-
Initialize project folder
npm init fastify -
Install dependencies
npm install
- Entry point
app.js: exports an async function
function(fastifyInstance, opts, next){
// A plugin is a function which invokes next() or returns a promise
}-
Register a Plugin
fastify.register(pluginFunction, options)
-
Notes
-
Everything is a plugin in Fastify.
Entry point is a plugin. Routes are plugins. Plugins are also plugins.
Files inpluginsfolder are commonly de-encapsulated plugins, which are accessed by sibling plugins. -
Plugins are called only at initialization time.
-
Plugins are always asynchronous.
-
Root plugin is the exported async function of app.js
-
Reply does NOT have
end()method! -
process.env.NODE_ENVis not set when runningnpm run devwhich means it will returnundefinedif you try to access it. So the method used to check the environment is based on string -'production'not'dev'.
-
-
Run server
fastify start app.js -
Fastify CLI flags
-
-p
Specify port. Default port is 3000 -
-P
Prettify log output -
-w
Watch file and reload the project -
-lLog level (defaults to fatal)
-
-
--integrate将 Fastify 集成到现有的项目中去
npm init fastify -- --integrateThe usage of integrate mode mentioned on fastify repo is
npm init fastify --integrate. But it turns out it will complain about the exisingpackage.jsonfile in my project. So I edited this note.注意
集成模式会覆盖现有项目中的以下文件:
- .gitignore
- app.js
- plugins
- routes
- test
集成模式会修改现有项目中的以下文件:
- package.json
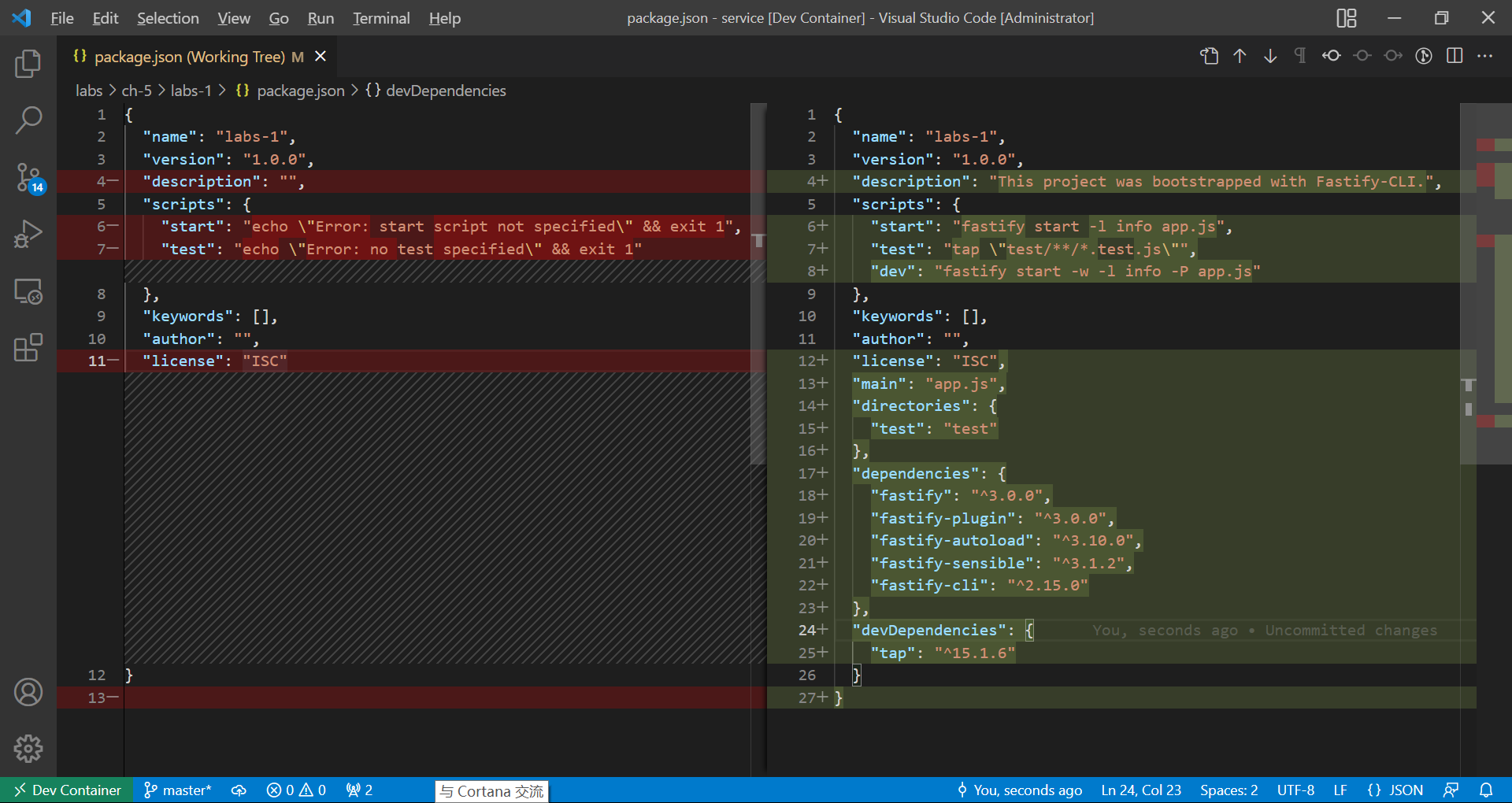
The following picture demonstrates details about how fastify integrate mode modifies an existing package.json file.
- fastify.get('/', asyncRouteHandler)
- fastify.post('/', asyncRouteHandler)
- fastify.put('/', asyncRouteHandler)
- fastify.delete('/', asyncRouteHandler)
Notes:
-
Not to forget
returnclause in the handlerasync function(request, reply){ // Whatever returned by this handler will be sent as the content of the HTTP response. // Alternatively, reply.send(content) can also used to do the same job. // If return a string, it would be better to append '\n' to the end of the string in case // the server being accessed by command line tool to present a nice response which is // easily readable by human. // Stream can also be returned by this handler. // The behavior would be the same as passing a stream to `reply.send()`. // Fastify will pipe the stream returned or passed to the HTTP response. }
-
request.method
Possible values:- 'GET'
-
request.queryThe queries of URL.
For example:greetingin/hello?greeting=Ahoy
reply instance
reply.type('text/html')
Set Content-Type headerreply.status(405)
Set HTTP status codereply.send(anything even a stream)Send response to a request. If an Error object is passed to it, it will automatically generate a 500 Server Error status code.
Learn more about request and reply.
fastify.setNotFoundHandler(ROUTER_HANDLER)
Define what to do if NO pathes or HTTP verbs match
-
/also being passed to registration methods for non-root routes thanks tofastify-autoloadplugin. It will register the route prefixed with the name of subfolder. -
How to use callback-based api in an
asyncroute handler?- Add
await replyat the end of the handler. promisfythe callback-based API.
- Add
-
What kinds of callback-based API can be
promisfyed?The ones invoking callbacks in an error-first result-last argument style.
function thisIsACallbackBasedApi (myArgumentsAreNoneOfYourBusiness, theCallback) { doingMyOwnBusiness(); theCallback(error, result) }
-
Always
returnin an async route handler otherwise the promise of the handler will never be fulfilled.
-
fastify-static
Serve static content. Due to it is not recommended to serve static content from Node process, we usually install it as a dev dependency.Options:
root
Serve all files under this directory.
Decorations:
-
reply
- sendFile()
Used to manually respond with the contents of a file for a route.
Example:
reply.sendFile('hello.html')This example will findhello.htmlfromrootoption set whenfastify.register()fastify-static plugin(e.g, ifrootoption is set topublic,sendFile('hello.html')will send the contents ofpublic\hello.html).
- sendFile()
Notes:
-
There is no need to append spcific filename -
index.htmlto the host URL.Takehttp://localhost/as an example, if you navigate to this URL and no root route defined in the fastify instance, then browser will automatically load index.html. On the other hand, if root route is available, then you'll need to navigate tohttp://localhost/index.htmlin order to loadindex.htmlinstead. -
If you hope that there is only route path in the URL and no filename exposed in the URL. For example, not
http://localhost/hello.htmlbuthttp://localhost/hello, you can set up/helloroute and usereply.sendFile('hello.html')to send a html file as a response.reply.sendFile()method is decoration fromfastify-static.
-
point-of-view Fastify's view rendering plugin.
Supported template engine:
- handlebars
Notes:-
Raw interpolation syntax:
{{{ body }}}. HTML syntax will not be escaped. -
Escaped interpolation syntax:
{{ body }}.<in HTML code will be escaped to<
-
Options:
-
engine
The value should be an object. The keys of this object should be the name of the engine and value should be the engine library. For example:engine: { handlebars } -
root
The path where to find views. -
layout
With this option being set, pluginpoint-of-viewwill automatically create a template local -body
Decorations:
-
reply
- view(
template file name,object store of template locals)
DO NOT forgetreturn!
Invoke template engine to render specific views and send the result as respone.
For example:return reply.view('index.hbs')searchesindex.hbstemplate inrootoption and render it then send the result.
- view(
Template local created:
body
Available iflayoutoption ofpoint-of-viewused.
- handlebars
-
Defaults for Fastify which people need.
Usage:
fastify.register(require('fastify-sensible'))
If you initialize the project with
create-fastify, you won't need to run the lines above because it is registered already inplugins/senseble.jsAPIs are listed here
-
Decorations
-
reply-
notFound()- Set response status code to 404.
- Generate JSON output describing
Not Founderror.
-
-
-
Expossions
-
fastify.httpErrorsThis object exposes all
4xxand5xxerror constructor!fastify.httpErrors.notFound()
-
-
-
It will help fastify to load all plugins found in a directory and automatically configures routes matching the folder structure.
So, the magic of fastify being able to automatically detect route path comes from this plugin.Usage:
const autoload = require('fastify-autoload') app.register(autoload, { dir: path.join(__dirname, 'plugins') })
- How to pass options to the main plugin function defined in
app.js?