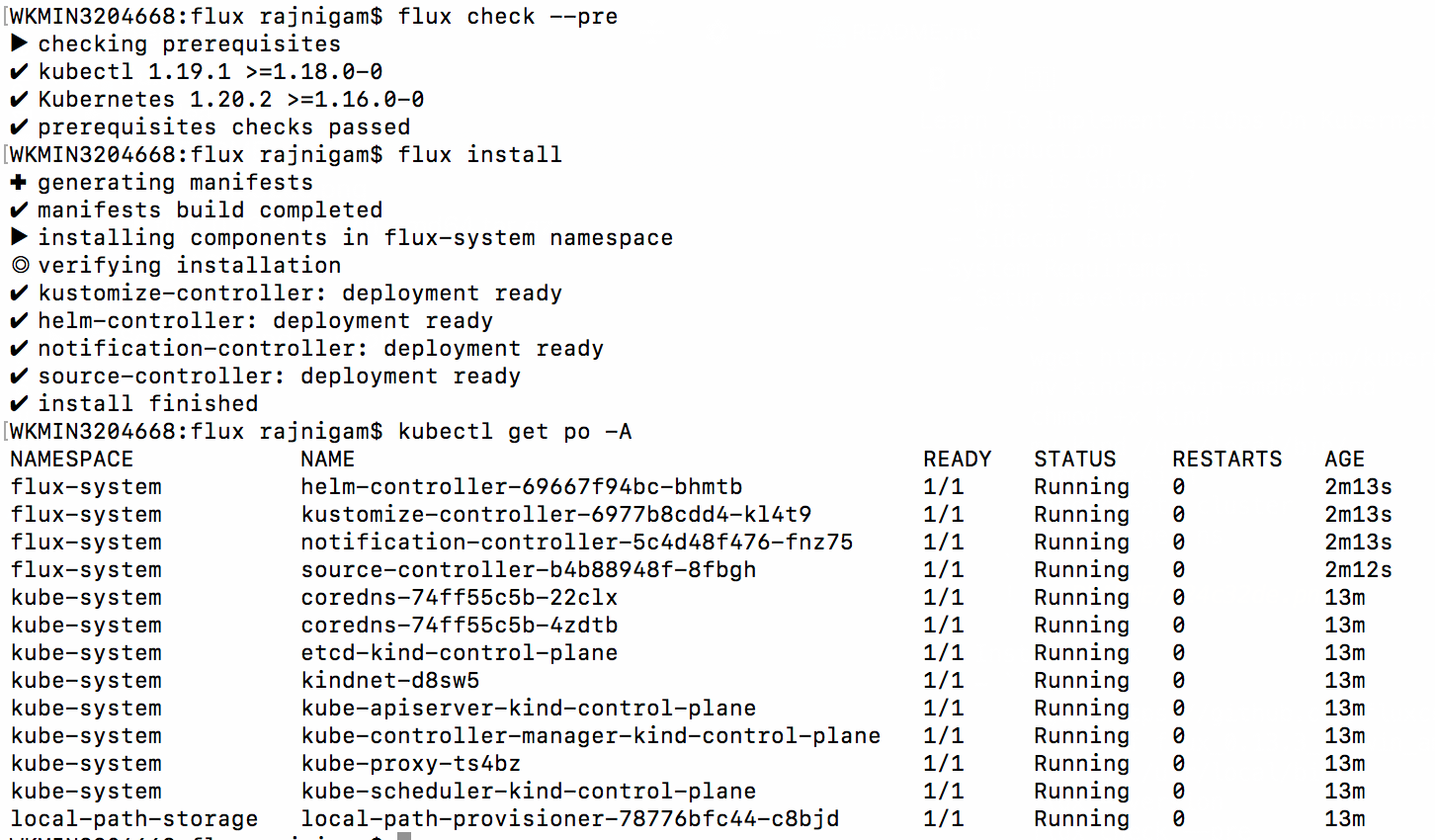
-
flux bootstrap git app-flux-infra --url=https://github.com/rajat965ng/app-flux-infra.git -u <GIT_USERNAME> -p <GIT_PAT> --token-auth=true --path=./cluster/dev/
- To avoid bot crawling on my repository, add the following robots.txt file:
echo -e “User-Agent: *\nDisallow: /” > robots.txt - Lint the helm chart
helm lint helm-chart/* - Package helm chart
cd helm-chart/ && helm package ms-template/ - Create index.yaml for ms-template
helm repo index --url=https://rajat965ng.github.io/app-flux-infra/helm-chart/ .
-
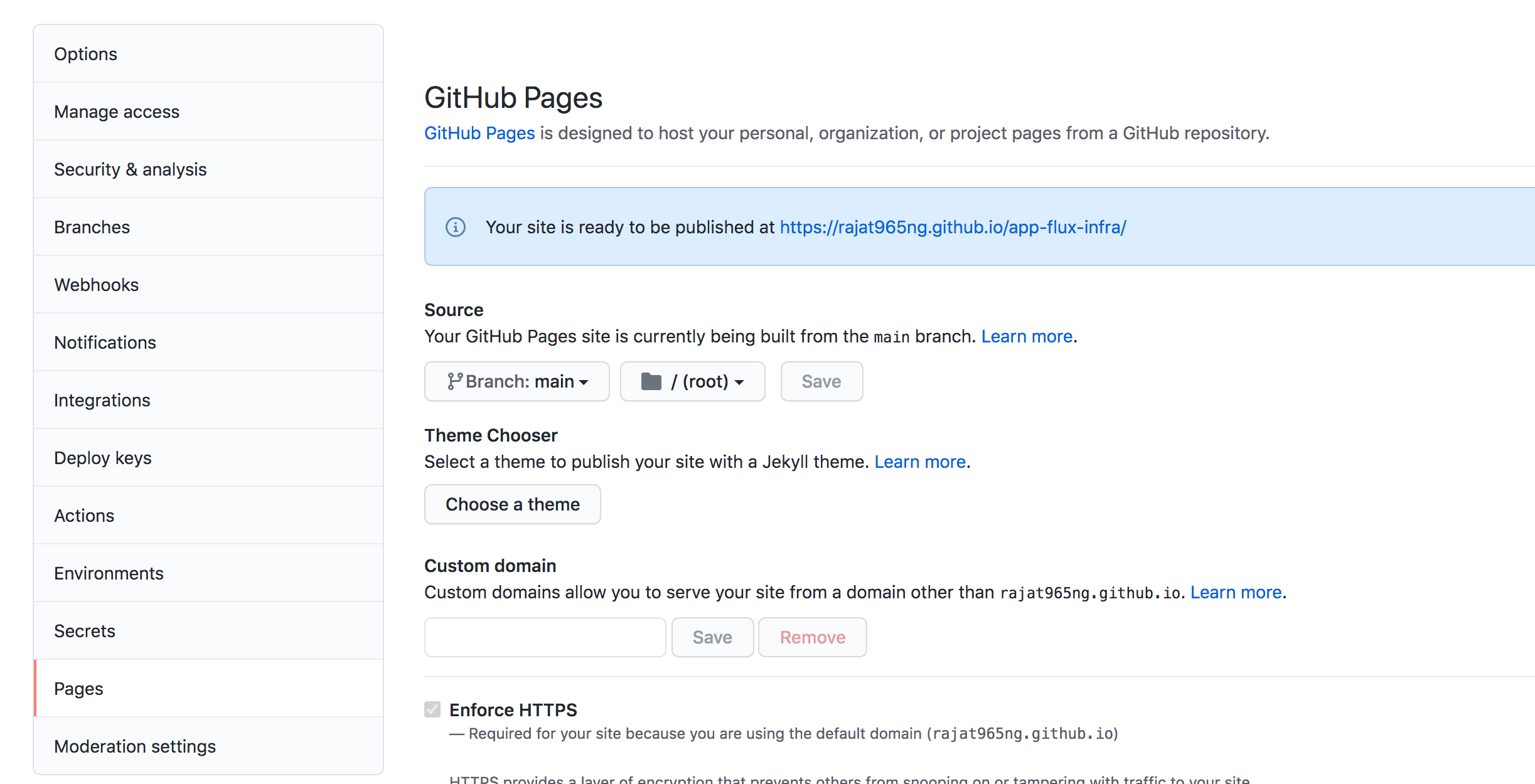
Click on Git repository "Settings"
-
Scroll down options to choose "Pages"
-
Select "Branch" -> "main" from dropDown and click "save"
-
flux create source helm ms-template --interval=1m -n ms-template --url=https://rajat965ng.github.io/app-flux-infra/helm-chart/
-
flux create hr app --source=HelmRepository/ms-template --chart=ms-template --interval=1m -n ms-template -
kubectl get po -n ms-template
-
Update image tag from "1.16.0" --to--> "1.20.0" in values.yaml and version "0.1.0" --to--> "0.1.1" in Chart.yaml
-
helm package ms-template/ helm repo index --url=https://rajat965ng.github.io/app-flux-infra/helm-chart/ .
- Off-load the hassle of securely managing "kubeconfigs" in CI tools/Vault/buckets etc.
- The deployment and release process is completely version controlled.
- Implicit audit provided by Git.
- Roll-out production release on PR approval.
- No need to open firewall between CI tool and Kubernetes cluster. Promotes secure CI/CD.
- Increase confidence in Zero-Trust network implementation.
- Zero pipeline failures due to network disruption or node failures.
- Environments achieve its absolute state, as soon Kubernetes cluster recovers from any disaster.
- Can be combined with Flagger for the automation of promoting canary deployments using Service Mesh like Istio.
- Extends support with GitHub, GitLab, Harbor etc. with in-built webhooks.
- Can publish post-release alerts on Slack, MS Teams or SMTP.
- GitOps and Kubernetes - Continuous Deployment with Argo CD, Jenkins X, and Flux By Billy Yuen, Alexander Matyushentsev, Todd Ekenstam, and Jesse Suen [https://www.manning.com/books/gitops-and-kubernetes]
- KIND [https://kind.sigs.k8s.io/]
- Flux [https://fluxcd.io/]
- Source Code [https://github.com/rajat965ng/app-flux-infra]