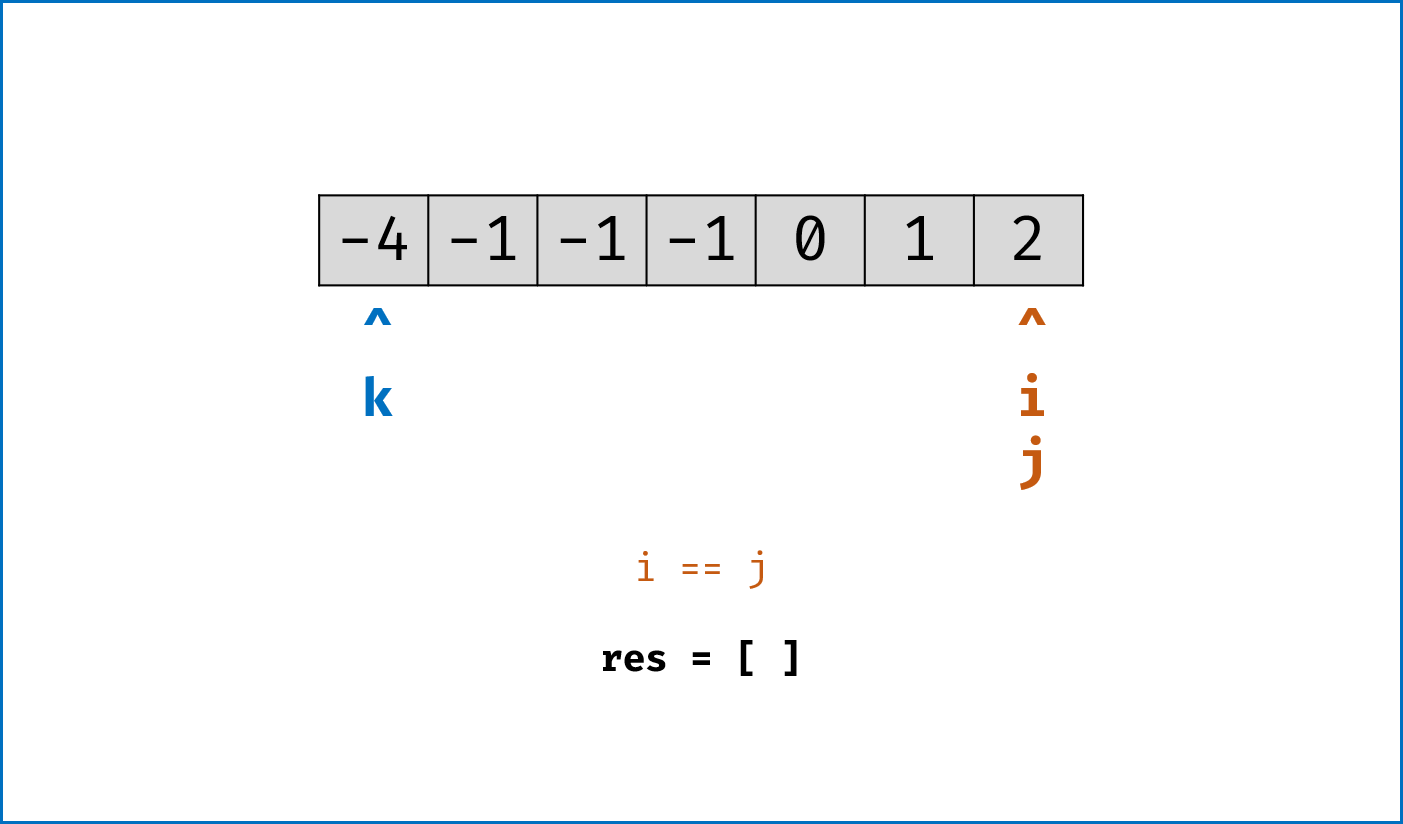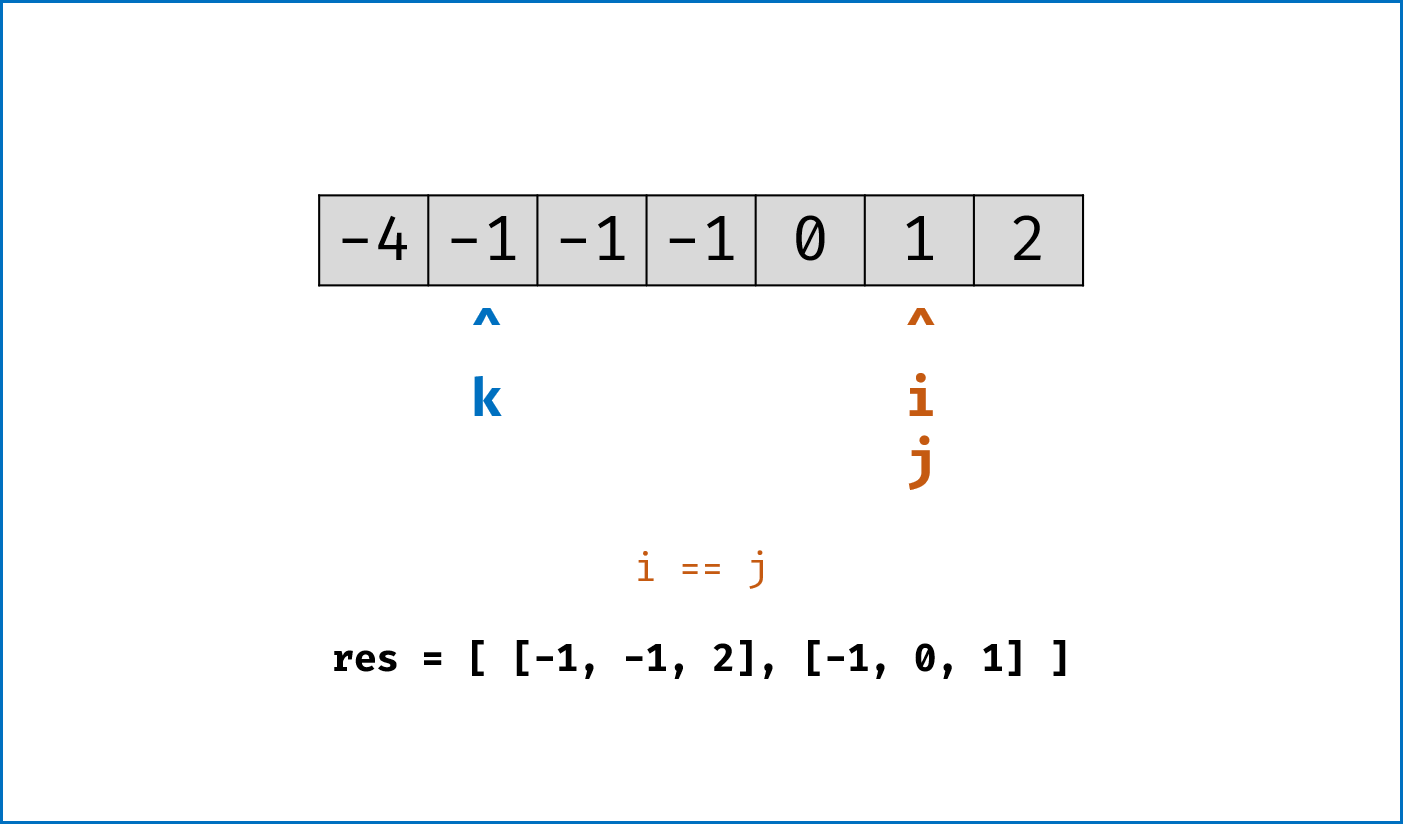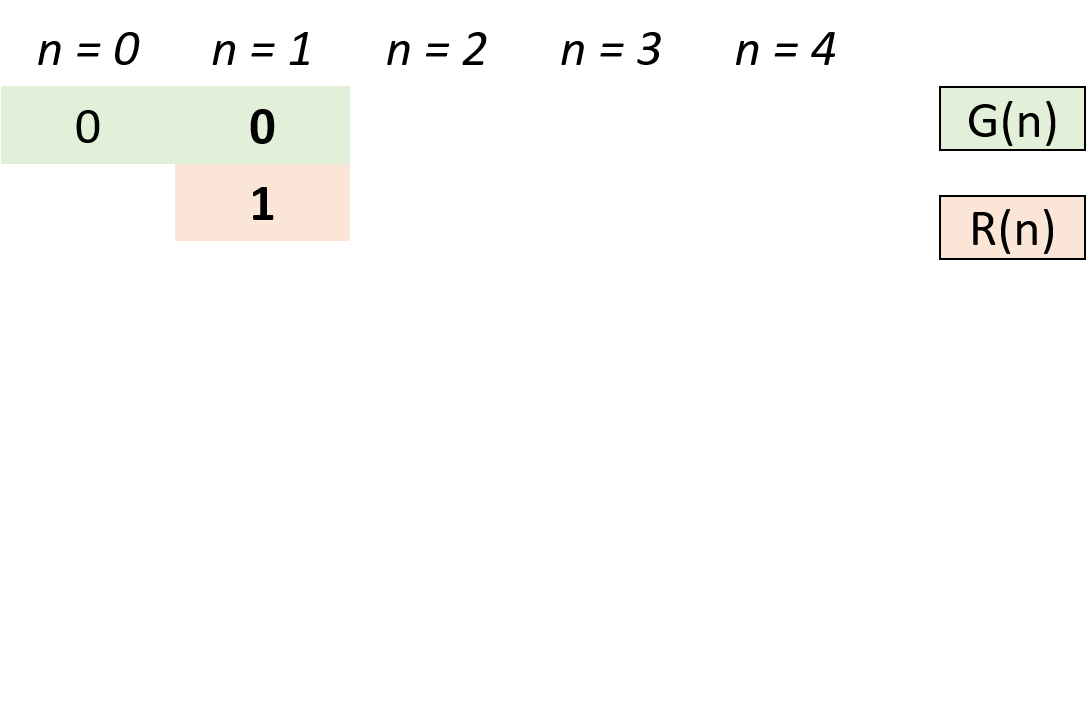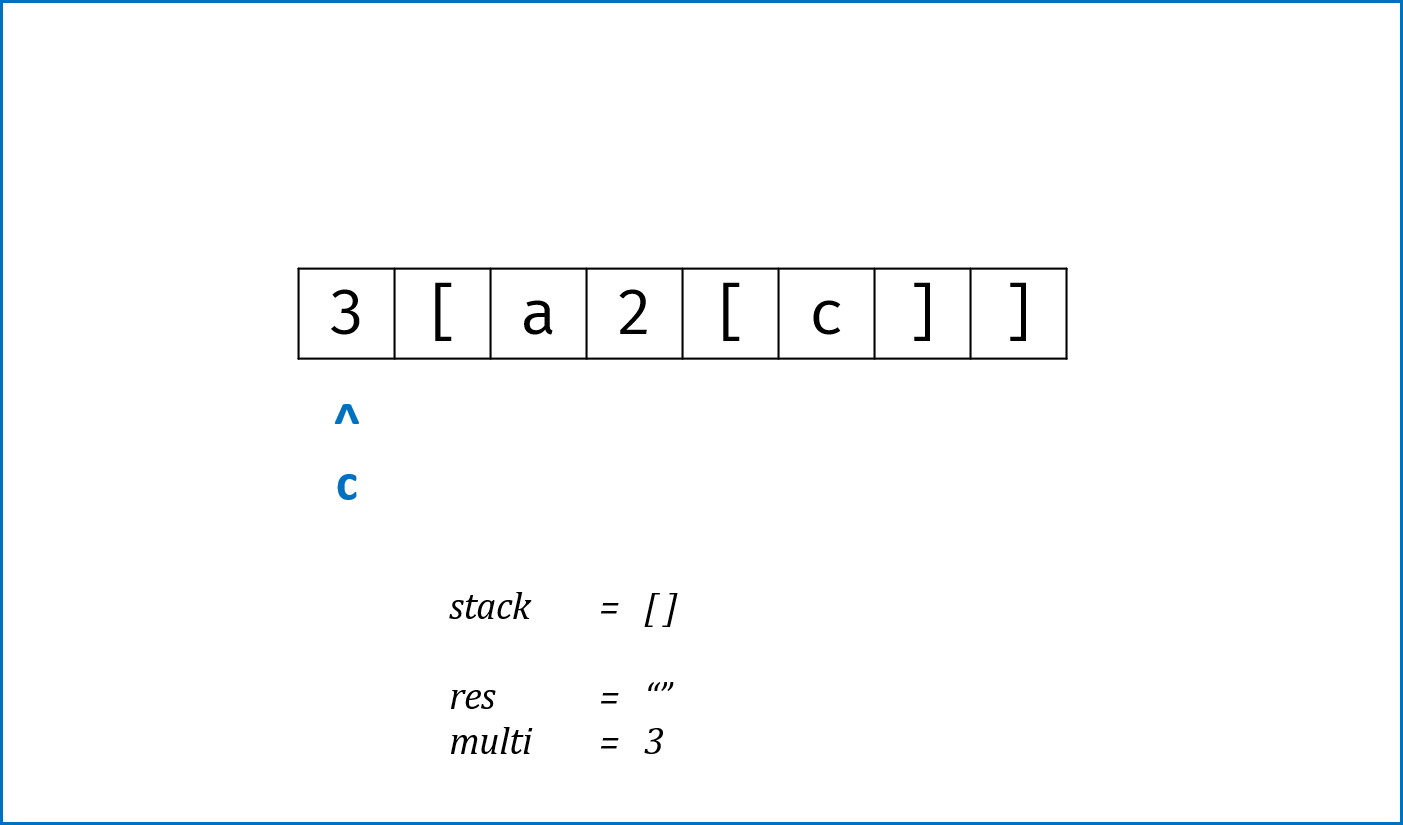This repository includes coding solutions of Leetcode and 剑指offer using Python and Java.
如果您喜欢我的题解请SATR~ (>_<) 欢迎留言,我会认真尽快回复。
The solutions of leetcode are updated daily, while using Python and Java.
标签:数组,哈希表Hash
- 建立HashMap,遍历数组
nums,key存储nums[i],value存储i; - 遍历过程中,判断HashMap里是否有
target - nums[i]的key值,若有直接返回两个数字index。
class Solution:
def twoSum(self, nums, target):
dic = {}
for i in range(len(nums)):
if str(target - nums[i]) in dic:
return [dic[str(target - nums[i])], i]
dic[str(nums[i])] = iclass Solution {
public int[] twoSum(int[] nums, int target) {
Map<Integer, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
for(int i = 0; i < nums.length;i++) {
int x = nums[i];
if(map.containsKey(target - x)){
return new int[] { map.get(target-x), i};
}
map.put(x, i);
}
return null;
}
}标签:链表
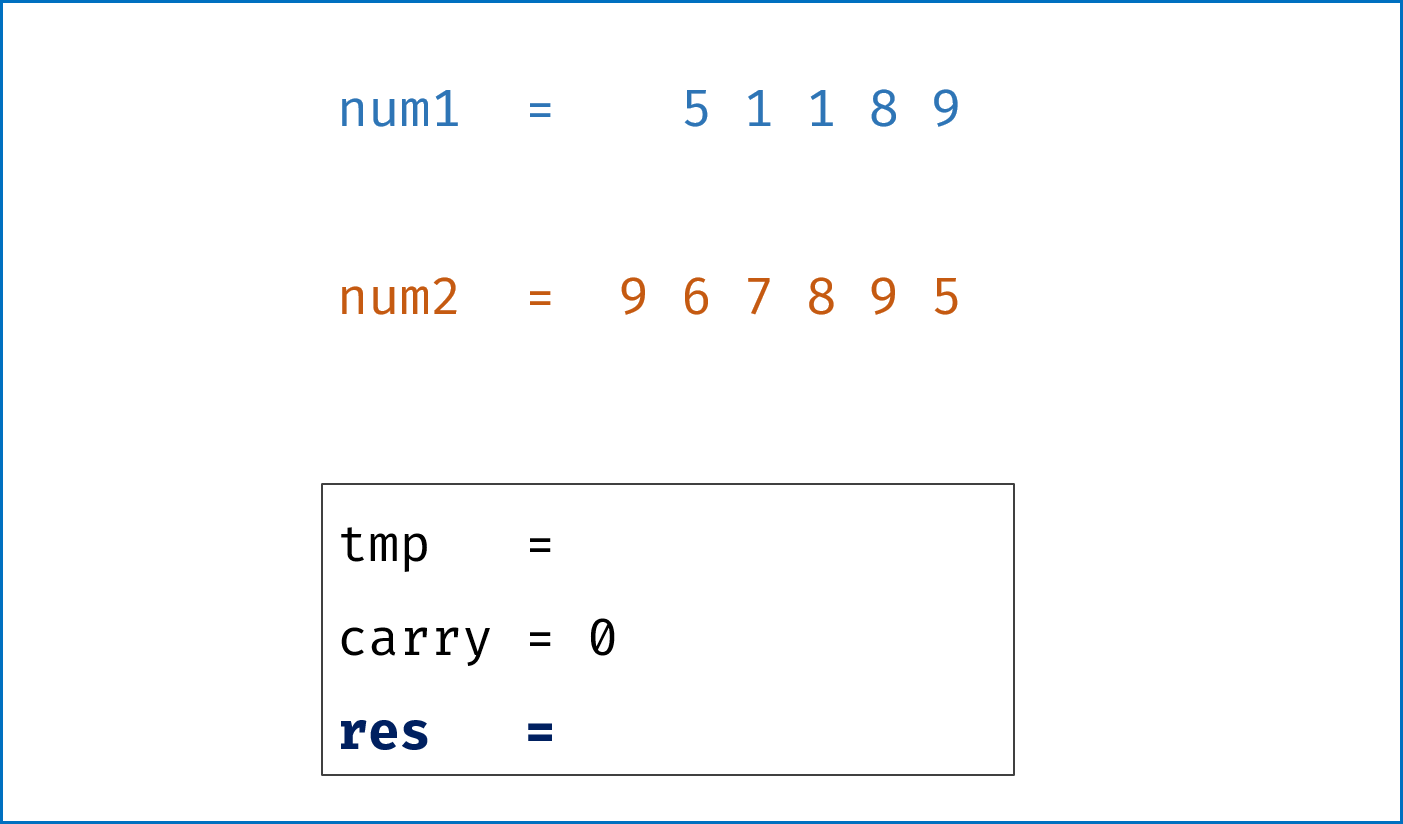
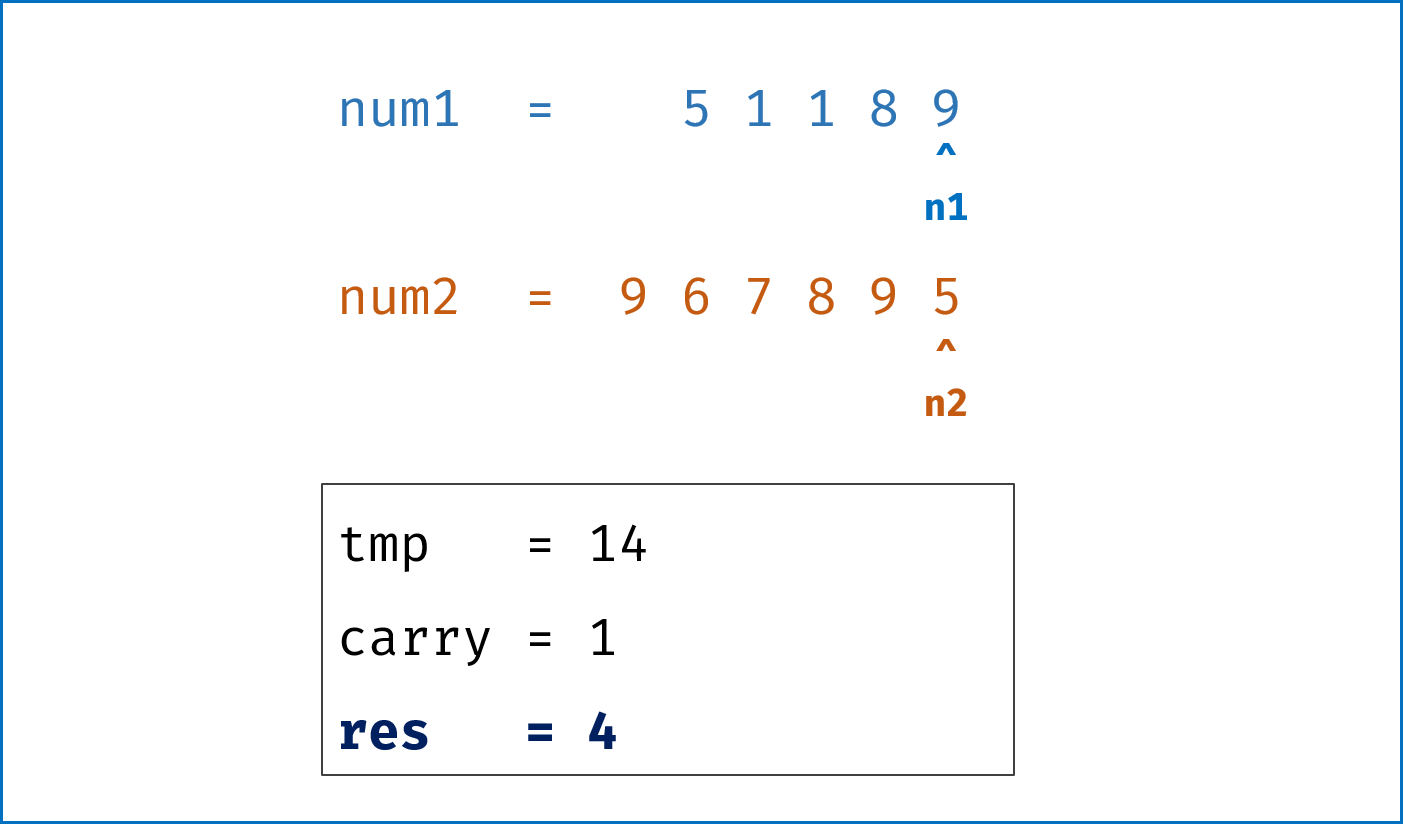
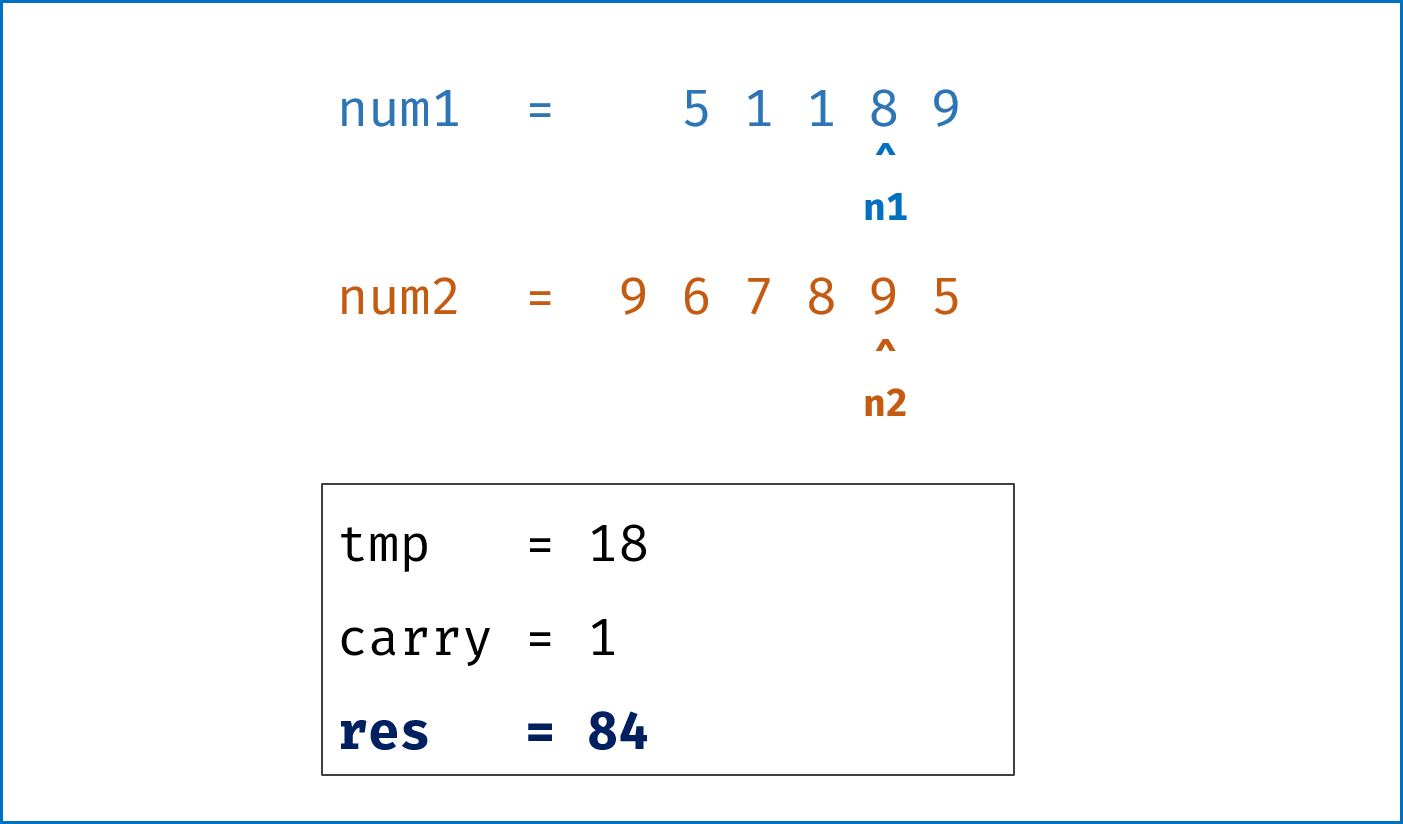
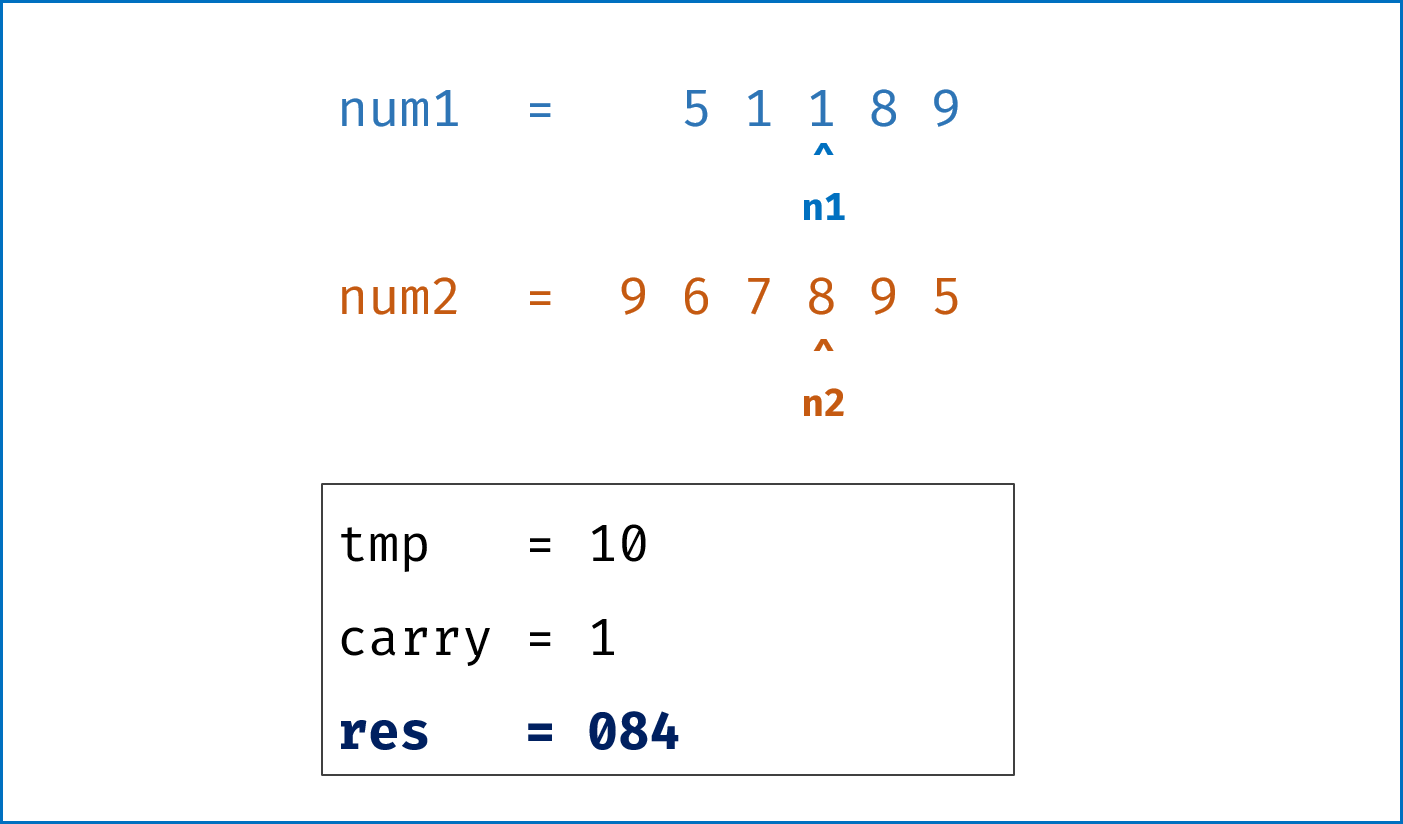
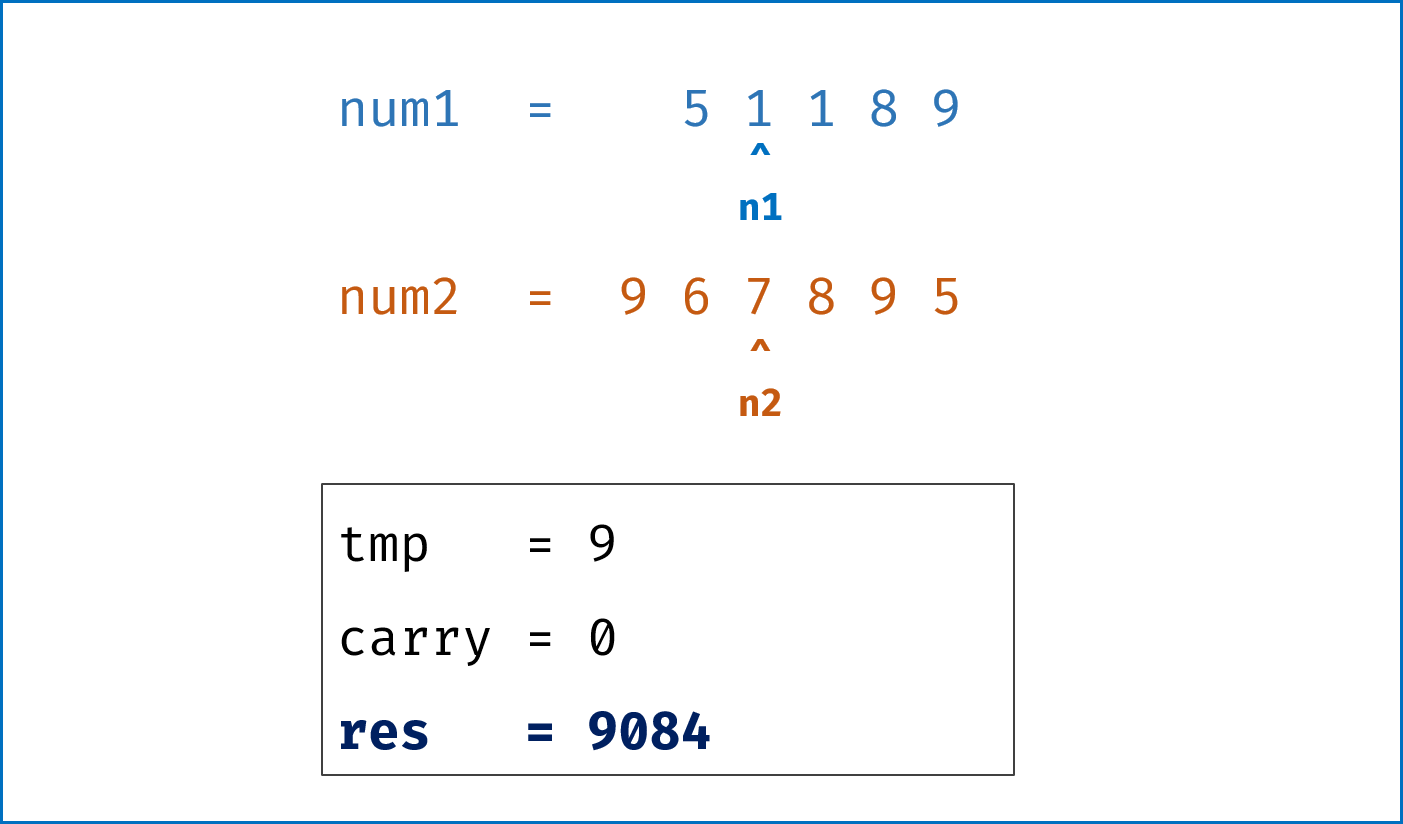
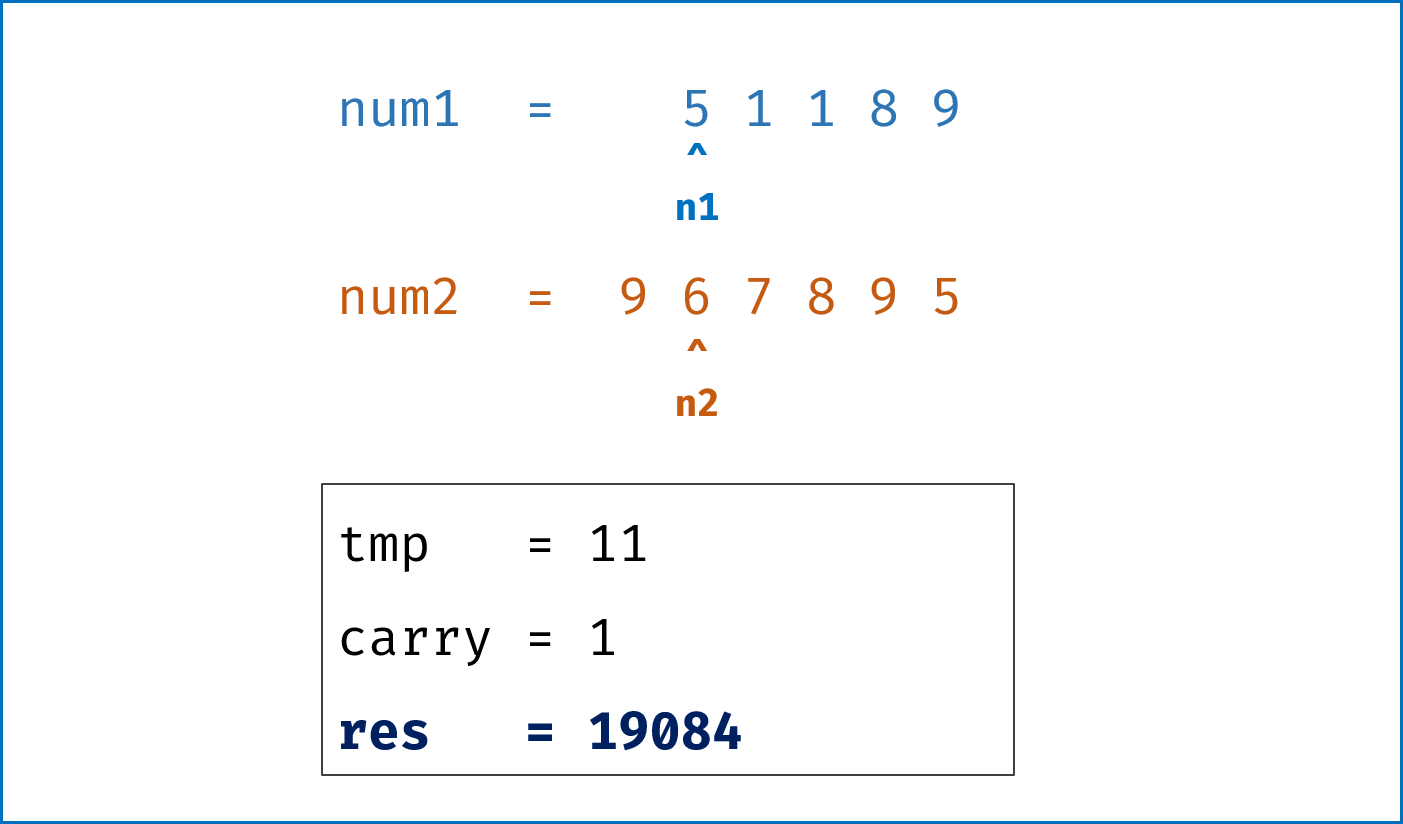
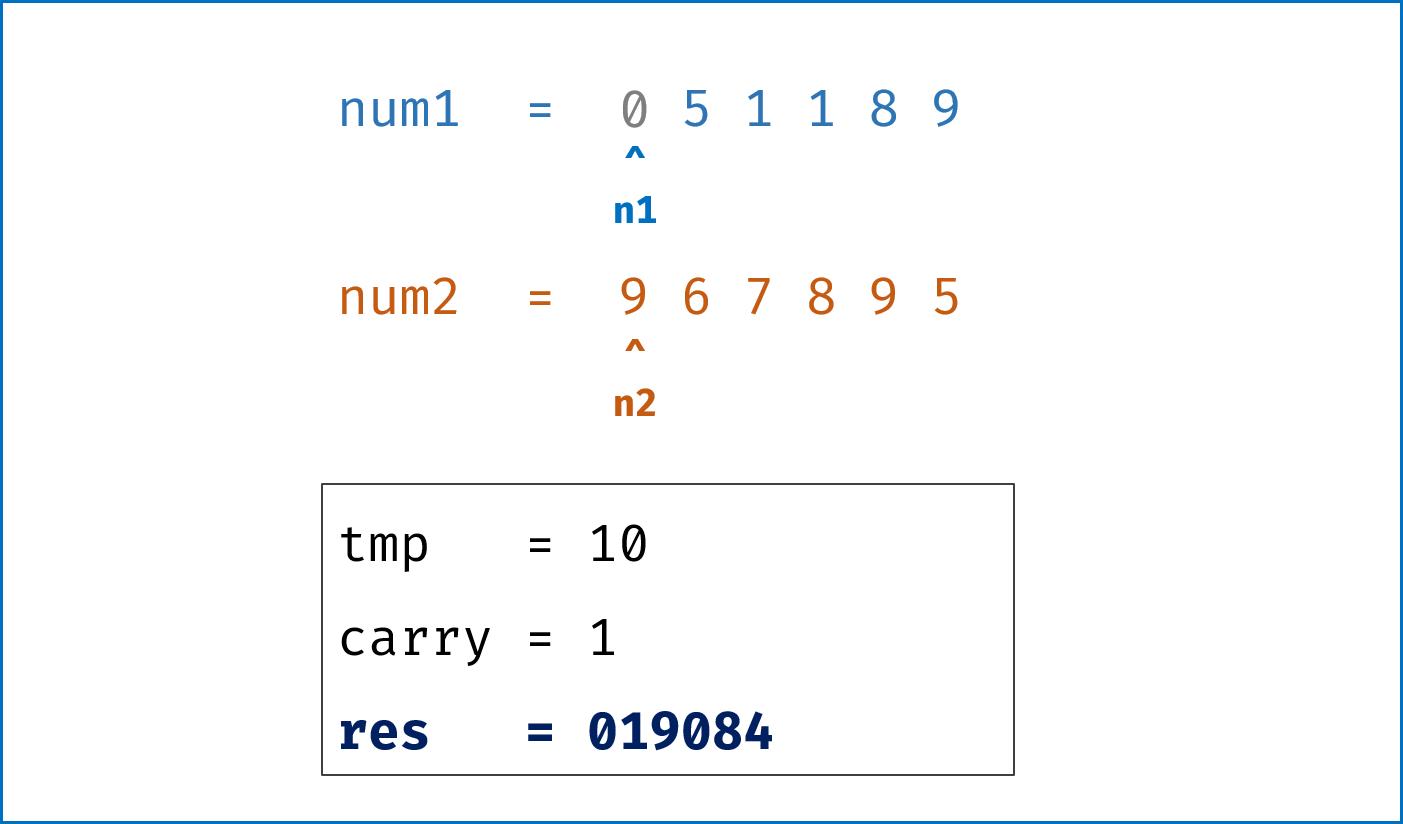
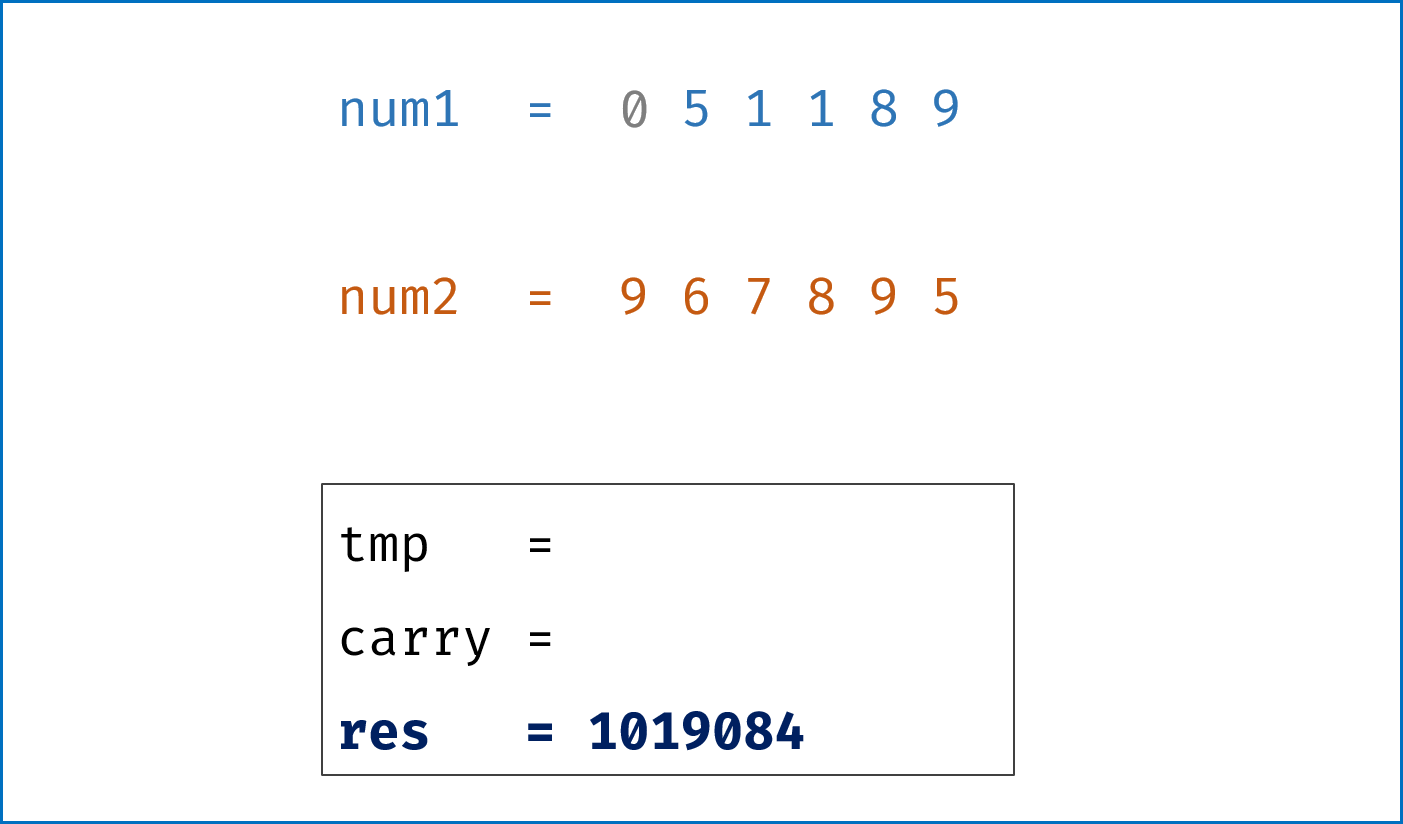
- 模拟整个做加法的过程,
carry记录进位,需要注意两点:- 由于两链表长度可能不同,因此在做加法时,要将超出短链表的值填
0再计算; - 当
l1,l2都遍历完后,还需要判断是否有进位,如果有需要再添一位1。
- 由于两链表长度可能不同,因此在做加法时,要将超出短链表的值填
class Solution:
def addTwoNumbers(self, l1: ListNode, l2: ListNode) -> ListNode:
carry = 0
head = ListNode(0)
res = head
while l1 or l2:
num1 = l1.val if l1 else 0
num2 = l2.val if l2 else 0
tmp = num1 + num2 + carry
carry = 1 if tmp >= 10 else 0
head.next = ListNode(tmp % 10)
head = head.next
if l1: l1 = l1.next
if l2: l2 = l2.next
if carry: head.next = ListNode(1)
return res.nextclass Solution {
public ListNode addTwoNumbers(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) {
ListNode head = new ListNode(0);
ListNode res = head;
int carry = 0;
while(l1 != null || l2!= null){
int num1 = l1 != null ? l1.val : 0;
int num2 = l2 != null ? l2.val : 0;
int tmp = num1 + num2 + carry;
carry = tmp / 10;
head.next = new ListNode(tmp % 10);
head = head.next;
if(l1 != null) l1 = l1.next;
if(l2 != null) l2 = l2.next;
}
if(carry == 1) head.next = new ListNode(1);
return res.next;
}
}标签:双指针,哈希表Hash,字符串
- 设定左右双指针
l和r,遍历字符串; - 哈希表存储某字符
s[i]最新在字符串中出现的位置index + 1,key, value对应s[i], i; - 左指针在遍历过程中:
- 若
s[i]不在HashMap中,则跳过; - 否则,
l指针设定为l和dic[s[r]]的最大值,即修改之后,保证新字符串中没有重复字符。 - 每次更新长度最大值
res。
- 若
class Solution:
def lengthOfLongestSubstring(self, s: str) -> int:
dic = {}
l, res = 0, 0
for r in range(len(s)):
if s[r] in dic:
l = max(dic[s[r]], l)
dic[s[r]] = r + 1
res = max(res, r - l + 1)
return resclass Solution {
public int lengthOfLongestSubstring(String s) {
int res = 0;
Map<Character, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
for (int i = 0, j = 0; j < s.length(); j++) {
if (map.containsKey(s.charAt(j))) {
i = Math.max(map.get(s.charAt(j)), i);
}
map.put(s.charAt(j), j + 1);
res = Math.max(res, j - i + 1);
}
return res;
}
}标签:字符串,双指针
- 遍历
s,以每个char以及两个char中点为中心,计算以此点为中心的最长回文串;- 例如: 字符串
abcba共有5(字母) + 4(两字母间) = 9个中心点; - 因此,长度为
N的string共有2N-1个中心。
- 例如: 字符串
- 我们的目标就是统计以这
2N-1个点为中心的最长回文串s1,s2,..,s2N-1,并从中挑出全局最长回文串。 - 保留最大长度回文串
index,记为left和right; - 完成遍历后返回以
left和right为边界的substring。
class Solution:
def longestPalindrome(self, s: str) -> str:
left, right = 0, 0
for i in range(len(s)):
odd = self.mid_expand(s, i, i)
even = self.mid_expand(s, i, i+1)
m = max(odd, even)
if m > right - left:
left = i - (m - 1) // 2
right = i + m // 2
return s[left:right+1]
def mid_expand(self, s, left, right):
while left >= 0 and right < len(s) and s[left] == s[right]:
left -= 1
right += 1
return right - left - 1class Solution {
public String longestPalindrome(String s) {
if(s.length() == 0) return "";
int left = 0, right = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < s.length(); i++) {
int odd = midExpand(s, i, i);
int even = midExpand(s, i, i + 1);
int m = Math.max(odd, even);
if (m > right - left) {
left = i - (m - 1) / 2;
right = i + m / 2;
}
}
return s.substring(left, right + 1);
}
private int midExpand(String s, int left, int right) {
while (left >= 0 && right < s.length() && s.charAt(left) == s.charAt(right)) {
left--;
right++;
}
return right - left - 1;
}
}标签:位运算
- 思路为对当前数取对10的余数,再一项项填入res尾部,即可完成int翻转。
- 难点在于如何处理边界情况,int取值范围为
[-2^31, 2^31 - 1],如果翻转数字溢出,则立即return 0。python存储数字理论上是无限长度,因此每次计算完后判断res与of的大小即可;java数字计算会溢出,因此要判断res和of / 10的大小关系(即确定再添一位一定会溢出)。
- python负数取余操作与java不同,由于python的
//操作是向下取整,导致正负数取余操作结果不一致,因此python需要将原数字转为正数操作。
class Solution:
def reverse(self, x: int) -> int:
y, res = abs(x), 0
of = (1 << 31) - 1 if x > 0 else 1 << 31
while y != 0:
res = res * 10 + y % 10
if res > of: return 0
y //= 10
return res if x > 0 else -resclass Solution {
public int reverse(int x) {
int res = 0;
int of = ((1 << 31) - 1) / 10;
while (x != 0) {
if (Math.abs(res) > ((1 << 31) - 1) / 10) return 0;
res = res * 10 + x % 10;
x /= 10;
}
return res;
}
}标签:字符串
- 过滤空格;
- 判断是否为正负号并存储;
- 得到int数字;
- 处理溢出;
- 根据正负号返回。
class Solution:
def myAtoi(self, s: str) -> int:
i, res, neg, over = 0, 0, False, (1 << 31) - 1
while i < len(s) and s[i] == ' ': # ignore space first
i += 1
if i < len(s) and (s[i] == '-' or s[i] == '+'): # save '-'
neg = s[i] == '-'
i += 1
while i < len(s) and '0' <= s[i] <= '9': # generate number
res = res * 10 + int(s[i])
i += 1
if res > over: # handle the overflow
res = over + 1 if neg else over
return -res if neg else res标签:运算机制
- 首先,考虑
双指针法,但int类型无法遍历每一位,转化为str需要额外空间,不符合题意; - 其次,考虑
数字反转,若反转后数字和原数字一样则为回文; - 本解采用半倒置,即只取数字后一半并反转:
- 由于return的判断机制,
x % 10 == 0要直接返回false; x < 0直接返回false。
- 由于return的判断机制,
class Solution:
def isPalindrome(self, x: int) -> bool:
if x < 0 or not x % 10 and x: return False
r = 0
while x > r:
x, rem = x // 10, x % 10
r = r * 10 + rem
return x == r or x == r // 10class Solution {
public boolean isPalindrome(int x) {
if(x < 0 || x % 10 == 0 && x != 0) return false;
int y = 0;
while(x > y){
y = y * 10 + x % 10;
x = x / 10;
}
return x == y || x == y / 10;
}
}标签:双指针
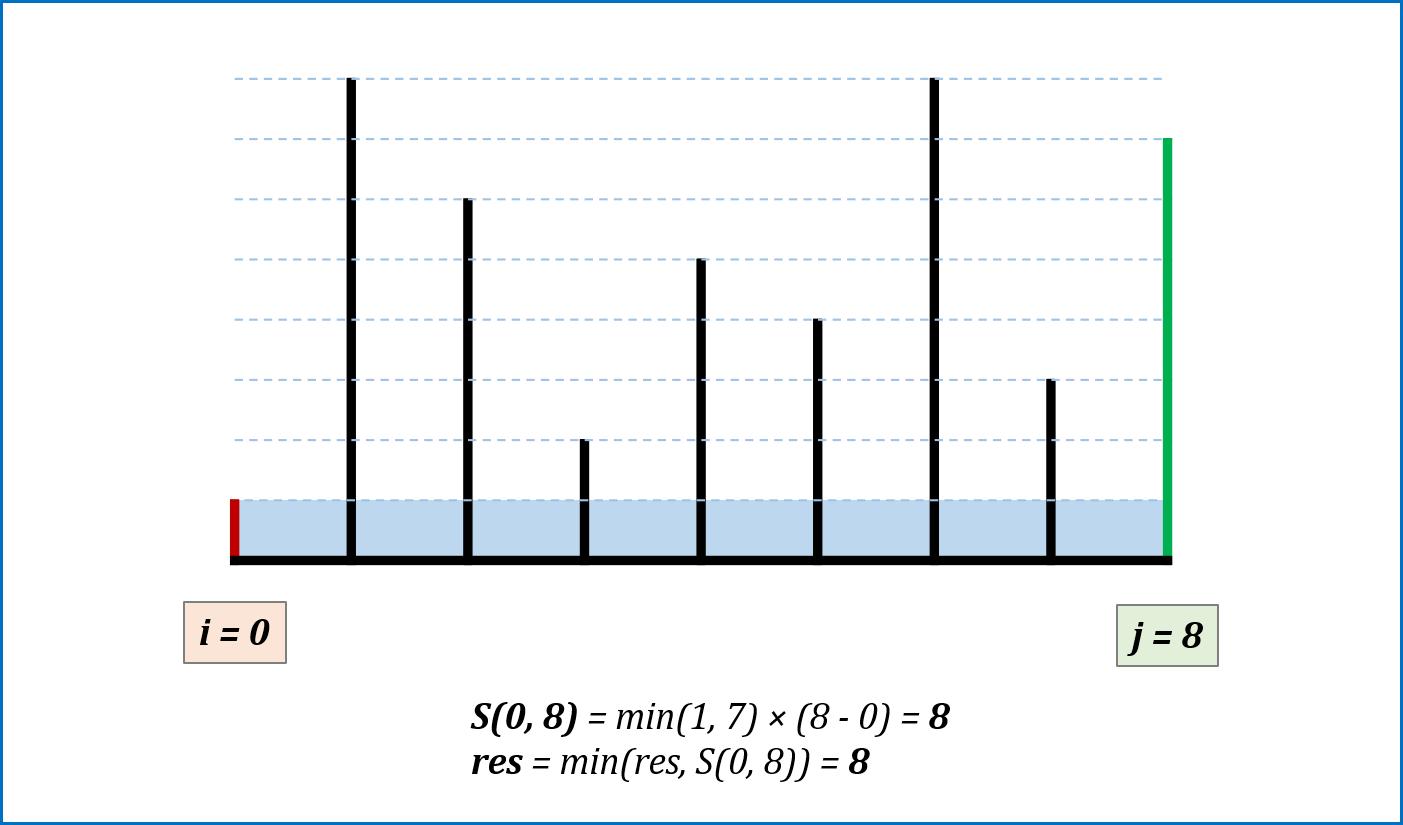
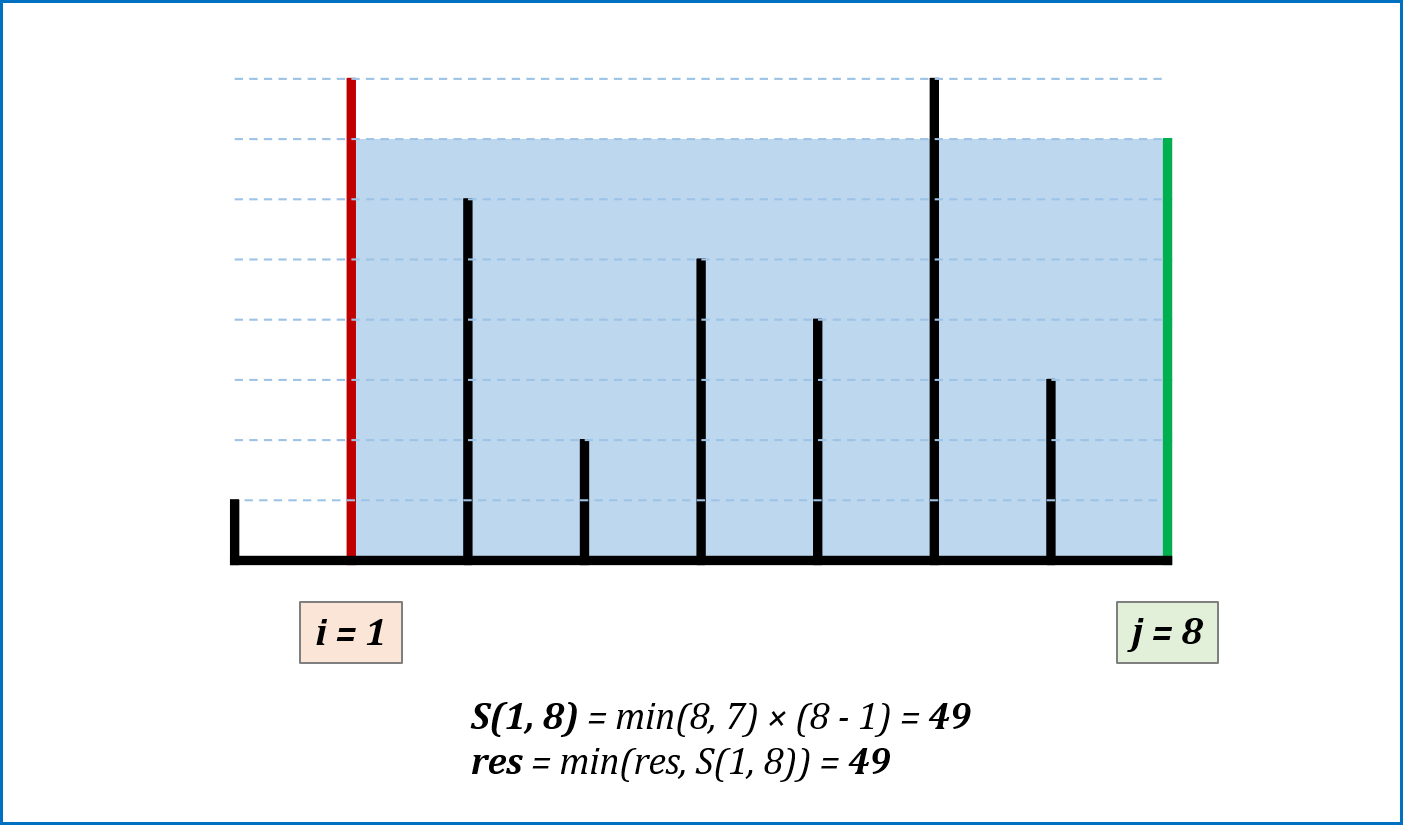
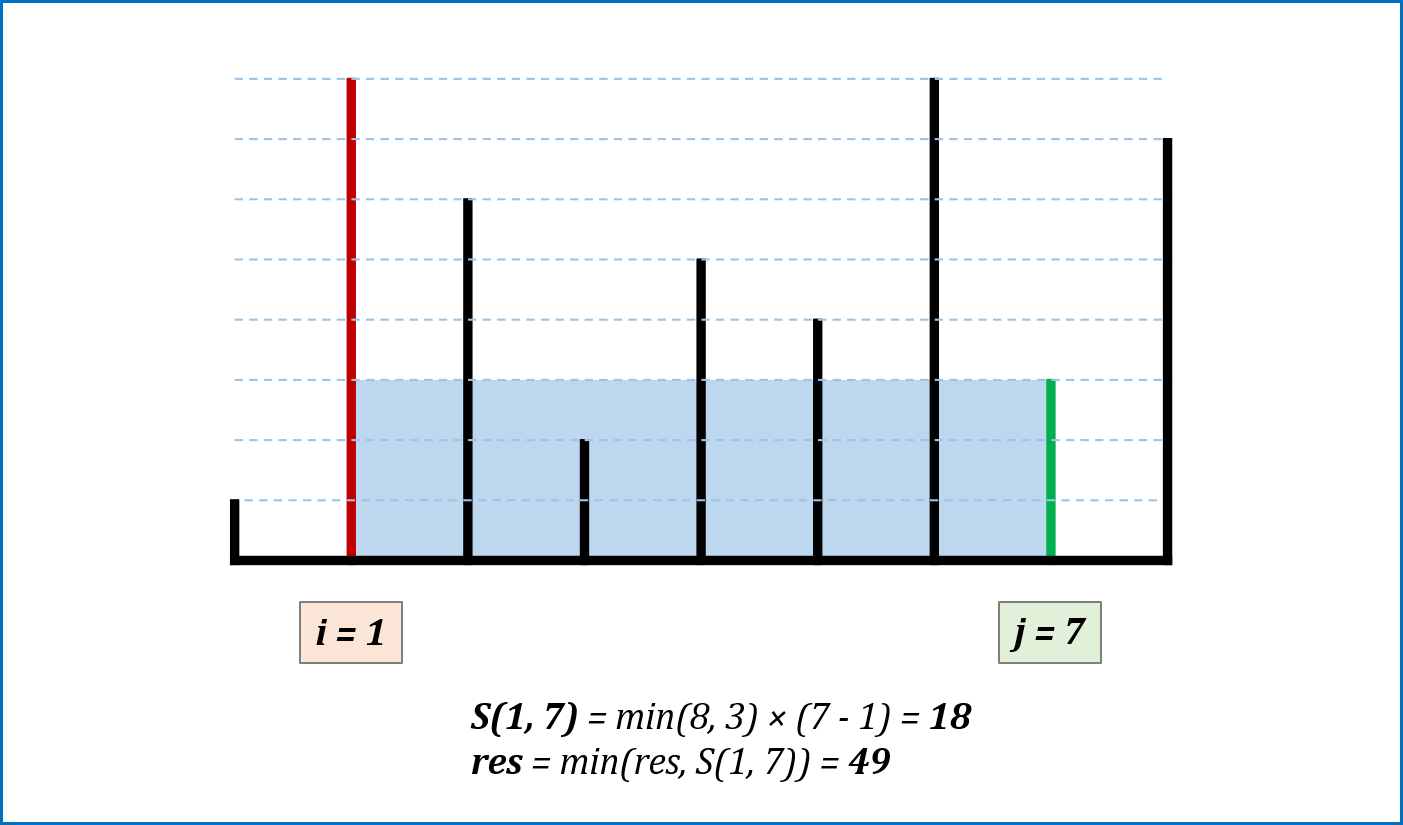
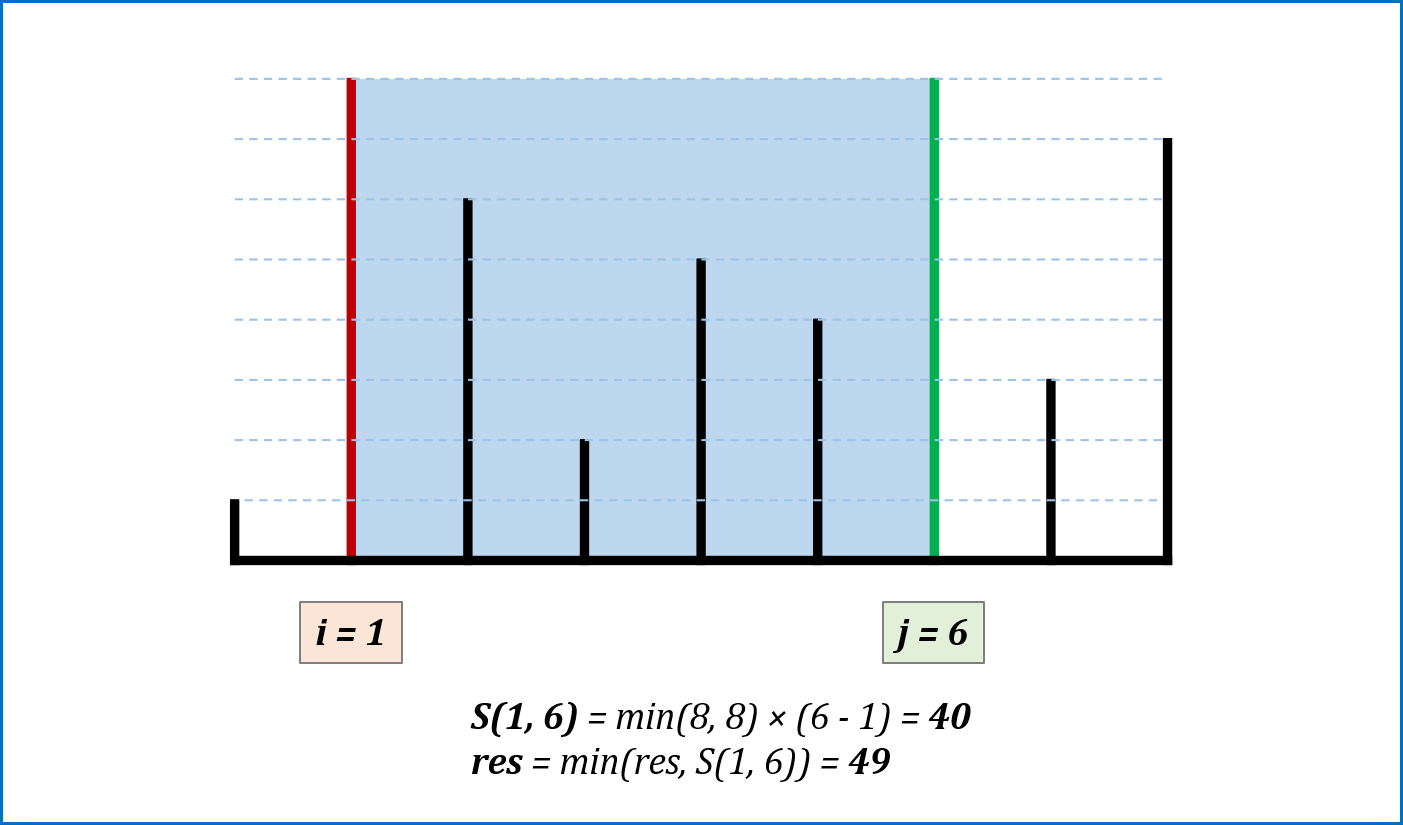
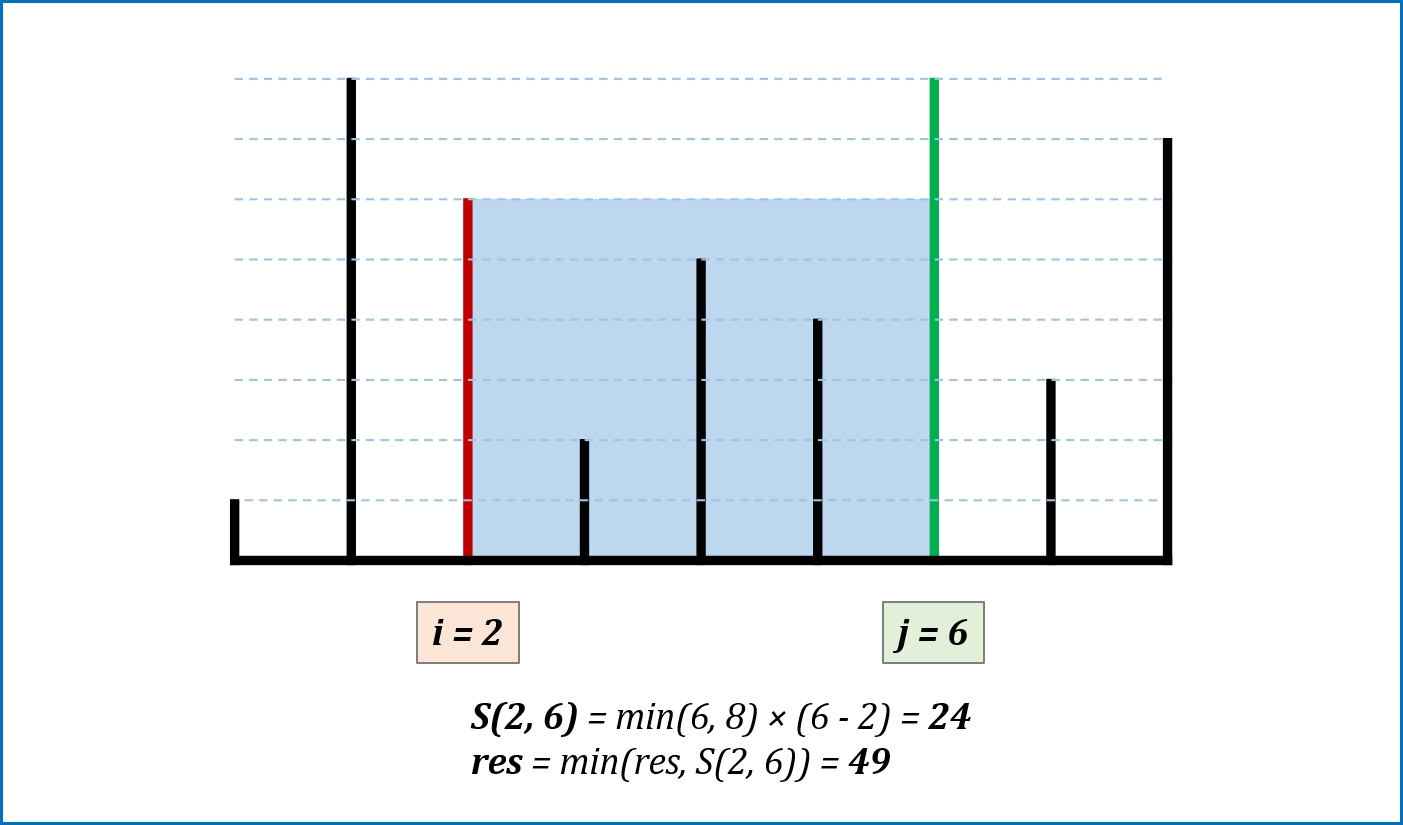
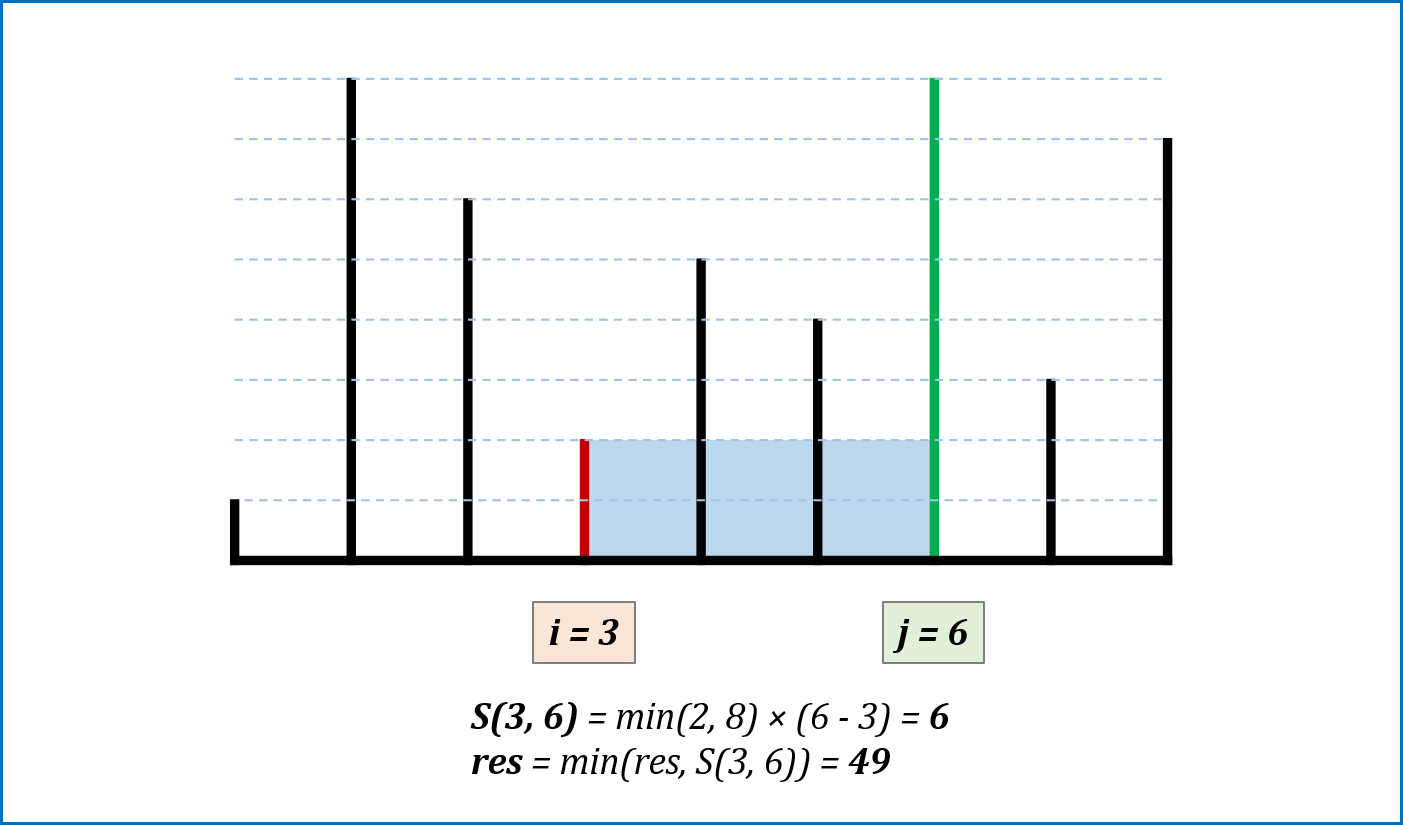
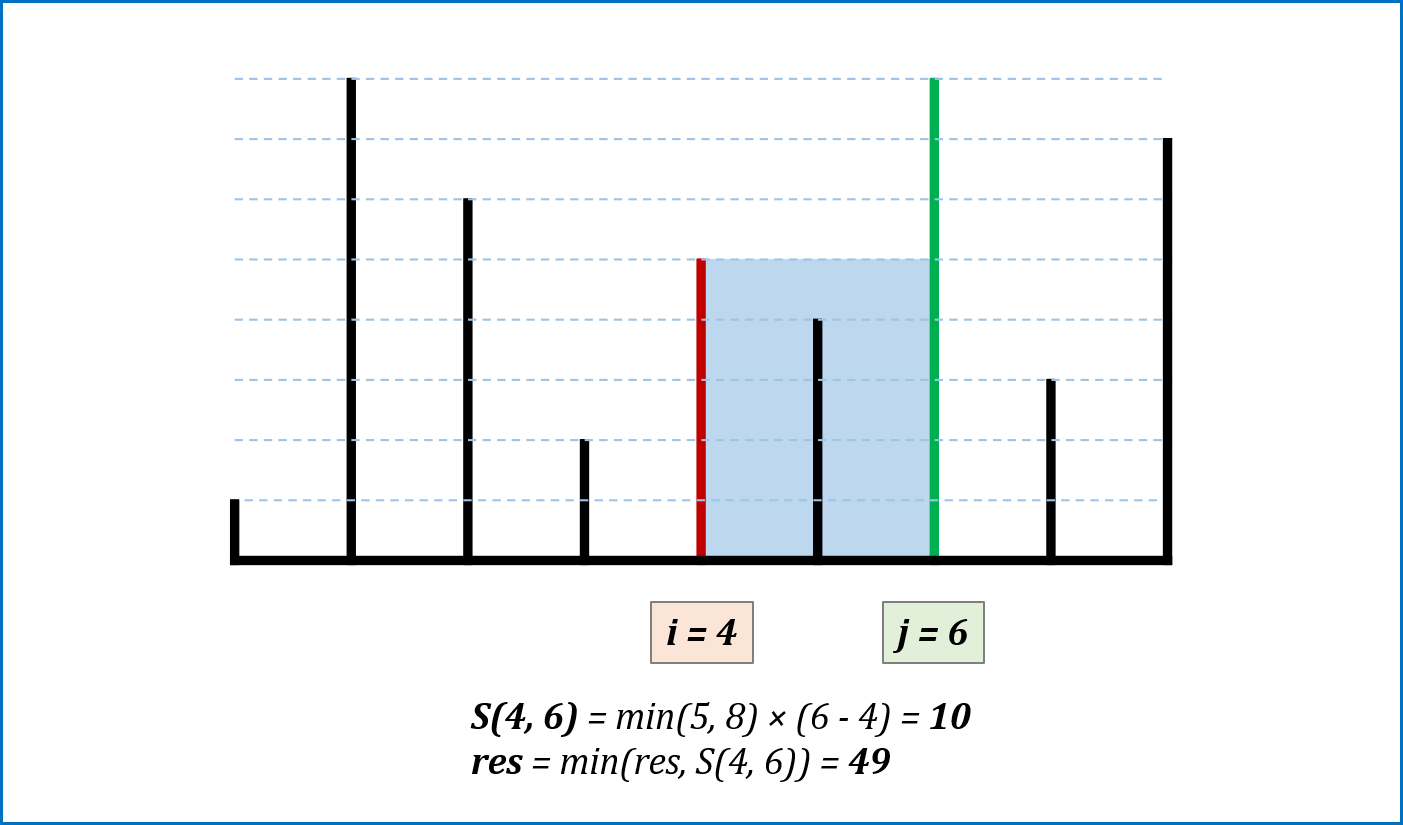
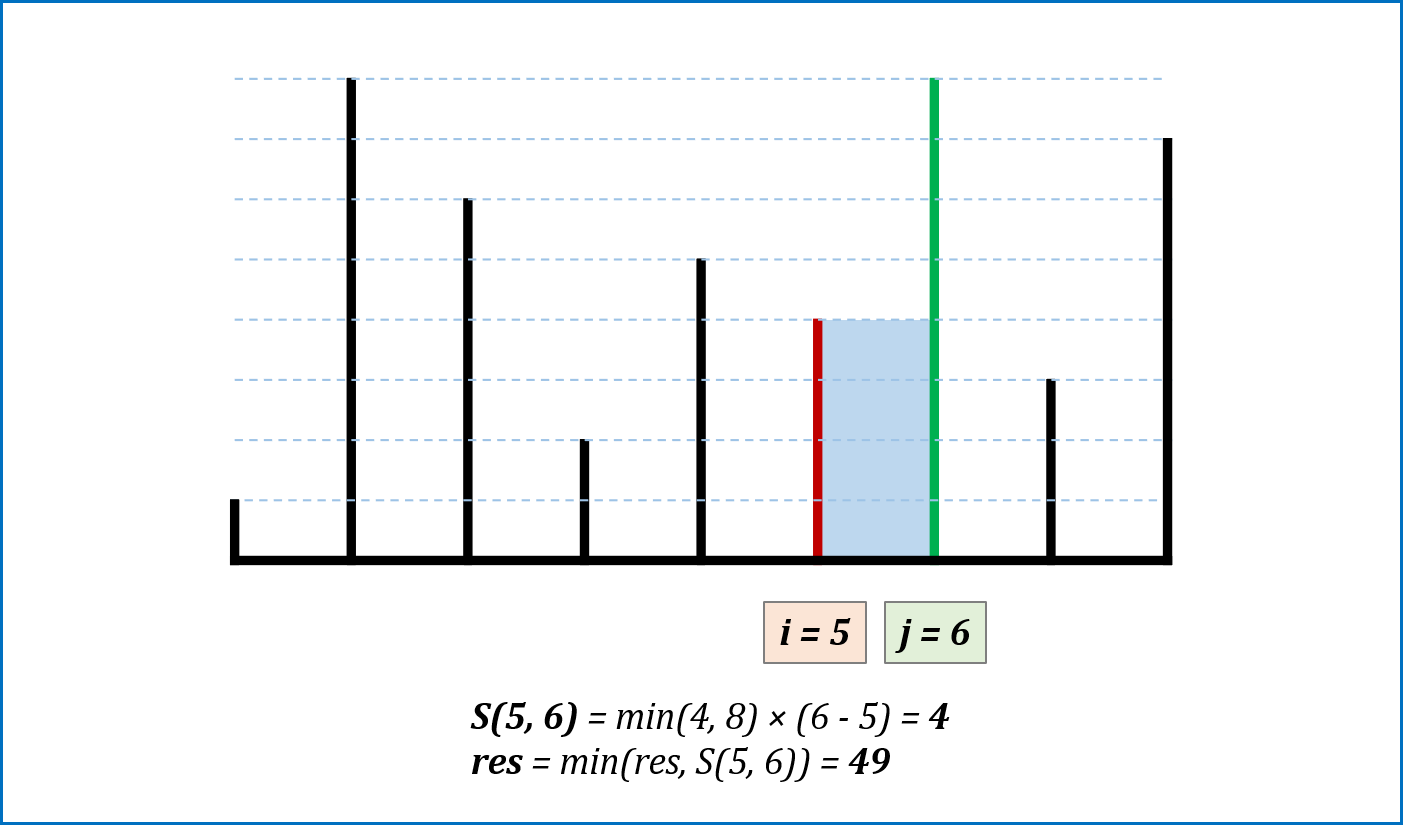
-
算法流程: 设置双指针
$i$ ,$j$ 分别位于容器壁两端,根据规则移动指针(后续说明),并且更新面积最大值res,直到i == j时返回res。 -
指针移动规则与证明: 每次选定围成水槽两板高度
$h[i]$ ,$h[j]$ 中的短板,向中间收窄$1$ 格。以下证明:- 设每一状态下水槽面积为
$S(i, j)$ ,$(0 <= i < j < n)$,由于水槽的实际高度由两板中的短板决定,则可得面积公式$S(i, j) = min(h[i], h[j]) × (j - i)$ 。 - 在每一个状态下,无论长板或短板收窄
$1$ 格,都会导致水槽 底边宽度$-1$ :- 若向内移动短板,水槽的短板
$min(h[i], h[j])$ 可能变大,因此水槽面积$S(i, j)$ 可能增大。 - 若向内移动长板,水槽的短板
$min(h[i], h[j])$ 不变或变小,下个水槽的面积一定小于当前水槽面积。
- 若向内移动短板,水槽的短板
- 因此,向内收窄短板可以获取面积最大值。换个角度理解:
- 若不指定移动规则,所有移动出现的
$S(i, j)$ 的状态数为$C(n, 2)$ ,即暴力枚举出所有状态。 - 在状态
$S(i, j)$ 下向内移动短板至$S(i + 1, j)$ (假设$h[i] < h[j]$ ),则相当于消去了${S(i, j - 1), S(i, j - 2), ... , S(i, i + 1)}$ 状态集合。而所有消去状态的面积一定$<= S(i, j)$ :- 短板高度:相比
$S(i, j)$ 相同或更短($<= h[i]$); - 底边宽度:相比
$S(i, j)$ 更短。
- 短板高度:相比
- 因此所有消去的状态的面积都
$< S(i, j)$ 。通俗的讲,我们每次向内移动短板,所有的消去状态都不会导致丢失面积最大值 。
- 若不指定移动规则,所有移动出现的
- 设每一状态下水槽面积为
-
复杂度分析:
- 时间复杂度
$O(N)$ ,双指针遍历一次底边宽度$N$ 。 - 空间复杂度
$O(1)$ ,指针使用常数额外空间。
- 时间复杂度
class Solution:
def maxArea(self, height: List[int]) -> int:
i, j, res = 0, len(height) - 1, 0
while i < j:
if height[i] < height[j]:
res = max(res, height[i] * (j - i))
i += 1
else:
res = max(res, height[j] * (j - i))
j -= 1
return resclass Solution {
public int maxArea(int[] height) {
int i = 0, j = height.length - 1, res = 0;
while(i < j){
res = height[i] < height[j] ?
Math.max(res, (j - i) * height[i++]):
Math.max(res, (j - i) * height[j--]);
}
return res;
}
}标签:字符串
- 将整数转化为roman字符串,总体思路是先处理高位字符,舍去高位后再处理低位字符。如
1437,先将1000的字符加入,再处理437,将400字符加入,再处理37…… - 有两种特例需要处理
9xx,4xx,但总体上还是可以约化为先处理高位再处理低位的问题,如1900,先加入1000,再加入特例900…… - 开辟两个数组分别存储数字和对应字符,对
num处理算出当前位需要几个字符,k++遍历下个字符,直到num = 0时返回。
class Solution:
def intToRoman(self, num: int) -> str:
res = ""
values = [1000, 900, 500, 400,
100, 90, 50, 40,
10, 9, 5, 4,
1]
symbols = ['M', 'CM', 'D', 'CD',
'C', 'XC', 'L', 'XL',
'X', 'IX', 'V', 'IV',
'I']
i = 0
while num > 0:
count = num // values[i]
res += "".join([symbols[i] for _ in range(count)])
num -= count * values[i]
i += 1
return resclass Solution {
private static final int[] values = {
1000, 900, 500, 400,
100, 90, 50, 40,
10, 9, 5, 4,
1};
private static final String[] symbols = {
"M", "CM", "D", "CD",
"C", "XC", "L", "XL",
"X", "IX", "V", "IV",
"I"};
public String intToRoman(int num) {
StringBuilder res = new StringBuilder();
int k = 0;
while(num > 0){
int count = num / values[k];
for(int i = 0; i< count;i++){
res.append(symbols[k]);
num -= values[k];
}
k++;
}
return res.toString();
}
}标签:字符串,哈希表Hash
- 整体思路是用
Hash存储字符key和数字value的关系,然后遍历roman字符串,在Hash表中取得对应数字加到结果中,遍历完成后返回; Python可以用字典做;Java可以用HashMap做,本题解两语言细节方法不同:Python代码将两个字母的判断优先级放的更高,这样是为了优先处理40、90等由两个char表示的数字;Java代码在遍历过程中记录上个字符,判断当前字符和上个字符关系再进行操作。
class Solution:
def romanToInt(self, s: str) -> int:
dic = {'M':1000, 'CM': 900, 'D': 500, 'CD': 400,
'C':100, 'XC':90, 'L':50, 'XL':40,
'X':10, 'IX': 9, 'V':5, 'IV':4,
'I':1}
i = res = 0
while i < len(s):
if i+1 < len(s) and s[i] + s[i+1] in dic:
res += dic[s[i] + s[i+1]]
i += 2
elif s[i] in dic:
res += dic[s[i]]
i += 1
return resclass Solution {
private Map<Character, Integer> roman = new HashMap<Character, Integer>() {
{
put('M', 1000);
put('D', 500);
put('C', 100);
put('L', 50);
put('X', 10);
put('V', 5);
put('I', 1);
}
};
public int romanToInt(String s) {
int res = 0, pre = 0;
for(Character c : s.toCharArray()){
int cur = roman.get(c);
res += cur > pre ? cur - 2 * pre : cur;
pre = cur;
}
return res;
}
}标签:
- 先统计
strs中最短字符串长度min,之后用min做判断边界; - 判断
[0,min]范围内,所有字符串的公共头部,若发现不同则直接返回; - 若
[0,min]范围内所有字符串相同则直接返回。min == 0需要做特殊处理。
class Solution:
def longestCommonPrefix(self, strs: [str]) -> str:
if not strs: return ""
mi = len(strs[0])
for s in strs[1:]: mi = min(mi, len(s))
for i in range(mi):
for j in range(len(strs) - 1):
if strs[j][i] != strs[j + 1][i]:
return strs[j][:i]
return strs[0][:i+1] if mi else ""class Solution {
public String longestCommonPrefix(String[] strs) {
if(strs.length == 0) return "";
int min = strs[0].length(), i = 0;
for(String s : strs) min = Math.min(min, s.length());
for(; i < min; i++) {
for(int j = 0; j < strs.length - 1; j++){
if(strs[j].charAt(i) != strs[j+1].charAt(i)) return strs[j].substring(0,i);
}
}
return min > 0 ? strs[0].substring(0, i) : "";
}
}标签:双指针
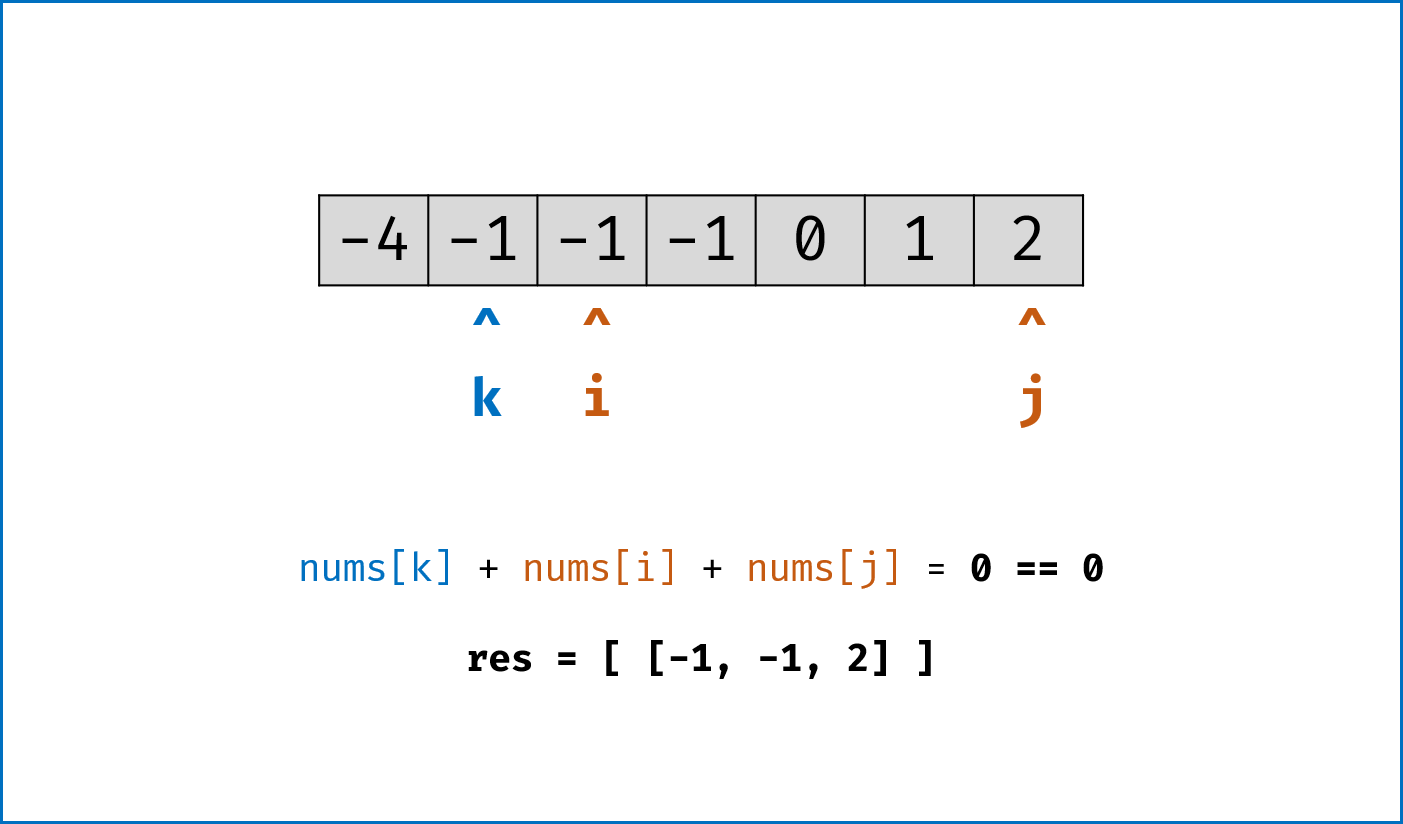
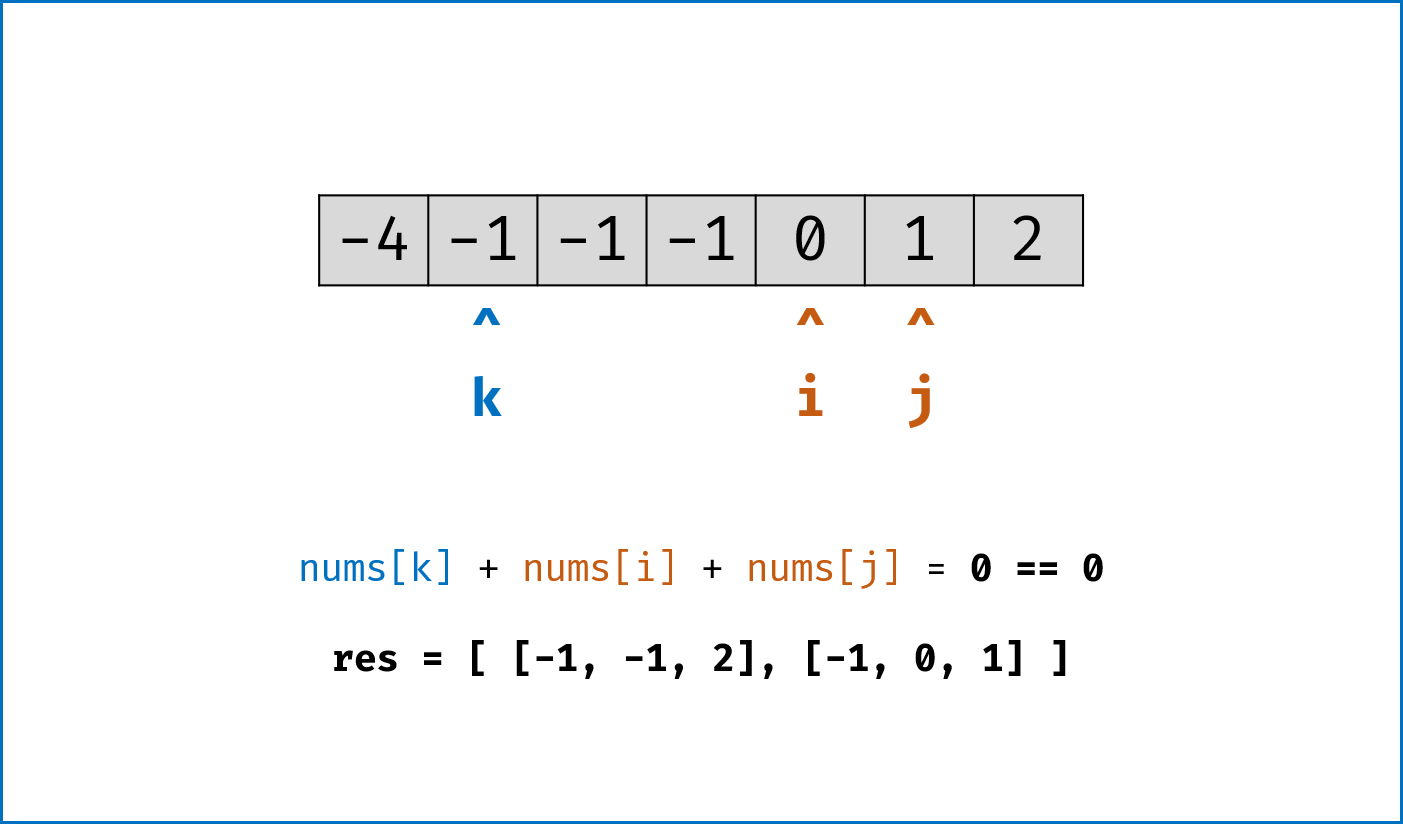
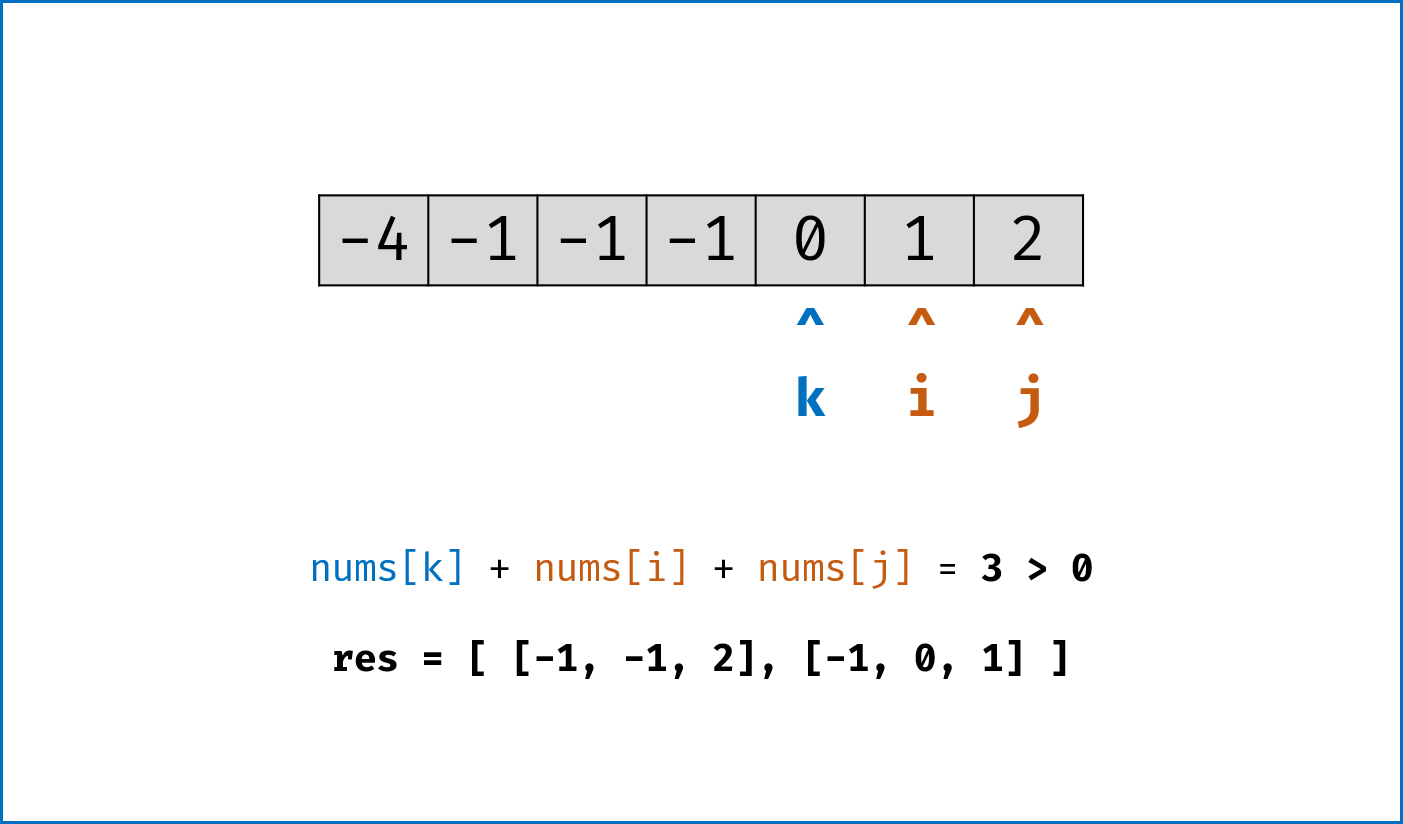
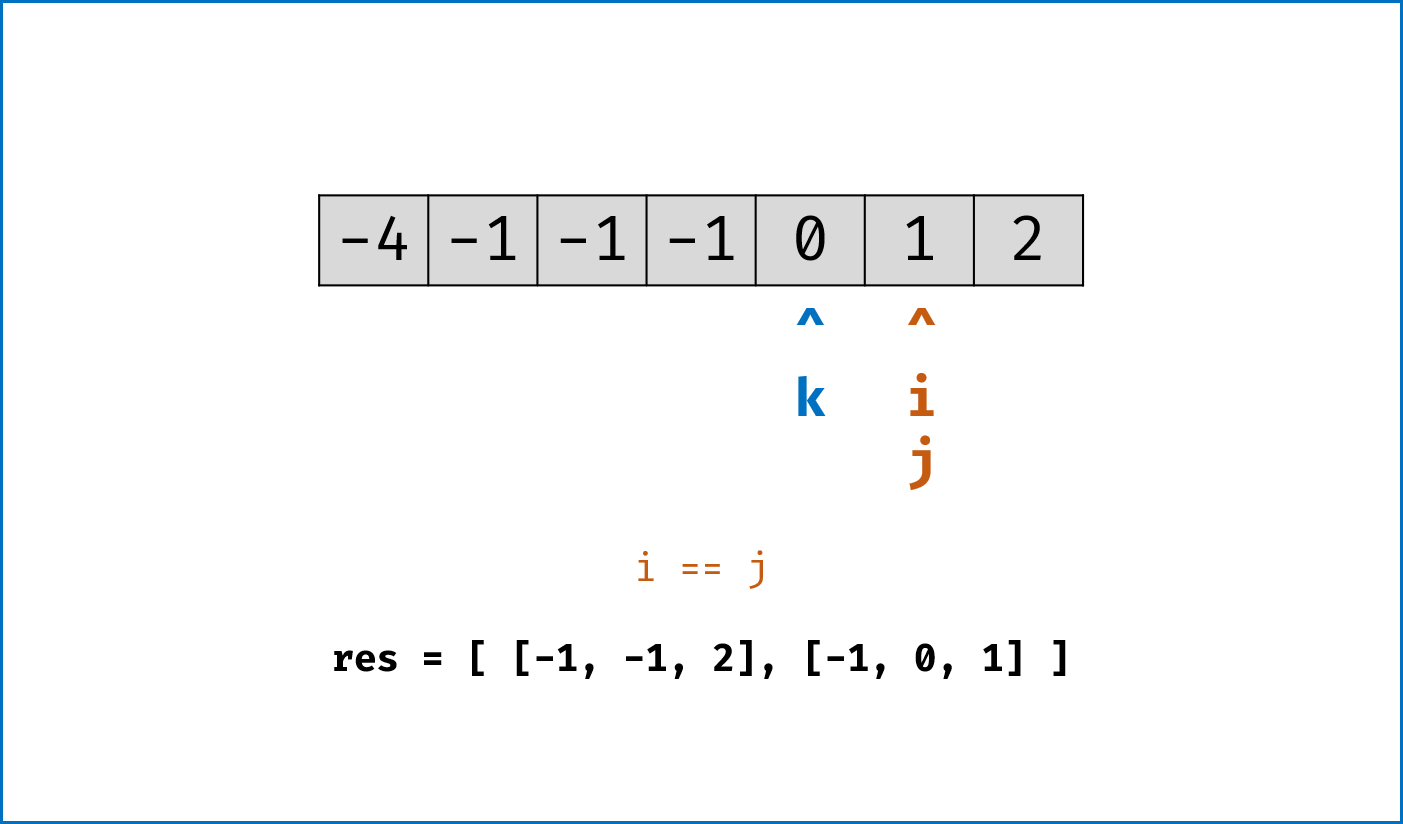
- 暴力法搜索为
$O(N^3)$ 时间复杂度,可通过双指针动态消去无效解来优化效率。 -
双指针法铺垫: 先将给定
nums排序,复杂度为$O(NlogN)$ 。 -
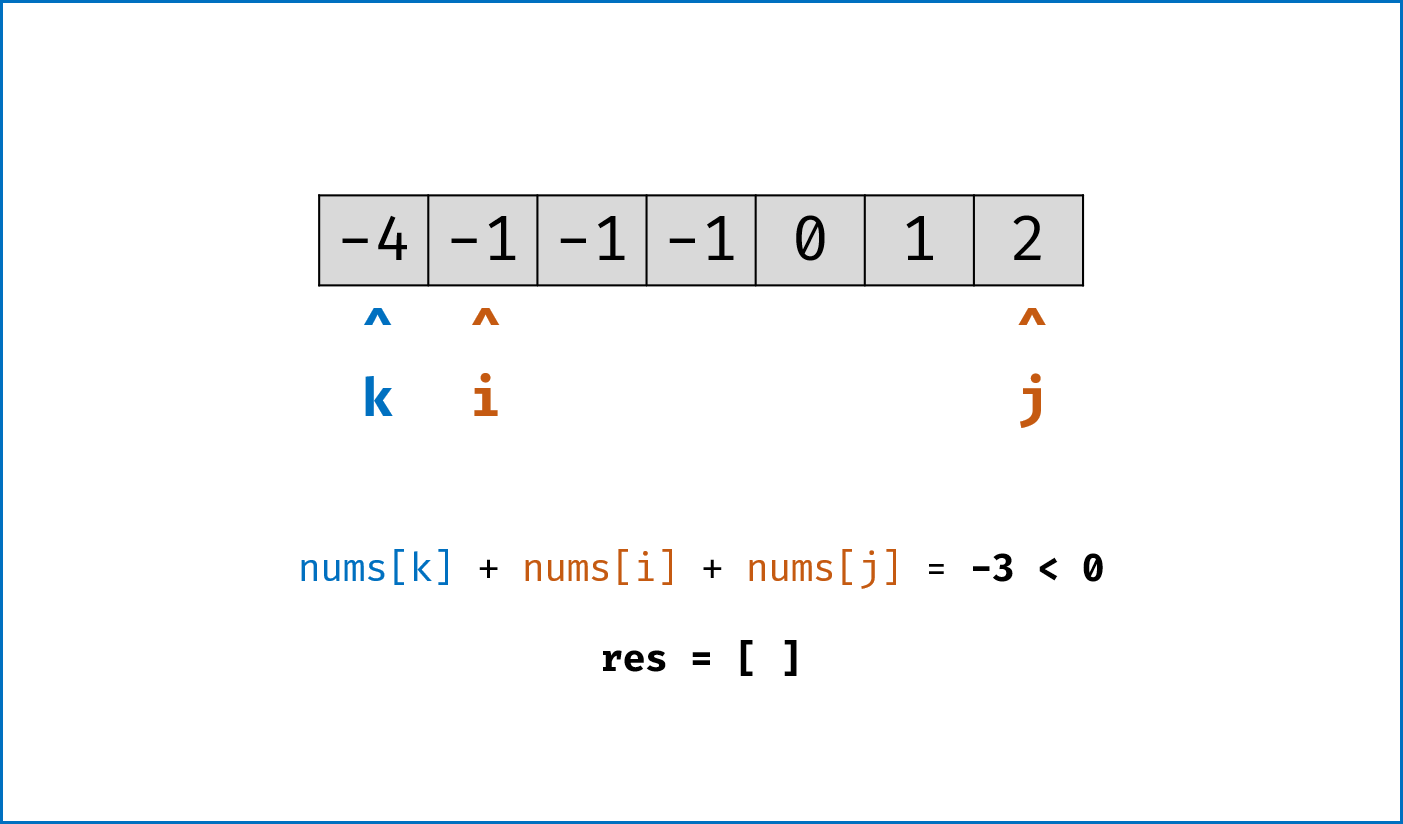
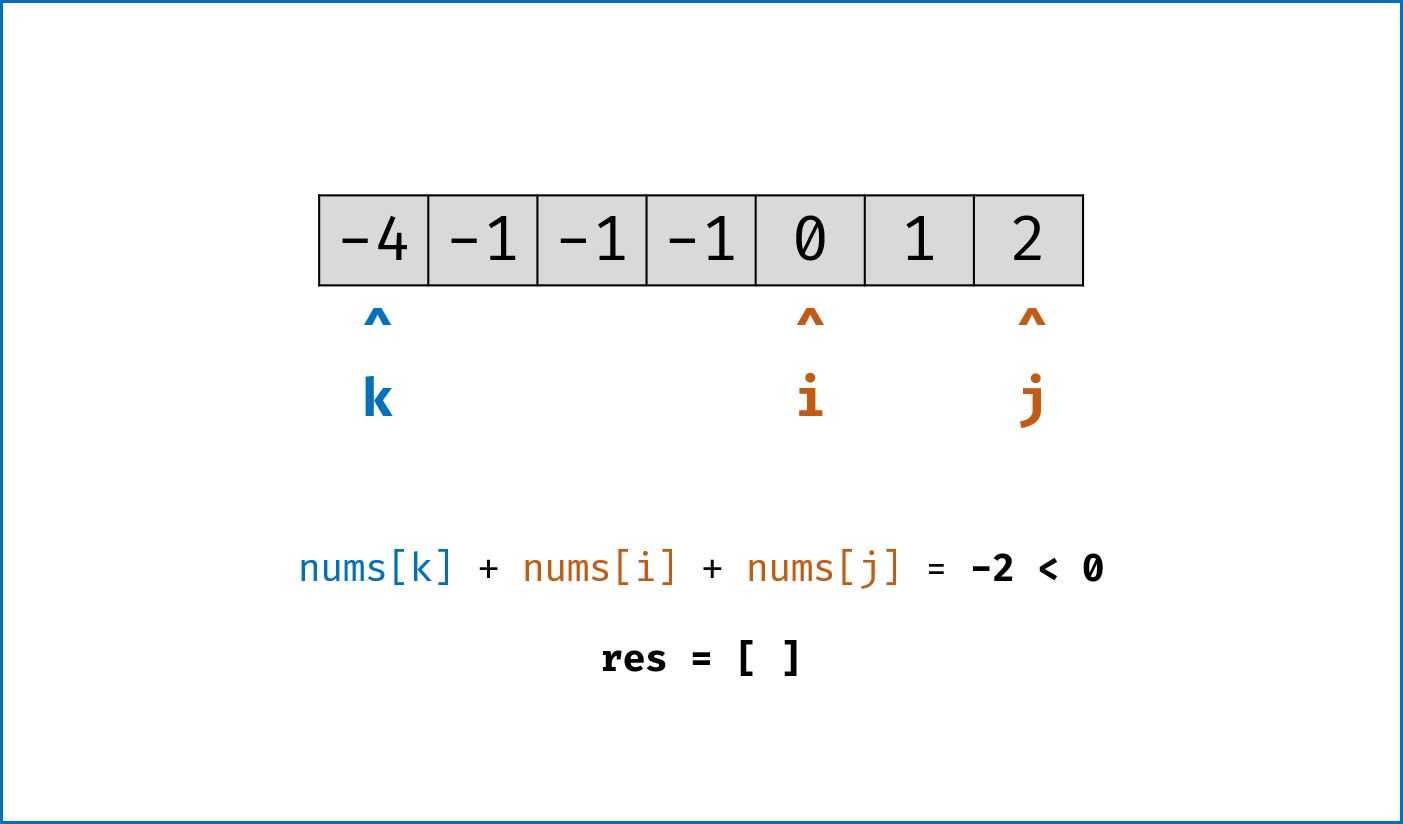
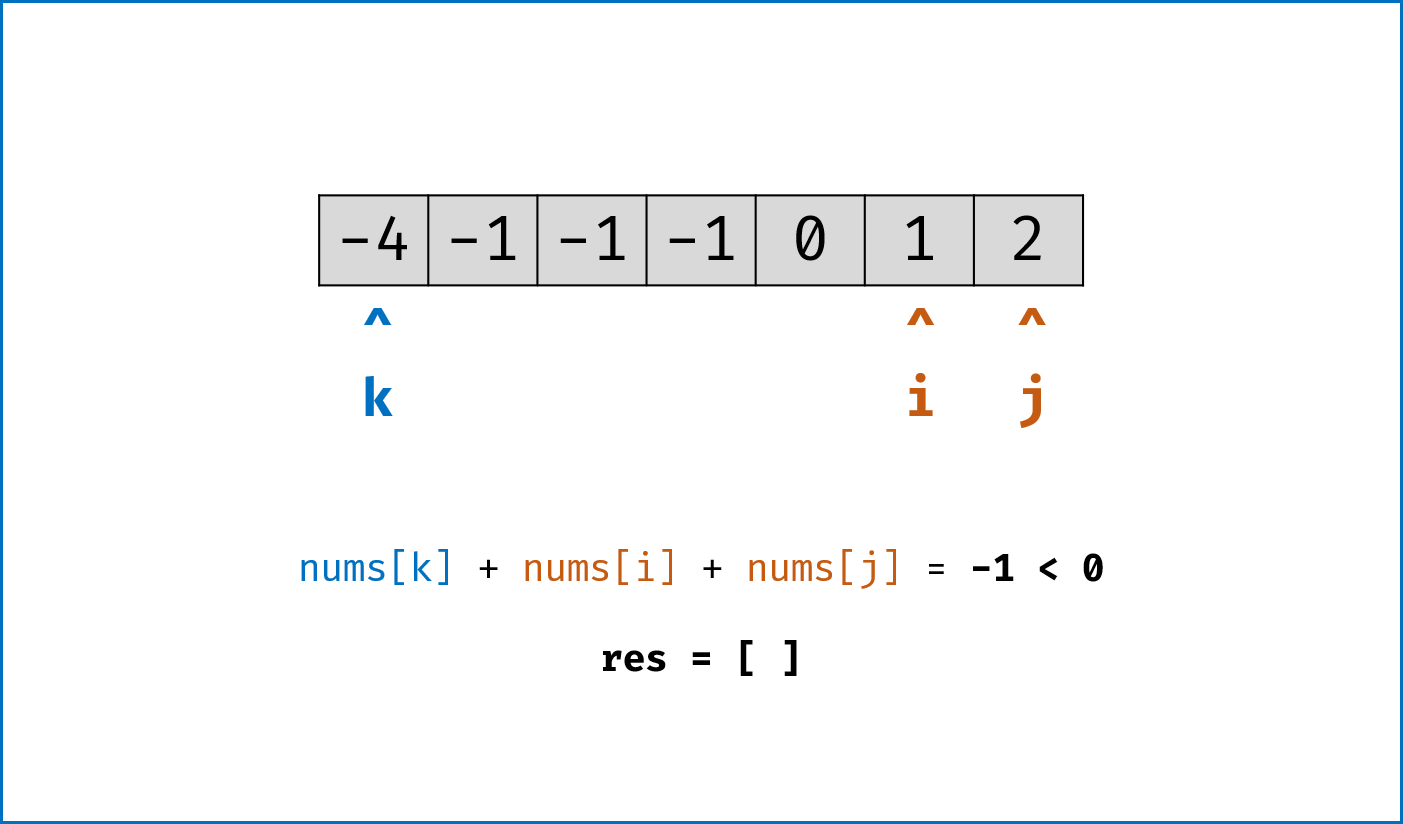
双指针法思路: 固定
$3$ 个指针中最左(最小)数字的指针k,双指针i,j分设在数组索引$(k, len(nums))$ 两端,通过双指针交替向中间移动,记录对于每个固定指针k的所有满足nums[k] + nums[i] + nums[j] == 0的i,j组合:- 当
nums[k] > 0时直接break跳出:因为nums[j] >= nums[i] >= nums[k] > 0,即$3$ 个数字都大于$0$ ,在此固定指针k之后不可能再找到结果了。 - 当
k > 0且nums[k] == nums[k - 1]时即跳过此元素nums[k]:因为已经将nums[k - 1]的所有组合加入到结果中,本次双指针搜索只会得到重复组合。 -
i,j分设在数组索引$(k, len(nums))$ 两端,当i < j时循环计算s = nums[k] + nums[i] + nums[j],并按照以下规则执行双指针移动:- 当
s < 0时,i += 1并跳过所有重复的nums[i]; - 当
s > 0时,j -= 1并跳过所有重复的nums[j]; - 当
s == 0时,记录组合[k, i, j]至res,执行i += 1和j -= 1并跳过所有重复的nums[i]和nums[j],防止记录到重复组合。
- 当
- 当
-
复杂度分析:
- 时间复杂度
$O(N^2)$ :其中固定指针k循环复杂度$O(N)$ ,双指针i,j复杂度$O(N)$ 。 - 空间复杂度
$O(1)$ :指针使用常数大小的额外空间。
- 时间复杂度
class Solution:
def threeSum(self, nums: [int]) -> [[int]]:
nums.sort()
res, k = [], 0
for k in range(len(nums) - 2):
if nums[k] > 0: break # 1. because of j > i > k.
if k > 0 and nums[k] == nums[k - 1]: continue # 2. skip the same `nums[k]`.
i, j = k + 1, len(nums) - 1
while i < j: # 3. double pointer
s = nums[k] + nums[i] + nums[j]
if s < 0:
i += 1
while i < j and nums[i] == nums[i - 1]: i += 1
elif s > 0:
j -= 1
while i < j and nums[j] == nums[j + 1]: j -= 1
else:
res.append([nums[k], nums[i], nums[j]])
i += 1
j -= 1
while i < j and nums[i] == nums[i - 1]: i += 1
while i < j and nums[j] == nums[j + 1]: j -= 1
return resclass Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> threeSum(int[] nums) {
Arrays.sort(nums);
List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>();
for(int k = 0; k < nums.length - 2; k++){
if(nums[k] > 0) break;
if(k > 0 && nums[k] == nums[k - 1]) continue;
int i = k + 1, j = nums.length - 1;
while(i < j){
int sum = nums[k] + nums[i] + nums[j];
if(sum < 0){
while(i < j && nums[i] == nums[++i]);
} else if (sum > 0) {
while(i < j && nums[j] == nums[--j]);
} else {
res.add(new ArrayList<Integer>(Arrays.asList(nums[k], nums[i], nums[j])));
while(i < j && nums[i] == nums[++i]);
while(i < j && nums[j] == nums[--j]);
}
}
}
return res;
}
}标签:栈,哈希表Hash
- 如果使用Brute force,时间复杂度为
O(n3),可以进一步简化。 - 简化思路和
15题类似:先将数组排序,再使用双指针法:- 指针
k遍历整个排序数组,目标是找到所有不重复nums[k]的所有解tmp,并更新记录最优解; - 对于每个nums[k],将i,j双指针置于
k+1, len(nums) - 1,双指针根据tmp与target大小关系逐渐向中间逼近,直到i == j跳出。得到每个解后,判断其与当前最优解谁更优,并更新res。 - 本解答
Java代码在ij指针逼近过程中跳过重复元素,可以减少计算tmp次数,提升效率。
- 指针
- 排序复杂度
O(nlogn),算法整体复杂度O(n2)。
class Solution:
def threeSumClosest(self, nums: [int], target: int) -> int:
nums.sort()
res = float("inf")
for k in range(len(nums) - 2):
if k > 0 and nums[k] == nums[k - 1]: continue
i, j = k + 1, len(nums) - 1
while i < j:
tmp = nums[k] + nums[i] + nums[j]
if abs(tmp - target) < abs(res - target): res = tmp
if tmp > target: j -= 1
elif tmp < target: i += 1
else: return target
return resclass Solution {
public int threeSumClosest(int[] nums, int target) {
Arrays.sort(nums);
long res = (long)Integer.MAX_VALUE;
for (int k = 0; k < nums.length - 2; k++) {
if(k > 0 && nums[k] == nums[k - 1]) continue;
int i = k + 1, j = nums.length - 1;
while(i < j) {
int tmp = nums[k] + nums[i] + nums[j];
if(Math.abs(tmp - target) < Math.abs(res - target)) res = tmp;
if(tmp > target) while(i < j && nums[j] == nums[--j]);
else if(tmp < target) while(i < j && nums[i] == nums[++i]);
else return target;
}
}
return (int)res;
}
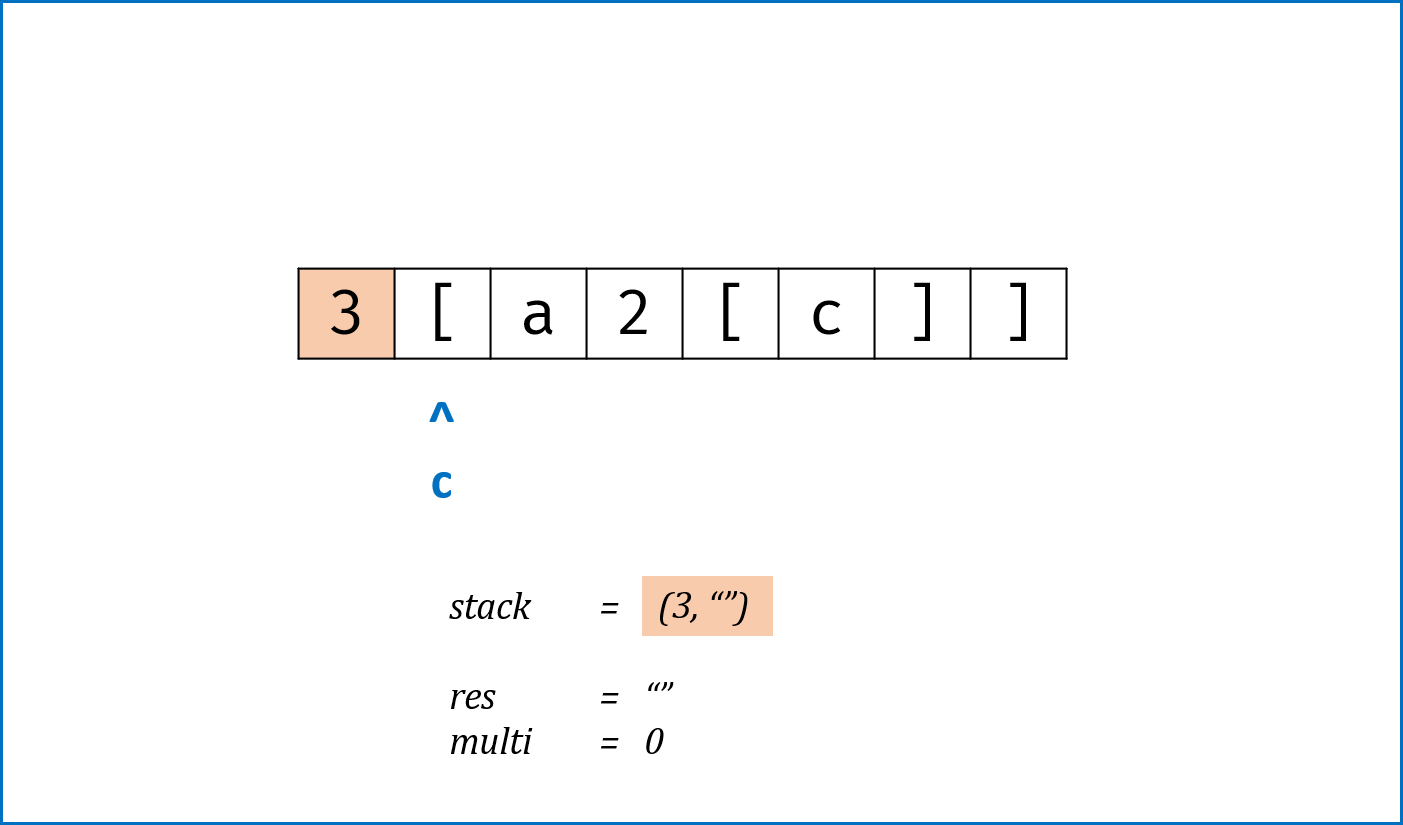
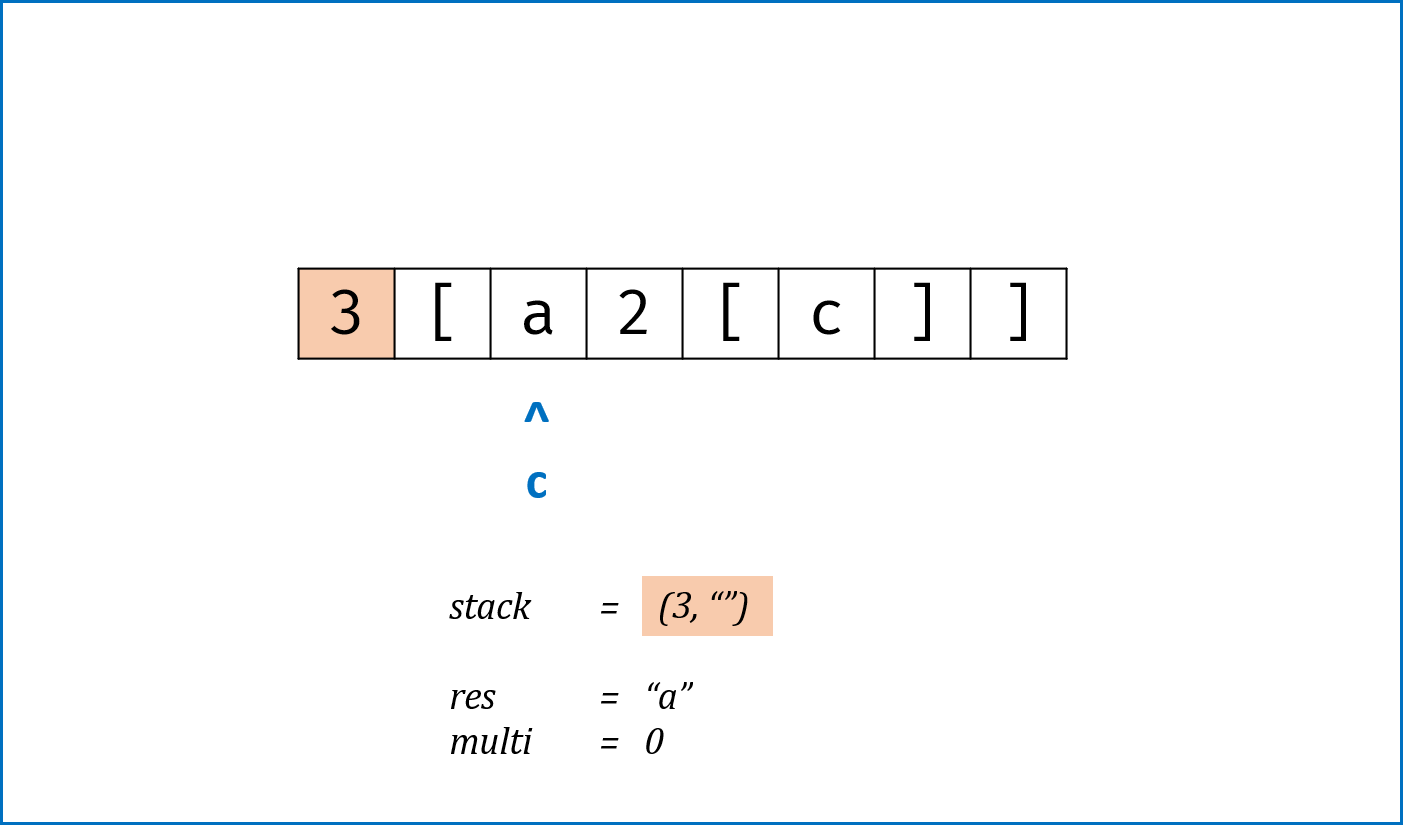
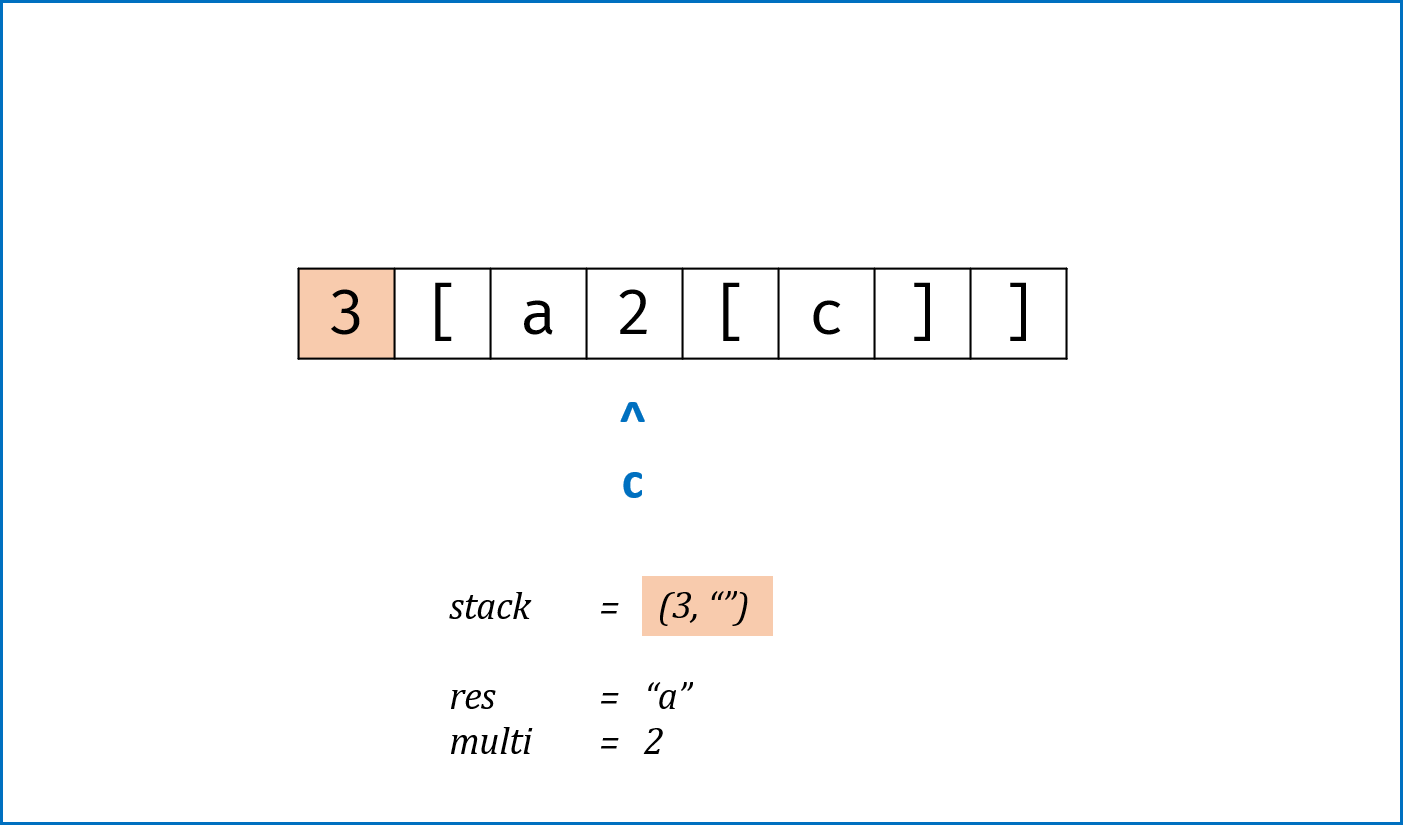
}标签:栈,哈希表Hash
- 建立
HashMap构建左右括号对应关系,key左括号,value右括号。 - 遍历
s中所有括号,借助栈先入后出的特点,每次判断:- 如果
stack为空 orc是左括号,则入栈; - 如果
stack栈顶与c形成一对括号,则栈顶出栈; - 否则,到此处已经违背了括号对应原则,直接返回
false。
- 如果
- 此迭代过程遇到
s中第一个元素为右括号的情况时,无法提前返回,因此在进入迭代前进行单独处理。 - 跳出迭代后,如果
stack为空则是符合括号原则的(为了处理"[","]"这类特殊情况)。
class Solution:
def isValid(self, s: str) -> bool:
dic = {'{': '}', '[': ']', '(': ')'}
if s and s[0] not in dic: return False
stack = []
for c in s:
if not stack or c in dic: stack.append(c)
elif stack[-1] in dic and dic[stack[-1]] == c: stack.pop()
else: return False
return not stackclass Solution {
private static final Map<Character,Character> map = new HashMap<Character,Character>(){{
put('{','}'); put('[',']'); put('(',')');
}};
public boolean isValid(String s) {
if(s.length() > 0 && !map.containsKey(s.charAt(0))) return false;
Stack<Character> stack = new Stack<>();
for(Character c : s.toCharArray()){
if(stack.isEmpty() || map.containsKey(c)) stack.push(c);
else if(map.get(stack.peek()) == c) stack.pop();
else return false;
}
return stack.isEmpty();
}
}标签:双指针,链表
- 建立一个辅助
node作为链表头部; - 设两指针
l1,l2分别指向两链表头部,根据指针node值大小改变next指向,交替前进; - 最后将
l1、l2剩余尾部加入,返回即可。
class Solution:
def mergeTwoLists(self, l1: ListNode, l2: ListNode) -> ListNode:
head = ListNode(0)
res = head
while l1 and l2:
if l1.val <= l2.val: head.next, l1 = l1, l1.next
else: head.next, l2 = l2, l2.next
head = head.next
head.next = l1 if not l2 else l2
return res.nextclass Solution {
public ListNode mergeTwoLists(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) {
ListNode head = new ListNode(0);
ListNode res = head;
while (l1 != null && l2 != null) {
if(l1.val <= l2.val){
head.next = l1;
l1 = l1.next;
}
else{
head.next = l2;
l2 = l2.next;
}
head = head.next;
}
head.next = l2 == null ? l1 : l2;
return res.next;
}
}标签:链表,归并,分治
- 在
21题合并两个list的基础上,将k个链表两两合并,再对剩下k/2个链表两两合并……直到合并为一个链表。 - 本质上是归并排序的merge过程,时间复杂度
O(n k logk)。
class Solution:
def mergeKLists(self, lists: List[ListNode]) -> ListNode:
while len(lists) > 1:
lists.append(self.merge(lists.pop(0), lists.pop(0)))
return lists[0] if lists else None
def merge(self, h1, h2):
res = head = ListNode(0)
while h1 and h2:
if h1.val <= h2.val: head.next, h1 = h1, h1.next
else: head.next, h2 = h2, h2.next
head = head.next
head.next = h1 if not h2 else h2
return res.nextclass Solution {
public ListNode mergeKLists(ListNode[] lists) {
LinkedList<ListNode> res = new LinkedList(Arrays.asList(lists));
while (res.size() > 1) {
res.addLast(merge(res.removeFirst(),res.removeFirst()));
}
return res.size() == 0 ? null : res.get(0);
}
private ListNode merge(ListNode h1, ListNode h2) {
ListNode head = new ListNode(0);
ListNode res = head;
while (h1 != null && h2 != null) {
if (h1.val <= h2.val) {
head.next = h1;
h1 = h1.next;
} else {
head.next = h2;
h2 = h2.next;
}
head = head.next;
}
head.next = h2 == null ? h1 : h2;
return res.next;
}
}标签:链表,递归
- 遍历链表,一一修改指针,有
迭代和递归两种做法。
class Solution:
def swapPairs(self, head: ListNode) -> ListNode:
pre = ListNode(0)
res = pre
while head and head.next:
nex = head.next.next
pre.next = head.next
pre = head
head.next.next = head
head = nex
pre.next = head
return res.nextclass Solution:
def swapPairs(self, head: ListNode) -> ListNode:
if not head or not head.next: return head
nex = head.next
head.next = self.swapPairs(nex.next)
nex.next = head
return nexclass Solution {
public ListNode swapPairs(ListNode head) {
ListNode pre = new ListNode(0);
ListNode res = pre;
while(head != null && head.next != null){
ListNode nex = head.next.next;
pre.next = head.next;
pre = head;
head.next.next = head;
head = nex;
}
pre.next = head;
return res.next;
}
}标签:双指针
- 需要做两件事:
- 统计数组中不同数字数量
k; - 修改数组前
k个元素为这些不同数字。
- 统计数组中不同数字数量
- 由于数组已经完成排序,因此设定第一个指针
i,遍历数组,每遇到nums[i] != nums[i - 1],就说明遇到了新的不同数字,记录之; - 设定第二个指针
k,每遇到新的不同数字执行k += 1,k有两个用途:- 记录数组中不同数字的数量;
- 作为修改数组元素的
index。
- 最终,返回
k即可。
class Solution:
def removeDuplicates(self, nums: [int]) -> int:
if not nums: return 0
k = 1
for i in range(1, len(nums)):
if nums[i] != nums[i - 1]:
nums[k] = nums[i]
k += 1
return kclass Solution {
public int removeDuplicates(int[] nums) {
if (nums.length == 0) return 0;
int k = 1;
for (int i = 1; i < nums.length; i++) {
if (nums[i] != nums[i - 1]) {
nums[k] = nums[i];
k++;
}
}
return k;
}
}标签:字符串
- 暴力法,复杂度O(MN)
class Solution(object):
def strStr(self, haystack, needle):
"""
:type haystack: str
:type needle: str
:rtype: int
"""
if not needle: return 0
l_h, l_n = len(haystack), len(needle)
for i in range(l_h + 1):
for j in range(l_n + 1):
if j == l_n: return i
if i + j == l_h: return -1
if haystack[i+j] != needle[j]: break
def strStr1(self, haystack, needle):
return haystack.find(needle)class Solution {
public int strStr(String haystack, String needle) {
if (needle == "") return 0;
for (int i = 0;; i++) {
for (int j = 0;; j++) {
if (j == needle.length()) return i;
if (i + j == haystack.length()) return -1;
if (haystack.charAt(i + j) != needle.charAt(j)) break;
}
}
}
}标签:二分法
- 题目要求复杂度
O(logN),自然联想到二分法。 - 若是一个普通排序数组,直接
二分查找就可以,本题的复杂处在于给定数组已被旋转; - 因此,我们先使用二分法找到旋转数组的分界点
i,再确定target在哪段数组中,再应用一次二分查找,返回index。- 本题解找到的分界点
i是第二段数组的第一个元素,某些数组未被旋转,也将其看作第二段数组处理; - 若当前数字不在第一段且不在第二段数组,直接返回
-1; 二分查找未找到target,返回-1。
- 本题解找到的分界点
class Solution:
def search(self, nums: [int], target: int) -> int:
if not nums: return -1
i, j = 0, len(nums) - 1
while i < j:
m = (i + j) // 2
if nums[m] < nums[j]: j = m
else: i = m + 1
if nums[i] <= target <= nums[-1]: i, j = i, len(nums) - 1
elif nums[0] <= target <= nums[i - 1]: i, j = 0, i - 1
else: return -1
while i <= j:
m = (i + j) // 2
if nums[m] > target: j = m - 1
elif nums[m] < target: i = m + 1
else: return m
return -1class Solution {
public int search(int[] nums, int target) {
if(nums.length == 0) return -1;
int i = 0, j = nums.length - 1;
while(i < j){
int m = (i + j) / 2;
if(nums[m] < nums[j]) j = m;
else i = m + 1;
}
if(i == 0 || nums[i] <= target && target <= nums[nums.length - 1])
j = nums.length - 1;
else if(nums[0] <= target && target <= nums[i - 1]){
j = i - 1;
i = 0;
}
else return -1;
while(i <= j) {
int m = (i + j) / 2;
if(nums[m] < target) i = m + 1;
else if(nums[m] > target) j = m - 1;
else return m;
}
return -1;
}
}标签:数组,二分法
寻找插入点使用二分法,但与寻找某数字不同的是,需要考虑一些边界条件:- 当插入数字和
nums中某数字相等时,插入到左边还是右边?本题要求插到左边; - 插入数字在
nums第一个数字左边,或在最后一个数字右边;
- 当插入数字和
- 推荐记住其中的几个关键点写法。
class Solution:
def searchInsert(self, nums: [int], target: int) -> int:
left, right = 0, len(nums) - 1
while left <= right:
mid = (left + right) // 2
if nums[mid] < target: left = mid + 1 # insert left side
else: right = mid - 1
return leftclass Solution {
public int searchInsert(int[] nums, int target) {
int left = 0, right = nums.length - 1;
while (left <= right) {
int mid = (left + right) / 2;
if (nums[mid] < target) left = mid + 1;
else right = mid - 1;
}
return left;
}
}标签:
- 设两数字
num1,num2,其乘积等于num2每一位与num1相乘,再将所有结果相加。 - 模拟这个竖式乘法的过程即可。
class Solution:
def multiply(self, num1: str, num2: str) -> str:
if num1 == "0" or num2 == "0": return "0"
res = []
for loc in range(len(num2)): # multiply
x2 = ord(num2[len(num2) - 1 - loc]) - ord('0')
ans, tmp, car = [], 0, 0
for n1 in num1[::-1]:
x1 = ord(n1) - ord('0')
tmp = x1 * x2 + car
car = tmp // 10
ans.append(str(tmp % 10))
if car: ans.append(str(car))
ans.reverse()
ans.extend(['0' for _ in range(loc)])
i, j, car = len(res) - 1, len(ans) - 1, 0
res_tmp = []
while i >= 0 or j >= 0: # add
a1 = ord(res[i]) - ord('0') if i >= 0 else 0
a2 = ord(ans[j]) - ord('0') if j >= 0 else 0
tmp = a1 + a2 + car
car = tmp // 10
res_tmp.append(str(tmp % 10))
i, j = i - 1, j - 1
if car: res_tmp.append("1")
res_tmp.reverse()
res = res_tmp
return "".join(res)标签:递归
- 将第
j个数字与第j,j+1,j+2,...,len(nums) - 1个数字分别交换,得到len(nums) - j种情况; - 在每种情况下递归,将第
j+1处数字与第j+1,j+2,...,len(nums) - 1处数字分别交换;- 每个递归跳出后,要将交换过的元素还原,这样才能实现第一条所说的内容。
- 直到
j == len(nums) - 1,代表此种交换组合下已经交换完毕,记录答案。
class Solution:
def permute(self, nums: [int]) -> [[int]]:
self.res = []
self.swap(nums, 0)
return self.res
def swap(self, nums, j):
if j == len(nums) - 1: self.res.append(list(nums))
for i in range(j, len(nums)):
nums[i], nums[j] = nums[j], nums[i]
self.swap(nums, j+1)
nums[i], nums[j] = nums[j], nums[i]class Solution {
private List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>();
public List<List<Integer>> permute(int[] nums) {
swap(nums, 0);
return res;
}
private void swap(int[] nums, int j) {
if (j == nums.length - 1) {
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
for (int num : nums) list.add(num);
res.add(list);
}
for (int i = j; i < nums.length; i++) {
int tmp = nums[i];
nums[i] = nums[j]; nums[j] = tmp;
swap(nums, j + 1);
nums[j] = nums[i]; nums[i] = tmp;
}
}
}标签:动态规划,数组
- 动态规划典型题:遍历数组,记录
max(nums[i-1] + nums[i], nums[i]),即判断后面subarray是否舍去前面的加和; - 最后return加和中最大值。
class Solution:
def maxSubArray(self, nums: List[int]) -> int:
for i in range(1,len(nums)):
nums[i] = max(nums[i-1] + nums[i], nums[i])
return max(nums)class Solution {
public int maxSubArray(int[] nums) {
int res = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
for(int i = 1; i < nums.length; i++){
nums[i] = Math.max(nums[i], nums[i] + nums[i - 1]);
res = Math.max(res, nums[i]);
}
return res;
}
}标签:数组
- 此方法不使用额外空间
O(1),时间复杂度O(MN):i,j记录目前走到的位置;h,l记录剩余矩阵的高度、宽度;- 沿着右下左上的顺序走,每走完一条直线将对应
高度/宽度-1; - 若剩余矩阵
高度or宽度==0,代表已经走完break。
class Solution:
def spiralOrder(self, matrix: [[int]]) -> [int]:
if not matrix: return []
res = []
h, l = len(matrix), len(matrix[0])
i, j = 0, -1
while True:
for _ in range(l):
j += 1
res.append(matrix[i][j])
h -= 1
if not h: break
for _ in range(h):
i += 1
res.append(matrix[i][j])
l -= 1
if not l: break
for _ in range(l):
j -= 1
res.append(matrix[i][j])
h -= 1
if not h: break
for _ in range(h):
i -= 1
res.append(matrix[i][j])
l -= 1
if not l: break
return resclass Solution {
public List<Integer> spiralOrder(int[][] matrix) {
List<Integer> res = new ArrayList<>();
if (matrix.length == 0) return res;
int h = matrix.length, l = matrix[0].length;
int i = 0, j = -1;
while (true) {
for (int k = 0; k < l; k++)
res.add(matrix[i][++j]);
if (--h == 0) break;
for (int k = 0; k < h; k++)
res.add(matrix[++i][j]);
if (--l == 0) break;
for (int k = 0; k < l; k++)
res.add(matrix[i][--j]);
if (--h == 0) break;
for (int k = 0; k < h; k++)
res.add(matrix[--i][j]);
if (--l == 0) break;
}
return res;
}
}标签:数组
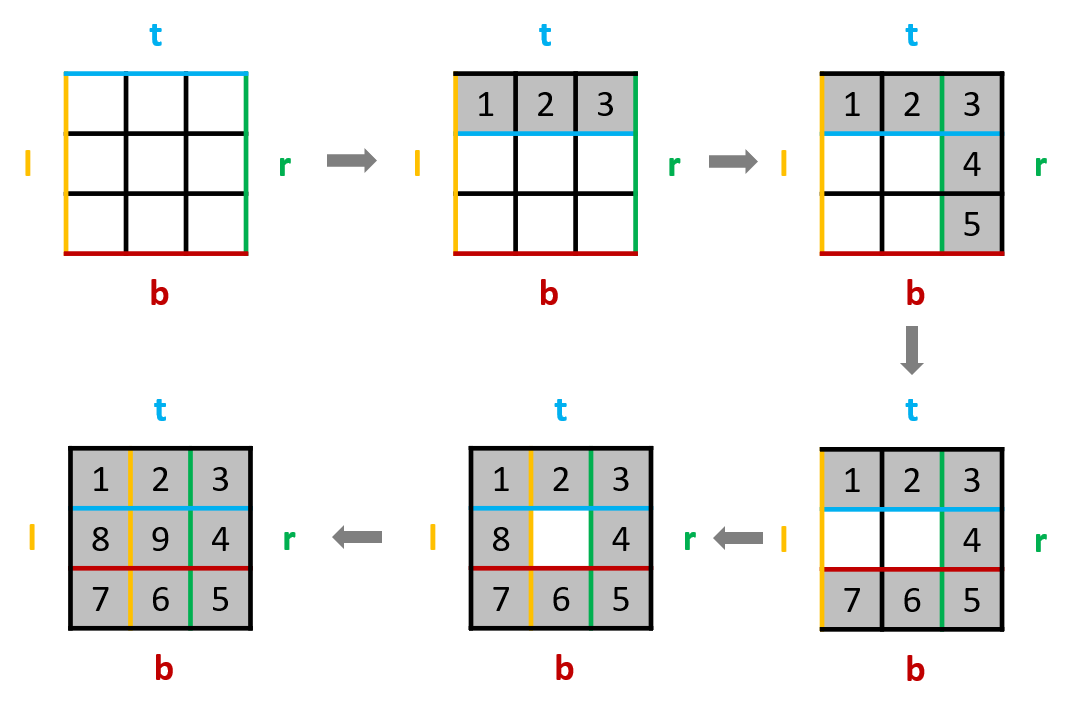
- 生成一个
n×n空矩阵mat,随后模拟整个向内环绕的填入过程:- 定义当前左右上下边界
l,r,t,b,初始值num = 1,迭代终止值tar = n * n; - 当
num <= tar时,始终按照从左到右从上到下从右到左从下到上填入顺序循环,每次填入后:- 执行
num += 1:得到下一个需要填入的数字; - 更新边界:例如从左到右填完后,上边界
t += 1,相当于上边界向内缩 1。
- 执行
- 使用
num <= tar而不是l < r || t < b作为迭代条件,是为了解决当n为奇数时,矩阵中心数字无法在迭代过程中被填充的问题。
- 定义当前左右上下边界
- 最终返回
mat即可。
class Solution {
public int[][] generateMatrix(int n) {
int l = 0, r = n - 1, t = 0, b = n - 1;
int[][] mat = new int[n][n];
int num = 1, tar = n * n;
while(num <= tar){
for(int i = l; i <= r; i++) mat[t][i] = num++; // left to right.
t++;
for(int i = t; i <= b; i++) mat[i][r] = num++; // top to bottom.
r--;
for(int i = r; i >= l; i--) mat[b][i] = num++; // right to left.
b--;
for(int i = b; i >= t; i--) mat[i][l] = num++; // bottom to top.
l++;
}
return mat;
}
}class Solution:
def generateMatrix(self, n: int) -> [[int]]:
l, r, t, b = 0, n - 1, 0, n - 1
mat = [[0 for _ in range(n)] for _ in range(n)]
num, tar = 1, n * n
while num <= tar:
for i in range(l, r + 1): # left to right
mat[t][i] = num
num += 1
t += 1
for i in range(t, b + 1): # top to bottom
mat[i][r] = num
num += 1
r -= 1
for i in range(r, l - 1, -1): # right to left
mat[b][i] = num
num += 1
b -= 1
for i in range(b, t - 1, -1): # bottom to top
mat[i][l] = num
num += 1
l += 1
return mat标签:动态规划,数组
- 设
m×n方格有f(m,n)个不同解,则先让机器人向上走一步 or 向左走一步,可以推出f(m,n) = f(m-1,n) + f(m,n-1)。 - 创建
m+1 × n+1的矩阵,根据以上规则计算对角线方格的值:- 要加一行一列,是为了解决
f(0,0) = f(-1,0) + f(0,-1)出现的边界问题; - 将
f(0,1)置$1$ 是为了给迭代启动值(m×n地图第一行和第一列值都应为1)。
- 要加一行一列,是为了解决
- 时间复杂度
$O(MN)$ ,空间复杂度$O(MN)$ 。
class Solution:
def uniquePaths(self, m: int, n: int) -> int:
matrix = [[0 for _ in range(n+1)] for _ in range(m+1)]
matrix[0][1] = 1
for i in range(1, len(matrix)):
for j in range(1, len(matrix[0])):
matrix[i][j] = matrix[i-1][j] + matrix[i][j-1]
return matrix[-1][-1]class Solution {
public int uniquePaths(int m, int n) {
int[][] matrix = new int[m + 1][n + 1];
matrix[0][1] = 1;
for (int i = 1; i < matrix.length; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j < matrix[0].length; j++) {
matrix[i][j] = matrix[i - 1][j] + matrix[i][j - 1];
}
}
return matrix[m][n];
}
}标签:动态规划,数组
- 和
62题动态规划思路类似,不同的是,需要对障碍物做处理:f(m,n) = f(m-1,n)+f(m,n-1)ifmap(m)(n) != 1elsef(m,n) = 0; - 此处理的含义是
f(m,n)对f(m+1,n)和f(m,n+1)的贡献归零,这样就可以把所有经过障碍物的路线排除掉。
class Solution:
def uniquePathsWithObstacles(self, obstacleGrid: List[List[int]]) -> int:
matrix = [[0 for _ in range(len(obstacleGrid[0])+1)]
for _ in range(len(obstacleGrid)+1)]
matrix[0][1] = 1
for i in range(1, len(matrix)):
for j in range(1, len(matrix[0])):
matrix[i][j] = matrix[i-1][j] + matrix[i][j - 1] \
if obstacleGrid[i-1][j-1] != 1 else 0
return matrix[-1][-1]class Solution {
public int uniquePathsWithObstacles(int[][] obstacleGrid) {
if (obstacleGrid.length == 0) return 0;
int[][] matrix = new int[obstacleGrid.length + 1][obstacleGrid[0].length + 1];
matrix[0][1] = 1;
for (int i = 1; i < matrix.length; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j < matrix[0].length; j++) {
matrix[i][j] = obstacleGrid[i - 1][j - 1] != 1 ? matrix[i - 1][j] + matrix[i][j - 1] : 0;
}
}
return matrix[matrix.length - 1][matrix[0].length - 1];
}
}标签:自动机,哈希表Hash
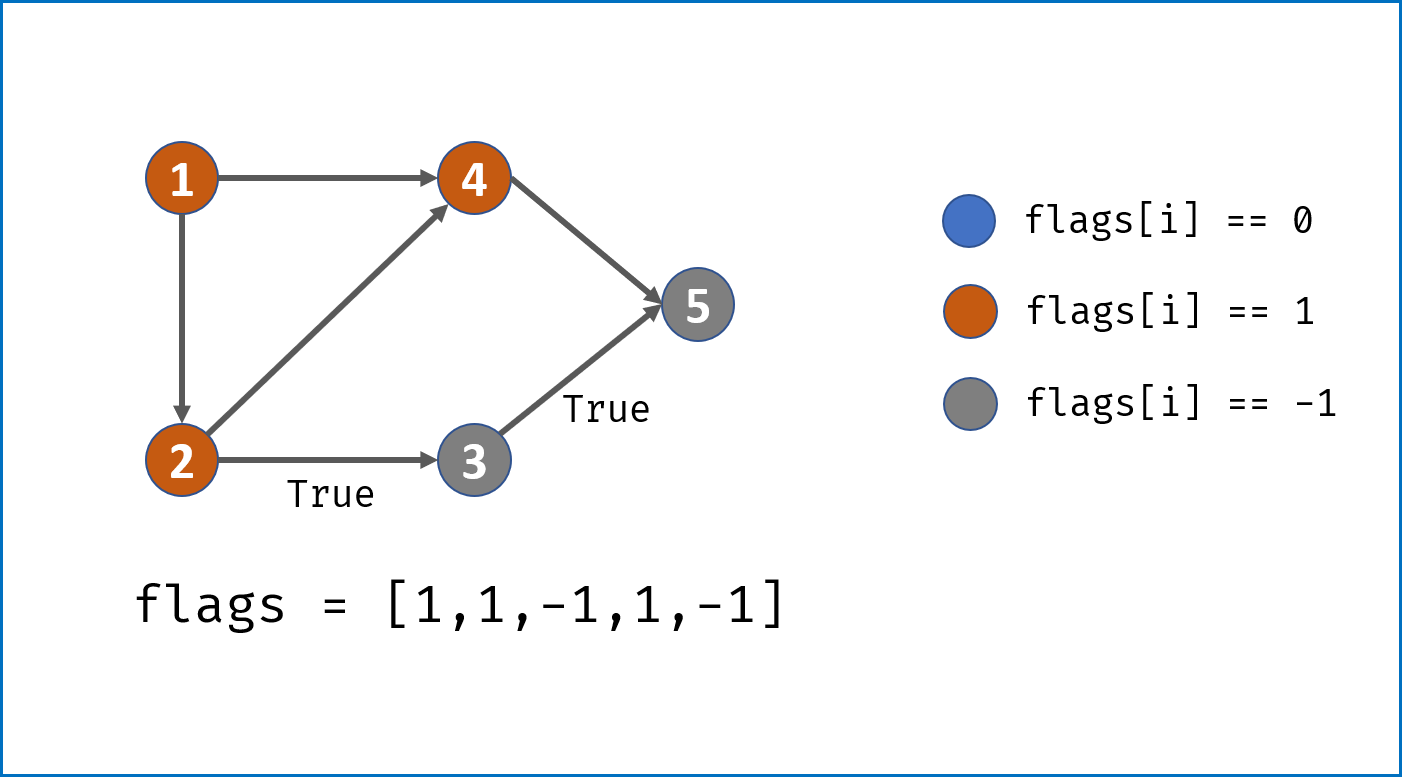
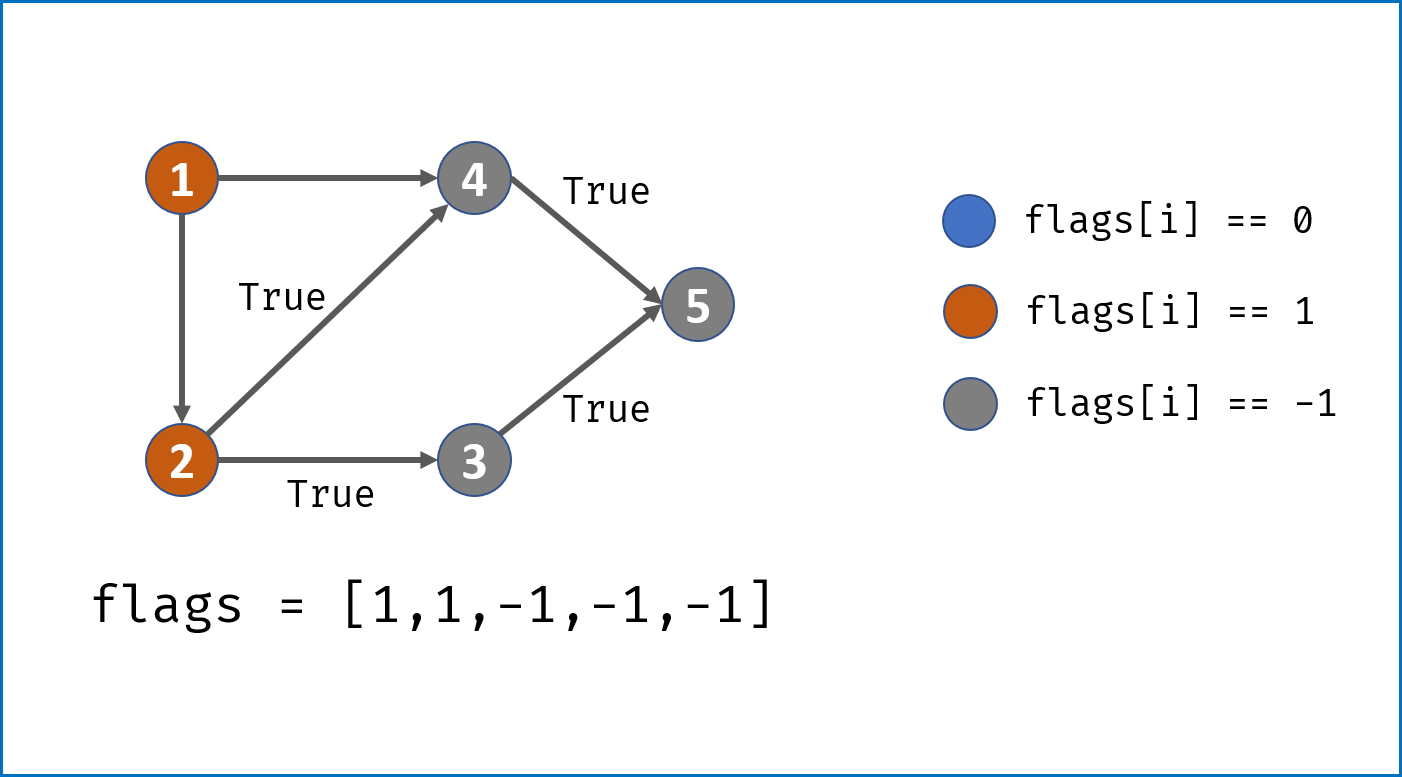
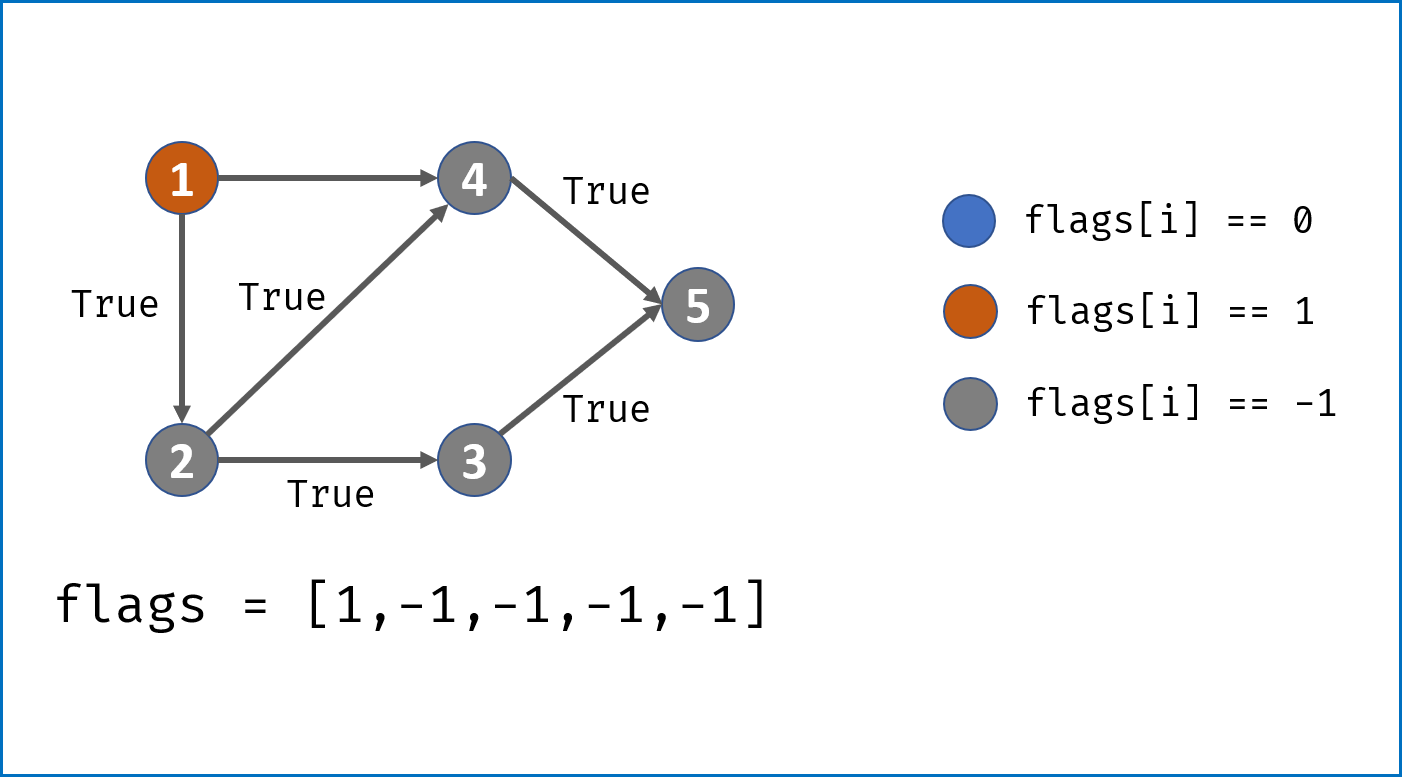
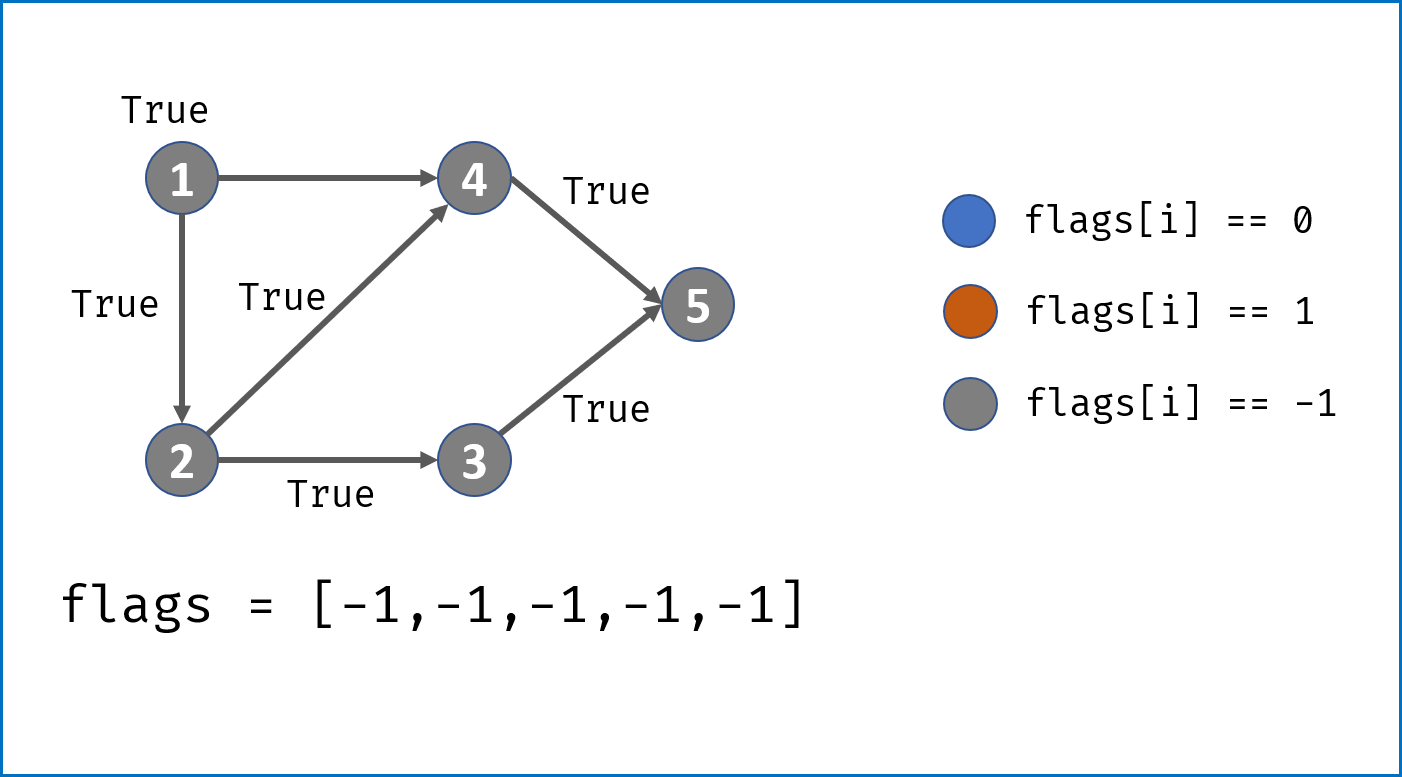
- 画出
状态转移表,结构为states[n]存储n个状态; states[i]为一个HashTable,表示从此状态允许跳转到的状态。- 主循环中遍历字符串,通过状态转移表判断结构是否成立:
- 若中途遇到无法跳转的状态,直接返回
False; - 若成功遍历完字符串,要判断结束状态是否在允许的结束状态内,本题为
[2, 3, 7, 8]。
- 若中途遇到无法跳转的状态,直接返回
class Solution:
def isNumber(self, s: str) -> bool:
states = [
{ 'b': 0, 's': 1, 'd': 2, '.': 4 }, # 0. start
{ 'd': 2, '.': 4 } , # 1. 'sign' before 'e'
{ 'd': 2, '.': 3, 'e': 5, 'b': 8 }, # 2. 'digit' before 'dot'
{ 'd': 3, 'e': 5, 'b': 8 }, # 3. 'dot' with 'digit'
{ 'd': 3 }, # 4. no 'digit' before 'dot'
{ 's': 6, 'd': 7 }, # 5. 'e'
{ 'd': 7 }, # 6. 'sign' after 'e'
{ 'd': 7, 'b': 8 }, # 7. 'digit' after 'e'
{ 'b': 8 } # 8. end with
]
p = 0
for c in s:
if '0' <= c <= '9': typ = 'd'
elif c == ' ': typ = 'b'
elif c == '.': typ = '.'
elif c == 'e': typ = 'e'
elif c in "+-": typ = 's'
else: typ = '?'
if typ not in states[p]: return False
p = states[p][typ]
return p in [2, 3, 7, 8]标签:
- 遍历
digits,判断每位是否为9,若不是则+1并返回,否则将此位置0; - 对于
digits里全为9的情况,需要扩展list,并将首位置为1。
class Solution:
def plusOne(self, digits: [int]) -> [int]:
for i in range(len(digits)-1, -1, -1):
if digits[i] != 9:
digits[i] += 1
return digits
digits[i] = 0
digits[0] = 1
digits.append(0)
return digitsclass Solution {
public int[] plusOne(int[] digits) {
for (int i = digits.length - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
if(digits[i] != 9){
digits[i]++;
return digits;
}
digits[i] = 0;
}
digits = new int[digits.length + 1];
digits[0] = 1;
return digits;
}
}标签:动态规划
- 设爬
n个台阶有f(n)种可能:- 假设先爬
1阶,剩下n-1阶有f(n-1)种可能; - 假设先爬
2阶,剩下n-2阶有f(n-2)种可能, - 因此爬
n阶可以转化为两种爬n-1阶问题之和:f(n) = f(n-1) + f(n-2);
- 假设先爬
- 不难看出,这就是
斐波那契数列公式,此题可转化为求斐波那契数列第n项。
class Solution:
def climbStairs(self, n: int) -> int:
a, b = 1, 1
for _ in range(n-1):
a, b = a + b, a
return aclass Solution {
public int climbStairs(int n) {
int a = 1, b = 1;
for(int i = 0; i < n - 1; i++){
int tmp = a;
a = a + b;
b = tmp;
}
return a;
}
}标签:动态规划
- 典型动态规划题:
- 状态的定义:将
word1前i个字符转化为word2前j个字符最少需要dp[i][j]步; - 状态转移方程:
- 若当前两字符相等
word1[i] == word2[j],则易得最小步数不变dp[i][j] = dp[i-1][j-1]; - 否则,最小步数为增删改的步数1 + 增删改后对应的最小步数,即
dp[i][j] = 1 + min(dp[i-1][j], dp[i][j-1], dp[i-1][j-1]),具体有3种情况:-
dp[i-1][j]+ 删除word1[i]操作;(删除word1[i]后就从dp[i][j]转化为了dp[i-1][j],以下同理) -
dp[i][j-1]+ 在word1[i]后添加word2[j]操作; -
dp[i-1][j-1]+ 将word1[i]修改为word2[j]操作。
-
- 若当前两字符相等
- 返回
dp[-1][-1],即为最少步数。
- 状态的定义:将
- 时空间复杂度均为
$O(MN)$ 。
class Solution:
def minDistance(self, word1: str, word2: str) -> int:
dp = [[0 for _ in range(len(word2) + 1)] for _ in range(len(word1) + 1)]
for i in range(1, len(dp)): dp[i][0] = i
for i in range(1, len(dp[0])): dp[0][i] = i
for i in range(1, len(dp)):
for j in range(1, len(dp[0])):
dp[i][j] = 1 + min(dp[i-1][j], dp[i][j-1], dp[i-1][j-1]) if word1[i-1] != word2[j-1] else dp[i-1][j-1]
return dp[-1][-1]class Solution {
public int minDistance(String word1, String word2) {
int[][] dp = new int[word1.length() + 1][word2.length() + 1];
for(int i = 1; i < dp.length; i++) dp[i][0] = i;
for(int i = 1; i < dp[0].length; i++) dp[0][i] = i;
for(int i = 1; i < dp.length; i++) {
for(int j = 1; j < dp[0].length; j++) {
dp[i][j] = word1.charAt(i - 1) != word2.charAt(j - 1) ?
1 + Math.min(dp[i-1][j-1], Math.min(dp[i-1][j], dp[i][j-1])) : dp[i-1][j-1];
}
}
return dp[word1.length()][word2.length()];
}
}标签:回溯法
- 从空子集开始,遍历
$[j ,nums]$ 并迭代,添加每个分支。
class Solution(object):
def subsets(self, nums):
res = []
def children(j, tmp):
res.append(tmp)
for i in range(j, len(nums)):
children(i + 1, tmp + [nums[i]])
children(0, [])
return resclass Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> subsets(int[] nums) {
List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>();
children(nums, 0, res, new ArrayList<>());
return res;
}
private void children(int[] nums, int j, List<List<Integer>> res, List<Integer> tmp) {
res.add(new ArrayList<>(tmp));
for(int i = j; i < nums.length; i++){
tmp.add(nums[i]);
children(nums, i + 1, res, tmp);
tmp.remove(tmp.size() - 1);
}
}
}- 对于集合
$nums$ 的所有组合$res$ ,若向$nums$ 中添加数字$n$ ,则新组合等于$res ∪ (res + n)$。其中$res + n$ 为给$res$ 中所有组合尾部添加数字$n$。
class Solution:
def subsets(self, nums: [int]) -> [[int]]:
res = [[]]
for i in nums:
res = res + [num + [i] for num in res]
return resclass Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> subsets(int[] nums) {
List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>();
res.add(new ArrayList<Integer>());
for(int num : nums){
int size = res.size();
for(int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
List<Integer> tmp = new ArrayList<>(res.get(i));
tmp.add(num);
res.add(tmp);
}
}
return res;
}
}标签:数组、双指针
- 题目关于合并两个数组,我们自然想到双指针,通过比较两指针当前元素大小添加至新数组,完成数组合并,复杂度
O(M+N)。 - 本题目要求将
nums2合并至nums1,即需要考虑在合并过程中,不能影响nums1指针未到达元素(如果从数组头部开始,一直向前修改nums1的值,但num1的指针还未到达那些值,则会造成nums1值的丢失)。 - 因此,考虑设置两指针
ij分别从nums1nums2数字尾部开始,修改点tail从nums[m + n - 1]即整个尾部开始修改。这样就解决了nums1元素丢失的问题(因为一定有tail >= i)。 - 第一轮循环合并完后,由于可能
nums2指针未走完,需要将nums2剩余首部覆盖至nums1首部。nums1指针未走完不需要做任何多余操作,因为覆盖前后相同。
class Solution:
def merge(self, nums1: List[int], m: int, nums2: List[int], n: int) -> None:
tail, i, j = m + n - 1, m - 1, n - 1
while i >= 0 and j >= 0:
if nums1[i] > nums2[j]:
nums1[tail] = nums1[i]
i -= 1
else:
nums1[tail] = nums2[j]
j -= 1
tail -= 1
for k in range(j, -1, -1): nums1[k] = nums2[k]class Solution {
public void merge(int[] nums1, int m, int[] nums2, int n) {
int tail = m + n - 1, i = m - 1, j = n - 1;
while (i >= 0 && j >= 0) {
if (nums1[i] > nums2[j]) nums1[tail] = nums1[i--];
else nums1[tail] = nums2[j--];
tail--;
}
for(int k = j; k >= 0; k--) nums1[k] = nums2[k];
}
}标签:
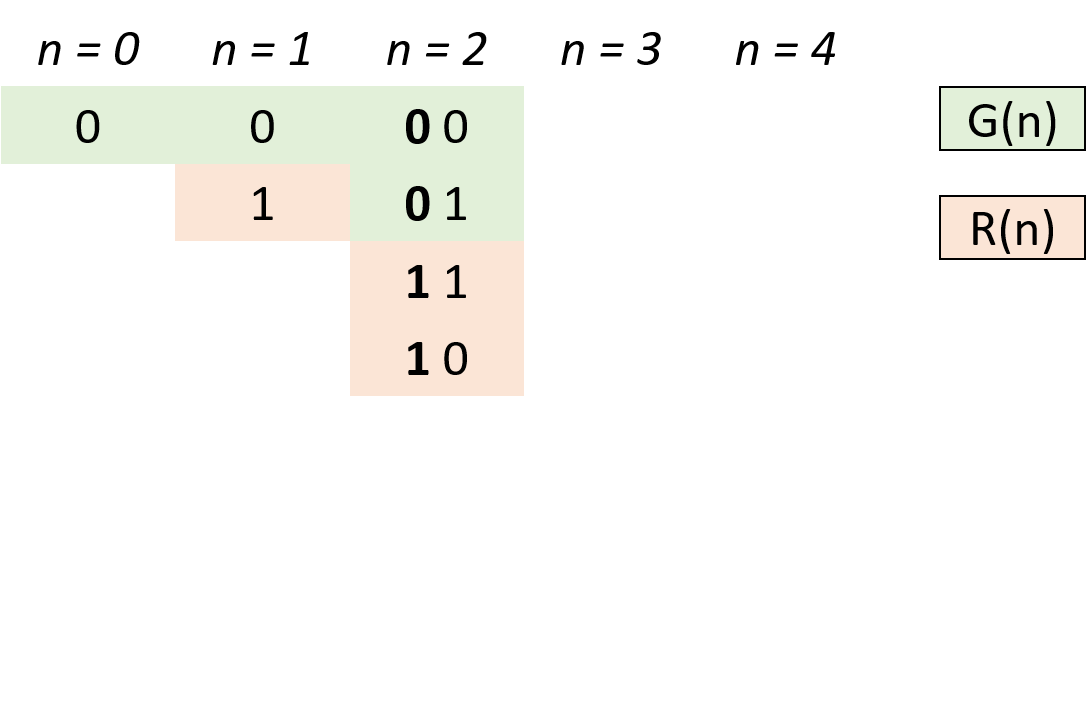
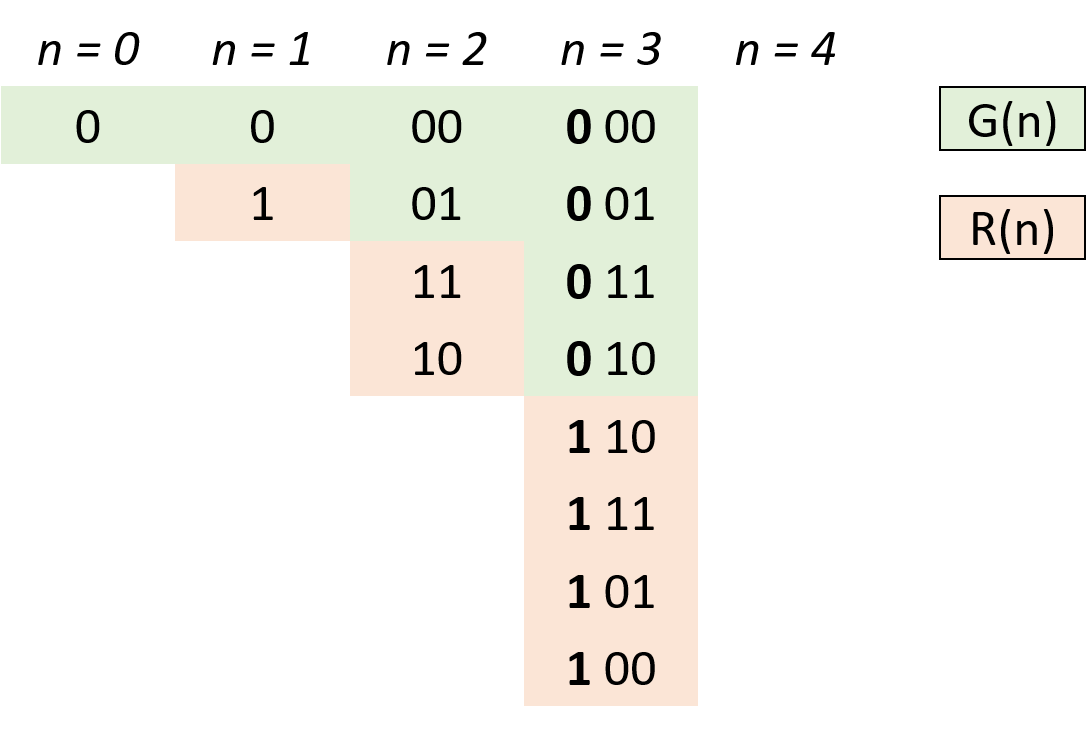
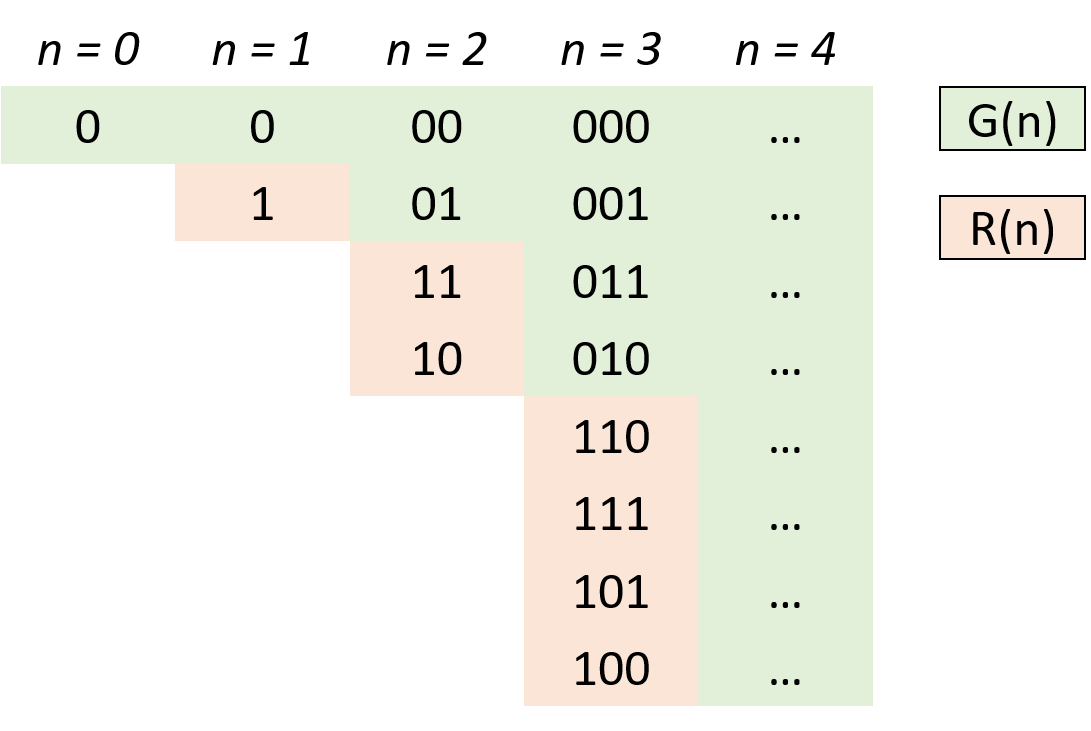
- 设
$n$ 阶格雷码集合为$G(n)$ ,则$G(n+1)$ 阶格雷码为:- 给
$G(n)$ 阶格雷码每个元素二进制形式前面添加$0$ ,得到$G'(n)$ ; - 设
$G(n)$ 集合倒序(镜像)为$R(n)$ ,给$R(n)$ 每个元素二进制形式前面添加$1$ ,得到$R'(n)$ ; -
$G(n+1) = G'(n) ∪ R'(n)$ 拼接两个集合即可得到下一阶格雷码。
- 给
- 根据以上规律,可从
$0$ 阶格雷码推导致任何阶格雷码。 - 代码解析:
- 由于最高位前默认为
$0$ ,因此$G'(n) = G(n)$ ,只需在res(即$G(n)$ )后添加$R'(n)$ 即可; - 计算
$R'(n)$ :执行head = 1 << i计算出对应位数,以给$R(n)$ 前添加$1$ 得到对应$R'(n)$ ; - 倒序遍历
res(即$G(n)$ ):依次求得$R'(n)$ 各元素添加至res尾端,遍历完成后res(即 $G(n+1)$)。
- 由于最高位前默认为
class Solution:
def grayCode(self, n: int) -> List[int]:
res, head = [0], 1
for i in range(n):
for j in range(len(res) - 1, -1, -1):
res.append(head + res[j])
head <<= 1
return resclass Solution {
public List<Integer> grayCode(int n) {
List<Integer> res = new ArrayList<Integer>() {{ add(0); }};
int head = 1;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = res.size() - 1; j >= 0; j--)
res.add(head + res.get(j));
head <<= 1;
}
return res;
}
}标签:二叉搜索树BST,中序遍历
- 二叉搜索树的中序遍历是一个已排序
List,我们可以根据此性质对树进行中序遍历并判断: - 设置一个全局变量
tmp,记录中序遍历上一个值,始终比较当前值和上一个值大小,若当前值<=上一个值则返回false; - 当找到不符搜索树性质情况时,一路
返回false,以下python和java使用两种写法,但原理上是等价的。
class Solution:
def __init__(self):
self.tmp = -float('inf')
def isValidBST(self, root: TreeNode) -> bool:
if not root: return True
if not self.isValidBST(root.left): return False
if self.tmp >= root.val: return False
self.tmp = root.val
if not self.isValidBST(root.right): return False
return Trueclass Solution {
long tmp = Long.MIN_VALUE;
public boolean isValidBST(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null) return true;
if (isValidBST(root.left)) {
if (tmp < root.val) {
tmp = root.val;
return isValidBST(root.right);
}
}
return false;
}
}标签:深度优先搜索DFS
- 构建一个match函数,通过深度优先遍历DFS判断是否为对称二叉树,思路是在遍历过程中,每次对比当前点与对称点的值是否相等。
- 参数:
- 节点
l节点r,每轮递归比较两节点值是否相等l.val == r.val;
- 节点
- 返回值:
- 节点
l和r值是否相等 且 - 节点
l的左子树和节点r右子树是否对称 且 - 节点
l的右子树和节点r左子树是否对称
- 节点
- 终止条件:
- 节点
l和r同时为null则返回true,代表同时越过叶子节点,以上全部值相同; - 节点
l和r有一个为null则返回false,代表只有一边越过叶子节点,意味着树不对称。
- 节点
- 参数:
class Solution:
def isSymmetric(self, root: TreeNode) -> bool:
def match(l, r):
if not l and not r: return True
if not l or not r: return False
return l.val == r.val and \
match(l.left, r.right) and \
match(l.right, r.left)
return match(root, root)class Solution {
public boolean isSymmetric(TreeNode root) {
return match(root, root);
}
private boolean match(TreeNode l, TreeNode r) {
if (l == null && r == null) return true;
if (l == null || r == null) return false;
return l.val == r.val &&
match(l.left, r.right) &&
match(l.right, r.left);
}
}标签:广度优先搜索BFS
-
cur存储当前层节点,遍历cur并执行:- 统计
cur每个节点值保存至tmp中; - 统计
cur中每个节点的左右非空节点,保存至nex中;
- 统计
- 遍历
cur完成后,将当前层值tmp添加进res中;并且cur = nex将当前层切换至下一层,继续迭代。 - 最终返回
res即可。 - 时间空间复杂度均为
$O(N)$ 。
class Solution:
def levelOrder(self, root: TreeNode) -> List[List[int]]:
if not root: return []
cur, nex, tmp, res = [root], [], [], []
while cur:
for r in cur:
tmp.append(r.val)
if r.left: nex.append(r.left)
if r.right: nex.append(r.right)
res.append(tmp[:])
cur, nex, tmp = nex, [], []
return resclass Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> levelOrder(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null) return new ArrayList<>();
List<TreeNode> cur = new ArrayList<>(), nex = new ArrayList<>();
cur.add(root);
List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>();
List<Integer> tmp = new ArrayList<>();
while(cur.size() > 0){
for(TreeNode r : cur) {
tmp.add(r.val);
if(r.left != null) nex.add(r.left);
if(r.right != null) nex.add(r.right);
}
res.add(tmp);
cur = nex;
tmp = new ArrayList<>();
nex = new ArrayList<>();
}
return res;
}
}标签:递归、深度优先搜索DFS
递归公式:树深度 = max(左子树深度,右子树深度) + 1终止条件:越过叶子节点,return 0
class Solution:
def maxDepth(self, root: TreeNode) -> int:
if not root: return 0
return max(self.maxDepth(root.left), self.maxDepth(root.right)) + 1class Solution {
public int maxDepth(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) return 0;
return Math.max(maxDepth(root.left), maxDepth(root.right)) + 1;
}
}标签:
- 前序遍历和中序遍历有以下特点:
- 前序遍历: 根节点 | 左子树 | 右子树 ; 例如:
[1 | 2 4 5 | 3 6 7] - 中序遍历: 左子树 | 根节点 | 右子树 ; 例如:
[4 2 5 | 1 | 6 3 7] - 对于每个左子树、右子树的前序遍历和中序遍历依然有此规律。
- 前序遍历: 根节点 | 左子树 | 右子树 ; 例如:
- 思路:
- 按前序遍历的顺序每次pop并建立节点
root,在中序遍历中找到root的对应index,划分出哪些节点构成此节点的左子树inorder[:i],哪些构成右子树inorder[i+1:]。 - 返回值: 递归构建完当前节点
root左右子树后,返回root,作为上轮递归父节点的left或right。 - 终止条件: 当
inorder[:i]中序遍历无剩余元素时,说明当前root已经越过叶子节点,直接返回None。
- 按前序遍历的顺序每次pop并建立节点
class Solution:
def buildTree(self, preorder: [int], inorder: [int]) -> TreeNode:
if not inorder: return
root = TreeNode(preorder.pop(0))
i = inorder.index(root.val)
root.left = self.buildTree(preorder, inorder[:i])
root.right = self.buildTree(preorder, inorder[i+1:])
return rootclass Solution {
public TreeNode buildTree(int[] preorder, int[] inorder) {
return build(preorder, 0, inorder, 0, inorder.length);
}
private TreeNode build(int[] preorder, int p, int[] inorder, int i, int j){
if(i >= j) return null;
TreeNode root = new TreeNode(preorder[p]);
int k = 0;
while(inorder[k] != root.val) k++;
root.left = build(preorder, p + 1, inorder, i, k);
root.right = build(preorder, p + 1 + k - i, inorder, k + 1, j);
return root;
}
}标签:平衡二叉树BBT,二叉搜索树BST
- 将一个排序array转化为平衡二叉搜索树:
平衡二叉树:对于每个根节点,左右子树高度差 <= 1;二叉搜索树:对于每个节点,其左子树值<此节点值,右子树>此节点值。
- 要满足以上两个特点,我们自然想到以
array中点值作为根节点值,并递归重建,这样就可以同时保证以上两个条件。
class Solution:
def sortedArrayToBST(self, nums: List[int]) -> TreeNode:
if not nums: return
mid = len(nums) // 2
root = TreeNode(nums[mid])
root.left = self.sortedArrayToBST(nums[:mid])
root.right = self.sortedArrayToBST(nums[mid+1:])
return rootclass Solution {
public TreeNode sortedArrayToBST(int[] nums) {
return toBST(nums, 0, nums.length - 1);
}
private TreeNode toBST(int[] nums, int left, int right) {
if(left > right) return null;
int mid = (left + right) / 2;
TreeNode root = new TreeNode(nums[mid]);
root.left = toBST(nums, left, mid - 1);
root.right = toBST(nums, mid + 1, right);
return root;
}
}标签:二叉搜索树BST,深度优先搜索DFS,回溯法
- 做过数组还原平衡二叉搜索树(推荐先做
题号108),我们知道,在array中每次取中点作为根节点,左右分别构建左右子树,递归直至根节点为空。 - 链表的特性导致我们无法像数组那样通过下标访问各个元素。若想按照
108题的做法,就需要设置两个指针p1p2,p1每走一步p2走两步,这样p2结束时p1就在中点。但这样会导致每次递归都需要重复遍历链表,效率较低。 - 我们考虑是否可以让建立节点的顺序匹配链表元素顺序?这样每次建立节点时,只需要获取链表下一个元素即可。
- 使用递归模拟
中序遍历过程,建立节点的顺序即与链表元素顺序一一对应,bottom-up建立树,最终返回根节点。 - 递归前需要统计链表长度
n,整体算法复杂度O(N)。
class Solution:
def __init__(self):
self.head = None
def sortedListToBST(self, head: ListNode) -> TreeNode:
n, self.head = 0, head
while head:
head = head.next
n += 1
return self.to_bst(0, n - 1)
def to_bst(self, left, right):
if left > right: return
m = (left + right) // 2
left_child = self.to_bst(left, m - 1)
father = TreeNode(self.head.val)
self.head = self.head.next
father.left = left_child
father.right = self.to_bst(m + 1, right)
return fatherclass Solution {
private ListNode node;
public TreeNode sortedListToBST(ListNode head) {
int n = 0;
node = head;
while(head != null){
head = head.next;
n++;
}
return toBST(0, n-1);
}
private TreeNode toBST(int left, int right){
if(left > right) return null;
int m = (left + right) / 2;
TreeNode left_child = toBST(left, m-1);
TreeNode father = new TreeNode(node.val);
node = node.next;
father.left = left_child;
father.right = toBST(m+1, right);
return father;
}
}标签:平衡二叉树BBT,递归
- 对二叉树做深度优先遍历DFS,递归过程中:
- 终止条件:当DFS越过叶子节点时,返回高度
0; - 返回值:
- 从底至顶,返回以每个节点
root为根节点的子树最大高度(左右子树中最大的高度值加1max(left,right) + 1); - 当我们发现有一例
左/右子树高度差 > 1的情况时,代表此树不是平衡树,返回-1;
- 从底至顶,返回以每个节点
- 当发现不是平衡树时,后面的高度计算都没有意义了,因此一路返回
-1,避免后续多余计算。
- 终止条件:当DFS越过叶子节点时,返回高度
- 最差情况是对树做一遍完整DFS,时间复杂度为
O(N)。
class Solution:
def isBalanced(self, root: TreeNode) -> bool:
return self.depth(root) != -1
def depth(self, root):
if not root: return 0
left = self.depth(root.left)
if left == -1: return -1
right = self.depth(root.right)
if right == -1: return -1
return max(left, right) + 1 if abs(left - right) < 2 else -1class Solution {
public boolean isBalanced(TreeNode root) {
return depth(root) != -1;
}
private int depth(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) return 0;
int left = depth(root.left);
if(left == -1) return -1;
int right = depth(root.right);
if(right == -1) return -1;
return Math.abs(left - right) < 2 ? Math.max(left, right) + 1 : -1;
}
}- 构造一个获取当前节点最大深度的方法
depth(),通过比较左右子树最大高度差abs(self.depth(root.left) - self.depth(root.right)),来判断以此节点为根节点下是否是二叉平衡树; - 从顶至底DFS,以每个节点为根节点,递归判断是否是平衡二叉树:
- 若所有根节点都满足平衡二叉树性质,则返回
True; - 若其中任何一个节点作为根节点时,不满足平衡二叉树性质,则返回
False。
- 若所有根节点都满足平衡二叉树性质,则返回
- 本方法产生大量重复的节点访问和计算,最差情况下时间复杂度
O(N^2)。
class Solution:
def isBalanced(self, root: TreeNode) -> bool:
if not root: return True
return abs(self.depth(root.left) - self.depth(root.right)) <= 1 and \
self.isBalanced(root.left) and self.isBalanced(root.right)
def depth(self, root):
if not root: return 0
return max(self.depth(root.left), self.depth(root.right)) + 1class Solution {
public boolean isBalanced(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) return true;
return Math.abs(depth(root.left) - depth(root.right)) <= 1 && isBalanced(root.left) && isBalanced(root.right);
}
private int depth(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) return 0;
return Math.max(depth(root.left), depth(root.right)) + 1;
}
}标签:二叉树,递归
- 这道题和
maximum depth题正好相反,是求根节点到叶子节点的最小深度,为确保统计的是根节点到叶子节点的深度,需要注意:- 当前节点
左右子树有一个为空时,返回的应是非空子树的最小深度,而不是空子树深度0;若返回0相当于把当前节点认为成叶子节点,与此节点有非空子树矛盾。 - 当
左右子树都不为空时,和maximum depth题一样,返回左右子树深度的最小值。 - 当
左右子树都为空时,只有1个根节点深度为1(根节点与叶子节点重合)。
- 当前节点
class Solution:
def minDepth(self, root: TreeNode) -> int:
if not root: return 0
if not root.left: return self.minDepth(root.right) + 1
if not root.right: return self.minDepth(root.left) + 1
return min(self.minDepth(root.left), self.minDepth(root.right)) + 1class Solution {
public int minDepth(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null) return 0;
if(root.left == null) return minDepth(root.right) + 1;
if(root.right == null) return minDepth(root.left) + 1;
return Math.min(minDepth(root.left),minDepth(root.right)) + 1;
}
}标签:二叉树,递归
- 根据题目样例,可以看出生成链表的节点顺序为树前序遍历的顺序。因此,我们思路是对树执行前序遍历,并修改每个节点的指针指向。
- 我们使用递归方法前序遍历,其中:
- 终止条件:越过叶子节点,即
root == null,直接返回; - 指针修改:
- 用一个全局变量
pre保存上一个节点:将pre右子树指针指向当前节点root;将pre左子树指针清空。 - 进入下轮递归前,将当前节点
root赋给pre; - 由于在
self.flatten(root.left)方法执行后执行flatten(root.right),但root.right指向节点可能已经改变,造成错误的递归顺序,因此需要在执行此方法前存储root.right至right变量,用此变量做每个节点的右子树递归。
- 用一个全局变量
- 终止条件:越过叶子节点,即
- 本题无需返回值,时空间复杂度均为
O(N)。
class Solution:
def __init__(self):
self.pre = None
def flatten(self, root: TreeNode) -> None:
if not root: return
if self.pre: self.pre.right, self.pre.left = root, None
self.pre = root
right = root.right
self.flatten(root.left)
self.flatten(right)class Solution {
private TreeNode pre;
public void flatten(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null) return;
if(pre != null){
pre.right = root;
pre.left = null;
}
pre = root;
TreeNode right = root.right;
flatten(root.left);
flatten(right);
}
}标签:
- 题意要求先买在卖,找到利润最大的卖卖方案。
- 按时间顺序,从前到后遍历股票价格数组
prices,每次迭代做两件事:- 统计直至目前的最低成本
cost,因为今日卖出的利润等于今日price减去前几日的price最小值(即最小成本); - 计算直至目前的最高利润
profit。
- 统计直至目前的最低成本
- 最终,返回最高利润
profit。
class Solution:
def maxProfit(self, prices: List[int]) -> int:
cost, profit = float("+inf"), 0
for price in prices:
cost = min(price, cost)
profit = max(price - cost, profit)
return profitclass Solution {
public int maxProfit(int[] prices) {
int profit = 0, cost = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
for (int price : prices) {
cost = Math.min(cost, price);
profit = Math.max(profit, price - cost);
}
return profit;
}
}标签:
- 考虑买股票的策略:设今天价格
p1,明天价格p2,若p1 < p2则今天买入明天卖出,赚取p2 - p1;- 若遇到价格连续上涨的交易日,第一天买最后一天卖收益最大,等价于每天买卖(因为没有交易手续费);
- 若遇到价格连续下降的交易日,不买卖,因此永远不会亏钱。
- 赚到了所有交易日的钱,所有亏钱的交易日都未交易,理所当然会利益最大化。
class Solution:
def maxProfit(self, prices: List[int]) -> int:
profit = 0
for i in range(1, len(prices)):
tmp = prices[i] - prices[i - 1]
if tmp > 0: profit += tmp
return profitclass Solution {
public int maxProfit(int[] prices) {
int profit = 0;
for (int i = 1; i < prices.length; i++) {
int tmp = prices[i] - prices[i - 1];
if (tmp > 0) profit += tmp;
}
return profit;
}
}标签:二叉树,递归
- 根据题意,最大路径和可能出现在:
- 左子树中
- 右子树中
- 包含根节点与左右子树
- 我们的思路是递归从bottom向top
return的过程中,记录左子树和右子树中路径更大的那个,并向父节点提供当前节点和子树组成的最大值。 - 递归设计:
- 返回值:
(root.val) + max(left, right)即此节点与左右子树最大值之和,较差的解直接被舍弃,不会再被用到。- 需要注意的是,若计算结果
tmp <= 0,意味着对根节点有负贡献,不会在任何情况选这条路(父节点中止),因此返回0。
- 需要注意的是,若计算结果
- 递归终止条件:越过叶子节点,返回
0; - 记录最大值:当前节点
最大值 = root.val + left + right。
- 返回值:
- 最终返回所有路径中的全局最大值即可。
class Solution:
def maxPathSum(self, root: TreeNode) -> int:
self.max = float('-inf')
self.max_path(root)
return self.max
def max_path(self, root):
if not root: return 0
left = self.max_path(root.left)
right = self.max_path(root.right)
self.max = max(left + right + root.val, self.max)
tmp = max(left, right) + root.val
return tmp if tmp > 0 else 0class Solution {
private int max = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
public int maxPathSum(TreeNode root) {
maxPath(root);
return max;
}
private int maxPath(TreeNode root){
if(root == null) return 0;
int left = maxPath(root.left);
int right = maxPath(root.right);
max = Math.max(root.val + left + right, max);
int tmp = Math.max(left, right) + root.val;
return tmp > 0 ? tmp : 0;
}
}标签:字符串,双指针
- 设置左、右
双指针,向中间判断; - 跳过
非数字字母的字符; - 将字母全部转化为
小写体,之后判断。 java用了库函数,python纯自己实现(运行时间不太理想)。
class Solution:
def isPalindrome(self, s: str) -> bool:
left, right = 0, len(s) - 1
case = abs(ord('a') - ord('A'))
while left < right:
while left < right and self.not_letters_digits(s[left]): left += 1
while left < right and self.not_letters_digits(s[right]): right -= 1
s_l = ord(s[left]) - case if s[left] >= 'a' else ord(s[left])
s_r = ord(s[right]) - case if s[right] >= 'a' else ord(s[right])
if s_l != s_r: return False
left += 1
right -= 1
return True
def not_letters_digits(self, c):
return not 'A' <= c <= 'Z' and not 'a' <= c <= 'z' and not '0' <= c <= '9'class Solution {
public boolean isPalindrome(String s) {
int i = 0, j = s.length() - 1;
while(i < j){
while(i < j && !Character.isLetterOrDigit(s.charAt(i))) i++;
while(i < j && !Character.isLetterOrDigit(s.charAt(j))) j--;
if(Character.toLowerCase(s.charAt(i)) != Character.toLowerCase(s.charAt(j))) return false;
i++; j--;
}
return true;
}
}标签:图,深度优先遍历DFS
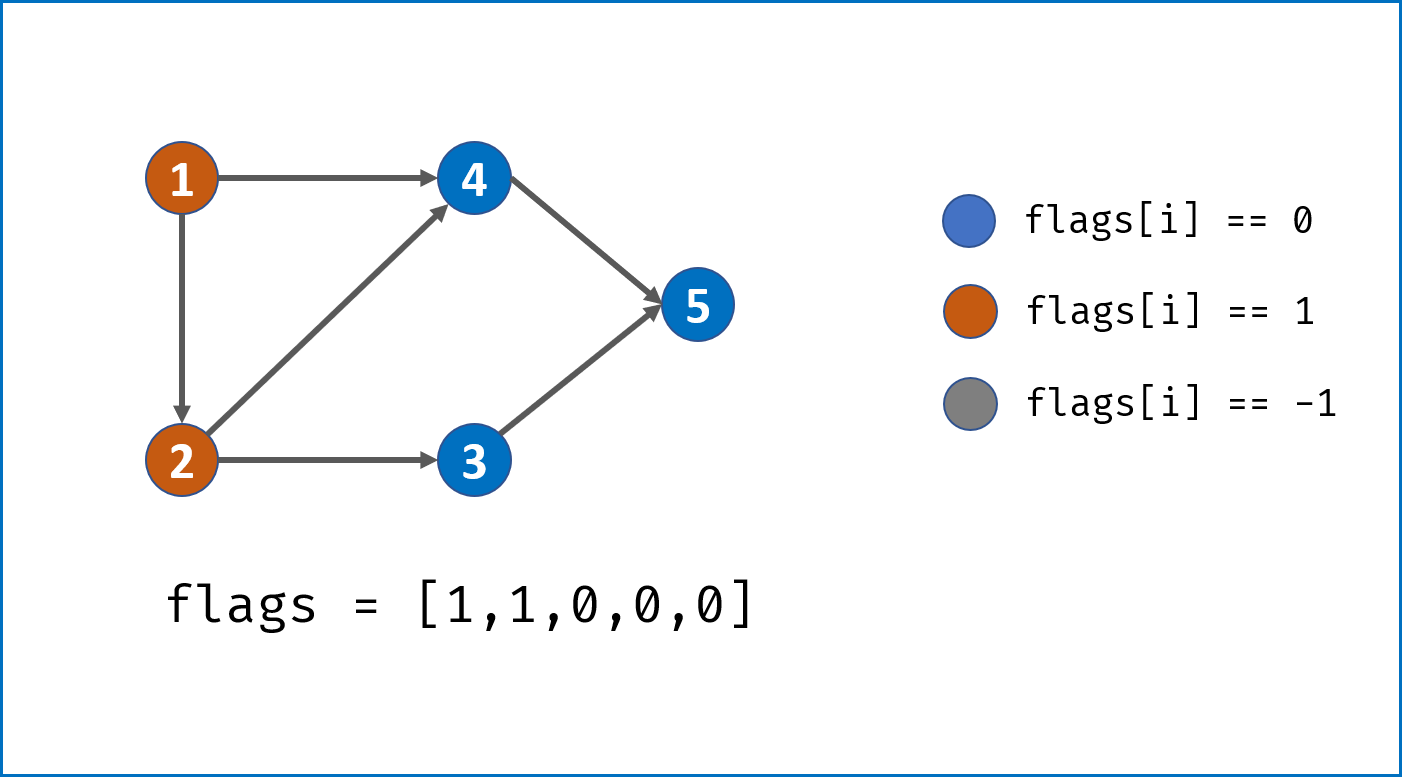
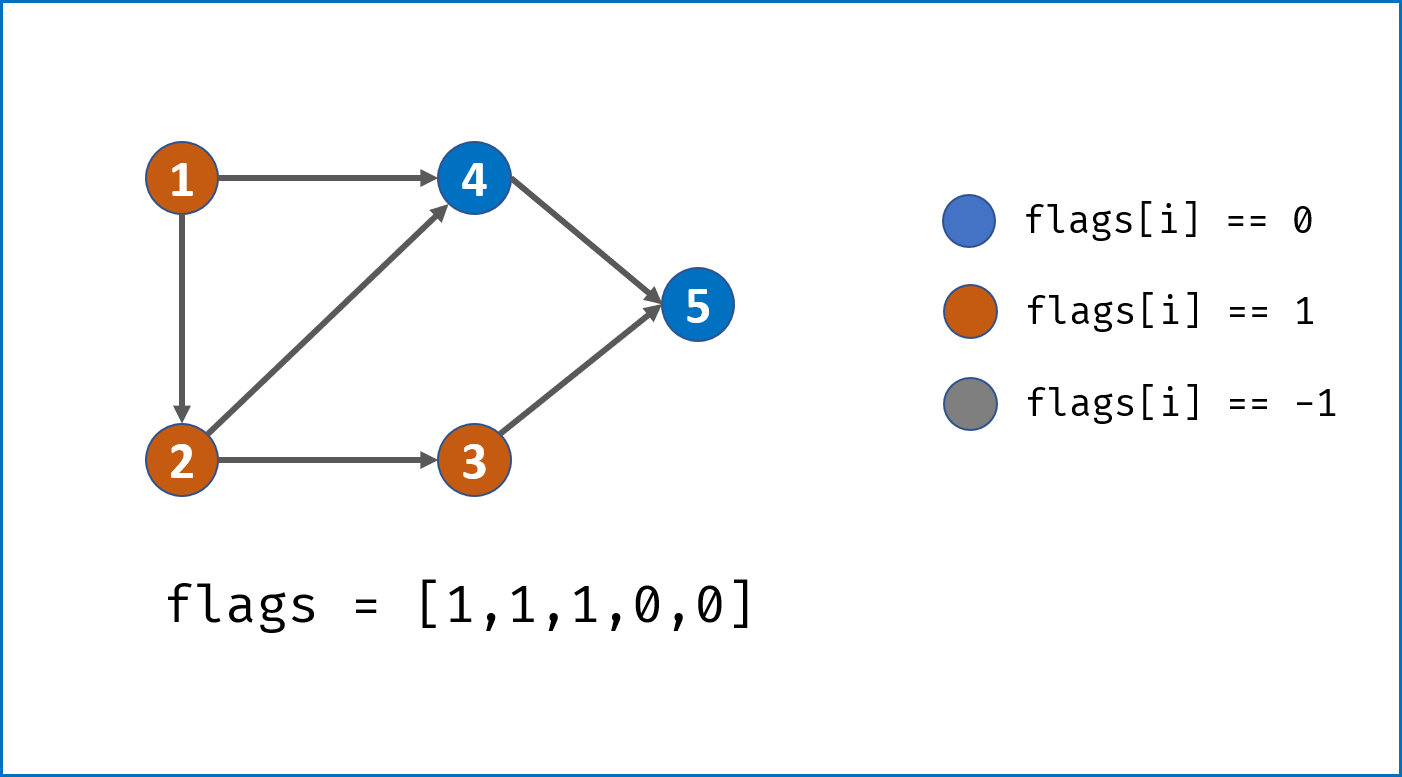
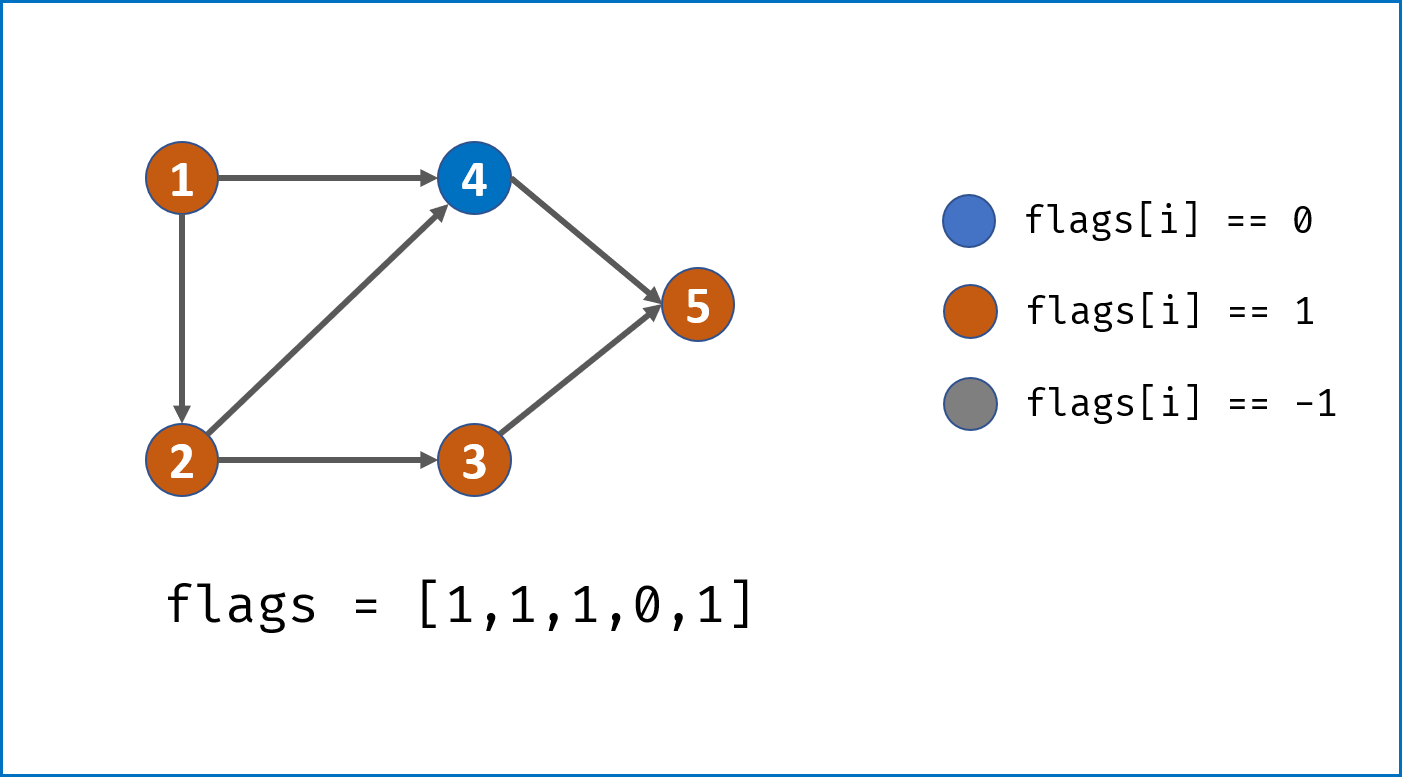
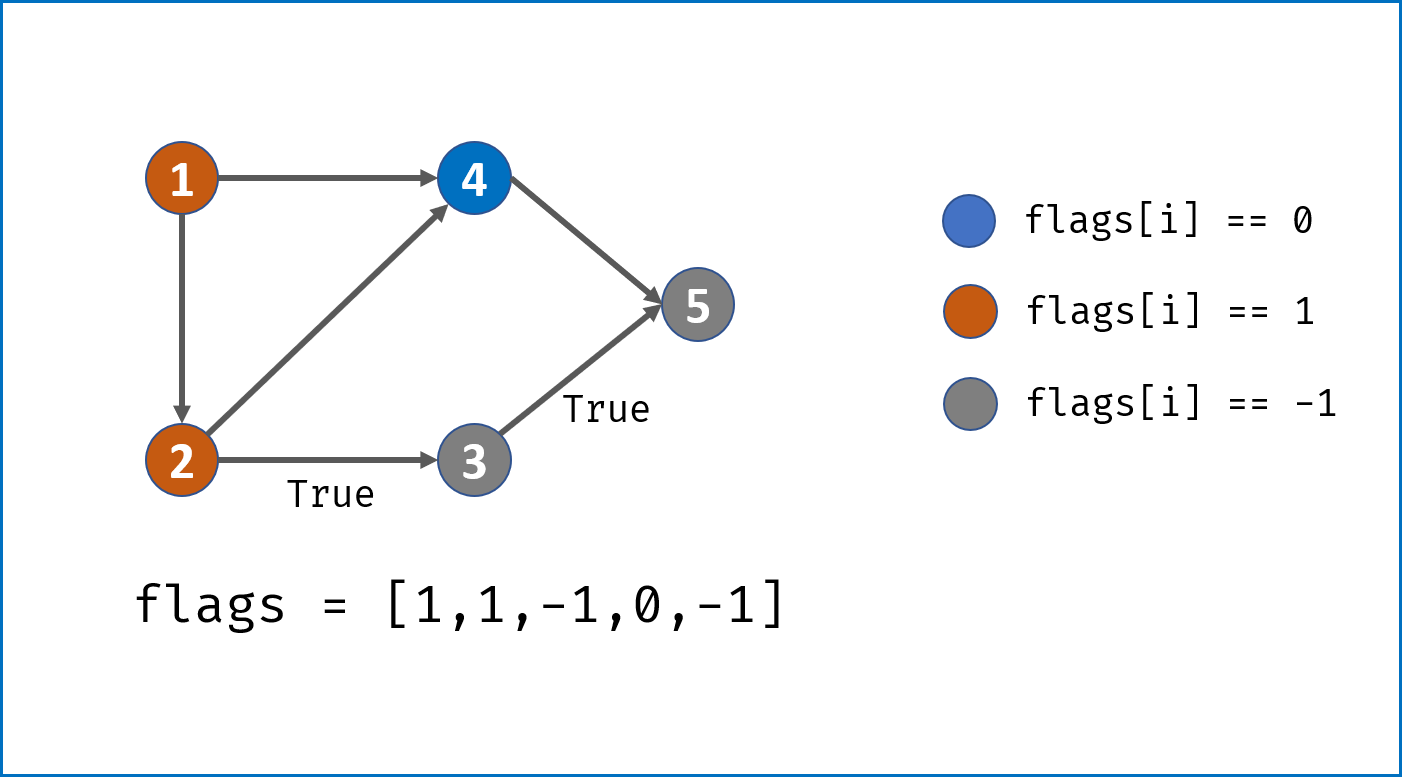
- 从给定节点开始,使用DFS遍历整个图,建立
node节点的复制copy节点; - 递归遍历
node.neighbors,建立copy节点的各个neighbor; - 每次建立
copy时,将节点添加进HashMap:key = node,value = copy
终止条件:每次dfs首先判断HashMap中是否已经存在此node节点,若存在则直接return此HashMap中的copy节点。
class Solution:
def cloneGraph(self, node: 'Node') -> 'Node':
self.dic = {} # store all the copy nodes: dic[node] = copy
return self.dfs(node)
def dfs(self, node):
if node not in self.dic:
self.dic[node] = copy = Node(node.val, []) # get copy of the node 'node' and add it into the dictionary.
for nei in node.neighbors: # recursive: get the neighbors of the node 'copy'.
copy.neighbors.append(self.dfs(nei))
return self.dic[node] # return the node 'copy'.class Solution {
private Map<Node, Node> map;
public Node cloneGraph(Node node) {
map = new HashMap<>();
return dfs(node);
}
private Node dfs(Node node) {
if(!map.containsKey(node)){
Node copy = new Node(node.val, new ArrayList<Node>());
map.put(node, copy);
for(Node nei : node.neighbors){
copy.neighbors.add(dfs(nei));
}
}
return map.get(node);
}
}标签:贪心算法
- 先从左至右遍历一遍学生,按照以下规则给糖:
- 先给所有小朋友1颗糖;
- 若第
i名学生比i - 1名学生分数高,则第i名学生糖应比第i - 1名学生多一个。
- 在此规则下,可以保证所有学生左边学生的糖数量符合规则。
- 同理,从右至左遍历一遍学生,保证所有学生右边学生的糖数量符合规则。
- 最终,取两遍遍历对应学生糖果数最大值(这样对于每个学生,左右学生糖果数量都满足),即可得最少糖果数量。
- 时间空间复杂度都为
$O(N)$ 。
class Solution:
def candy(self, ratings: List[int]) -> int:
left = [1 for _ in range(len(ratings))]
right = left[:]
for i in range(1, len(ratings)):
if ratings[i] > ratings[i - 1]: left[i] = left[i - 1] + 1
count = left[-1]
for i in range(len(ratings) - 2, -1, -1):
if ratings[i] > ratings[i + 1]: right[i] = right[i + 1] + 1
count += max(left[i], right[i])
return countclass Solution {
public int candy(int[] ratings) {
int[] left = new int[ratings.length];
int[] right = new int[ratings.length];
Arrays.fill(left, 1);
Arrays.fill(right, 1);
for(int i = 1; i < ratings.length; i++)
if(ratings[i] > ratings[i - 1]) left[i] = left[i - 1] + 1;
int count = left[ratings.length - 1];
for(int i = ratings.length - 2; i >= 0; i--) {
if(ratings[i] > ratings[i + 1]) right[i] = right[i + 1] + 1;
count += Math.max(left[i], right[i]);
}
return count;
}
}标签:数组,位运算
- 通过题目已知信息,需要
O(N)时间复杂度和O(1)空间复杂度,即遍历一遍arr就需要得出答案,考虑:- 最多遍历一次
arr就要得到答案; - 两个相同的数字经过此运算为
0; - 满足
交换律,即打乱arr元素排列顺序不改变答案。
- 最多遍历一次
- 因此,想到
异或xor操作,异或有以下两个性质:a ^ a = 00 ^ a = a
- 从而遍历
arr后,留下来的数字即为只出现一次的数字。
class Solution:
def singleNumber(self, nums: List[int]) -> int:
res = 0
for num in nums:
res ^= num
return resclass Solution {
public int singleNumber(int[] nums) {
int res = 0;
for(int num : nums){
res ^= num;
}
return res;
}
}标签:数组,位运算
-
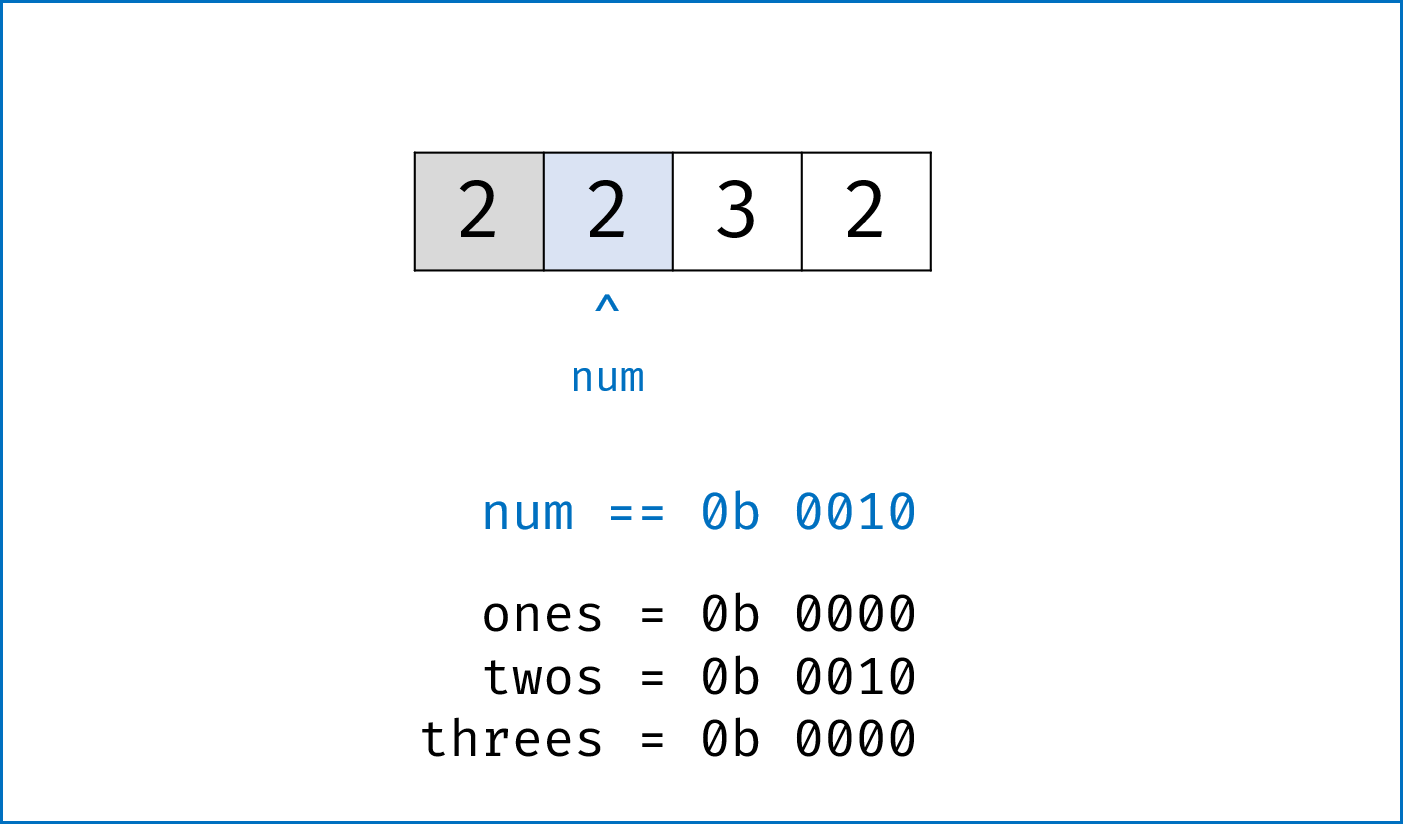
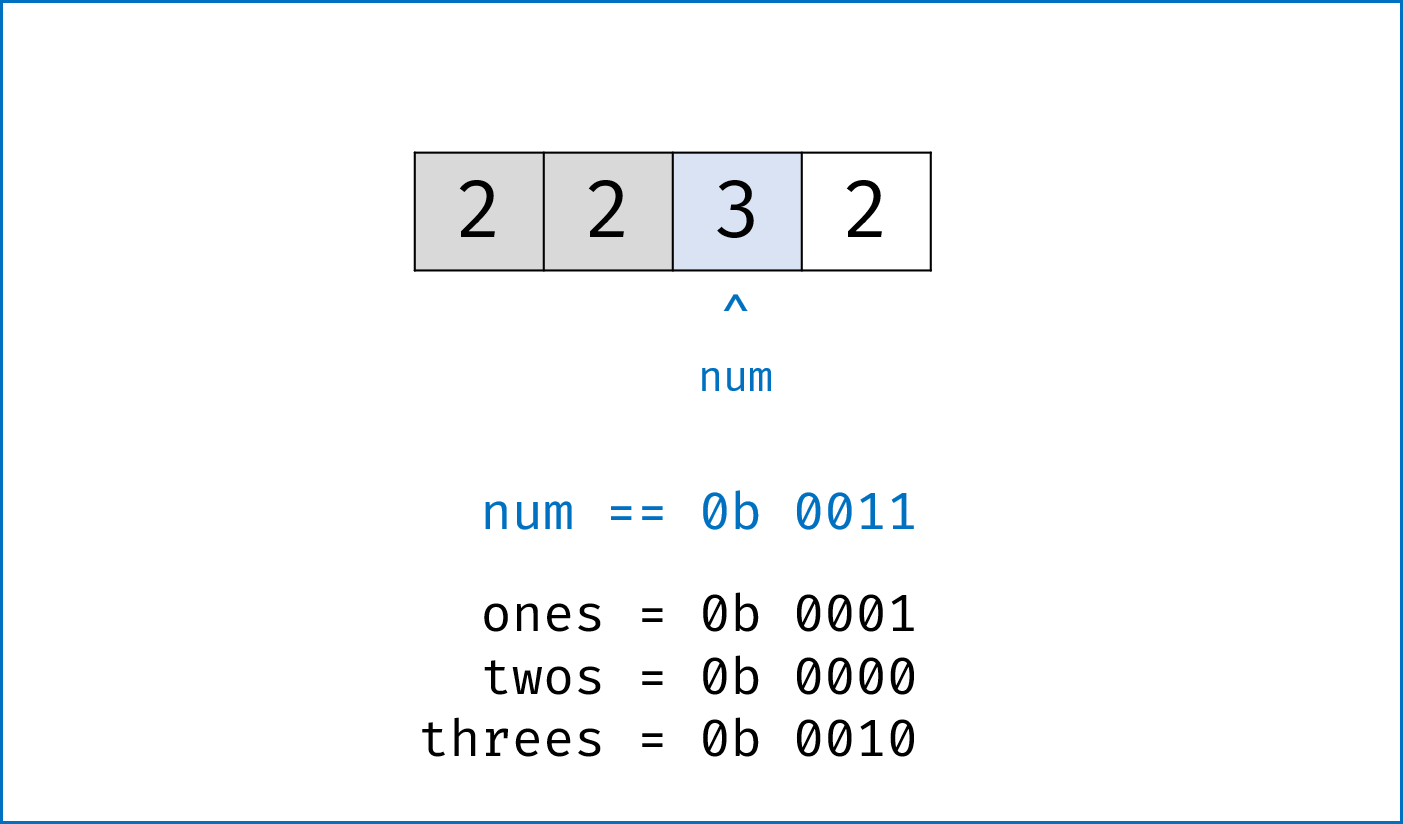
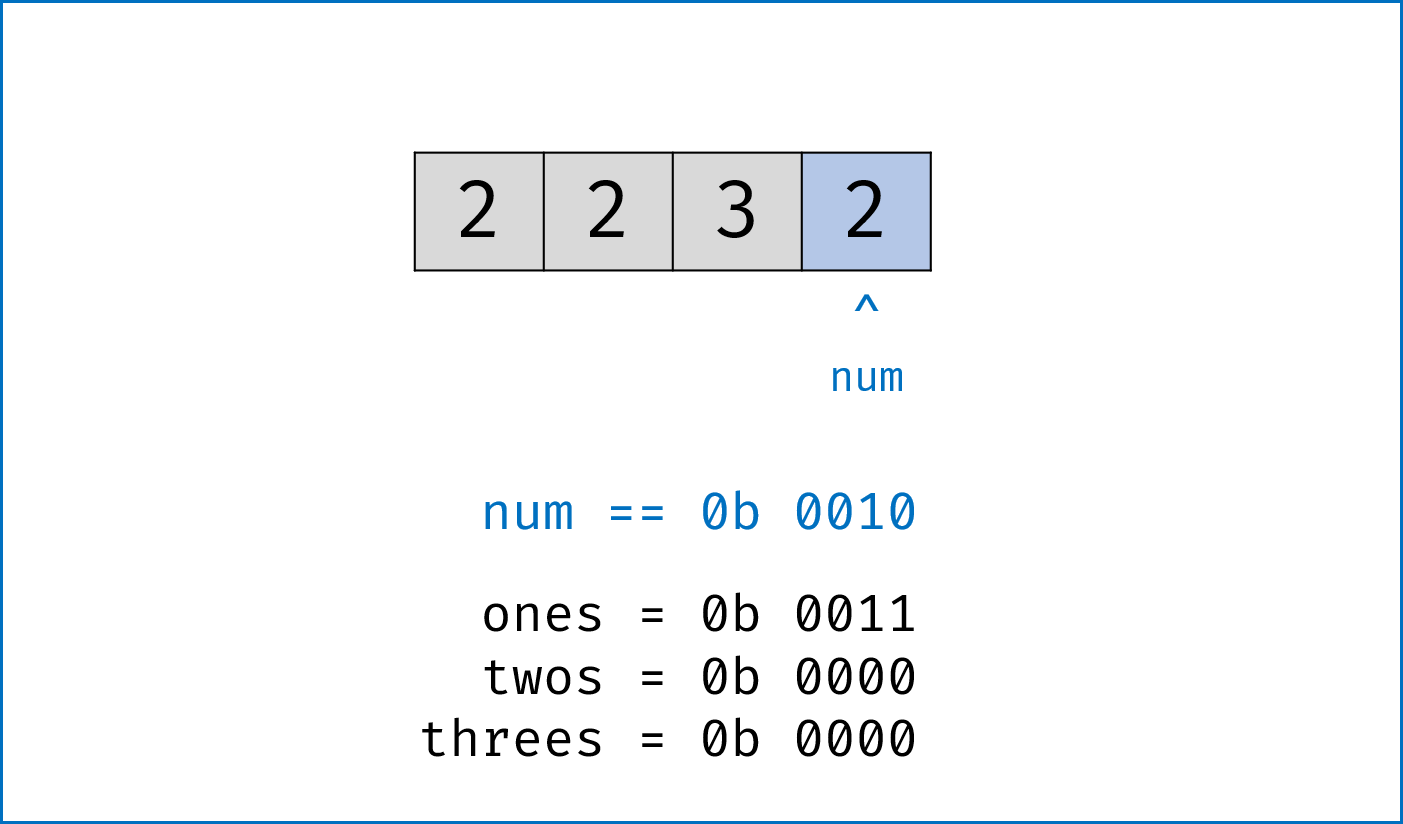
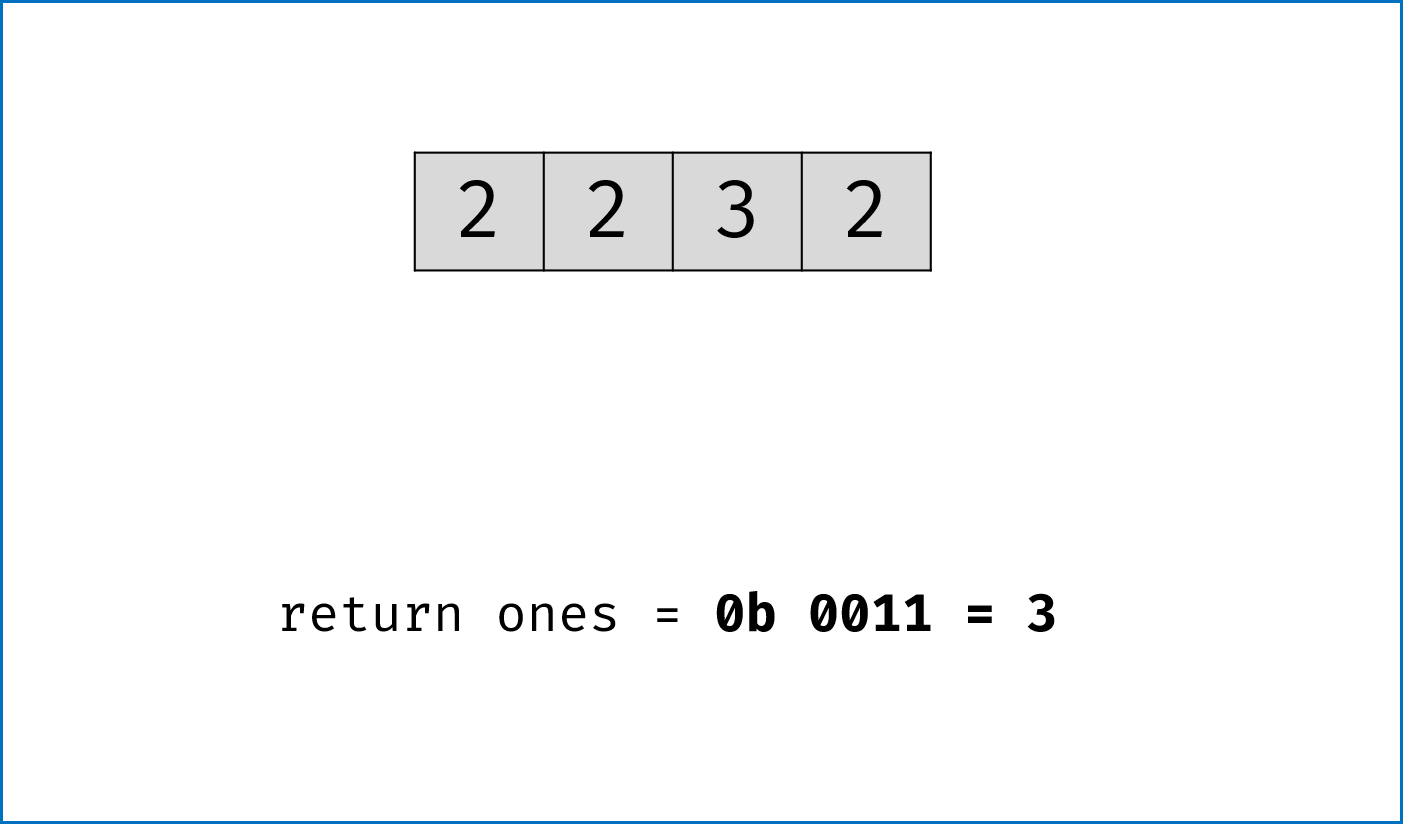
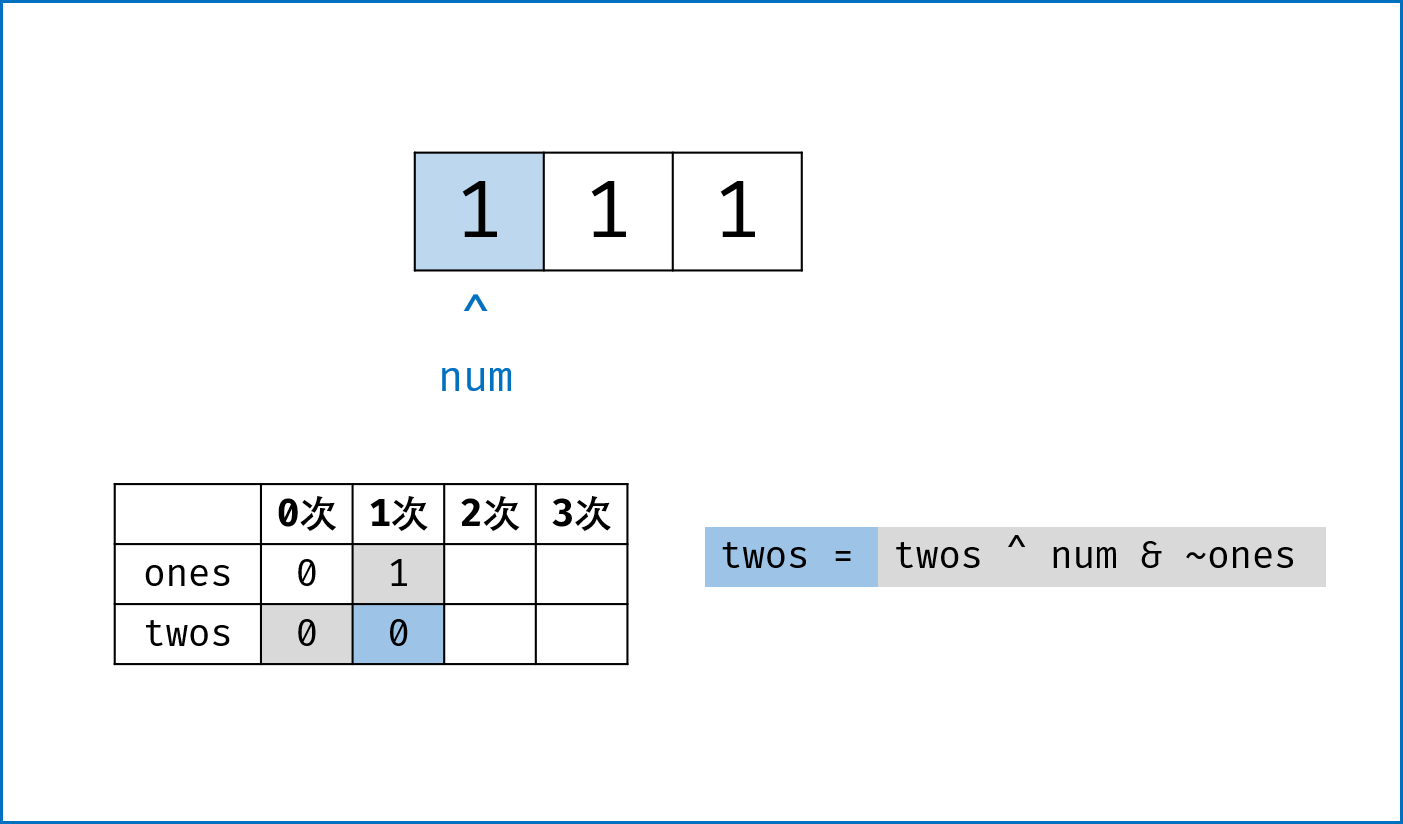
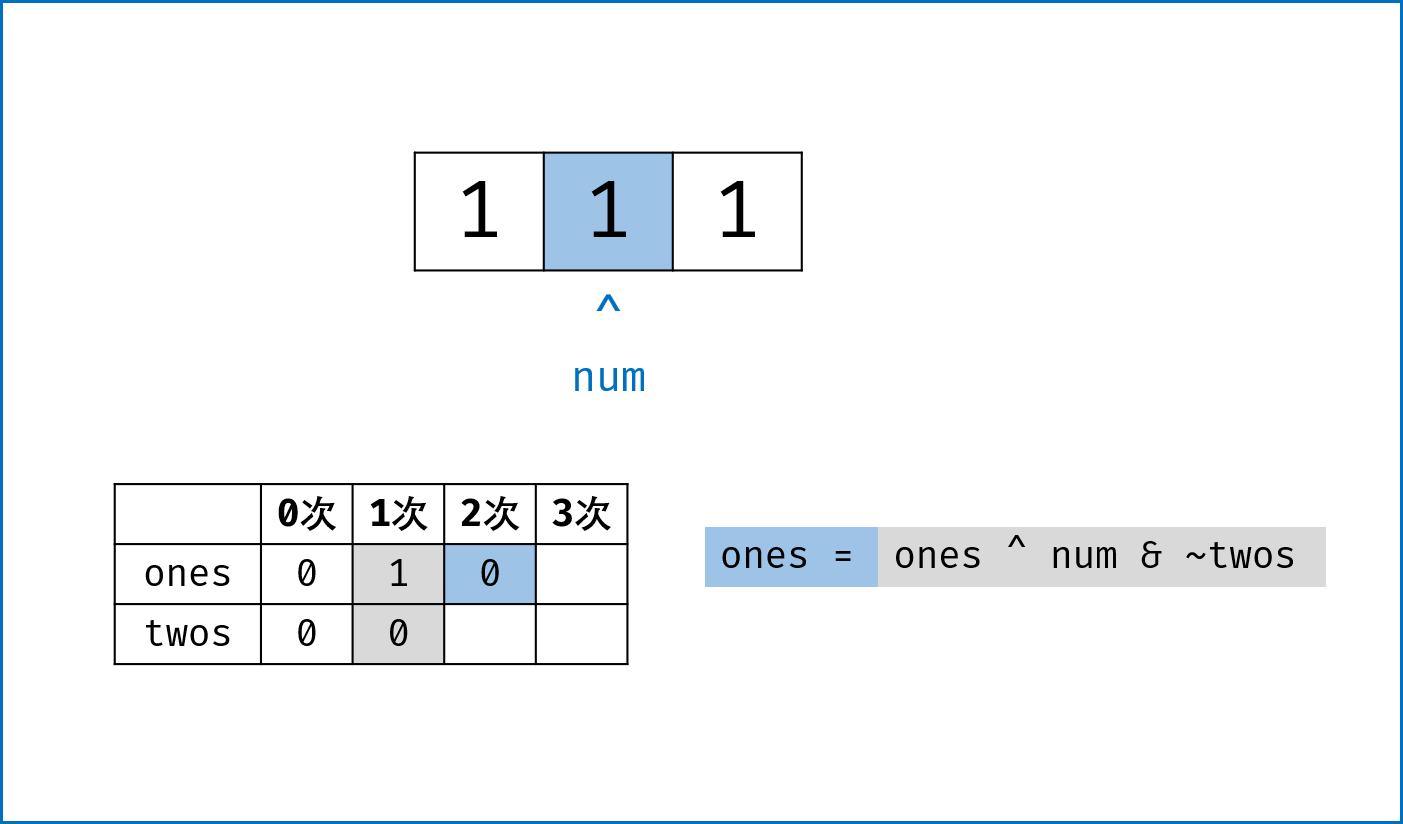
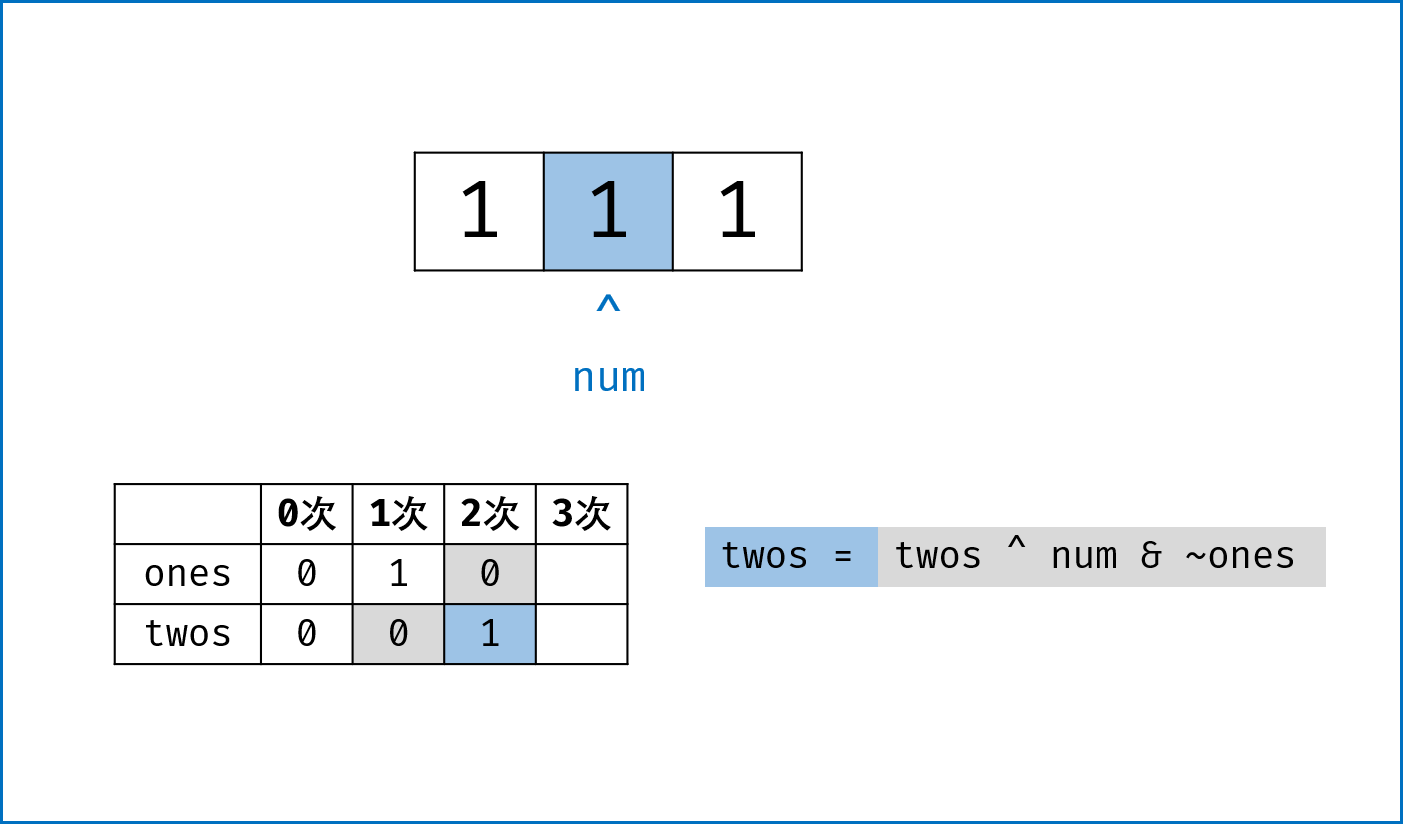
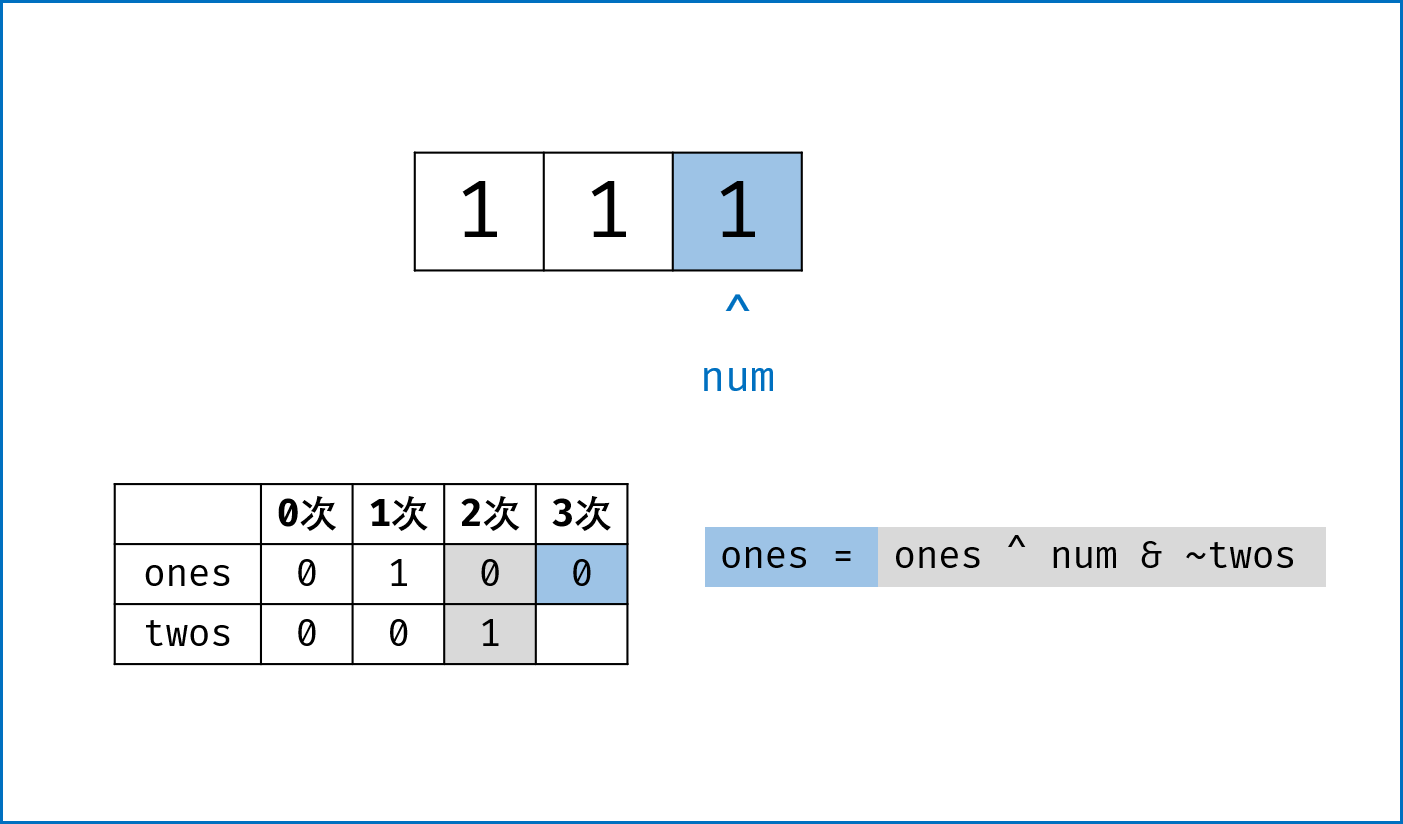
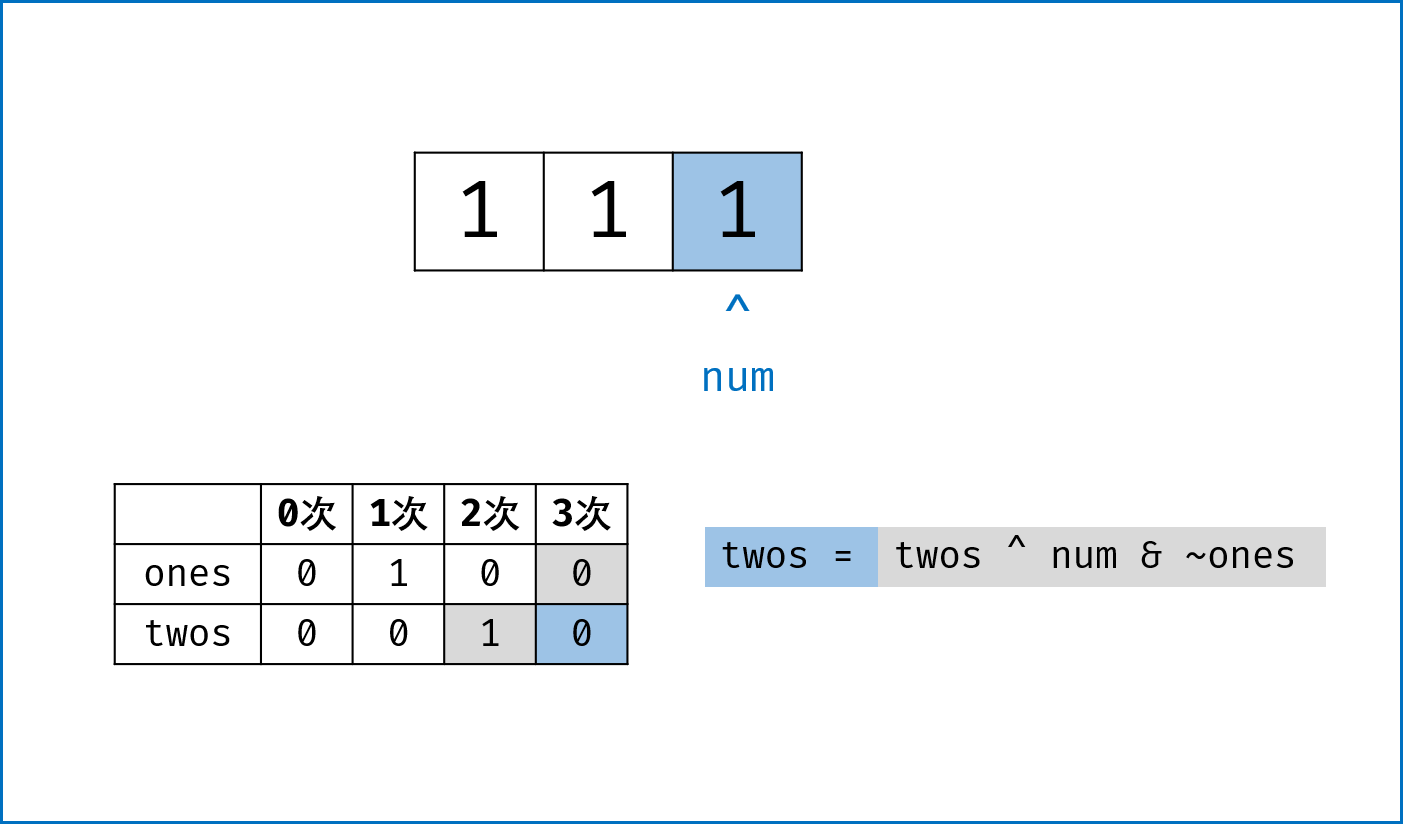
二进制下不考虑进位的加法:本题为 136. Single Number 的拓展,136 题中我们用到了异或运算。实际上,异或运算的含义是二进制下不考虑进位的加法,即:$0 xor 0=0+0=0$,
$0 xor 1=0+1=1$ ,$1 xor 0=1+0=1$ ,$1 xor 1=1+1=0$ (不进位)。 -
三进制下不考虑进位的加法:通过定义某种运算
$#$ ,使得$0 # 1 = 1$ ,$1 # 1 = 2$ ,$2 # 1 = 0$ 。在此运算规则下,出现了$3$ 次的数字的二进制所有位全部抵消为$0$ ,而留下只出现$1$ 次的数字二进制对应位为$1$ 。因此,在此运算规则下将整个arr中数字遍历加和,留下来的结果则为只出现$1$ 次的数字。 -
代码分析: 请结合代码注释和图表理解。
-
ones ^= num:记录至目前元素num,二进制某位出现$1$ 次(当某位出现$3$ 次时有$ones = 1$ ,与$twos = 1$ 共同表示“出现$3$ 次”); -
twos |= ones & num:记录至目前元素num,二进制某位出现$2$ 次 (当某位出现$2$ 次时,$twos = 1$ 且$ones = 0$ ); -
threes = ones & twos:记录至目前元素num,二进制某位出现$3$ 次(即当$ones$ 和$twos$ 对应位同时为$1$ 时$three = 1$ )。 -
one &= ~threes,two &= ~threes:将$ones$ ,$twos$ 中出现了$3$ 次的对应位清零,实现 “不考虑进位的三进制加法” 。
-
-
复杂度分析:
- 时间复杂度
$O(N)$ :遍历一遍nums需要线性时间复杂度; - 空间复杂度
$O(1)$ :使用常数额外空间。
- 时间复杂度
class Solution:
def singleNumber(self, nums: [int]) -> int:
ones, twos, threes = 0, 0, 0
for num in nums:
twos |= ones & num # 二进制某位出现1次时twos = 0,出现2, 3次时twos = 1;
ones ^= num # 二进制某位出现2次时ones = 0,出现1, 3次时ones = 1;
threes = ones & twos # 二进制某位出现3次时(即twos = ones = 1时)three = 1,其余即出现1, 2次时three = 0;
ones &= ~threes # 将二进制下出现3次的位置零,实现`三进制下不考虑进位的加法`;
twos &= ~threes
return onesclass Solution {
public int singleNumber(int[] nums) {
int ones = 0, twos = 0, threes = 0;
for(int num : nums){
twos |= ones & num;
ones ^= num;
threes = ones & twos;
ones &= ~threes;
twos &= ~threes;
}
return ones;
}
}- 以上过程本质上是通过构建
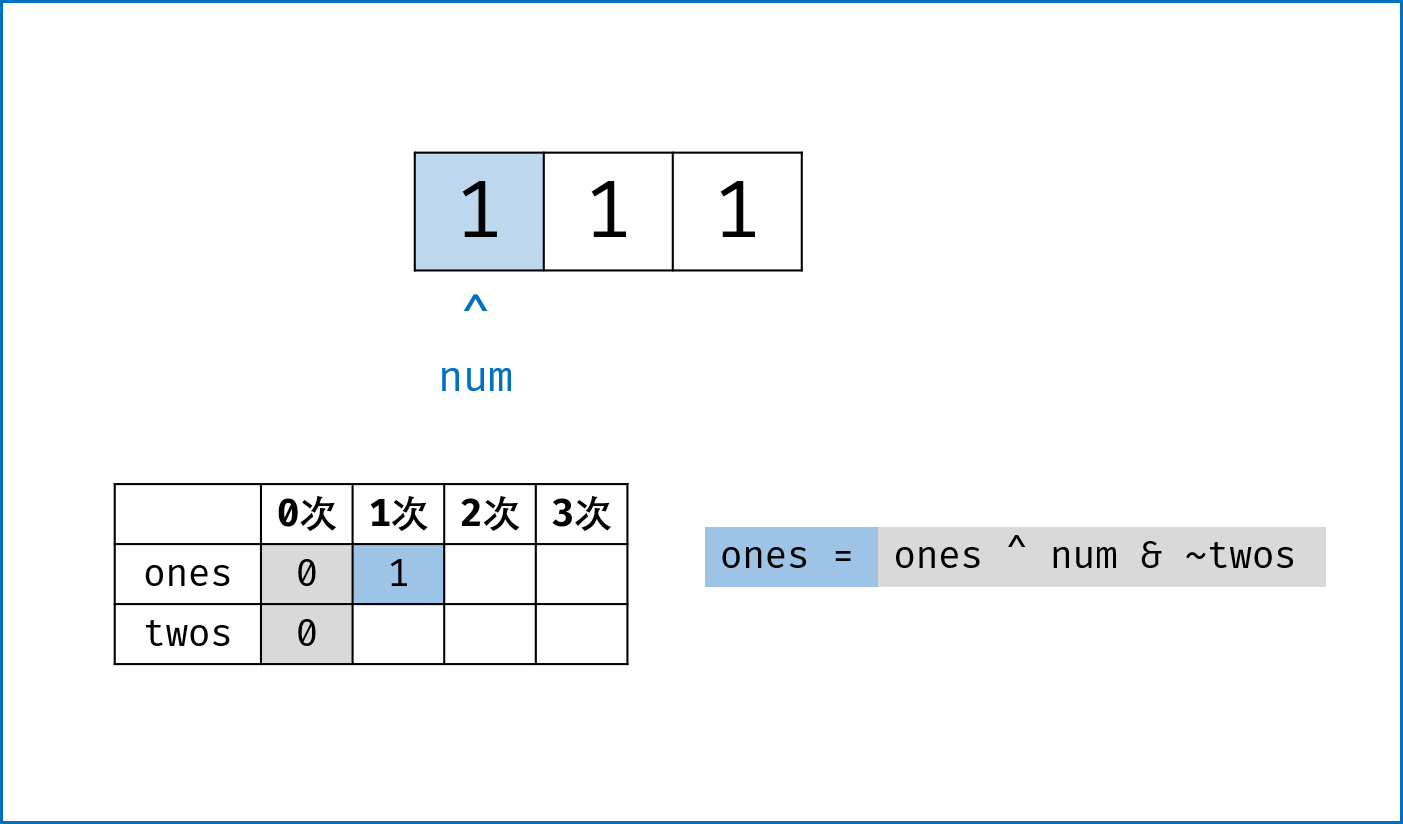
$3$ 个变量的状态转换表来表示对应位的出现次数:使所有数字“相加”后出现$3N+1$ 次的位$ones = 1$ ,出现$3N, 3N+2$次的位为$ones = 0$ 。由于$three$ 其实是ones & twos的结果,因此我们可以舍弃$threes$ ,仅使用$ones$ 和$twos$ 来记录出现次数。
| 某位出现 | 1次 | 2次 | 3次 | 4次 | 5次 | 6次 | ... |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ones | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | ... |
| twos | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | ... |
| ... |
-
代码分析:
-
ones = ones ^ num & ~twos:- 当
$num = 1$ 时,只当$ones = twos = 0$ 时将$ones$ 置$1$ ,代表出现$3N+1$ 次;其余置$0$ ,根据$twos$ 值分别代表出现$3N$ 次和$3N+2$ 次; - 当
$num = 0$ 时,$ones$ 不变;
- 当
-
twos = twos ^ num & ~ones:- 当
$num = 1$ 时,只当$ones = twos = 0$ 时将$twos$ 置$1$ ,代表出现$3N+2$ 次;其余置$0$ ,根据$ones$ 值分别代表出现$3N$ 次和$3N+1$ 次。 - 当
$num = 0$ 时,$twos$ 不变。
- 当
-
感谢评论区$angus123$的精彩代码分享。
class Solution:
def singleNumber(self, nums: [int]) -> int:
ones, twos = 0, 0
for num in nums:
ones = ones ^ num & ~twos
twos = twos ^ num & ~ones
return onesclass Solution {
public int singleNumber(int[] nums) {
int ones = 0, twos = 0;
for(int num : nums){
ones = ones ^ num & ~twos;
twos = twos ^ num & ~ones;
}
return ones;
}
}标签:链表,多指针
- 复制与合并:假设原链表为
ABCDE……,从前到后复制得到A'B'C'D'E'……,合并得到AA'BB'CC'DD'EE'……。此步骤是为了从空间上构建random对应关系; - 设置复制链表的random项:
A.next.random = A.random.next; - 将两列表分离,返回deepcopy链表表头。
class Solution:
def copyRandomList(self, head: 'Node') -> 'Node':
if not head: return
pre, cur = Node(0, None, None), head
while cur: # copy and merge.
nex = cur.next
pre.next = cur
cur.next = Node(cur.val, None, None)
pre = cur.next
cur = nex
cur = head
while cur: # set the 'random' nodes.
cur.next.random = cur.random.next if cur.random else None
cur = cur.next.next
cur, res = head, head.next
while cur.next: # divide the two linked lists.
nex = cur.next
cur.next = nex.next
cur = nex
return resclass Solution {
public Node copyRandomList(Node head) {
if(head == null) return null;
Node pre = new Node(0, null, null), cur = head, nex = cur.next;
while(cur != null){
nex = cur.next;
pre.next = cur;
cur.next = new Node(cur.val, null, null);
pre = cur.next;
cur = nex;
}
cur = head;
while(cur != null){
cur.next.random = cur.random != null ? cur.random.next : null;
cur = cur.next.next;
}
cur = head;
Node res = head.next;
while(cur.next != null){
nex = cur.next;
cur.next = nex.next;
cur = nex;
}
return res;
}
}标签:链表,双指针
- 设两指针
fastslow指向链表头部head,迭代:fast每轮走两步,slow每轮走一步,这样两指针每轮后距离+1;- 若链表中存在环,
fast和slow一定会在将来相遇(距离连续+1,没有跳跃);
- 若
fast走到了链表尾部,则说明链表无环。
class Solution(object):
def hasCycle(self, head):
fast, slow = head, head
while fast and fast.next:
fast = fast.next.next
slow = slow.next
if fast == slow: return True
return Falsepublic class Solution {
public boolean hasCycle(ListNode head) {
ListNode fast = head, slow = head;
while (fast != null && fast.next != null) {
fast = fast.next.next;
slow = slow.next;
if (fast == slow) return true;
}
return false;
}
}标签:链表,双指针
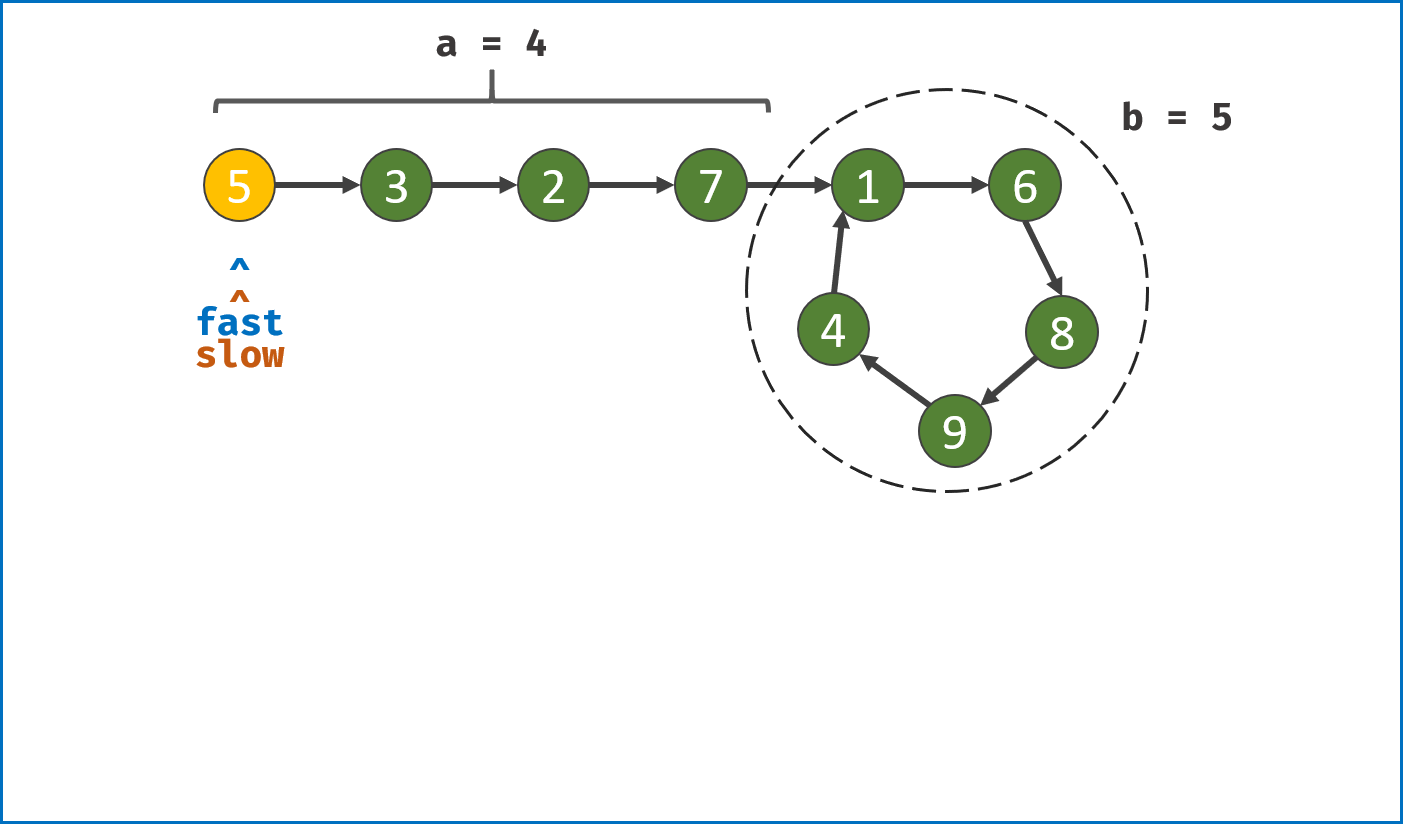
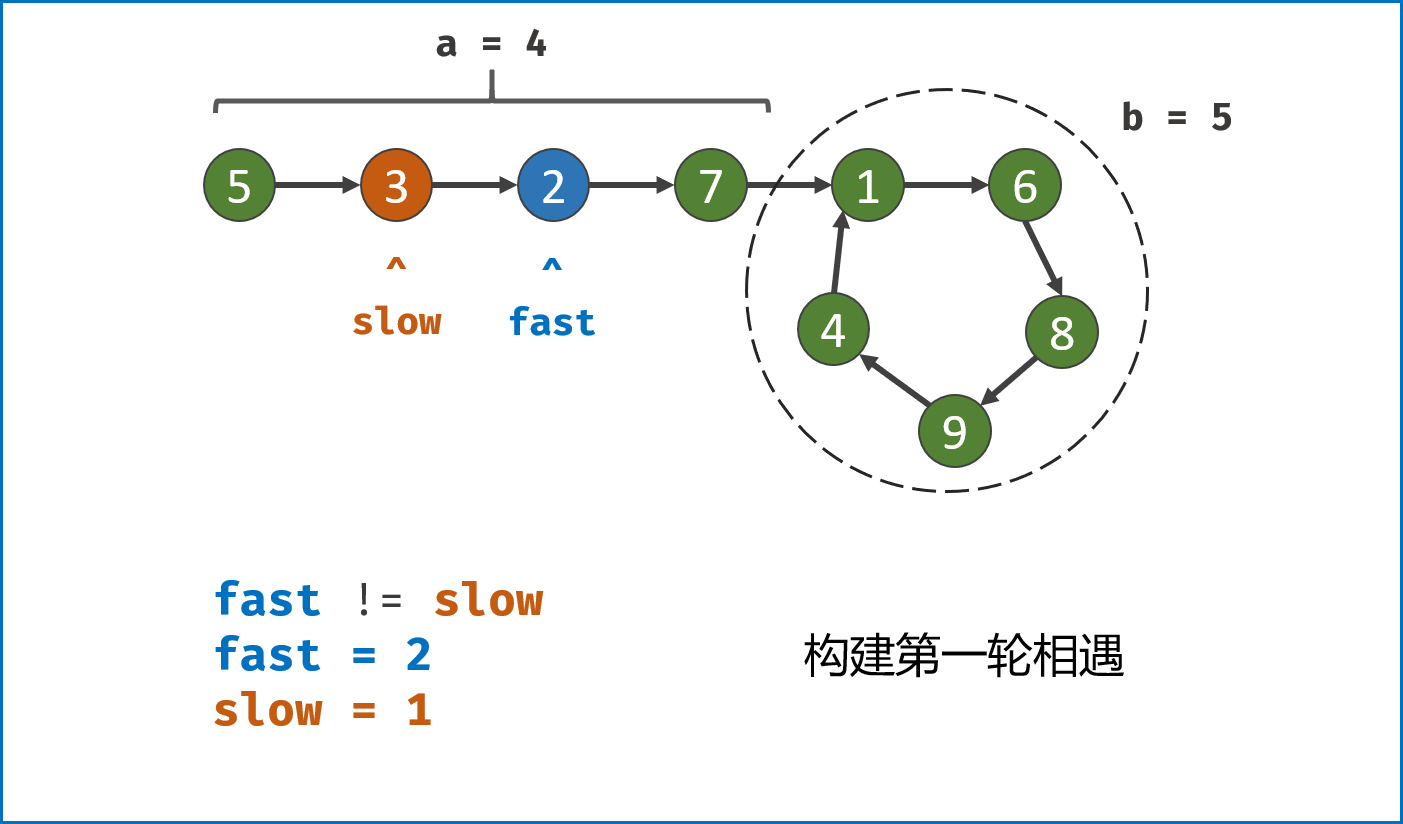
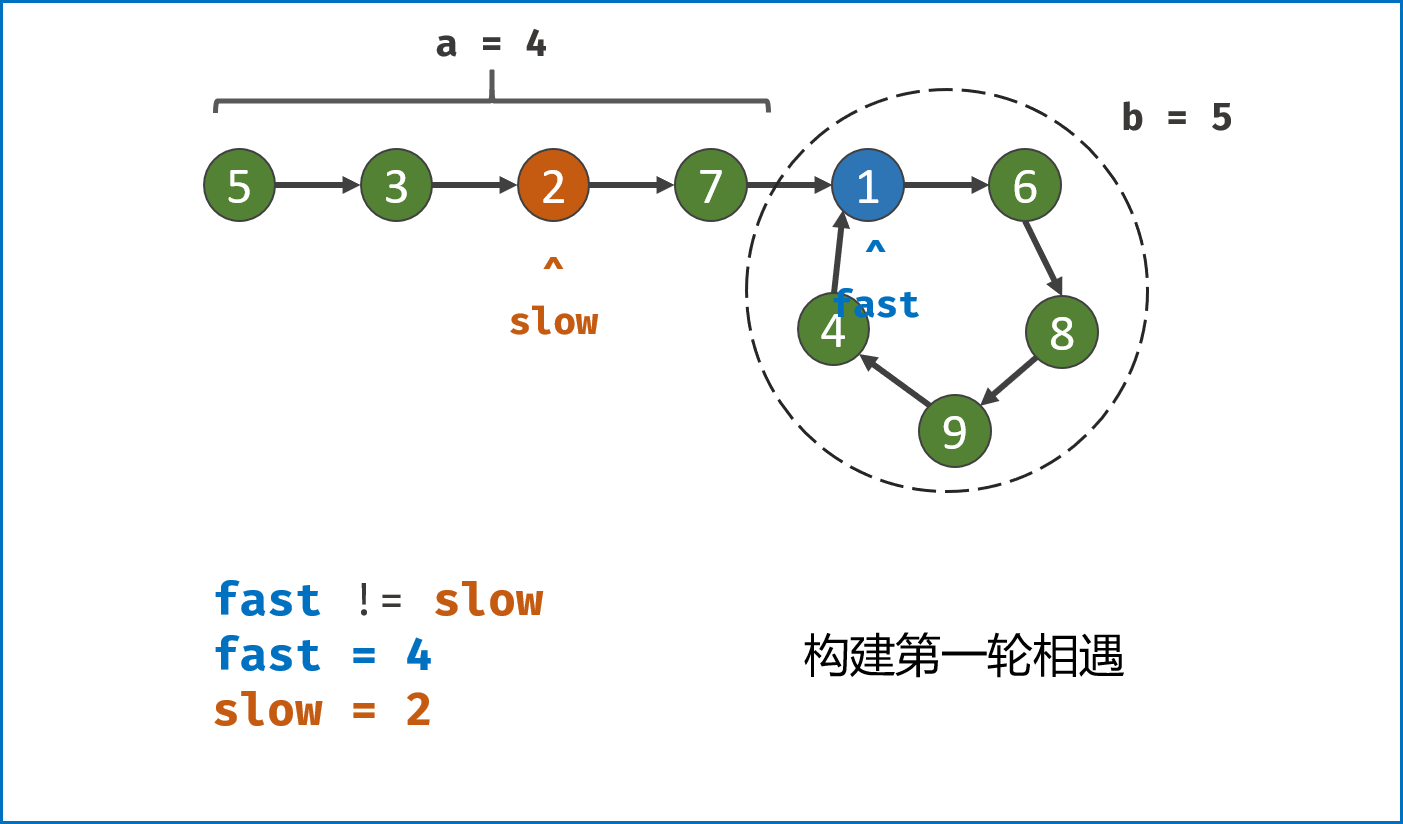
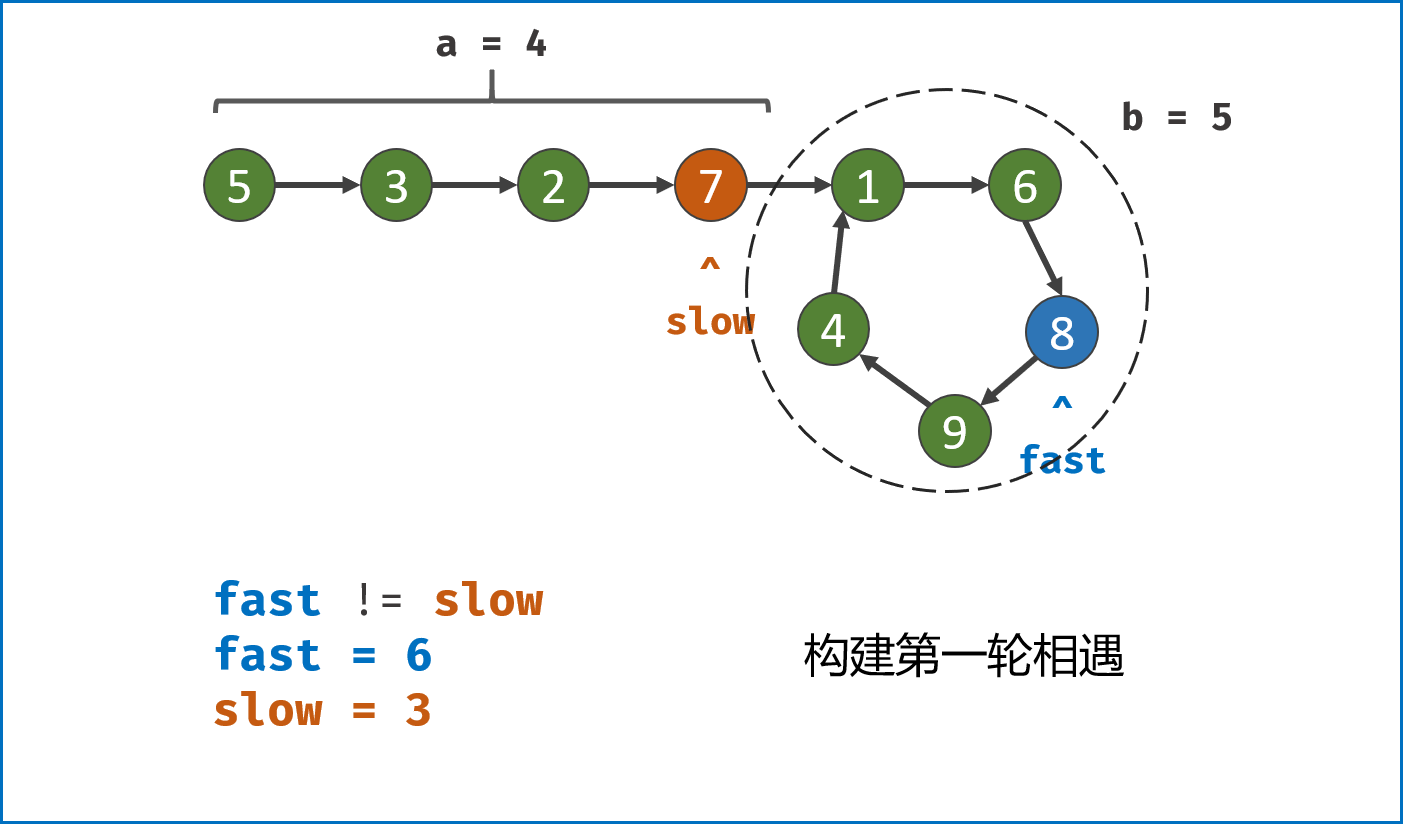
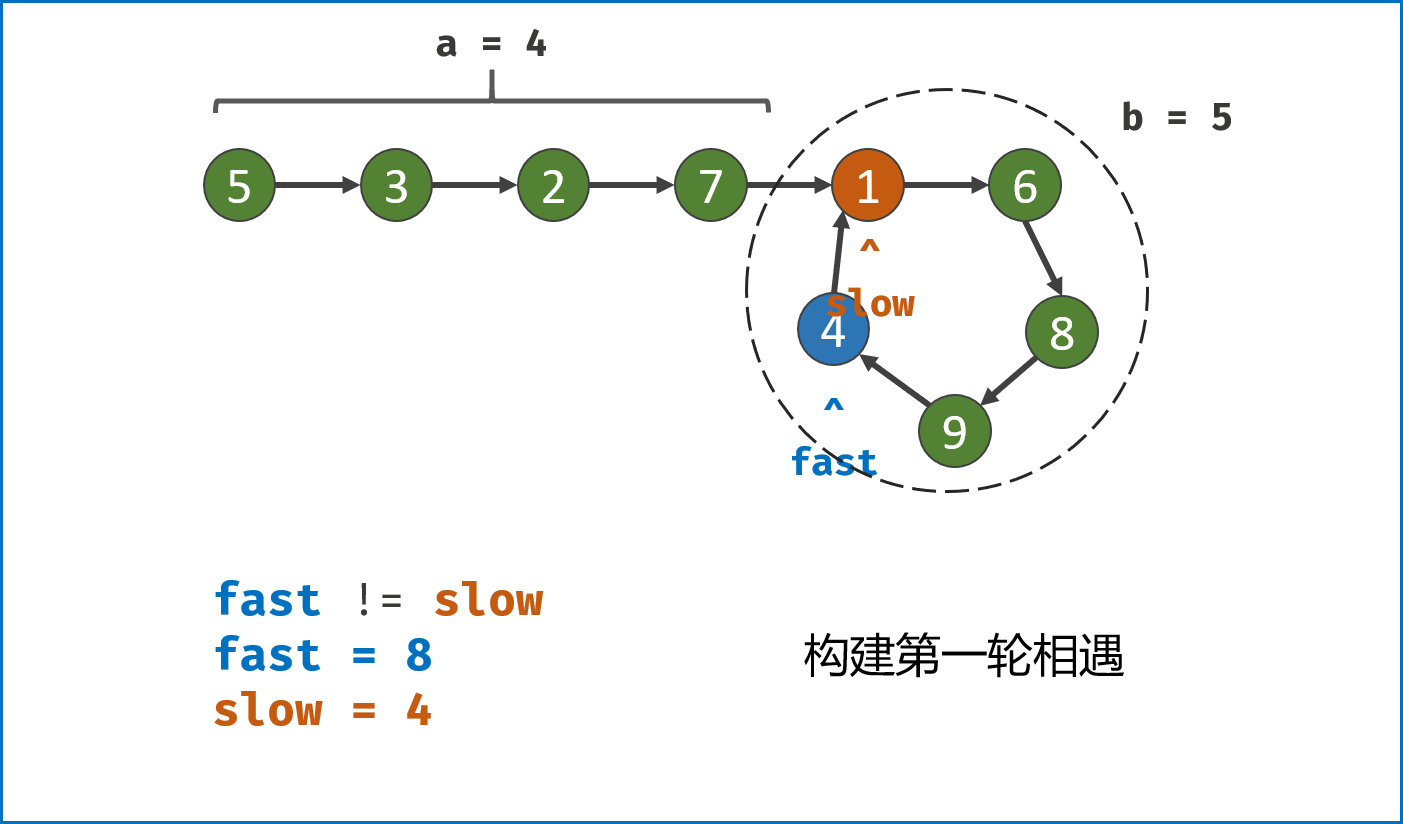
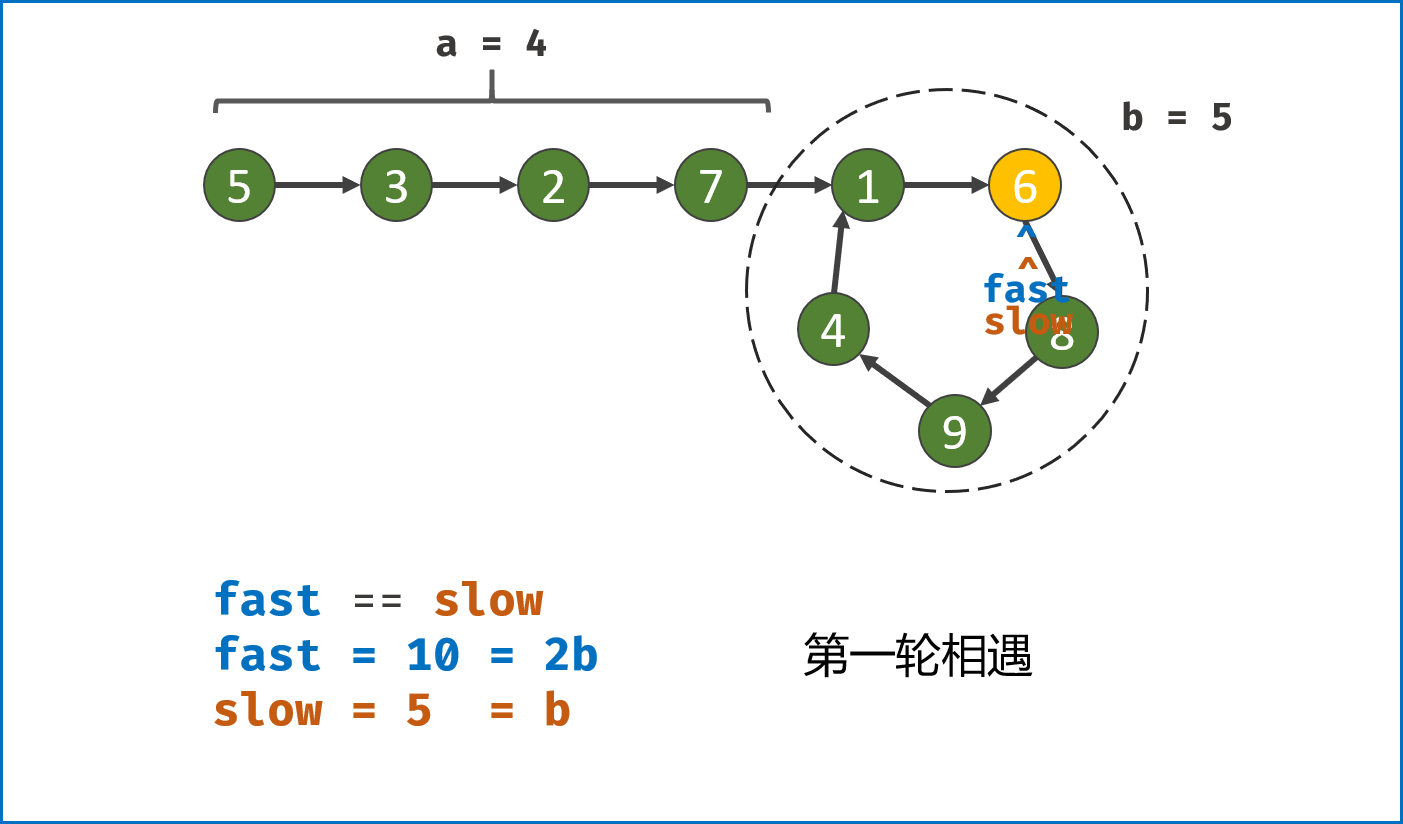
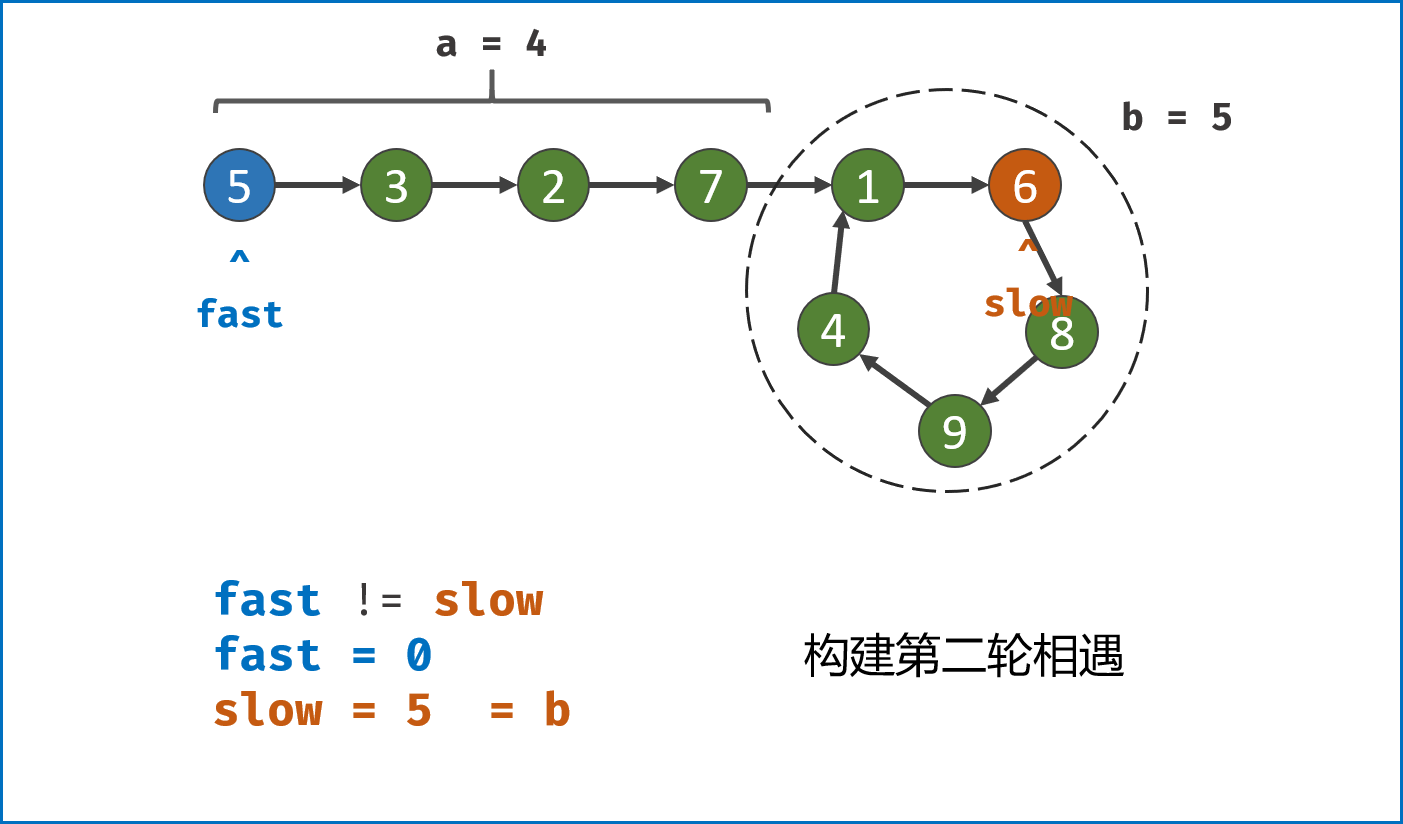
-
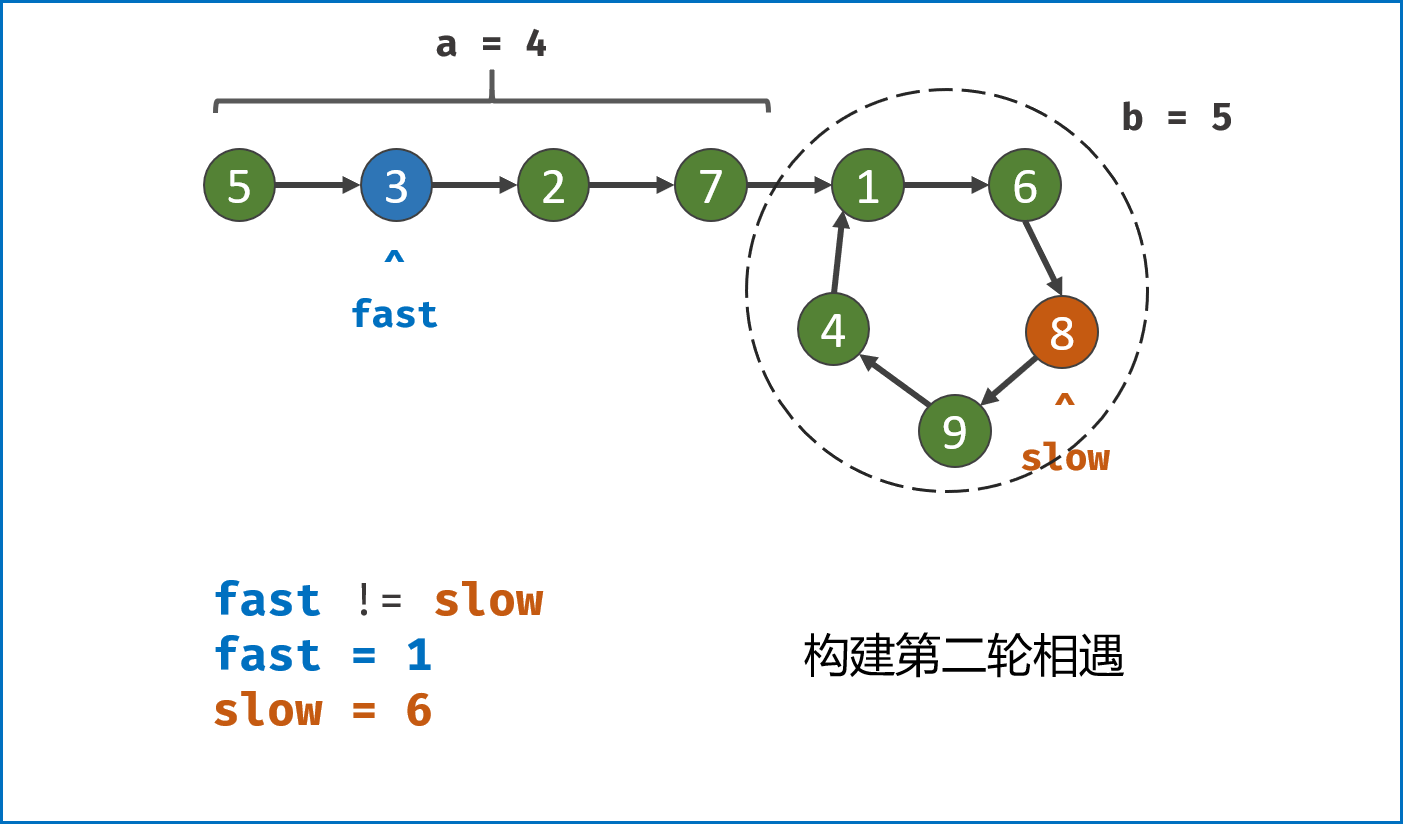
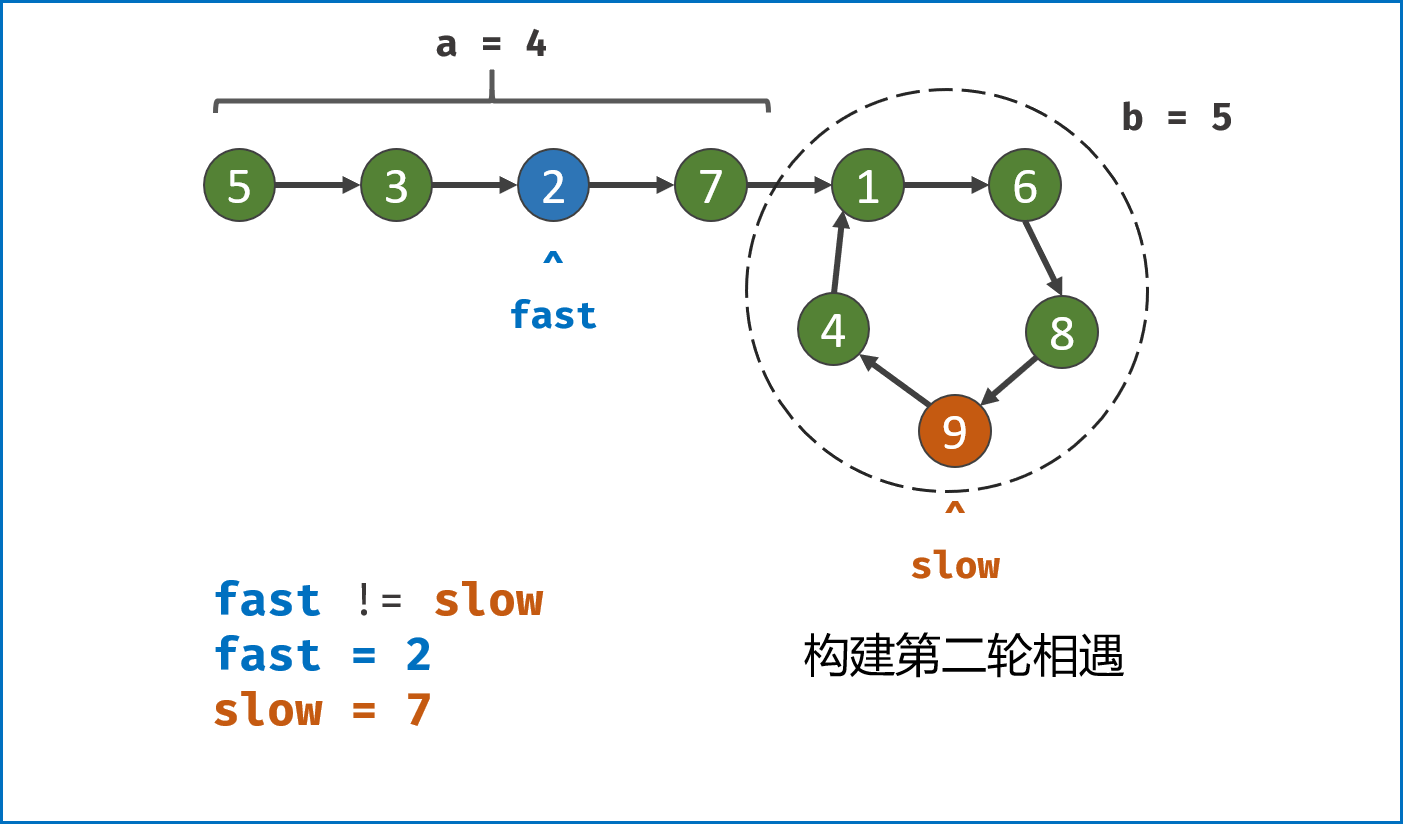
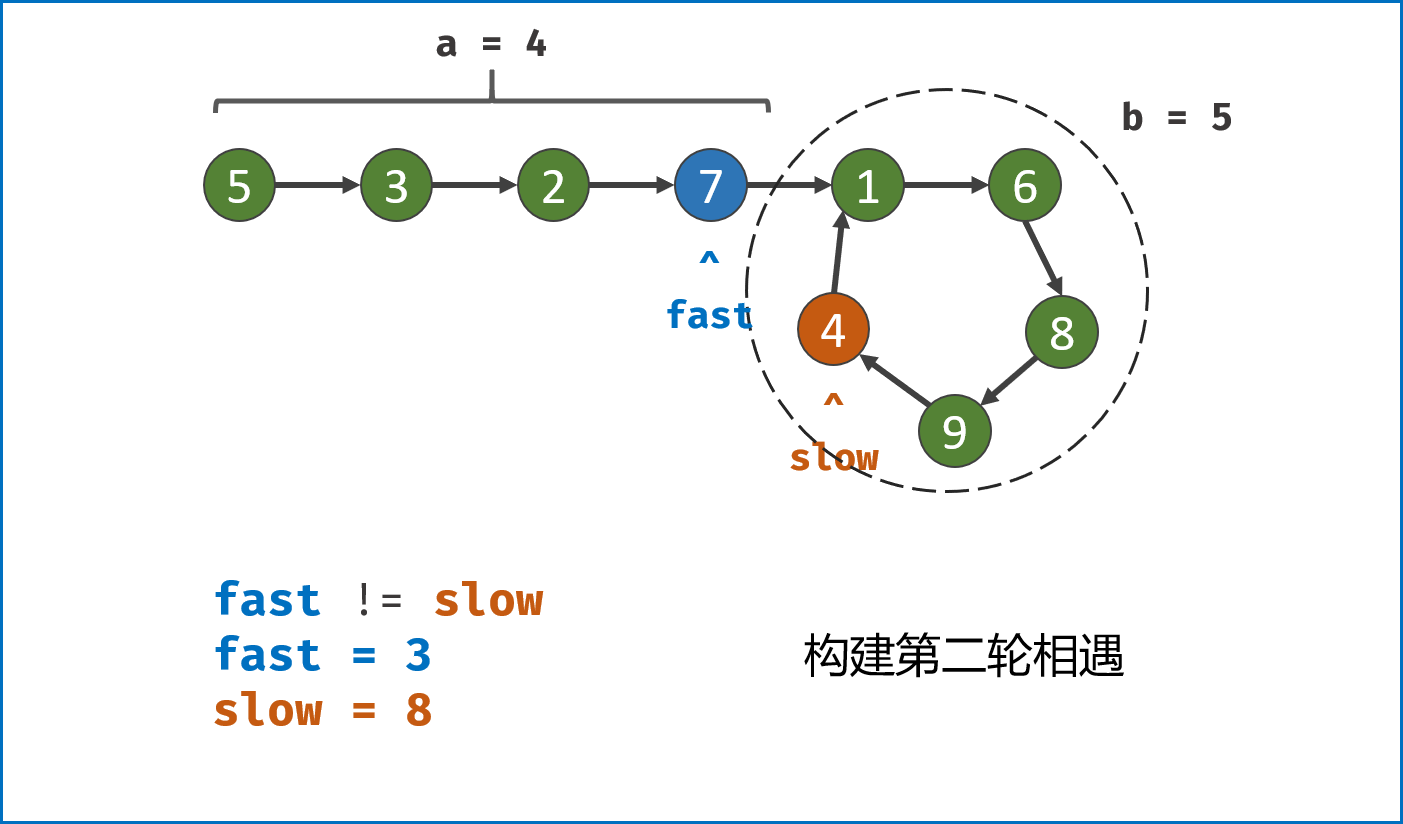
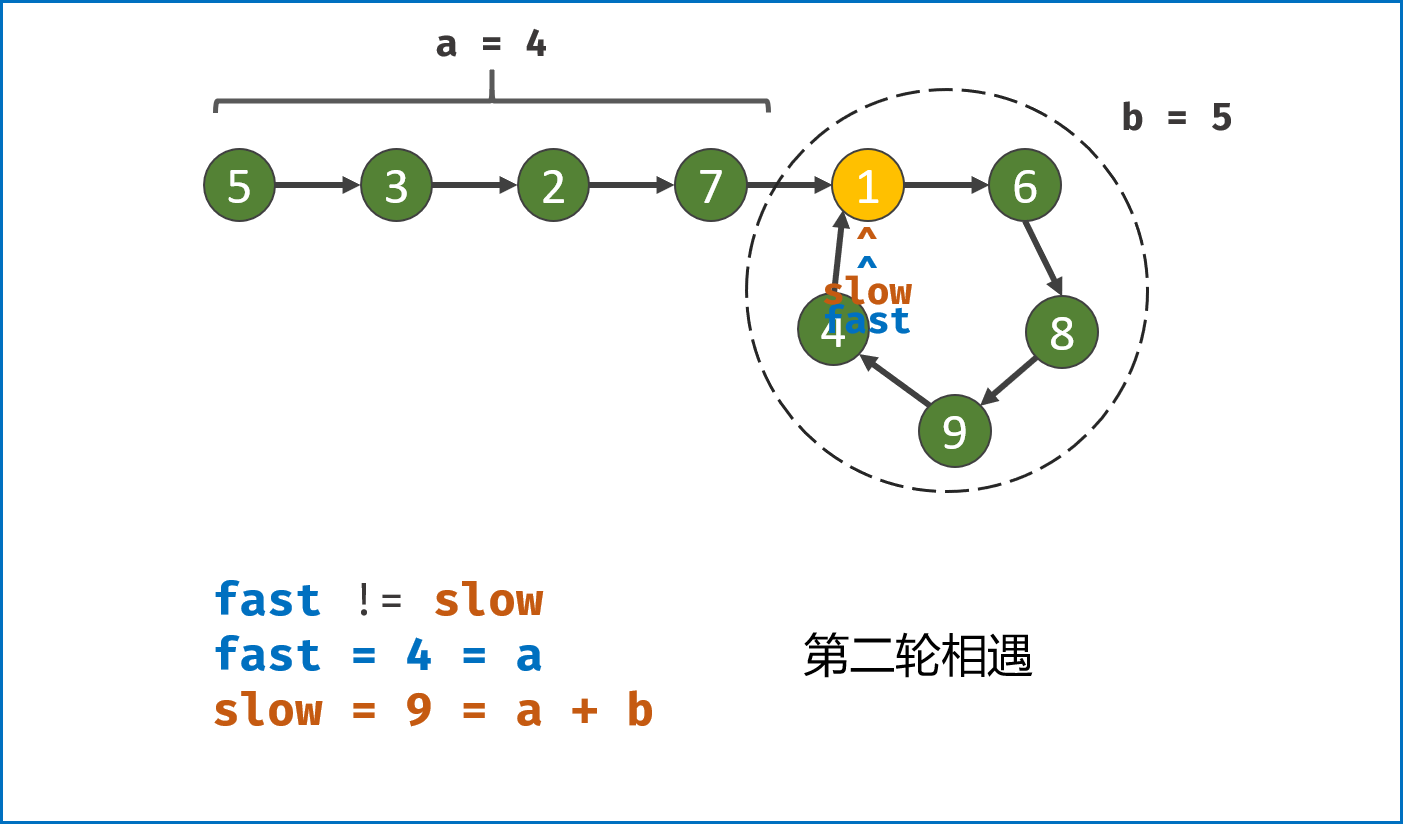
构建双指针第一次相遇:
- 设两指针
fast,slow指向链表头部head,fast每轮走$2$ 步,slow每轮走$1$ 步; - 若
fast指针走过链表末端,说明链表无环,直接返回null(因为每走$1$ 轮,fast与slow的间距$+1$ ,若有环,快慢两指针终会相遇); - 当
fast == slow时,代表两指针在环中 第一次相遇 ,此时执行$break$ 跳出迭代; -
第一次相遇时步数分析:
- 设两指针分别走了
$f$ ,$s$ 步,设链表头部到环需要走$a$ 步,链表环走一圈需要$b$ 步; - 快指针走了慢指针
$2$ 倍的路程,即$f = 2s$ ; - 快指针比慢指针多走了
$n$ 个环的长度,即$f = s + nb$ ; - 代入可推出:
$f = 2nb$ ,$s = nb$ ,即快慢指针分别走了$2n$ ,$n$ 个环的周长。
- 设两指针分别走了
- 设两指针
-
构建双指针第二次相遇:
- 将
fast指针重新指向链表头部head,slow指针位置不变,此时fast走了$0$ 步,slow指针走了$nb$ 步; - 令双指针一起向前走,两指针每轮都走
$1$ 步; - 当
fast指针走到$a$ 步时,slow指针正好走到$a + nb$ 步,此时 两指针重合并同时指向链表环入口 。 - 最终返回
fast或slow即可。
- 将
-
复杂度分析:
-
时间复杂度
$O(N)$ :第二次相遇中,慢指针须走步数$a < a + b$ ;第一次相遇中,慢指针须走步数$a + b - x < a + b$ ,其中$x$ 为双指针重合点与环入口距离;因此总体为线性复杂度; -
空间复杂度
$O(1)$ :双指针使用常数大小的额外空间。
-
时间复杂度
class Solution(object):
def detectCycle(self, head):
fast, slow = head, head
while True:
if not (fast and fast.next): return
fast, slow = fast.next.next, slow.next
if fast == slow: break
fast = head
while fast != slow:
fast, slow = fast.next, slow.next
return fastpublic class Solution {
public ListNode detectCycle(ListNode head) {
ListNode fast = head, slow = head;
while (true) {
if (fast == null || fast.next == null) return null;
fast = fast.next.next;
slow = slow.next;
if (fast == slow) break;
}
fast = head;
while (slow != fast) {
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next;
}
return fast;
}
}标签:哈希表,双向链表
-
使用
python和java自带的 双向链表 + 哈希表 数据结构实现。Python为collections.OrderedDict(),Java为LinkedHashMap<>()。原理是将哈希表中所有key使用双向链表连接起来,链表按照 访问顺序 排序,访问操作包括:添加、获取。 -
get(int key)设计:- 返回哈希表中
key对应的value; - 在返回前,需要将此
key移动至双向链表的尾部(代表为最新元素)。
- 返回哈希表中
-
put(int key, int value)设计:- 若哈希表中已存在此
key,先将此key移动至链表尾部(代表为最新元素); - 若
key不在哈希表中,则判断双向链表当前元素个数是否等于容量capacity大小:若等于则将最老元素(链表首部元素)从哈希表和双向链表中删除;- 此步
Python调用self.dic.popitem(0)实现,Java通过重写LinkedHashMap类中的removeEldestEntry()方法实现。
- 此步
- 在哈希表中加入此键值对,并在链表末端加入此
key。
- 若哈希表中已存在此
class LRUCache:
def __init__(self, capacity: int):
self.dic, self.cap = collections.OrderedDict(), capacity
def get(self, key: int) -> int:
if key not in self.dic: return -1
self.dic.move_to_end(key)
return self.dic[key]
def put(self, key: int, value: int) -> None:
if key in self.dic: del self.dic[key]
elif len(self.dic) == self.cap: self.dic.popitem(0)
self.dic[key] = valueclass LRUCache {
private LinkedHashMap<Integer, Integer> map;
public LRUCache(int capacity) {
map = new LinkedHashMap<Integer, Integer>(capacity, .75F, true) {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 4267176411845948333L;
protected boolean removeEldestEntry(Map.Entry<Integer, Integer> eldest) {
return map.size() > capacity;
}
};
}
public int get(int key) {
return map.getOrDefault(key, -1);
}
public void put(int key, int value) {
map.put(key,value);
}
}标签:链表,归并排序
-
题目要求时间空间复杂度分别为$O(nlogn)$和$O(1)$,根据时间复杂度我们自然想到二分法,从而联想到归并排序;
-
对数组做归并排序的空间复杂度为
$O(n)$ ,分别由新开辟数组$O(n)$和递归函数调用$O(logn)$组成,而根据链表特性:- 数组额外空间:链表可以通过修改引用来更改节点顺序,无需像数组一样开辟额外空间;
- 递归额外空间:递归调用函数将带来$O(logn)$的空间复杂度,因此若希望达到$O(1)$空间复杂度,则不能使用递归。
-
通过递归实现链表归并排序,有以下两个环节:
-
分割 cut 环节: 找到当前链表
中点,并从中点将链表断开(以便在下次递归cut时,链表片段拥有正确边界);- 我们使用
fast,slow快慢双指针法,奇数个节点找到中点,偶数个节点找到中心左边的节点。 - 找到中点
slow后,执行slow.next = None将链表切断。 - 递归分割时,输入当前链表左端点
head和中心节点slow的下一个节点tmp(因为链表是从slow切断的)。 -
cut 递归终止条件: 当
head.next == None时,说明只有一个节点了,直接返回此节点。
- 我们使用
-
合并 merge 环节: 将两个排序链表合并,转化为一个排序链表。
- 双指针法合并,建立辅助ListNode
h作为头部。 - 设置两指针
left,right分别指向两链表头部,比较两指针处节点值大小,由小到大加入合并链表头部,指针交替前进,直至添加完两个链表。 - 返回辅助ListNode
h作为头部的下个节点h.next。 - 时间复杂度
O(l + r),l, r分别代表两个链表长度。
- 双指针法合并,建立辅助ListNode
- 当题目输入的
head == None时,直接返回None。
-
分割 cut 环节: 找到当前链表
class Solution:
def sortList(self, head: ListNode) -> ListNode:
if not head or not head.next: return head # termination.
# cut the LinkedList at the mid index.
slow, fast = head, head.next
while fast and fast.next:
fast, slow = fast.next.next, slow.next
mid, slow.next = slow.next, None # save and cut.
# recursive for cutting.
left, right = self.sortList(head), self.sortList(mid)
# merge `left` and `right` linked list and return it.
h = res = ListNode(0)
while left and right:
if left.val < right.val: h.next, left = left, left.next
else: h.next, right = right, right.next
h = h.next
h.next = left if left else right
return res.nextclass Solution {
public ListNode sortList(ListNode head) {
if (head == null || head.next == null)
return head;
ListNode fast = head.next, slow = head;
while (fast != null && fast.next != null) {
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
}
ListNode tmp = slow.next;
slow.next = null;
ListNode left = sortList(head);
ListNode right = sortList(tmp);
ListNode h = new ListNode(0);
ListNode res = h;
while (left != null && right != null) {
if (left.val < right.val) {
h.next = left;
left = left.next;
} else {
h.next = right;
right = right.next;
}
h = h.next;
}
h.next = left != null ? left : right;
return res.next;
}
}- 对于非递归的归并排序,需要使用迭代的方式替换
cut环节:- 我们知道,
cut环节本质上是通过二分法得到链表最小节点单元,再通过多轮合并得到排序结果。 - 每一轮合并
merge操作针对的单元都有固定长度intv,例如:- 第一轮合并时
intv = 1,即将整个链表切分为多个长度为1的单元,并按顺序两两排序合并,合并完成的已排序单元长度为2。 - 第二轮合并时
intv = 2,即将整个链表切分为多个长度为2的单元,并按顺序两两排序合并,合并完成已排序单元长度为4。 - 以此类推,直到单元长度
intv >= 链表长度,代表已经排序完成。
- 第一轮合并时
- 根据以上推论,我们可以仅根据
intv计算每个单元边界,并完成链表的每轮排序合并,例如:- 当
intv = 1时,将链表第1和第2节点排序合并,第3和第4节点排序合并,……。 - 当
intv = 2时,将链表第1-2和第3-4节点排序合并,第5-6和第7-8节点排序合并,……。 - 当
intv = 4时,将链表第1-4和第5-8节点排序合并,第9-12和第13-16节点排序合并,……。
- 当
- 我们知道,
- 此方法时间复杂度$O(nlogn)$,空间复杂度$O(1)$。
- 模拟上述的多轮排序合并:
- 统计链表长度
length,用于通过判断intv < length判定是否完成排序; - 额外声明一个节点
res,作为头部后面接整个链表,用于:intv *= 2即切换到下一轮合并时,可通过res.next找到链表头部h;- 执行排序合并时,需要一个辅助节点作为头部,而
res则作为链表头部排序合并时的辅助头部pre;后面的合并排序可以将上次合并排序的尾部tail用做辅助节点。
- 在每轮
intv下的合并流程:- 根据
intv找到合并单元1和单元2的头部h1,h2。由于链表长度可能不是2^n,需要考虑边界条件:- 在找
h2过程中,如果链表剩余元素个数少于intv,则无需合并环节,直接break,执行下一轮合并; - 若
h2存在,但以h2为头部的剩余元素个数少于intv,也执行合并环节,h2单元的长度为c2 = intv - i。
- 在找
- 合并长度为
c1, c2的h1, h2链表,其中:- 合并完后,需要修改新的合并单元的尾部
pre指针指向下一个合并单元头部h。(在寻找h1, h2环节中,h指针已经被移动到下一个单元头部) - 合并单元尾部同时也作为下次合并的辅助头部
pre。
- 合并完后,需要修改新的合并单元的尾部
- 当
h == None,代表此轮intv合并完成,跳出。
- 根据
- 每轮合并完成后将单元长度×2,切换到下轮合并:
intv *= 2。
- 统计链表长度
class Solution:
def sortList(self, head: ListNode) -> ListNode:
h, length, intv = head, 0, 1
while h: h, length = h.next, length + 1
res = ListNode(0)
res.next = head
# merge the list in different intv.
while intv < length:
pre, h = res, res.next
while h:
# get the two merge head `h1`, `h2`
h1, i = h, intv
while i and h: h, i = h.next, i - 1
if i: break # no need to merge because the `h2` is None.
h2, i = h, intv
while i and h: h, i = h.next, i - 1
c1, c2 = intv, intv - i # the `c2`: length of `h2` can be small than the `intv`.
# merge the `h1` and `h2`.
while c1 and c2:
if h1.val < h2.val: pre.next, h1, c1 = h1, h1.next, c1 - 1
else: pre.next, h2, c2 = h2, h2.next, c2 - 1
pre = pre.next
pre.next = h1 if c1 else h2
while c1 > 0 or c2 > 0: pre, c1, c2 = pre.next, c1 - 1, c2 - 1
pre.next = h
intv *= 2
return res.next标签:字符串,栈
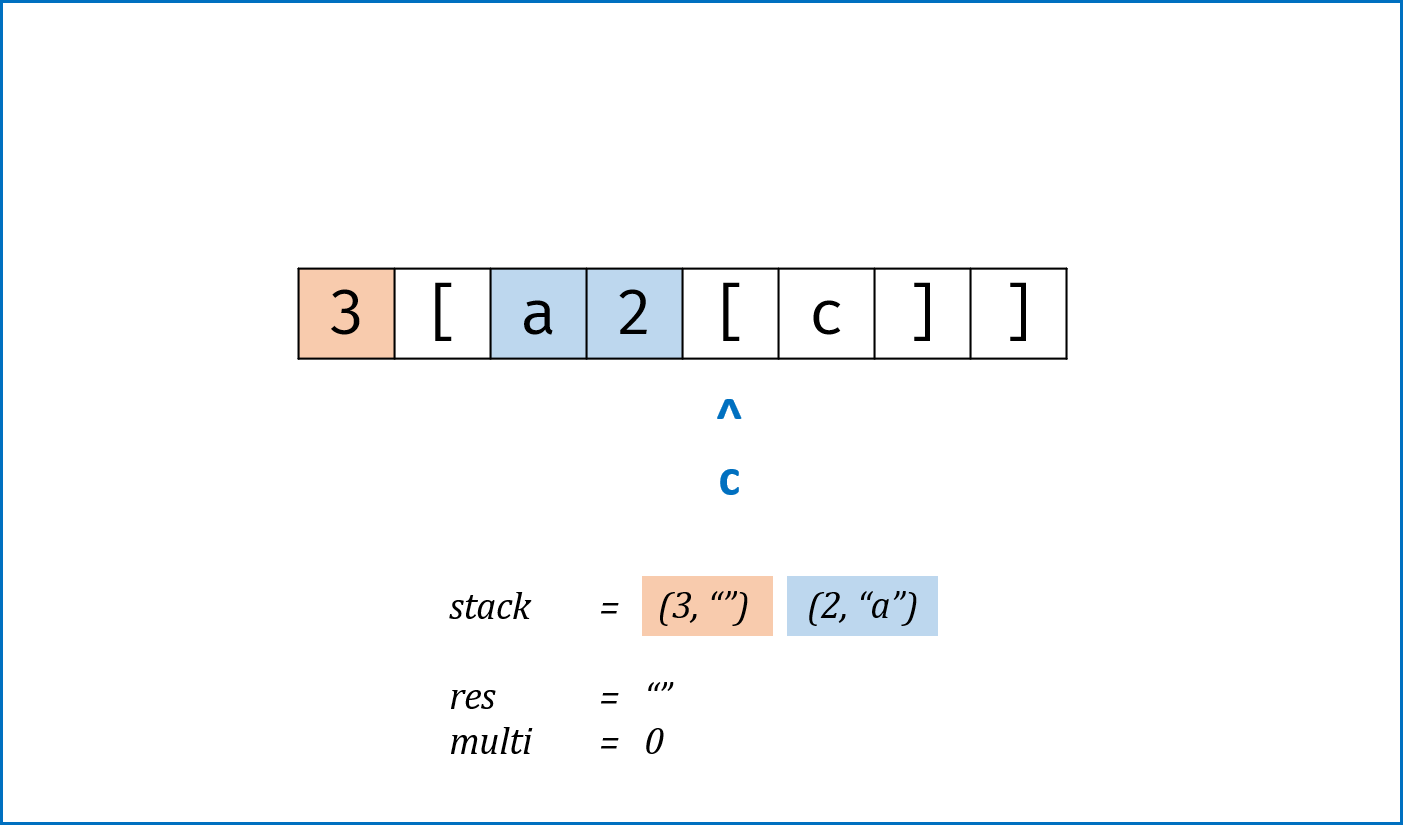
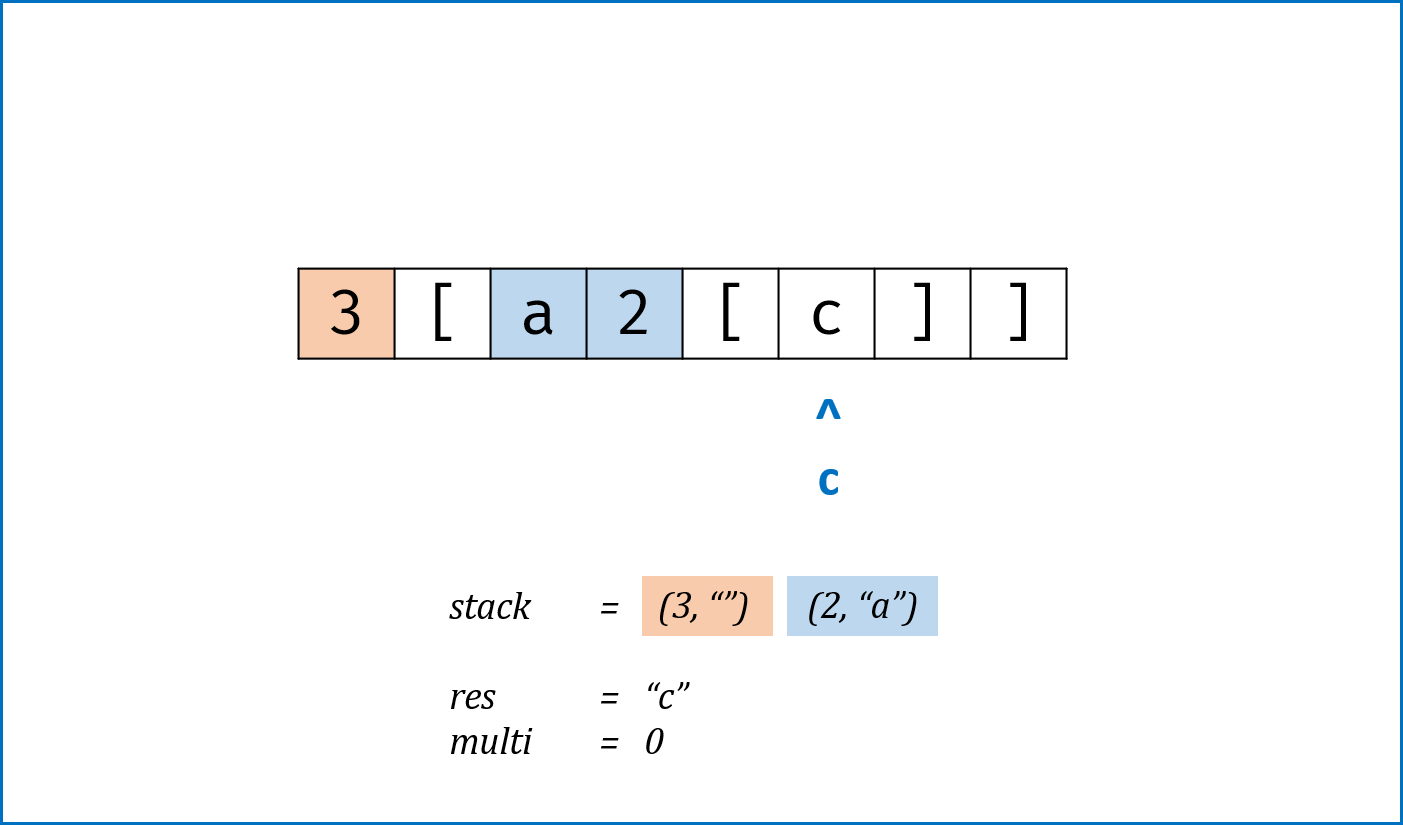
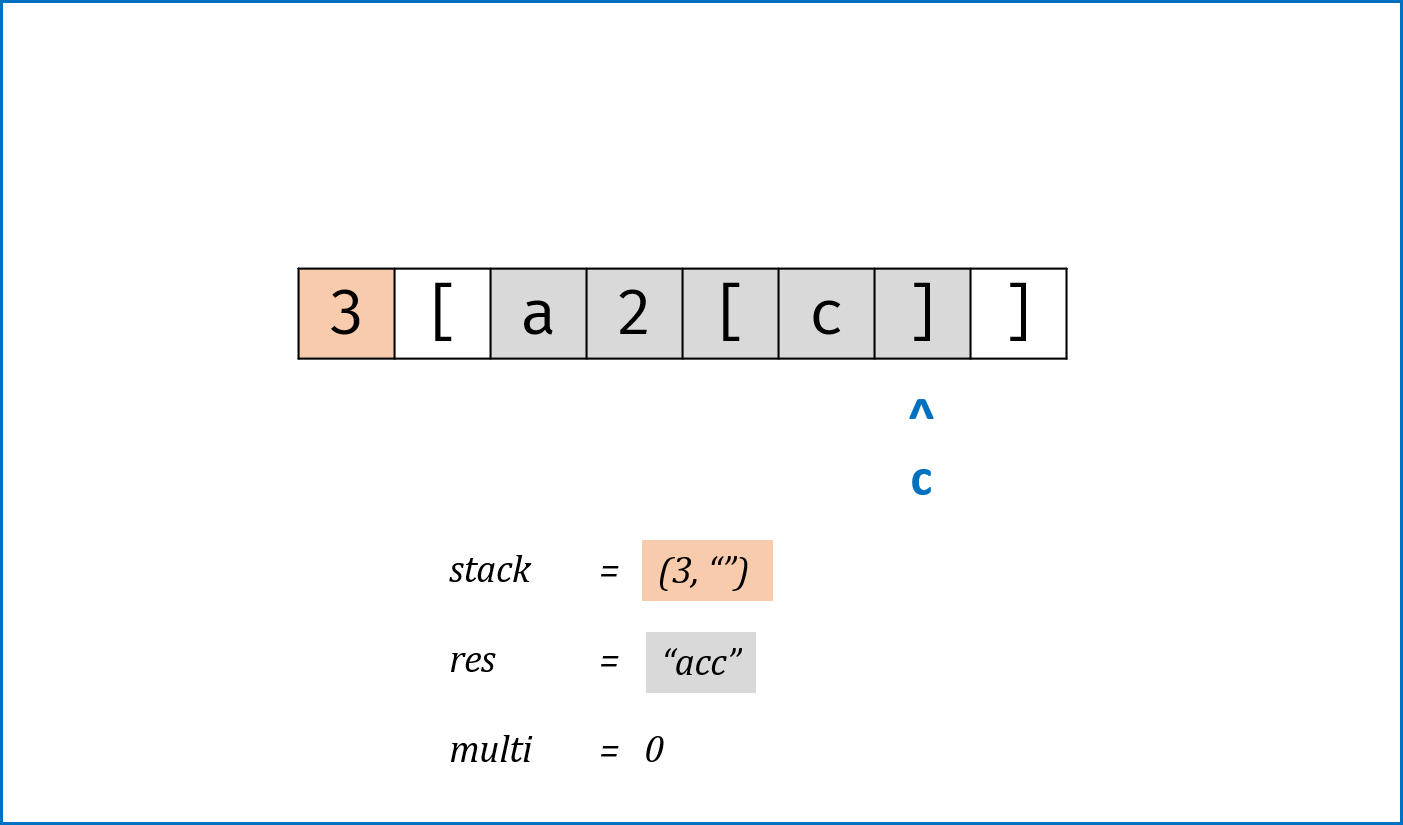
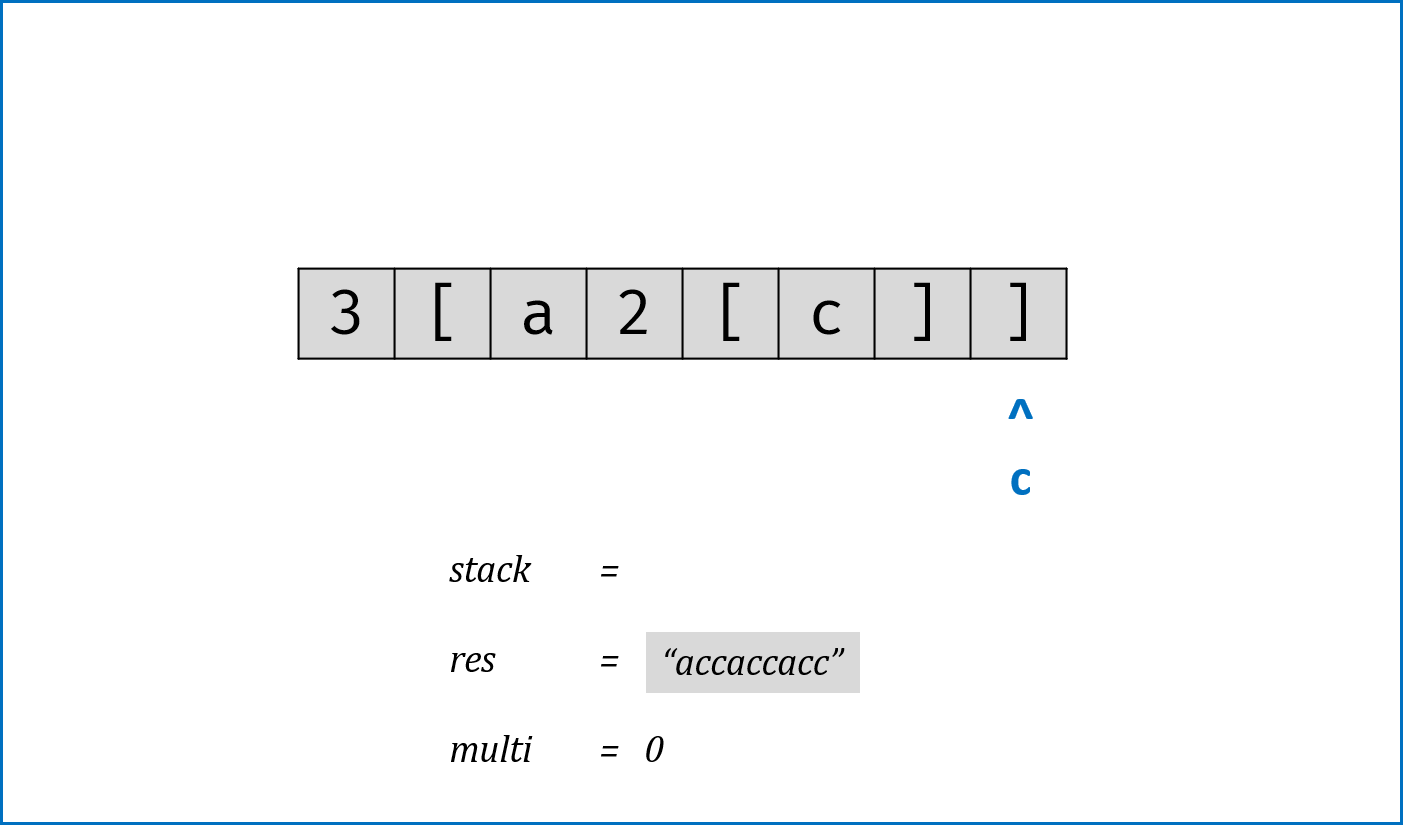
- 解析
逆波兰式(后缀表达式);同理还有前缀表达式、中缀表达式。 - 利用栈先进后出的特性遍历逆波兰式,当遇到计算符号时pop前两个字符进行计算,将计算结果push进stack;遇到数字时直接push进stack。
class Solution:
def evalRPN(self, tokens: [str]) -> int:
symbol = ['+', '-', '*', '/']
stack = []
for t in tokens:
if t in symbol:
stack.append(self.eval(stack.pop(-2), stack.pop(), t))
else:
stack.append(int(t))
return stack[-1]
def eval(self, x, y, symbol):
if symbol == '+': return x + y
if symbol == '-': return x - y
if symbol == '*': return x * y
if symbol == '/': return int(x / y)class Solution {
private static final Set<String> SYMBOLS = new HashSet<>(Arrays.asList("+","-","*","/"));
public int evalRPN(String[] tokens) {
Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<>();
for(String t : tokens){
if(SYMBOLS.contains(t)){
int y = stack.pop();
int x = stack.pop();
stack.push(eval(x, y, t));
} else {
stack.push(Integer.parseInt(t));
}
}
return stack.peek();
}
private int eval(int x, int y, String symbol){
switch(symbol){
case "+": return x + y;
case "-": return x - y;
case "*": return x * y;
default: return x / y;
}
}
}标签:字符串,双指针
- 先处理字符串,将首尾空格都删除;
- 倒序遍历字符串,当第一次遇到空格时,添加
s[i + 1: j](即添加一个完整单词); - 然后,将直至下一个单词中间的空格跳过,并记录下一个单词尾部
j; - 继续遍历,直至下一次遇到第一个空格,回到
1.步骤;
- 倒序遍历字符串,当第一次遇到空格时,添加
- 由于
s首部没有空格,因此最后需要将第一个单词加入,再return。 - python可一行实现。
class Solution:
def reverseWords(self, s: str) -> str:
s = s.strip()
res = ""
i, j = len(s) - 1, len(s)
while i > 0:
if s[i] == ' ':
res += s[i + 1: j] + ' '
while s[i] == ' ': i -= 1
j = i + 1
i -= 1
return res + s[:j] def reverseWords1(self, s: str) -> str:
return " ".join(s.split()[::-1])class Solution {
public String reverseWords(String s) {
StringBuffer res = new StringBuffer();
s = s.trim(); // delete leading or trailing spaces.
int i = s.length() - 1, j = s.length();
while (i > 0) {
if (s.charAt(i) == ' ') {
res.append(s.substring(i + 1, j));
res.append(' ');
while (s.charAt(i) == ' ') i--; // ignore extra spaces between words.
j = i + 1;
}
i--;
}
return res.append(s.substring(0, j)).toString();
}
}标签:动态规划,数组
- 此题与53题类似,不同处是
$53$ 题的运算是加法,本题是乘法。- 对于加法,在遍历数组中始终取
max(ma + nums[i], nums[i])即可,因为无论nums[i]的正负如何,最大值一定出现在当前最大值 + 当前值 or 当前值 中的一个。 - 对与乘法,在遍历数组中,若
nums[i]是负数,那么ma * nums[i](即当前最大值与nums[i]的乘积)会变成当前最小值(负数),因此不能简单的只记录最大值。
- 对于加法,在遍历数组中始终取
- 本题的解题思路是同时记录当前最大值和最小值
ma,mi:- 当
nums[i]是正数时,ma仍然是最大值,mi * nums[i]为最小值; - 当
nums[i]是负数时,ma将变成最小值,mi * nums[i]为最大值; - 因此,当
nums[i] < 0时,我们交换ma, mi。
- 当
- 在遍历
nums过程中,每次更新res获取全局最大值。
class Solution:
def maxProduct(self, nums: List[int]) -> int:
mi = ma = res = nums[0]
for i in range(1, len(nums)):
if nums[i] < 0: mi, ma = ma, mi
ma = max(ma * nums[i], nums[i])
mi = min(mi * nums[i], nums[i])
res = max(res, ma)
return resclass Solution {
public int maxProduct(int[] nums) {
int max = nums[0], min = nums[0], res = nums[0];
for(int i = 1; i < nums.length; i++){
if(nums[i] < 0){
int tmp = max;
max = min;
min = tmp;
}
max = Math.max(nums[i], max * nums[i]);
min = Math.min(nums[i], min * nums[i]);
res = Math.max(max, res);
}
return res;
}
}标签:数组,二分法
- 旋转排序数组
nums可以被拆分为2个排序数组nums1,nums2,并且nums1中所有元素比nums2大(因为nums中没有重复值); - 因此,考虑二分法寻找值
nums[i],满足nums[i] < nums[i-1]andnums[i] < nums[i+1] - 设置
left,right指针在nums数组两端,mid为中点:- 当
nums[mid] > nums[right]时,一定满足mid < i <= right,因此left = mid + 1; - 当
nums[mid] < nums[right]时,一定满足left < i <= mid,因此right = mid; - 当
nums[mid] == nums[right]时,说明数组长度len(num) == 1(因为计算mid向下取整);当left = right也满足,但本题left == right时跳出循环。
- 当
class Solution:
def findMin(self, nums: [int]) -> int:
left, right = 0, len(nums) - 1
while left < right:
mid = (left + right) // 2
if nums[mid] > nums[right]: left = mid + 1
else: right = mid
return nums[left]class Solution {
public int findMin(int[] nums) {
int left = 0, right = nums.length - 1;
while(left < right){
int mid = (left + right) / 2;
if(nums[mid] > nums[right]) left = mid + 1;
else right = mid;
}
return nums[left];
}
}标签:二分法,数组
- 旋转排序数组
$nums$ 可以被拆分为 2 个排序数组$nums1$ ,$nums2$ ,并且nums1任一元素 >= nums2任一元素;因此,考虑二分法寻找此两数组的分界点$nums[i]$ (即第 2 个数组的首个元素)。 - 设置
$left$ ,$right$ 指针在$nums$ 数组两端,$mid$ 为每次二分的中点:- 当
nums[mid] > nums[right]时,$mid$ 一定在第 1 个排序数组中,$i$ 一定满足mid < i <= right,因此执行left = mid + 1; - 当
nums[mid] < nums[right]时,$mid$ 一定在第 2 个排序数组中,$i$ 一定满足left < i <= mid,因此执行right = mid; - 当
nums[mid] == nums[right]时,是此题对比 153题 的难点(原因是此题中数组的元素可重复,难以判断分界点$i$ 指针区间);- 例如
$[1, 0, 1, 1, 1]$ 和$[1, 1, 1, 0, 1]$ ,在left = 0,right = 4,mid = 2时,无法判断$mid$ 在哪个排序数组中。 - 我们采用
right = right - 1解决此问题,证明:- 此操作不会使数组越界:因为迭代条件保证了
right > left >= 0; - 此操作不会使最小值丢失:假设
$nums[right]$ 是最小值,有两种情况:- 若
$nums[right]$ 是唯一最小值:那就不可能满足判断条件nums[mid] == nums[right],因为mid < right(left != right且mid = (left + right) // 2向下取整); - 若
$nums[right]$ 不是唯一最小值,由于mid < right而nums[mid] == nums[right],即还有最小值存在于$[left, right - 1]$ 区间,因此不会丢失最小值。
- 若
- 此操作不会使数组越界:因为迭代条件保证了
- 例如
- 当
- 以上是理论分析,可以代入以下数组辅助思考:
$[1, 2, 3]$ $[1, 1, 0, 1]$ $[1, 0, 1, 1, 1]$ $[1, 1, 1, 1]$
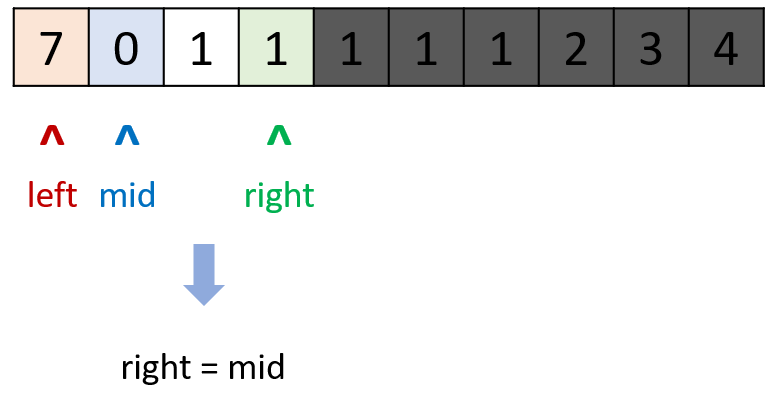
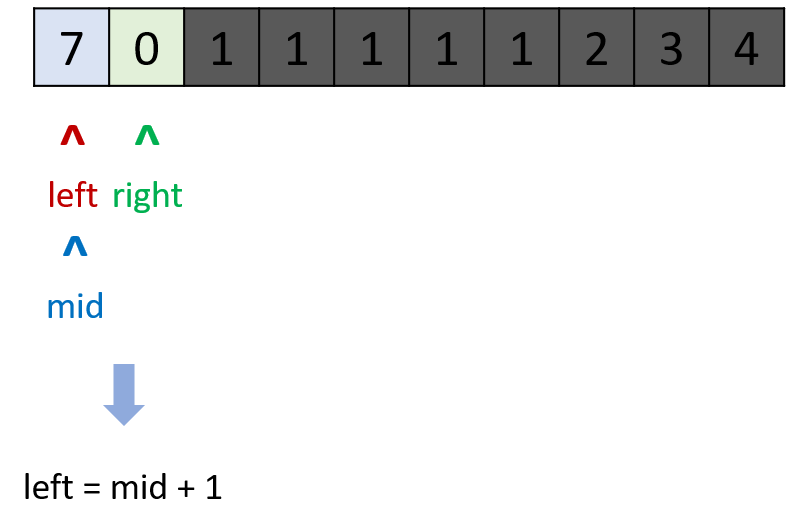
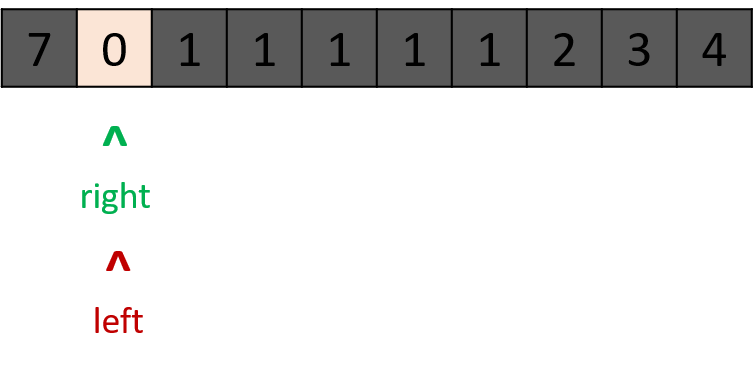
- 时间复杂度
$O(logN)$ ,在特例情况下会退化到$O(N)$ (例如$[1, 1, 1, 1]$ )。
class Solution:
def findMin(self, nums: List[int]) -> int:
left, right = 0, len(nums) - 1
while left < right:
mid = (left + right) // 2
if nums[mid] > nums[right]: left = mid + 1
elif nums[mid] < nums[right]: right = mid
else: right = right - 1 # key
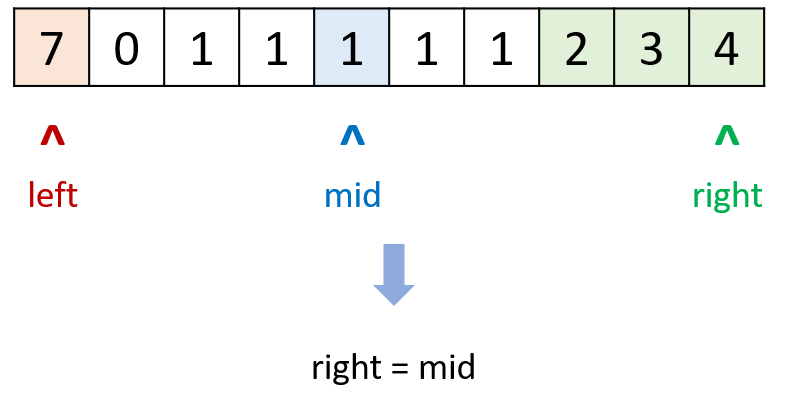
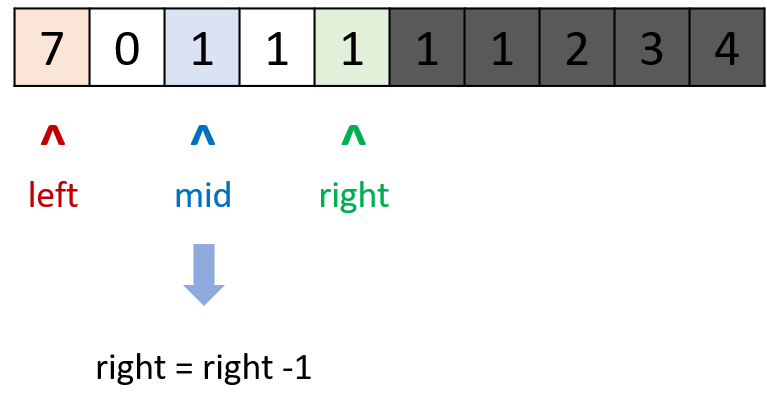
return nums[left]class Solution {
public int findMin(int[] nums) {
int left = 0, right = nums.length - 1;
while (left < right) {
int mid = (left + right) / 2;
if (nums[mid] > nums[right]) left = mid + 1;
else if (nums[mid] < nums[right]) right = mid;
else right = right - 1;
}
return nums[left];
}
}标签:栈,设计
- 借用一个辅助栈
min_stack,用于存储stack中最小值:push:每当push新值进来时,如果“小于等于”min_stack栈顶值,则一起push到min_stack,即更新了最小值;pop:判断pop出去的元素值是否是min_stack栈顶元素值(即最小值),如果是则将min_stack栈顶元素一起pop,这样可以保证min_stack栈顶元素始终是stack中的最小值。getMin:返回min_stack栈顶即可。
min_stack的作用是对stack中的元素做标记,标记的原则是min_stack中元素一定是降序的(栈底最大栈顶最小)。换个角度理解,min_stack等价于遍历stack所有元素,把升序的数字都删除掉,留下一个从栈底到栈顶降序的栈。本题要求获取最小值的复杂度是O(1),因此须构建辅助栈,在push与pop的过程中始终保持辅助栈为一个降序栈。- 时间空间复杂度都为
O(N),获取最小值复杂度为O(1)。
class MinStack:
def __init__(self):
"""
initialize your data structure here.
"""
self.stack = []
self.min_stack = []
def push(self, x: int) -> None:
self.stack.append(x)
if not self.min_stack or x <= self.min_stack[-1]:
self.min_stack.append(x)
def pop(self) -> None:
if self.stack.pop() == self.min_stack[-1]:
self.min_stack.pop()
def top(self) -> int:
return self.stack[-1]
def getMin(self) -> int:
return self.min_stack[-1]class MinStack {
private Stack<Integer> stack;
private Stack<Integer> min_stack;
/** initialize your data structure here. */
public MinStack() {
stack = new Stack<>();
min_stack = new Stack<>();
}
public void push(int x) {
stack.push(x);
if(min_stack.isEmpty() || x <= min_stack.peek())
min_stack.push(x);
}
public void pop() {
if(stack.pop().equals(min_stack.peek()))
min_stack.pop();
}
public int top() {
return stack.peek();
}
public int getMin() {
return min_stack.peek();
}
}标签:树,迭代
- 根据题目描述,树中任何节点的右子节点若存在一定有左子节点,因此思路是向左遍历树进行转化;
- 规律是:左子节点变父节点;父节点变右子节点;右子节点变父节点。
- 对于某节点
root,修改root.left,root.right之前,需要将三者都存下来:root.left是下一轮递归的主节点;root是下一轮递归root的root.right;root.right是下一轮递归root的root.left。
- 返回parent。
class Solution:
def upsideDownBinaryTree(self, root: TreeNode) -> TreeNode:
parent = parent_right = None
while root:
root_left = root.left
root.left = parent_right
parent_right = root.right
root.right = parent
parent = root
root = root_left
return parentclass Solution {
public TreeNode upsideDownBinaryTree(TreeNode root) {
TreeNode parent = null, parent_right = null;
while(root != null){
TreeNode root_left = root.left;
root.left = parent_right;
parent_right = root.right;
root.right = parent;
parent = root;
root = root_left;
}
return parent;
}
}标签:字符串,双指针
- 设置两指针
i,j指向str头部:j向右移动,dic[j]统计目前[i:j]间s[j]出现次数,dist统计不同字符的数量;j移动一格后,若dist > 2,移动左指针i,直到[i:j]间不同字符数量<=2;j每移动一格,需统计一次最大字串长度res = max(res, j - i + 1)。
class Solution:
def lengthOfLongestSubstringTwoDistinct(self, s: str) -> int:
dic = {}
i, dist, res = 0, 0, 0
for j in range(len(s)):
if s[j] in dic and dic[s[j]]:
dic[s[j]] += 1
else:
dic[s[j]] = 1
dist += 1
while dist > 2:
dic[s[i]] -= 1
if not dic[s[i]]: dist -= 1
i += 1
res = max(res, j - i + 1)
return resclass Solution {
public int lengthOfLongestSubstringTwoDistinct(String s) {
int[] count = new int[256];
int i = 0, numDistinct = 0, maxLen = 0;
for (int j = 0; j < s.length(); j++) {
if (count[s.charAt(j)] == 0) numDistinct++;
count[s.charAt(j)]++;
while (numDistinct > 2) {
count[s.charAt(i)]--;
if (count[s.charAt(i)] == 0) numDistinct--;
i++;
}
maxLen = Math.max(maxLen, j - i + 1);
}
return maxLen;
}
}标签:字符串、指针
- 我们通常做这种题的思路是设定两个指针分别指向两个链表头部,一起向前走直到其中一个到达末端,另一个与末端距离则是两链表的
长度差。再通过长链表指针先走的方式消除长度差,最终两链表即可同时走到相交点。 - 换个方式消除长度差: 拼接两链表。
设长-短链表为
C,短-长链表为D(分别代表长链表在前和短链表在前的拼接链表),则当C走到长短链表交接处时,D走在长链表中,且与长链表头距离为长度差; 以下图片帮助理解:当ha == hb时跳出,返回即可。
class Solution(object):
def getIntersectionNode(self, headA, headB):
ha, hb = headA, headB
while ha != hb:
ha = ha.next if ha else headB
hb = hb.next if hb else headA
return hapublic class Solution {
public ListNode getIntersectionNode(ListNode headA, ListNode headB) {
ListNode ha = headA, hb = headB;
while (ha != hb) {
ha = ha != null ? ha.next : headB;
hb = hb != null ? hb.next : headA;
}
return ha;
}
}标签:字符串、指针
s和t长度之差大于1,返回False,先通过交换s,t保证len(s) < len(t);- 第一段匹配方法相同,找到第一个不同的
char,第一段后如果已经走完s,则直接返回,有以下两种情况:- 若
长度之差=0,说明为两相同string,返回False; - 若
长度之差=1,说明只有最末位不同,返回True。
- 若
- 第二段匹配需要根据长度之差做不同处理:
- 若
长度之差=0,则s,t的index同时+1(同时越过此不同字符),继续比较; - 若
长度之差=1,则s的index不变,t的index+1(越过需要插入的字符),继续比较;
- 若
- 如果能够匹配完整个
s,返回True,否则说明有两个及以上不同字符or插入点,返回False。
class Solution:
def isOneEditDistance(self, s: str, t: str) -> bool:
i, dif = 0, len(t) - len(s)
if dif < 0: s, t, dif = t, s, -dif
if dif > 1: return False # 1.
while i < len(s) and s[i] == t[i]: i += 1 # 2.
if i == len(s): return bool(dif)
if not dif: i += 1 # 3.1
while i < len(s) and s[i] == t[i + dif]: i += 1 # 3.
return i == len(s) #5.class Solution {
public boolean isOneEditDistance(String s, String t) {
int dif = t.length() - s.length(), i = 0;
if (dif < 0) return isOneEditDistance(t, s);
if (dif > 1) return false;
while (i < s.length() && s.charAt(i) == t.charAt(i)) i++;
if (i == s.length()) return dif > 0;
if (dif == 0) i++;
while (i < s.length() && s.charAt(i) == t.charAt(i + dif)) i++;
return i == s.length();
}
}标签:数组,双指针
- 使用双指针
low、num,遍历nums添加对应范围即可; - 需要先向
nums尾部添加upper + 1。
class Solution:
def findMissingRanges(self, nums: [int], lower: int, upper: int) -> [str]:
res = []
low = lower - 1
nums.append(upper + 1)
for num in nums:
dif = num - low
if dif == 2: res.append(str(low+1))
elif dif > 2: res.append(str(low+1) + "->" + str(num-1))
low = num
return resclass Solution {
public List<String> findMissingRanges(int[] nums, int lower, int upper) {
List<String> res = new ArrayList<>();
long pre = (long)lower - 1; // prevent 'int' overflow
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
if (nums[i] - pre == 2) res.add(String.valueOf(pre + 1));
else if (nums[i] - pre > 2) res.add((pre + 1) + "->" + (nums[i] - 1));
pre = nums[i]; // 'int' to 'long'
}
if (upper - pre == 1) res.add(String.valueOf(pre + 1));
else if (upper - pre > 1) res.add((pre + 1) + "->" + upper);
return res;
}
}标签:数组,众数
- 我们假设将第一个数字作为众数看待,遍历数组,若
元素 == 当前众数res则count += 1,否则count -= 1; - 在下次
count == 0时,意味着当前众数res的数量为已遍历元素一半;这种情况下,剩余数组众数仍等于原数组众数(因为最坏的情况是已遍历数组中一半是数组众数,一半是非众数)。 - 因此,在每次
count == 0时,记录当前数字为当前众数,当遍历完整个数组时,留下的res一定为整个数组的众数(最坏情况是在最后一个元素才找到众数,前面的count全部抵消)。
class Solution:
def majorityElement(self, nums: [int]) -> int:
count = 0
for num in nums:
if not count: res = num
count += 1 if num == res else -1
return resclass Solution {
public int majorityElement(int[] nums) {
int res = 0, count = 0;
for(int num : nums){
if(count == 0) res = num;
count += num == res ? 1 : -1;
}
return res;
}
}标签:哈希表Hash
- HashMap法:时间复杂度
O(N),空间复杂度O(N); add:在将数字添加进nums数组的同时,将数字作为key存入map,map的value存此数字在数组的位置;find:在搜索是否有加和时,遍历整个数组nums,判断value - nums[i]是否在map中:- 若在,还需要判断
map[value - nums[i]] == i,这个是为了排除是否是数组中��一个元素的加和(题意是必须两个不同元素的加和);因为如果add了两个相同的数字,那么map[value - nums[i]]一定大于i,因为在add操作中每次会刷新此数字的最新index。 - 若不在,就继续遍历,直至遍历完
nums。
- 若在,还需要判断
class TwoSum:
def __init__(self):
"""
Initialize your data structure here.
"""
self.nums = []
self.dic = {}
def add(self, number: int) -> None:
"""
Add the number to an internal data structure..
"""
self.nums.append(number)
self.dic[number] = len(self.nums) - 1
def find(self, value: int) -> bool:
"""
Find if there exists any pair of numbers which sum is equal to the value.
"""
for i in range(len(self.nums)):
tar = value - self.nums[i]
if tar in self.dic and self.dic[tar] != i: return True
return Falseclass TwoSum {
private Map<Integer, Integer> map;
private List<Integer> nums = new ArrayList<>();
/** Initialize your data structure here. */
public TwoSum() {
map = new HashMap<>();
}
/** Add the number to an internal data structure.. */
public void add(int number) {
nums.add(number);
map.put(number, nums.size() - 1);
}
/** Find if there exists any pair of numbers which sum is equal to the value. */
public boolean find(int value) {
for(int i = 0; i < nums.size(); i++){
int tar = value - nums.get(i);
if(map.containsKey(tar) && map.get(tar) > i) return true;
}
return false;
}
}标签:字符串
- 题意要求空间复杂度O(1),因此必须要在原数组上直接修改;
- 设倒序操作为
T,str = a b c,则有:c b a = ( aT bT cT )T
- 因此,我们只需要将
a,b,c分别倒置,再将整个str倒置,即可得到c b a。
class Solution:
def reverseWords(self, s: [str]) -> None:
"""
Do not return anything, modify str in-place instead.
"""
i = 0
for j in range(len(s)): # aT bT c
if s[j] != ' ': continue
self.reverse(s, i, j)
i = j + 1
self.reverse(s, i, len(s)) # aT bT cT
self.reverse(s, 0, len(s)) # c b a
def reverse(self, s, i, j):
for k in range(i, (i + j) // 2):
g = j - 1 - k + i
s[k], s[g] = s[g], s[k]class Solution {
public void reverseWords(char[] str) {
int i = 0;
for(int j = 0; j < str.length; j++){ // aTbTc
if(str[j] != ' ') continue;
reverse(str, i, j);
i = j + 1;
}
reverse(str, i, str.length); // aTbTcT
reverse(str, 0, str.length); // cba
}
private void reverse(char[] str, int i, int j){
for(int k = i; k < (i + j) / 2; k++){
char tmp = str[k];
int g = j - 1 - k + i;
str[k] = str[g];
str[g] = tmp;
}
}
}标签:深度优先遍历DFS、广度优先遍历BFS
- 目标是找到矩阵中“岛屿的数量”,上下左右相连的
1都被认为是连续岛屿。 - dfs方法: 设目前指针指向一个岛屿中的某一点
(i, j),寻找包括此点的岛屿边界。- 从
(i, j)向此点的上下左右(i+1,j),(i-1,j),(i,j+1),(i,j-1)做深度搜索。 - 终止条件:
(i, j)越过矩阵边界;grid[i][j] == 0,代表此分支已越过岛屿边界。
- 搜索岛屿的同时,执行
grid[i][j] = '0',即将岛屿所有节点删除,以免之后重复搜索相同岛屿。
- 从
- 主循环:
- 遍历整个矩阵,当遇到
grid[i][j] == '1'时,从此点开始做深度优先搜索dfs,岛屿数count + 1且在深度优先搜索中删除此岛屿。
- 遍历整个矩阵,当遇到
- 最终返回岛屿数
count即可。
class Solution:
def numIslands(self, grid: [[str]]) -> int:
def dfs(grid, i, j):
if not 0 <= i < len(grid) or not 0 <= j < len(grid[0]) or grid[i][j] == '0': return
grid[i][j] = '0'
dfs(grid, i + 1, j)
dfs(grid, i, j + 1)
dfs(grid, i - 1, j)
dfs(grid, i, j - 1)
count = 0
for i in range(len(grid)):
for j in range(len(grid[0])):
if grid[i][j] == '1':
dfs(grid, i, j)
count += 1
return countclass Solution {
public int numIslands(char[][] grid) {
int count = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < grid.length; i++) {
for(int j = 0; j < grid[0].length; j++) {
if(grid[i][j] == '1'){
dfs(grid, i, j);
count++;
}
}
}
return count;
}
private void dfs(char[][] grid, int i, int j){
if(i < 0 || j < 0 || i >= grid.length || j >= grid[0].length || grid[i][j] == '0') return;
grid[i][j] = '0';
dfs(grid, i + 1, j);
dfs(grid, i, j + 1);
dfs(grid, i - 1, j);
dfs(grid, i, j - 1);
}
}- 主循环和思路一类似,不同点是在于搜索某岛屿边界的方法不同。
- bfs方法:
- 借用一个队列
queue,判断队列首部节点(i, j)是否未越界且为1:- 若是则置零(删除岛屿节点),并将此节点上下左右节点
(i+1,j),(i-1,j),(i,j+1),(i,j-1)加入队列; - 若不是则跳过此节点;
- 若是则置零(删除岛屿节点),并将此节点上下左右节点
- 循环
pop队列首节点,直到整个队列为空,此时已经遍历完此岛屿。
- 借用一个队列
class Solution:
def numIslands(self, grid: [[str]]) -> int:
def bfs(grid, i, j):
queue = [[i, j]]
while queue:
[i, j] = queue.pop(0)
if 0 <= i < len(grid) and 0 <= j < len(grid[0]) and grid[i][j] == '1':
grid[i][j] = '0'
queue += [[i + 1, j], [i - 1, j], [i, j - 1], [i, j + 1]]
count = 0
for i in range(len(grid)):
for j in range(len(grid[0])):
if grid[i][j] == '0': continue
bfs(grid, i, j)
count += 1
return countclass Solution {
public int numIslands(char[][] grid) {
int count = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < grid.length; i++) {
for(int j = 0; j < grid[0].length; j++) {
if(grid[i][j] == '1'){
bfs(grid, i, j);
count++;
}
}
}
return count;
}
private void bfs(char[][] grid, int i, int j){
Queue<int[]> list = new LinkedList<>();
list.add(new int[] { i, j });
while(!list.isEmpty()){
int[] cur = list.remove();
i = cur[0]; j = cur[1];
if(0 <= i && i < grid.length && 0 <= j && j < grid[0].length && grid[i][j] == '1') {
grid[i][j] = '0';
list.add(new int[] { i + 1, j });
list.add(new int[] { i - 1, j });
list.add(new int[] { i, j + 1 });
list.add(new int[] { i, j - 1 });
}
}
}
}标签:链表、双指针
- 遍历链表,在遍历的过程中更新两个指针
pre,head:pre,head分别指向前一个Node和当前Node,每次执行head.next = prenex用于提前保存下一个Node。
- 由于需要返回新的链表头部,所以设置跳出条件为
head.next == null,跳出后将最后head指向pre,并返回head。
class Solution:
def reverseList(self, head: ListNode) -> ListNode:
if not head: return
pre = None
while head.next:
nex = head.next
head.next = pre
pre = head
head = nex
head.next = pre
return headclass Solution {
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
if(head == null) return null;
ListNode pre = null, nex = null;
while(head.next != null) {
nex = head.next;
head.next = pre;
pre = head;
head = nex;
}
head.next = pre;
return head;
}
}标签:拓扑排序,深度优先遍历,广度优先遍历
- 本题可约化为:课程安排图是否是有向无环图(DAG)。即课程间规定了前置条件,但不能构成任何环路,否则课程前置条件将不成立。
- 思路是通过 拓扑排序 判断此课程安排图是否是 有向无环图(DAG)。
- 拓扑排序是对DAG的顶点进行排序,使得对每一条有向边
$(u, v)$ ,均有$u$ (在排序记录中)比$v$ 先出现。亦可理解为对某点$v$ 而言,只有当$v$ 的所有源点均出现了,$v$ 才能出现。
- 拓扑排序是对DAG的顶点进行排序,使得对每一条有向边
- 通过课程前置条件列表
prerequisites可以得到课程安排图的 邻接矩阵adjacency。
- 算法流程:
- 统计课程安排图中每个节点的入度,生成 入度表
indegrees。 - 借助一个队列
queue,将所有入度为$0$ 的节点入队。 - 当
queue非空时,依次将队首节点出队,在课程安排图中删除此节点pre:- 并不是真正从邻接表中删除此节点
pre,而是将此节点对应所有邻接节点cur的入度$-1$ ,即indegrees[cur] -= 1。 - 当入度
$-1$ 后邻接节点cur的入度为$0$ ,说明cur所有的前驱节点已经被“删除”,此时将cur入队。
- 并不是真正从邻接表中删除此节点
- 在每次
pre出队时,执行numCourses--;- 若整个课程安排图是有向无环图(即可以安排),则所有节点一定都入队/出队过,即完成拓扑排序。若有环,一定有节点的入度始终不为
$0$ 。 - 因此,拓扑排序出队次数等于课程个数,返回
numCourses == 0判断课程是否可以成功安排。
- 若整个课程安排图是有向无环图(即可以安排),则所有节点一定都入队/出队过,即完成拓扑排序。若有环,一定有节点的入度始终不为
-
复杂度分析:
- 时间复杂度
$O(N + M)$ ,遍历一个图需要访问所有节点和所有临边,$N$ 和$M$ 分别为节点数量和临边数量; - 空间复杂度
$O(N)$ ,为建立邻接矩阵所需额外空间。
- 时间复杂度
class Solution:
def canFinish(self, numCourses: int, prerequisites: List[List[int]]) -> bool:
indegrees = [0 for _ in range(numCourses)]
adjacency = [[] for _ in range(numCourses)]
queue = []
# Get the indegree and adjacency of every course.
for cur, pre in prerequisites:
indegrees[cur] += 1
adjacency[pre].append(cur)
# Get all the courses with the indegree of 0.
for i in range(len(indegrees)):
if not indegrees[i]: queue.append(i)
# BFS TopSort.
while queue:
pre = queue.pop(0)
numCourses -= 1
for cur in adjacency[pre]:
indegrees[cur] -= 1
if not indegrees[cur]: queue.append(cur)
return not numCoursesclass Solution {
public boolean canFinish(int numCourses, int[][] prerequisites) {
int[] indegrees = new int[numCourses];
for(int[] cp : prerequisites) indegrees[cp[0]]++;
LinkedList<Integer> queue = new LinkedList<>();
for(int i = 0; i < numCourses; i++){
if(indegrees[i] == 0) queue.addLast(i);
}
while(!queue.isEmpty()) {
Integer pre = queue.removeFirst();
numCourses--;
for(int[] req : prerequisites) {
if(req[1] != pre) continue;
if(--indegrees[req[0]] == 0) queue.add(req[0]);
}
}
return numCourses == 0;
}
}- 思路是通过 DFS 判断图中是否有环,算法流程如下:
- 借助一个标志列表
flags,用于判断每个节点i(课程)的状态:- 未被DFS访问:
i == 0; - 已被其他节点启动的DFS访问:
i == -1; - 已被当前节点启动的DFS访问:
i == 1。
- 未被DFS访问:
- 对
numCourses个节点依次执行 DFS,判断每个节点起步 DFS 是否存在环,若存在环直接返回$False$ 。DFS 流程;- 终止条件:
- 当
flag[i] == -1,说明当前访问节点已被其他节点启动的DFS访问,无需再重复搜索,直接返回$True$ 。 - 当
flag[i] == 1,说明在本轮DFS搜索中节点i被第$2$ 次访问,即课程安排图有环,直接返回$False$。
- 当
- 将当前访问节点
i对应flag[i]置$1$ ,即标记其被本轮 DFS 访问过; - 递归访问当前节点
i的所有邻接节点j,当发现环直接返回$False$ ; - 当前节点所有邻接节点已被遍历,并没有发现环,则将当前节点
flag置为$-1$ 并返回$True$ 。
- 终止条件:
- 若整个图DFS结束并未发现环,返回
$True$ 。
-
复杂度分析:
- 时间复杂度
$O(N + M)$ :遍历一个图需要访问所有节点和所有临边,$N$ 和$M$ 分别为节点数量和临边数量; - 空间复杂度
$O(N)$ ,为建立邻接矩阵所需额外空间。
- 时间复杂度
class Solution:
def canFinish(self, numCourses: int, prerequisites: List[List[int]]) -> bool:
def dfs(i, adjacency, flags):
if flags[i] == -1: return True
if flags[i] == 1: return False
flags[i] = 1
for j in adjacency[i]:
if not dfs(j, adjacency, flags): return False
flags[i] = -1
return True
adjacency = [[] for _ in range(numCourses)]
flags = [0 for _ in range(numCourses)]
for cur, pre in prerequisites:
adjacency[pre].append(cur)
for i in range(numCourses):
if not dfs(i, adjacency, flags): return False
return Trueclass Solution {
public boolean canFinish(int numCourses, int[][] prerequisites) {
int[][] adjacency = new int[numCourses][numCourses];
int[] flags = new int[numCourses];
for(int[] cp : prerequisites)
adjacency[cp[1]][cp[0]] = 1;
for(int i = 0; i < numCourses; i++){
if(!dfs(adjacency, flags, i)) return false;
}
return true;
}
private boolean dfs(int[][] adjacency, int[] flags, int i) {
if(flags[i] == 1) return false;
if(flags[i] == -1) return true;
flags[i] = 1;
for(int j = 0; j < adjacency.length; j++) {
if(adjacency[i][j] == 1 && !dfs(adjacency, flags, j)) return false;
}
flags[i] = -1;
return true;
}
}标签:数组,堆排序
- 最简单的方法就是使用
sort()对数组排序,然后直接返回nums[len(nums) - k],此方法的时间复杂度为O(nlogn); - 使用
堆可以进一步降低复杂度至O(nlogk),做法是:- 建立一个小顶堆,先把
nums中[0, k)的元素添加至小顶堆; - 对于
[k, len(nums) - 1]的元素,判断其与小顶堆堆顶元素大小关系,若大于则push进堆(每次push进堆时间复杂度为O(logk)),并将堆顶元素pop,这样做是为了保证小顶堆中始终有k`个元素; - 根据以上机制,最终小顶堆中将会保存
最大的k个元素,且堆顶为此k元素里最小的那个。
- 建立一个小顶堆,先把
- 最后返回堆顶即可。
import heapq
class Solution:
def findKthLargest(self, nums: [int], k: int) -> int:
heap = []
for num in nums[:k]:
heapq.heappush(heap, num)
for num in nums[k:]:
if num > heap[0]:
heapq.heappop(heap)
heapq.heappush(heap, num)
return heap[0]class Solution {
public int findKthLargest(int[] nums, int k) {
Queue<Integer> heap = new PriorityQueue<>();
for (int i = 0; i < k; i++)
heap.add(nums[i]);
for (int i = k; i < nums.length; i++) {
if (nums[i] > heap.peek()) {
heap.remove();
heap.add(nums[i]);
}
}
return heap.peek();
}
}标签:哈希表
- 使用
set或HashMap解,原理相同,都是利用其查询某元素为O(1)时间复杂度;- 遍历
nums,若set或HashMap中含有当前数字n,则直接返回true; - 直到遍历完毕,返回
false。
- 遍历
Python使用字典;Java使用HashSet。
class Solution:
def containsDuplicate(self, nums: List[int]) -> bool:
dic = {}
for n in nums:
if n in dic: return True
dic[n] = 1
return Falseclass Solution {
public boolean containsDuplicate(int[] nums) {
Set<Integer> set = new HashSet<>(nums.length);
for(int n : nums){
if(set.contains(n)) return true;
set.add(n);
}
return false;
}
}标签:BST,中序遍历
-
二叉搜索树BST有一个重要性质:中序遍历为排序数组,根据这个性质,我们可将问题转化为寻找中序遍历第$k$ 个节点的值; - 实现的方法是建立两个全局变量
res和count,分别用于存储答案与计数:- 在每次访问节点时,执行
count$-1$ ; - 当
count == 0时,代表已经到达第$k$ 个节点,此时记录答案至res;
- 在每次访问节点时,执行
- 找到答案后,已经不用继续遍历,因此每次判断
res是否为空,若不为空直接返回。
class Solution:
def kthSmallest(self, root: TreeNode, k: int) -> int:
self.res, self.count = None, k
def inorder(root):
if not (root and self.count): return
inorder(root.left)
self.count -= 1
if not self.count: self.res = root.val
inorder(root.right)
inorder(root)
return self.resclass Solution {
private int res, count;
public int kthSmallest(TreeNode root, int k) {
count = k;
inorder(root);
return res;
}
private void inorder(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null || count == 0) return;
inorder(root.left);
if(--count == 0) res = root.val;
inorder(root.right);
}
}标签:位运算
- 若满足
$n = 2^x$ 且$x$ 为整数,则一定满足以下条件:- 恒有
n & (n - 1) == 0,这是因为:- 二进制下,
$n$ 最高位为$1$ ,其余所有位为$0$ ; - 二进制下,
$n - 1$ 最高位为$0$ ,其余所有位为$1$ ;
- 二进制下,
- 一定有
$n > 0$ 。
- 恒有
- 因此,通过
n > 0且n & (n - 1) == 0即可判定是否满足$n = 2^x$ 。
| 2^x | n | n - 1 |
|---|---|---|
| ... | ... | ... |
class Solution:
def isPowerOfTwo(self, n: int) -> bool:
return n > 0 and n & (n - 1) == 0class Solution {
public boolean isPowerOfTwo(int n) {
return n > 0 && (n & (n - 1)) == 0;
}
}标签:BST
- 给定
p,q,最低的公共祖先有三种情况:p,q分别位于公共祖先的左子树和右子树;p为公共祖先,q在p的左右子树中;q为公共祖先,p在q的左右子树中。
- 根据二叉搜索树性质,根节点值一定大于左树中所有子节点值、小于右树中所有子节点值;
- 根据以上性质,此题是要在从上至下遍历二叉搜索树中,找第一个满足
p.val <= root.val <= q.val的节点(设p.val < q.val)。
class Solution:
def lowestCommonAncestor(self, root: 'TreeNode', p: 'TreeNode', q: 'TreeNode') -> 'TreeNode':
if p.val > q.val: p, q = q, p
while root:
if root.val < p.val: root = root.right
elif root.val > q.val: root = root.left
else: return rootclass Solution {
public TreeNode lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode root, TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {
int pv = Math.min(p.val, q.val), qv = Math.max(p.val, q.val);
while (root != null) {
if (root.val < pv) root = root.right;
else if (root.val > qv) root = root.left;
else return root;
}
return null;
}
}标签:后序遍历
- 对二叉树做
后序遍历,回溯:回溯时:捕获mid,即当前节点是否为p或q;- 当
leftrightmid三个中有两个为True时,说明当前节点是最近的公共节点,记录至res;
- 当
返回值:左子树或右子树或当前节点中包含p或q;
- 最终,返回最近公共节点
res。
class Solution:
def lowestCommonAncestor(self, root: 'TreeNode', p: 'TreeNode', q: 'TreeNode') -> 'TreeNode':
self.res = None
self.dfs(root, p, q)
return self.res
def dfs(self, root, p, q):
if not root: return 0
left = self.dfs(root.left, p, q)
right = self.dfs(root.right,p ,q)
mid = root == p or root == q
if left + right + mid > 1: self.res = root
return left or right or midclass Solution {
TreeNode res = null;
public TreeNode lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode root, TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {
dfs(root, p, q);
return res;
}
private int dfs(TreeNode root, TreeNode p, TreeNode q){
if(root == null) return 0;
int left = dfs(root.left, p, q);
int right = dfs(root.right, p, q);
int mid = root == p || root == q ? 1 : 0;
if(left + right + mid > 1) res = root;
return left + right + mid > 0 ? 1 : 0;
}
}标签:链表
- 由于只输入了需要删除的节点
node,因此无法获取删除节点node的前一个节点pre,从而也就无法将前一个节点pre指向删除节点的下一个节点nex; - 既然无法通过修改指针完成,那么肯定要修改链表节点的
值了。 - 将删除节点
node的值和指针都改为下一个节点nex的值和指针即可。
class Solution:
def deleteNode(self, node):
node.val = node.next.val
node.next = node.next.nextclass Solution {
public void deleteNode(ListNode node) {
node.val = node.next.val;
node.next = node.next.next;
}
}标签:
- 因为空间复杂度要求
$O(1)$ 、不能使用除法,因此一定需要在乘法过程中得到所有答案; - 我们可以将
res数组列成乘积形式,形成一个矩阵,可以发现矩阵次主角线全部为$1$ (因为当前数字不相乘,因此等价为乘$1$ ); - 因此,我们分别计算矩阵的
上三角和下三角,并且在计算过程中储存过程值,最终可以在遍历$2$ 遍nums下完成结果计算。
| res | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| res[0] = | 1 | num[1] | ... | num[n-2] | num[n-1] |
| res[1] = | num[0] | 1 | ... | num[n-2] | num[n-1] |
| ... | ... | ... | ... | num[n-2] | num[n-1] |
| res[n-2] = | num[0] | num[1] | ... | 1 | num[n-1] |
| res[n-1] = | num[0] | num[1] | ... | num[n-2] | 1 |
class Solution:
def productExceptSelf(self, nums: [int]) -> [int]:
res, p, q = [1], 1, 1
for i in range(len(nums) - 1): # top triangle
p *= nums[i]
res.append(p)
for i in range(len(nums) - 1, 0, -1): # bottom triangle
q *= nums[i]
res[i - 1] *= q
return resclass Solution {
public int[] productExceptSelf(int[] nums) {
int[] res = new int[nums.length];
int p = 1, q = 1;
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
res[i] = p;
p *= nums[i];
}
for (int i = nums.length - 1; i > 0 ; i--) {
q *= nums[i];
res[i - 1] *= q;
}
return res;
}
}标签:
- 每次可以扔
$1$ 或$2$ 或$3$ 个石头,并且自己先扔,因此可推出:-
情况1: 石头数量
$1,2,3$ 时,自己一定赢; -
情况2: 石头数量
$4$ 时,无论如何扔都会给对方留下$1$ 次能扔完的数量(让对方落入 情况1 ),因此对方一定赢。 -
情况3: 石头数量
$5,6,7$ 时,自己总能在扔一次后,使对方落入 情况2 ,因此自己一定赢; -
情况4: 石头数量
$8$ 时,自己在扔一次后,对方一定会落入 情况3 ,因此对方一定赢; - 以此类推……
-
情况1: 石头数量
- 通过以上分析可以看出,当石头数量为
$4$ 的倍数时自己一定会输,其余情况一定会赢。
class Solution:
def canWinNim(self, n: int) -> bool:
return n % 4 != 0class Solution {
public boolean canWinNim(int n) {
return n % 4 != 0;
}
}标签:数组,贪心算法
-
补齐数组特点:
- 假设数组
$arr$ 添加一个元素即可覆盖$[1, n)$ 内所有数字,那么添加的数字$m$ 一定满足m <= n。 - 假设数组
$arr$ 可以覆盖$[1, n)$ 的所有数字,则给$arr$ 内加元素$m$ :- 若
m <= n,新数组可以覆盖[1, m + n) = [1, n) ∪ [m, m + n)内所有数字;
- 若
- 假设数组
-
贪心法则: 对于一个覆盖
$[1, n)$ 的数组$arr$ 来说,添加数字$n$ 连续扩容范围最大(扩容至$[1, 2n)$ )。 -
思路: 设置一个初始范围
$[1, 1)$ ,通过不断确认并扩大数组可以覆盖的范围,最终计算出最少需要加入的数字。- 当
i < len(nums)且nums[i] <= add时:不需要加入新数字,循环确认并更新数组可以覆盖的范围[1, add + nums[i]),直到找到大于确认范围$add$ 的$nums[i]$ 或索引越界。 - 否则:无法根据现有数字构建更大的连续范围,,因此需要使用贪心策略向数组加入数字
$add$ ,将数组从覆盖$[1, add)$ 扩容至可覆盖$[1, 2add)$ 。 - 直到确认的范围
add > n,说明此时已经覆盖$[1, n]$ ,退出迭代并返回。
- 当
class Solution:
def minPatches(self, nums: List[int], n: int) -> int:
add, i, count = 1, 0, 0
while add <= n:
if i < len(nums) and nums[i] <= add:
add += nums[i] # from [1, add] to [1, add + nums[i]]
i += 1
else:
add += add # from [1, add] to [1, 2add]
count += 1
return countclass Solution {
public int minPatches(int[] nums, int n) {
int i = 0, count = 0;
long add = 1;
while(add <= n){
if(i < nums.length && nums[i] <= add) add += nums[i++];
else {
add += add;
count ++;
}
}
return count;
}
}标签:字符串,双指针
- 设置两指针
ij分别位于String两端,向中心逼近并交换字符即可。
class Solution:
def reverseString(self, s: List[str]) -> None:
i, j = 0, len(s) - 1
while i < j:
s[i], s[j] = s[j], s[i]
i, j = i + 1, j - 1class Solution {
public void reverseString(char[] s) {
int i = 0, j = s.length - 1;
while(i < j) {
char tmp = s[i];
s[i] = s[j];
s[j] = tmp;
i++; j--;
}
}
}标签:栈、递归
-
本题难点在于括号内嵌套括号,需要从内向外生成与拼接字符串,这与栈的先入后出特性对应。
-
算法流程:
- 构建辅助栈
stack, 遍历字符串s中每个字符c;- 当
c为数字时,将数字字符转化为数字multi,用于后续倍数计算; - 当
c为字母时,在res尾部添加c; - 当
c为[时,将当前multi和res入栈,并分别置空置$0$ :- 记录此
[前的临时结果res至栈,用于发现对应]后的拼接操作; - 记录此
[前的倍数multi至栈,用于发现对应]后,获取multi × [...]字符串。 - 进入到新
[后,res和multi重新记录。
- 记录此
- 当
c为]时,stack出栈,拼接字符串res = last_res + cur_multi * res,其中:-
last_res是上个[到当前[的字符串,例如"3[a2[c]]"中的a; -
cur_multi是当前[到]内字符串的重复倍数,例如"3[a2[c]]"中的2。
-
- 当
- 返回字符串
res。
- 构建辅助栈
-
复杂度分析:
- 时间复杂度
$O(N)$ ,一次遍历s; - 空间复杂度
$O(N)$ ,辅助栈在极端情况下需要线性空间,例如2[2[2[a]]]。
- 时间复杂度
class Solution:
def decodeString(self, s: str) -> str:
stack, res, multi = [], "", 0
for c in s:
if c == '[':
stack.append([multi, res])
res, multi = "", 0
elif c == ']':
cur_multi, last_res = stack.pop()
res = last_res + cur_multi * res
elif '0' <= c <= '9':
multi = multi * 10 + int(c)
else:
res += c
return resclass Solution {
public String decodeString(String s) {
StringBuilder res = new StringBuilder();
int multi = 0;
LinkedList<Integer> stack_multi = new LinkedList<>();
LinkedList<String> stack_res = new LinkedList<>();
for(Character c : s.toCharArray()) {
if(c == '[') {
stack_multi.addLast(multi);
stack_res.addLast(res.toString());
multi = 0;
res = new StringBuilder();
}
else if(c == ']') {
StringBuilder tmp = new StringBuilder();
int cur_multi = stack_multi.removeLast();
for(int i = 0; i < cur_multi; i++) tmp.append(res);
res = new StringBuilder(stack_res.removeLast() + tmp);
}
else if(c >= '0' && c <= '9') multi = multi * 10 + Integer.parseInt(c + "");
else res.append(c);
}
return res.toString();
}
}-
总体思路与辅助栈法一致,不同点在于将
[和]分别作为递归的开启与终止条件:- 当
s[i] == ']'时,返回当前括号内记录的res字符串与]的索引i(更新上层递归指针位置); - 当
s[i] == '['时,开启新一层递归,记录此[...]内字符串tmp和递归后的最新索引i,并执行res + multi * tmp拼接字符串。 - 遍历完毕后返回
res。
- 当
-
复杂度分析:
- 时间复杂度
$O(N)$ ,递归会更新索引,因此实际上还是一次遍历s; - 空间复杂度
$O(N)$ ,极端情况下递归深度将会达到线性级别。
- 时间复杂度
class Solution:
def decodeString(self, s: str) -> str:
def dfs(s, i):
res, multi = "", 0
while i < len(s):
if '0' <= s[i] <= '9':
multi = multi * 10 + int(s[i])
elif s[i] == '[':
i, tmp = dfs(s, i + 1)
res += multi * tmp
multi = 0
elif s[i] == ']':
return i, res
else:
res += s[i]
i += 1
return res
return dfs(s,0)class Solution {
public String decodeString(String s) {
return dfs(s, 0)[0];
}
private String[] dfs(String s, int i) {
StringBuilder res = new StringBuilder();
int multi = 0;
while(i < s.length()) {
if(s.charAt(i) >= '0' && s.charAt(i) <= '9')
multi = multi * 10 + Integer.parseInt(String.valueOf(s.charAt(i)));
else if(s.charAt(i) == '[') {
String[] tmp = dfs(s, i + 1);
i = Integer.parseInt(tmp[0]);
while(multi > 0) {
res.append(tmp[1]);
multi--;
}
}
else if(s.charAt(i) == ']')
return new String[] { String.valueOf(i), res.toString() };
else
res.append(String.valueOf(s.charAt(i)));
i++;
}
return new String[] { res.toString() };
}
}标签:字符串,双指针
-
算法流程: 设定
i,j两指针分别指向num1,num2尾部,模拟人工加法;-
计算进位: 计算
carry = tmp // 10,代表当前位相加是否产生进位; -
添加每位: 计算
tmp = n1 + n2 + carry,并将当前位tmp % 10添加至res头部; -
索引溢出处理: 当指针
i或j走过数字首部后,给n1,n2赋值为$0$ ,相当于给num1,num2中长度较短的数字前面填$0$ ,以便后续计算。 - 当遍历完
num1,num2后跳出循环,并根据carry值决定是否在头部添加进位$1$ ,最终返回res即可。
-
计算进位: 计算
-
复杂度分析:
- 时间复杂度
$O(max(M,N))$ :按位遍历一遍数字,以较长的数字为准; - 空间复杂度
$O(1)$ : 指针与变量使用常数大小空间。
- 时间复杂度
class Solution:
def addStrings(self, num1: str, num2: str) -> str:
res = ""
i, j, carry = len(num1) - 1, len(num2) - 1, 0
while i >= 0 or j >= 0:
n1 = int(num1[i]) if i >= 0 else 0
n2 = int(num2[j]) if j >= 0 else 0
tmp = n1 + n2 + carry
carry = tmp // 10
res = str(tmp % 10) + res
i, j = i - 1, j - 1
return "1" + res if carry else resclass Solution {
public String addStrings(String num1, String num2) {
StringBuilder res = new StringBuilder("");
int i = num1.length() - 1, j = num2.length() - 1, carry = 0;
while(i >= 0 || j >= 0){
int n1 = i >= 0 ? num1.charAt(i) - '0' : 0;
int n2 = j >= 0 ? num2.charAt(j) - '0' : 0;
int tmp = n1 + n2 + carry;
carry = tmp / 10;
res.append(tmp % 10);
i--; j--;
}
if(carry == 1) res.append(1);
return res.reverse().toString();
}
}标签:字符串,双指针
left,right双指针通过空格定位每个单词,并翻转每个单词;- Python可一行解决。
class Solution:
def reverseWords(self, s: str) -> str:
l = []
i, left, right = 0, 0, -2
while i < len(s) + 1:
if i == len(s) or s[i] == ' ':
left, right = right + 1, i - 1
for j in range(right, left, -1):
l.append(s[j])
l.append(' ')
i += 1
return "".join(l[:-1])class Solution:
def reverseWords(self, s: str) -> str:
return ' '.join(i[::-1] for i in s.split())class Solution557 {
public String reverseWords(String s) {
String[] strs = s.split(" ");
StringBuffer res = new StringBuffer("");
for(String str : strs){
StringBuffer tmp = new StringBuffer(str);
res.append(" ");
res.append(tmp.reverse().toString());
}
return res.toString().trim();
}
}标签:贪心算法
- 题意是模拟与顾客的收钱找零动作,需要明确:
- 一个柠檬5元,因此顾客付10元找5元,付20元找15元;
- 找零方案有:
10 = (5) + 5,20 = (10+5) + 5 = (5+5+5) + 5,其中小括号中是找零部分。可以看出,10元只能用5元找零,而20元则可以用10元或5元找零并有两种组合。 - 贪心策略:需要尽可能地多留5元在手上,防止10元的顾客无法找零。
- 模拟过程,如果顾客付5元则记录,付10元则找
5元,付20则优先找10+5若没有则找5+5+5。 - 在模拟过程中,若发现手上没有足够的零钱找零,则直接返回
false。
class Solution:
def lemonadeChange(self, bills: List[int]) -> bool:
five, ten = 0, 0
for b in bills:
if b == 5:
five += 1
elif b == 10:
if not five: return False
five -= 1
ten += 1
else:
if ten and five:
ten -= 1
five -= 1
elif five > 2:
five -= 3
else:
return False
return Trueclass Solution {
public boolean lemonadeChange(int[] bills) {
int five = 0, ten = 0;
for(int b : bills){
if(b == 5) five ++;
else if(b == 10) {
if(five-- == 0) return false;
ten++;
}
else {
if(five > 0 && ten > 0){
five--; ten--;
}
else if(five > 2){
five -= 3;
}
else return false;
}
}
return true;
}
}All 66 problems of 剑指offer are solved using Python, and the following is the details of 剑指offer全题目解析. To Ctri + F the topic of the problems is recommended.
在一个二维数组中(每个一维数组的长度相同),每一行都按照从左到右递增的顺序排序,每一列都按照从上到下递增的顺序排序。请完成一个函数,输入这样的一个二维数组和一个整数,判断数组中是否含有该整数。
标签:数组。
- 从右上角or左下角开始查找,以左下角开始查找为例,若当前值<目标值,则目标值一定在当前值所在列的右侧,因此列+1;反之将行-1。相当于循环一次就可以排除一列or一行。
- 对于m行n列矩阵,暴力查找时间复杂度O(mn),以下方法O(m+n)。
class Solution:
# array 二维列表
def Find(self, target, array):
# write code here
row = len(array)-1
col = 0
while row>=0 and col<len(array[0]):
if target == array[row][col]:
return True
elif target > array[row][col]:
col+=1
else:
row-=1
return False请实现一个函数,将一个字符串中的每个空格替换成“%20”。例如,当字符串为We Are Happy.则经过替换之后的字符串为We%20Are%20Happy。
标签:字符串。
- 先遍历确定' '个数,然后从后向前插入(相对于从前向后插入,此方法下每个字符只用被修改一次),对于第count个空格和第count+1空格之间的字符,需要向后移位2*count。
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| h | e | l | l | o | w | ||||||
| h | % | 2 | 0 | e | l | l | % | 2 | 0 | o | w |
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
class Solution:
# s 源字符串
def replaceSpace(self, s):
# write code here
l = list(s)
count = 0
for k in l:
if k == ' ':
count+=1
l.extend(['1','1'])
for i in range(len(s)-1,-1,-1):
if l[i]!=' ':
l[i+2*count]=l[i]
else:
count-=1
l[i+2*count]='%'
l[i+2*count+1]='2'
l[i+2*count+2]='0'
return ''.join(l)输入一个链表,按链表值从尾到头的顺序返回一个ArrayList。
标签:链表,递归
根据题意,使用递归完成。
class Solution:
# 返回从尾部到头部的列表值序列,例如[1,2,3]
def printListFromTailToHead(self, listNode):
# write code here
return self.printListFromTailToHead(listNode.next) + [listNode.val] if listNode else []输入某二叉树的前序遍历和中序遍历的结果,请重建出该二叉树。假设输入的前序遍历和中序遍历的结果中都不含重复的数字。例如输入前序遍历序列{1,2,4,7,3,5,6,8}和中序遍历序列{4,7,2,1,5,3,8,6},则重建二叉树并返回。
标签:二叉树,深度优先搜索DFS。
-
前序遍历: 根节点 | 左子树 | 右子树: [1 | 2 4 5 | 3 6 7], 中序遍历: 左子树 | 根节点 | 右子树: [4 2 5 | 1 | 6 3 7]
-
因此,可用中序遍历中根节点位置将前序遍历化为三段。对左子树和右子树分别可以进行相同的划分,例如:左子树前序遍历[2 | 4 | 5]和中序遍历[4 | 2 | 5],递归即可生成树。
-
以下代码中,pre.pop(0)代表此递归对应树的前序遍历,中序遍历list用于辅助确定当前节点的值。
class Solution:
def reConstructBinaryTree(self, pre, tin):
if not tin: return
root = TreeNode(pre.pop(0))
for i in range(len(tin)):
if root.val == tin[i]: break
root.left = self.reConstructBinaryTree(pre, tin[:i])
root.right = self.reConstructBinaryTree(pre, tin[i+1:])
return root用两个栈来实现一个队列,完成队列的Push和Pop操作。 队列中的元素为int类型。
标签:栈,队列。
-
根据题意,需要用两个栈来模拟队列的push和pop,其他例如获取队列内容等不需要考虑。
-
因此,push则向que最后添加node,pop则是将asi中的元素pop,其中asi可理解为que的reverse list。值得注意的是,当asi和que同时为空时应直接返回None。
class Solution:
def __init__(self):
self.que, self.asi = [], []
def push(self, node):
# write code here
self.que.append(node)
def pop(self):
# return xx
if not self.asi:
if not self.que: return
while self.que:
self.asi.append(self.que.pop())
return self.asi.pop()把一个数组最开始的若干个元素搬到数组的末尾,我们称之为数组的旋转。 输入一个非减排序的数组的一个旋转,输出旋转数组的最小元素。 例如数组{3,4,5,1,2}为{1,2,3,4,5}的一个旋转,该数组的最小值为1。 NOTE:给出的所有元素都大于0,若数组大小为0,请返回0。
标签:数组,双指针,二分法。
- 旋转排序数组
nums可以被拆分为2个排序数组nums1,nums2,并且nums1所有元素>=nums2所有元素; - 因此,考虑二分法寻找值
nums[i]; - 设置
left,right指针在nums数组两端,mid为中点:- 当
nums[mid] > nums[right]时,一定满足mid < i <= right,因此left = mid + 1; - 当
nums[mid] < nums[right]时,一定满足left < i <= mid,因此right = mid; - 当
nums[mid] == nums[right]时,是此题对比153题的难点(原因是此题中数组的元素可重复,相等就难以判断最小值的指针区间);先说结果:采用right = right - 1,下面证明:- 首先,此操作
不会使数组越界,因为right > left > 0; - 其次,此操作
不会使最小值丢失,证明:假设'nums[right]'是最小值,有两种情况:- 若
nums[right]是唯一最小值:那就不可能满足判断条件nums[mid] == nums[right],因为left != right且mid = left + right // 2 < right(向下取整); - 若有其他元素和
nums[right]同为最小值:还有最小值存在于[left, right -1]间,不会丢失最小值。
- 若
- 首先,此操作
- 当
- 以上是理论分析,可以用以下数组辅助思考:
[1, 2, 3][1, 1, 0, 1][1, 0, 1, 1, 1][1, 1, 1, 1]
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
class Solution:
def minNumberInRotateArray(self, nums):
# write code here
left, right = 0, len(nums) - 1
while left < right:
mid = (left + right) // 2
if nums[mid] > nums[right]: left = mid + 1
elif nums[mid] < nums[right]: right = mid
else: right = right - 1 # key
return nums[left]大家都知道斐波那契数列,现在要求输入一个整数n,请你输出斐波那契数列的第n项(从0开始,第0项为0)。
标签:迭代。
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
class Solution:
def Fibonacci(self, n):
# write code here
a, b = 0, 1
for _ in range(n-1):
a, b = b, a + b
return b if n > 0 else 0一只青蛙一次可以跳上1级台阶,也可以跳上2级。求该青蛙跳上一个n级的台阶总共有多少种跳法(先后次序不同算不同的结果)。
标签:动态规划。
一只青蛙一次可以跳上1级台阶,也可以跳上2级。求该青蛙跳上一个n级的台阶总共有多少种跳法(先后次序不同算不同的结果)。
发现台阶跳法规律,f(n)=f(n-1)+f(n-2),是斐波那契数列(详细解析同理于矩形覆盖)。
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
class Solution:
def jumpFloor(self, number):
# write code here
if number == 1:
return number
a=0
b=1
for _ in range(number):
a,b = b,a+b
return b一只青蛙一次可以跳上1级台阶,也可以跳上2级……它也可以跳上n级。求该青蛙跳上一个n级的台阶总共有多少种跳法。
标签:找规律。
看起来很变态,其实和跳台阶思路差不多,先找f(n)和f(n-1)....f(1)的关系,再由前面的项相加即可,对于n级台阶:
| 先跳 | 后面可能性 |
|---|---|
| 1 | f(n-1) |
| 2 | f(n-2) |
| ... | ... |
| n-1 | 1 |
| n | 1 |
如果用迭代做,重复计算太多了,因此考虑继续分解:
| f(x) | = |
|---|---|
| f(0) | = 1 |
| f(1) | = 1 |
| f(2) | = f(0) + f(1) |
| f(3) | = f(0) + f(1) + f(2) = 2[f(0)+f(1)] |
| f(4) | = f(0) + f(1) + f(2) + f(3) = 4[f(0)+f(1)] |
| ... | = ... |
| f(n) | = 2f(n-1) = 2^n-2 * [f(0)+f(1)] |
因此, f(n) = 2^n-1.
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
class Solution:
def jumpFloorII(self, number):
# write code here
return 2 ** (number - 1) # or pow(2, number - 1)我们可以用21的小矩形横着或者竖着去覆盖更大的矩形。请问用n个21的小矩形无重叠地覆盖一个2*n的大矩形,总共有多少种方法?
标签:动态规划。
设n个矩形有f(n)种放法,则将一个矩形如下放置,剩下矩形有f(n-1)种放法。
| 1 | 2 | ... | n |
|---|---|---|---|
| √ | |||
| √ |
则将一个矩形如下放置,剩下矩形有f(n-2)种放法,因为还有一个矩形必须放在×的位置,即有两个矩形固定。
| 1 | 2 | ... | n |
|---|---|---|---|
| √ | √ | ||
| × | × |
因此,f(n)=f(n-1)+f(n-2),是斐波那契数列。
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
class Solution:
def rectCover(self, number):
# write code here
if number == 0 or number == 1:
return number
a=0
b=1
for _ in range(number):
a,b = b,a+b
return b输入一个整数,输出该数二进制表示中1的个数。其中负数用补码表示。
标签:位运算。
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
class Solution:
def NumberOf1(self, n):
# write code here
n &= 0xffffffff
count = 0
while n:
count += n & 1
n >>= 1
return count-
python存取一个数,长度是无限制的(和java等不同,int是32位的)。当存储负数时,python会符号位前也有无限个1。例如,java中-1是以补码0xffffffff,但在python中0xffffffff前还有fffff……,因此对于负数无法直接求1的个数,会陷入死循环。
-
对于负数,需要做预先处理,即n &= 0xffffffff,这个即是n与0xffffffff求交,输出负数n的无符号形式(负号前面的1全部变为0,因此变成了正数,负号的1变为此正数的最高位)
print(hex(1)) #0x1
print(hex(-1)) #-0x1 = 0xffffffff(补码,二进制第一位是符号位,前面还有无限个1)
print(hex(1& 0xffffffff)) #0x1 = 0x00000001
print(hex(-1& 0xffffffff)) #0xffffffff,相当于把前面无限个1变为0,从符号位至最后一位保持不变,但符号位的1被提出到与其他位等价。
print(-1& 0xffffffff) #4294967295 = 2^32-1 = -1的无符号形式给定一个double类型的浮点数base和int类型的整数exponent。求base的exponent次方。
标签:快速幂法。
- 原始情况下, b ^ e = b * b * ... * b,可以分解成e个b的乘积,需要做e-1次乘法运算,效率很低。
- 然而我们发现 b ^ e = b ^ (1 + 2 + 4 + ... + 2n),所有的e都可以分解成此数列,其本质上是一个数的二进制表示,如3 = 0011 = 1 + 2, 5 = 0101 = 1 + 4, 9 = 1001 = 1 + 8..
- 这样我们存储 b ^ 1, b ^ 2 , b ^ 4 ... (即 base = base * base),通过 exp & 1 == 0 (判断exp最右位是否为1)来判断数字此位是否需要相乘,最终把相乘结果输出即可。
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
class Solution:
def Power(self, base, exponent):
# write code here
res, exp = 1, abs(exponent)
while exp != 0:
if exp & 1 != 0: res *= base
base *= base
exp >>= 1
return res if exponent > 0 else 1/res输入一个整数数组,实现一个函数来调整该数组中数字的顺序,使得所有的奇数位于数组的前半部分,所有的偶数位于数组的后半部分,并保证奇数和奇数,偶数和偶数之间的相对位置不变。
标签:数组,位运算。
空间换时间,借用两个辅助数组分别填入奇数偶数并返回,时间空间复杂度均为O(N)。
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
class Solution:
def reOrderArray(self, array):
# write code here
odd, even = [], []
for a in array:
odd.append(a) if a & 1 else even.append(a)
return odd + even输入一个链表,输出该链表中倒数第k个结点。
标签:链表,双指针。
声明两个指针n1, n2,指针n1先向前走k步,找到链表第k+1个node,然后指针n1,n2一起走,当n2走过最后一个node时(指向None),n1即是倒数第k个node
class Solution:
def FindKthToTail(self, head, k):
# write code here
node1, node2 = head, head
for _ in range(k):
if not node1: return
node1 = node1.next
while node1:
node1, node2 = node1.next, node2.next
return node2输入一个链表,反转链表后,输出新链表的表头。
标签:链表,三指针。
遍历链表,每次记录上次遍历点pre,三个指针交替向前行进。
class Solution:
# 返回ListNode
def ReverseList(self, pHead):
# write code here
cur, pre = pHead, None
while cur:
nex = cur.next
cur.next = pre
pre = cur
cur = nex
return pre输入两个单调递增的链表,输出两个链表合成后的链表,当然我们需要合成后的链表满足单调不减规则。
标签:链表,双指针。
借用一个链表头tmp,按照大小依次将head1,head2链表加入排序,最后将剩余部分加到链表尾部,返回tmp.next
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.next = None
class Solution:
# 返回合并后列表
def Merge(self, pHead1, pHead2):
# write code here
tmp = ListNode(0)
head = tmp
while pHead1 and pHead2:
if pHead1.val < pHead2.val:
tmp.next, pHead1 = pHead1, pHead1.next
else:
tmp.next, pHead2 = pHead2, pHead2.next
tmp = tmp.next
tmp.next = pHead2 if not pHead1 else pHead1
return head.next输入两棵二叉树A,B,判断B是不是A的子结构。(ps:我们约定空树不是任意一个树的子结构)
标签:二叉树、递归、深度优先搜索。
- 先找到子树根节点value = 父树根节点value的节点;
- 判断以此节点为根节点时,是否是子结构(r2为空则代表是子结构);
- 遍历pRoot1,方可确定是否为子结构。
class Solution:
def HasSubtree(self, pRoot1, pRoot2):
# write code here
if not pRoot1 or not pRoot2: return False
return self.is_subtree(pRoot1, pRoot2) or self.HasSubtree(pRoot1.left, pRoot2) or self.HasSubtree(pRoot1.right, pRoot2)
def is_subtree(self, r1, r2):
if not r2: return True
if not r1 or r1.val != r2.val: return False
return self.is_subtree(r1.left, r2.left) and self.is_subtree(r1.right, r2.right)操作给定的二叉树,将其变换为源二叉树的镜像。
标签:二叉树,递归,深度优先搜索。
镜像则是将整个树从上至下将每个根节点的左右子节点互换,因此使用递归即可。
class Solution:
# 返回镜像树的根节点
def Mirror(self, root):
# write code here
if not root: return
root.left, root.right = root.right, root.left
self.Mirror(root.left)
self.Mirror(root.right)
return root输入一个矩阵,按照从外向里以顺时针的顺序依次打印出每一个数字,例如,如果输入如下4 X 4矩阵: 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 则依次打印出数字1,2,3,4,8,12,16,15,14,13,9,5,6,7,11,10.
标签:记忆化。
旋转法:弹出并打印矩阵第一行内容,矩阵逆时针旋转90°,弹出并打印矩阵第一行内容…… 需要将逆时针旋转矩阵的公式推导出来。
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
class Solution:
# matrix类型为二维列表,需要返回列表
def printMatrix(self, matrix):
# write code here
res = matrix.pop(0)
while matrix:
matrix = [[matrix[i][j] for i in range(len(matrix))] for j in range(len(matrix[0])-1, -1, -1)]
res += matrix.pop(0)
return res设定边界法:
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
class Solution:
# matrix类型为二维列表,需要返回列表
def printMatrix(self, matrix):
if not matrix: return []
res = []
h, l = len(matrix), len(matrix[0])
i, j = 0, -1
while True:
for _ in range(l):
j += 1
res.append(matrix[i][j])
h -= 1
if not h: break
for _ in range(h):
i += 1
res.append(matrix[i][j])
l -= 1
if not l: break
for _ in range(l):
j -= 1
res.append(matrix[i][j])
h -= 1
if not h: break
for _ in range(h):
i -= 1
res.append(matrix[i][j])
l -= 1
if not l: break
return res定义栈的数据结构,请在该类型中实现一个能够得到栈中所含最小元素的min函数(时间复杂度应为O(1))。
标签:栈,设计。
-
题目要求min函数的时间复杂度O(1),所以需要在push,pop这些方法中动态更新栈最小值的情况;
-
构造辅助m_stack,当push的值小于等于目前最小值的时候,就将此值入m_stack,相当于给stack中按照栈底到栈顶的顺序给最小值打上标记。值得注意的是,条件是小于等于,这样才可以处理最小值有两个及以上的情况。当出栈时,若出栈元素等于最小值,m_stack则将此元素标记取消;
-
min函数则返回m_stack栈顶元素即可。
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
class Solution:
def __init__(self):
self.stack = []
self.m_stack = []
def push(self, node):
# write code here
self.stack.append(node)
if not self.m_stack or self.m_stack[-1] >= node:
self.m_stack.append(node)
def pop(self):
# write code here
if self.stack.pop() == self.m_stack[-1]:
self.m_stack.pop()
def top(self):
# write code here
return self.stack[-1]
def min(self):
# write code here
return self.m_stack[-1]输入两个整数序列,第一个序列表示栈的压入顺序,请判断第二个序列是否可能为该栈的弹出顺序。假设压入栈的所有数字均不相等。例如序列1,2,3,4,5是某栈的压入顺序,序列4,5,3,2,1是该压栈序列对应的一个弹出序列,但4,3,5,1,2就不可能是该压栈序列的弹出序列。(注意:这两个序列的长度是相等的)。
标签:栈,模拟。
-
这道题主要需理解题目的意思。题目意思是来了一串数据,在不违背栈先入后出的原则下随意push和pop,然后问push序列和pop序列是否可行。
-
例如对于数据流1,2,3,4,5,先push三个数据[1,2,3],然后pop两个数据[3, 2],然后push两个数据[4,5],再pop三个数据[5,4,1],因此总的push和pop顺序就是[1,2,3,4,5]和[3,2,5,4,1]。但像[2,5,3,4,1]就不可能,因为若先pop5,那么3就不可能在4前pop。
-
解题思路是创建一个栈,模拟这个过程,根据模拟成功结果返回。
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
class Solution:
def IsPopOrder(self, pushV, popV):
# write code here
imi = [pushV.pop(0)]
while imi:
cur = popV.pop(0)
while imi[-1] != cur:
if not pushV: return False
imi.append(pushV.pop(0))
imi.pop()
return True从上往下打印出二叉树的每个节点,同层节点从左至右打印。
标签:二叉树,广度优先遍历BFS。
按层打印使用迭代。思路是tmp存储每层节点,通过此层节点获取下层节点(同时保存val至res),并循环直到tmp为空。
class Solution:
# 返回从上到下每个节点值列表,例:[1,2,3]
def PrintFromTopToBottom(self, root):
# write code here
if not root: return []
res, tmp = [], [root]
while tmp:
t = tmp.pop(0)
res.append(t.val)
if t.left: tmp.append(t.left)
if t.right: tmp.append(t.right)
return res输入一个整数数组,判断该数组是不是某二叉搜索树的后序遍历的结果。如果是则输出Yes,否则输出No。假设输入的数组的任意两个数字都互不相同。
标签:二叉搜索树BST,深度优先搜索DFS,后序遍历。
- 二叉搜索树的性质是左子树节点都比根节点值小,右子树节点都比根节点值大。
- 根据这个定义,考虑后序遍历序列可以划分为[左子树(小)| 右子树(大)| 根节点],通过对每棵子树拆分,可以判定是否满足二叉搜索树的性质。
- 递归遍历整个树,若发现某子树不满足此规律则返回False。
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
class Solution:
def VerifySquenceOfBST(self, sequence):
# write code here
return self.verify(sequence) if sequence else False
def verify(self, sequence):
if not sequence: return True
for i in range(len(sequence)):
if sequence[i] >= sequence[-1]: break
for j in range(i, len(sequence)-1):
if sequence[j] <= sequence[-1]: return False
return self.verify(sequence[:i]) and self.verify(sequence[i+1:-1])输入一颗二叉树的跟节点和一个整数,打印出二叉树中结点值的和为输入整数的所有路径。路径定义为从树的根结点开始往下一直到叶结点所经过的结点形成一条路径。(注意: 在返回值的list中,数组长度大的数组靠前)
标签:二叉树,深度优先搜索DFS,记忆化。
-
先序遍历递归,过程中累计target值并记录path;
-
若到达叶子节点,且刚好累计到target值,则将路径添加到res里;
-
递归返回到父节点时,path要弹出当前节点。
class Solution:
# 返回二维列表,内部每个列表表示找到的路径
def FindPath(self, root, expectNumber):
# write code here
self.res, self.path = [], []
self.search(root, expectNumber)
return self.res
def search(self, root, target):
if not root or target < 0: return
target -= root.val
self.path.append(root.val)
if not (root.left or root.right or target):
self.res.append(list(self.path))
self.search(root.left, target)
self.search(root.right, target)
self.path.pop()输入一个复杂链表(每个节点中有节点值,以及两个指针,一个指向下一个节点,另一个特殊指针指向任意一个节点),返回结果为复制后复杂链表的head。(注意,输出结果中请不要返回参数中的节点引用,否则判题程序会直接返回空)。
标签:链表。
此链表复杂在有random项,即在复制时不止需要考虑next的顺序问题,还要找到每个节点random的对应节点。
三步法:
- 链表[h1, h2, ...],复制链表[g1, g2, ...],并将其交叉合并为[h1, g1, h2, g2, ...],获得关系h1.random.next = h1.next.random;
- 根据以上关系,将random属性一一对应起来;
- 将合并链表拆分为两个单独链表,获得[g1,g2,...]并返回。
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
# class RandomListNode:
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.label = x
# self.next = None
# self.random = None
class Solution:
# 返回 RandomListNode
def Clone(self, head):
# write code here
if not head: return
h = head
while h:
tmp = RandomListNode(h.label)
nex = h.next
h.next, h, tmp.next = tmp, nex, nex
h = head
while h.next.next:
if h.random: h.next.random = h.random.next
h = h.next.next
h, res = head, head.next
while h.next:
tmp = h.next
h.next, h = h.next.next, tmp
return res输入一棵二叉搜索树,将该二叉搜索树转换成一个排序的双向链表。要求不能创建任何新的结点,只能调整树中结点指针的指向。
标签:二叉搜索树BST,中序遍历。
- 二叉搜索树的中序遍历即是排序list;
- 使用递归中序遍历,在递归过程中记录上一个节点pre,修改pre.right和root.left的指针指向;
- 返回中序遍历的第一个节点。
class Solution:
def Convert(self, pRootOfTree):
# write code here
self.pre = TreeNode(0)
res = self.pre
self.traversal(pRootOfTree)
if res.right: res.right.left = None
return res.right
def traversal(self, root):
if not root: return
self.traversal(root.left)
self.pre.right = root
root.left = self.pre
self.pre = root
self.traversal(root.right)输入一个字符串,按字典序打印出该字符串中字符的所有排列。例如输入字符串abc,则打印出由字符a,b,c所能排列出来的所有字符串abc,acb,bac,bca,cab和cba。
标签:字符串,递归,排序。
- 使用递归解决,固定第1个字符,求后面n-1字符的组合。例如abc固定a,有bc和cb两种组合。
- 将第1个字符和后面n-1个字符分别交换,再递归。例如abc有bac,cba两种变化。
- 对于相同字符不做交换(因为交换后情况重复)。例如aab,则只用求aab和baa两种情况下组合。
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
class Solution:
def Permutation(self, ss):
# write code here
self.res, self.sort = [], list(ss)
self.sort_dic(0, len(ss))
self.res.sort()
return self.res
def sort_dic(self, s, e):
if e - s == 1: self.res.append(''.join(self.sort))
same = {}
for i in range(s, e):
if self.sort[i] in same: continue
same[self.sort[i]] = 1
self.sort[s], self.sort[i] = self.sort[i], self.sort[s]
self.sort_dic(s+1, e)
self.sort[s], self.sort[i] = self.sort[i], self.sort[s]数组中有一个数字出现的次数超过数组长度的一半,请找出这个数字。例如输入一个长度为9的数组{1,2,3,2,2,2,5,4,2}。由于数字2在数组中出现了5次,超过数组长度的一半,因此输出2。如果不存在则输出0。
标签:数组,哈希表Hash。
- 循环找出list中不同的2个数字删除,若有数字占数组长度一半以上,则留下的一定是此数字(最坏情况下,此数字也不可能被全部删除);
- 利用此推断,模拟删除,复杂度O(N);
- 得到留下的数字,再遍历一遍list,确认此数字数量超过list长度一半,复杂度O(N)。
- 也可以用HashMap做,时间空间复杂度都为O(N)。
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
class Solution:
def MoreThanHalfNum_Solution(self, numbers):
# write code here
tmp = list(numbers) # copy the list
i = 1
while i < len(tmp):
if tmp[0] == tmp[i]:
i += 1
else:
del tmp[0], tmp[i-1]
i = 1
if not tmp: return 0
count = 0
for num in numbers:
if num == tmp[0]: count += 2
return tmp[0] if count > len(numbers) else 0输入n个整数,找出其中最小的K个数。例如输入4,5,1,6,2,7,3,8这8个数字,则最小的4个数字是1,2,3,4。
标签:数组,排序,堆。
- 使用
heapq + 负数模拟大顶堆:- 先向大顶堆添加
tinput数组前k个数; - 后面的数,若
n < heap[0](堆顶),从堆pop()最大值,并将n值push()入堆; - 最后,将堆中值都
pop()出res,并倒置res返回。
- 先向大顶堆添加
import heapq
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
class Solution:
def GetLeastNumbers_Solution(self, tinput, k):
# write code here
if not k or k > len(tinput): return []
heap, res = [], []
for n in tinput:
if len(heap) < k:
heapq.heappush(heap, -n)
elif -n > heap[0]:
heapq.heappush(heap, -n)
heapq.heappop(heap)
while heap:
res.append(-heapq.heappop(heap))
res.reverse()
return resHZ偶尔会拿些专业问题来忽悠那些非计算机专业的同学。今天测试组开完会后,他又发话了:在古老的一维模式识别中,常常需要计算连续子向量的最大和,当向量全为正数的时候,问题很好解决。但是,如果向量中包含负数,是否应该包含某个负数,并期望旁边的正数会弥补它呢?例如:{6,-3,-2,7,-15,1,2,2},连续子向量的最大和为8(从第0个开始,到第3个为止)。给一个数组,返回它的最大连续子序列的和,你会不会被他忽悠住?(子向量的长度至少是1)
标签:数组,动态规划。
- 使用动态规划,遍历一遍list,记录累加值;
- 当遍历到第i项时,舍弃前面累积的条件为上次累计值为负值;
- 例如:array = [1, -2, 3, 10, -4, 7, 2, -5], tmp = [1, -1, 3, 13, 9, 16, 18, 13],舍弃前面累计值-1,直接选取array对应值3。
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
class Solution:
def FindGreatestSumOfSubArray(self, array):
# write code here
tmp = [array[0]]
for i in range(1, len(array)):
tmp += [array[i]] if tmp[i-1] < 0 else [array[i] + tmp[i-1]]
return max(tmp)求出1
13的整数中1出现的次数,并算出1001300的整数中1出现的次数?为此他特别数了一下1~13中包含1的数字有1、10、11、12、13因此共出现6次,但是对于后面问题他就没辙了。ACMer希望你们帮帮他,并把问题更加普遍化,可以很快的求出任意非负整数区间中1出现的次数(从1 到 n 中1出现的次数)。标签:找规律。
| range | num |
|---|---|
| 0-9 | 1 |
| 0-99 | 10+10 = 1 * 10 + 10 |
| 0-999 | 200 + 100 = 20*10 + 100 |
- 根据以上规律可以推出各数位对应1出现次数的关系,例如1136 = 1000 + 100 + 30 + 6,分别算出各项1出现的次数相加即可;
- 需要区分的是当前数位是否为1。若为1,则需要加上低位的数字。例如136,百位1对应的1出现次数为20(0-99) + 37(100-136) = 57。
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
class Solution:
def NumberOf1Between1AndN_Solution(self, n):
# write code here
total, deno, count, end = 0, 1, 0, 0
while n != 0:
num = n % (deno * 10)
n -= num
if num > deno:
count += total * num / deno + deno
elif num == deno:
count += total + 1 + end
total = total*10 + deno
end += num
deno *= 10
return int(count)输入一个正整数数组,把数组里所有数字拼接起来排成一个数,打印能拼接出的所有数字中最小的一个。例如输入数组{3,32,321},则打印出这三个数字能排成的最小数字为321323。
标签:思维拓展。
- 这道题如果换成[2,1,3,5,8,4],让排序出最小组合,是不是就很简单了?但对于题目中[32,3,321],仅仅考虑数字之间大小难以解决。但仔细想想,本质上,题目是要寻找列表中每个元素的“大小关系”,对整个list进行排序。
- 对于[2,1,3,5,8,4]来说,2 > 1 因此2应该在1右边,这是十进制的特性决定的。对于[32,3,321],我们把每个列表元素当作整体看待,元素的“大小”比较等价于
"32" + "3" = “323” < “332” = "3" + "32",即比较两元素在两种拼接方案后的大小。 - 自写一个比较函数
compare(),然后选择一种效率高的排序方法将整个list按照此规则进行排序即可。
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
class Solution:
def PrintMinNumber(self, numbers):
# write code here
self.quick_sort(numbers, 0, len(numbers)-1)
return "".join([str(num) for num in numbers])
def quick_sort(self, arr, l, r):
if l > r: return
base, i, j = arr[l], l, r
while i != j:
while self.compare(arr[j], base) and i < j: j -= 1
while self.compare(base, arr[i]) and i < j: i += 1
arr[i], arr[j] = arr[j], arr[i]
arr[l], arr[i] = arr[i], arr[l]
self.quick_sort(arr, l, i-1)
self.quick_sort(arr, i+1, r)
def compare(self, a, b):
str1, str2 = str(a) + str(b), str(b) + str(a)
return 0 if str1 < str2 else 1把只包含质因子2、3和5的数称作丑数(Ugly Number)。例如6、8都是丑数,但14不是,因为它包含质因子7。 习惯上我们把1当做是第一个丑数。求按从小到大的顺序的第N个丑数。
标签:多指针。
-
任何一个丑数n可以写作 n = 2x or 3y or 5z,即其中至少有2,3,5因子中的其中一个;
-
找到了丑数数列生成规律,在丑数数列中res设置三个指针t2, t3, t5,每次比较三指针生成的下个数字大小,取最小值为下个丑数;
-
某些生成轮会有指针生成值重合现象,此时生成值相同的指针都需要+=1,例如下情况:下个丑数为6,res[t2] * 2 = res[t3] * 2 = 6,则两指针都要+=1。
1 2 3 4 5 6 t2 t3 t5
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-class Solution:
def GetUglyNumber_Solution(self, index):
# write code here
if index < 7: return index
t2 = t3 = t5 = 0
res = [1]
for i in range(1,index):
r2, r3, r5 = res[t2] * 2, res[t3] * 3, res[t5] * 5
res.append(min([r2, r3, r5]))
if res[i] == r2: t2 += 1
if res[i] == r3: t3 += 1
if res[i] == r5: t5 += 1
return res[-1]在一个字符串(0<=字符串长度<=10000,全部由字母组成)中找到第一个只出现一次的字符,并返回它的位置, 如果没有则返回 -1(需要区分大小写)。
标签:哈希表Hash。
- 题目中没有说list中有几个只出现一次的字符,因此不能用异或等运算性质解决;
- 建立一个Hash table,长度为字母'A'至'Z'的ASCII码之差;
- 先遍历一遍list,在
HashMap中记录每个字符的出现次数; - 再遍历list,在
HashMap中按list顺序查询字符出现数量,返回第一个数量为1的字符。
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
class Solution:
def FirstNotRepeatingChar(self, s):
# write code here
dic = {}
for c in s:
if c in dic: dic[c] += 1
else: dic[c] = 1
for i in range(len(s)):
if dic[s[i]] == 1: return i
return -1在数组中的两个数字,如果前面一个数字大于后面的数字,则这两个数字组成一个逆序对。输入一个数组,求出这个数组中的逆序对的总数P。并将P对1000000007取模的结果输出。 即输出P%1000000007
标签:二分法,归并排序,回溯算法。
-
使用冒泡/插入排序可以记录排序过程中的操作数量,此操作数量即为逆序对数量,但复杂度为O(N^2);
-
使用归并排序可以将复杂度降至O(N log2 N),需要解决的是如何在归并排序中统计逆序对数量;
-
归并排序下list像递归二叉树一样被展开,从下至上依次统计count。
53421687 5342 1687 53 42 16 87
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
class Solution:
def InversePairs(self, data):
# write code here
self.arr, self.count = data, 0
self.merge_sort(0, len(data)-1)
return self.count % 1000000007
def merge_sort(self, l, r):
if l >= r: return
m = int((l+r+1)/2)
self.merge_sort(l, m-1)
self.merge_sort(m, r)
i, j, merge = l, m, []
while i < m and j <= r:
if self.arr[i] < self.arr[j]:
merge.append(self.arr[i])
i += 1
else:
merge.append(self.arr[j])
j += 1
self.count += m - i
for x in range(j,r+1): merge.append(self.arr[x])
for x in range(i,m): merge.append(self.arr[x])
for i in range(l, r+1): self.arr[i] = merge[i-l]输入两个链表,找出它们的第一个公共结点。
标签:链表,双指针。
- 若两个链表有公共节点,那么其一定有公共的尾部(公共结点后的所有节点一致);
- 先分别统计两个链表的长度,得到两链表的长度差k;
- 长链表指针先走k-1步,之后两指针一起走,直到寻找到相同结点return
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.next = None
class Solution:
def FindFirstCommonNode(self, pHead1, pHead2):
# write code here
length1 = length2 = 0
head1, head2 = pHead1, pHead2
while head1:
head1 = head1.next
length1 += 1
while head2:
head2 = head2.next
length2 += 1
[k, lon, sho] = [length1 - length2, pHead1, pHead2] if length1 > length2 else [length2 - length1, pHead2, pHead1]
for _ in range(k):
lon = lon.next
while lon:
if lon == sho: return lon
lon, sho = lon.next, sho.next统计一个数字在排序数组中出现的次数。
标签:数组,二分法,二分插入。
- 直接遍历list统计次数,时间复杂度O(N);
- 使用二分法,寻找k - 0.1和k + 0.1的插入点,时间复杂度O(log2 N)。
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
class Solution:
def GetNumberOfK(self, data, k):
# write code here
return self.findLocation(data, k + 0.1) - self.findLocation(data, k - 0.1)
def findLocation(self, data, k):
left, right = 0, len(data) - 1
while left <= right:
mid = int((left + right) / 2)
if data[mid] > k: right = mid - 1
else: left = mid + 1
return left输入一棵二叉树,求该树的深度。从根结点到叶结点依次经过的结点(含根、叶结点)形成树的一条路径,最长路径的长度为树的深度。
标签:二叉树,深度优先遍历DFS,回溯算法。
- 统计深度要遍历所有节点,统计所有叶子节点到根节点的最大值;
- 和按层遍历类似,每遍历一层就将depth += 1,直到最后一层结束并返回。
class Solution:
def TreeDepth(self, pRoot):
# write code here
if not pRoot: return 0
return max(self.TreeDepth(pRoot.left), self.TreeDepth(pRoot.right)) + 1输入一棵二叉树,判断该二叉树是否是平衡二叉树。
标签:平衡二叉树,深度优先搜索DFS,回溯法。
- 递归遍历整个树,判断左右子树深度差是否大于1;
- 叶节点返回1;返回根节点时,判断左子树和右子树深度差是否大于1,若大于则返回-1;
- 若已经发现返回-1的子树,则说明不是平衡二叉树,一路返回-1。
class Solution:
def IsBalanced_Solution(self, pRoot):
# write code here
return self.getDepth(pRoot) != -1
def getDepth(self, pRoot):
if not pRoot: return 0
dl = self.getDepth(pRoot.left)
dr = self.getDepth(pRoot.right)
return max(dl,dr) + 1 if dl != -1 and dr != -1 and -2 < dl - dr < 2 else -1一个整型数组里除了两个数字之外,其他的数字都出现了两次。请写程序找出这两个只出现一次的数字。
标签:数组,位运算。
- 根据异或性质,对于任何数字a,a ^ a = 0, a ^ 0 = a,并且异或满足交换律;因此,若一个list里只有1个出现1次的数字,其余都出现2次,我们将list从头到尾依次执行异或操作,结果一定是那个只出现1次的数字;
- 根据以上性质,自然想到如何把此数组切分成两个数组,其中出现一次的数字a, b分别分布在两个数组中,这样就可以按照此性质来求得a, b;
- 先对list从头到尾异或,得到的结果是num_xor = a ^ b,对num_xor的二进制形式遍历,找到一个为1的数位。这个1代表a, b在这个对应数位上的数字不同。接下来按照这个数位为1和为0将list划分,则a, b就被划分到两个list里了,并且出现了两次的数字也被按对划分到两个list里。
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
class Solution:
# 返回[a,b] 其中ab是出现一次的两个数字
def FindNumsAppearOnce(self, array):
# write code here
num_xor = array[0]
for a in array[1:]:
num_xor ^= a
index = 0
while num_xor & 1 != 1:
num_xor >>= 1
index += 1
n0, n1 = 0, 0
for a in array:
if a >> index & 1: n0 ^= a
else: n1 ^= a
return [n0,n1]小明很喜欢数学,有一天他在做数学作业时,要求计算出9~16的和,他马上就写出了正确答案是100。但是他并不满足于此,他在想究竟有多少种连续的正数序列的和为100(至少包括两个数)。没多久,他就得到另一组连续正数和为100的序列:18,19,20,21,22。现在把问题交给你,你能不能也很快的找出所有和为S的连续正数序列? Good Luck!
标签:数组,双指针。
- 设定两个指针,从1, 2出发,通过判断总和与目标值大小关系移动指针;
- 当等于时,添加list至res,由于是从1,2出发,因此先添加进去的list一定最长(数字较小);
- 为避免反复计算,总和s随着指针移动动态计算。
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
class Solution:
def FindContinuousSequence(self, tsum):
# write code here
res, l, r, s = [], 1, 2, 3
while l < r:
if s >= tsum:
if s == tsum: res.append(list(range(l,r+1)))
s -= l
l += 1
else:
r += 1
s += r
return res输入一个递增排序的数组和一个数字S,在数组中查找两个数,使得他们的和正好是S,如果有多对数字的和等于S,输出两个数的乘积最小的。
标签:数组,双指针。
- 仍然是双指针法,指针先设在list两端,根据与目标值的比较逐渐向中间逼近;
- 当找到第一个结果时返回,即是乘积最小的结果,因为指针是从两段向中间逼近的(周长相等,长宽差距越大面积越小)。
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
class Solution:
def FindNumbersWithSum(self, array, tsum):
# write code here
l, r = 0, len(array) - 1
while l < r:
if array[l] + array[r] < tsum: l += 1
elif array[l] + array[r] > tsum: r -= 1
else: return [array[l], array[r]]
return []汇编语言中有一种移位指令叫做循环左移(ROL),现在有个简单的任务,就是用字符串模拟这个指令的运算结果。对于一个给定的字符序列S,请你把其循环左移K位后的序列输出。例如,字符序列S=”abcXYZdef”,要求输出循环左移3位后的结果,即“XYZdefabc”。是不是很简单?OK,搞定它!
标签:字符串,时间换空间。
- 设对于一个字符串x,其转置记为xT;则(yx)T = xT yT;
- 根据以上性质,yx = (xT yT)T,即做三次翻转即可。
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
class Solution:
def LeftRotateString(self, s, n):
# write code here
res, length = list(s), len(s)
if n > length : return ""
for i in range(int(n/2)):
res[i], res[n-1-i] = res[n-1-i], res[i]
for i in range(n, int((n+length)/2)):
res[i], res[length-1-i+n] = res[length-1-i+n], res[i]
for i in range(int(length/2)):
res[i], res[length-1-i] = res[length-1-i], res[i]
return "".join(res)牛客最近来了一个新员工Fish,每天早晨总是会拿着一本英文杂志,写些句子在本子上。同事Cat对Fish写的内容颇感兴趣,有一天他向Fish借来翻看,但却读不懂它的意思。例如,“student. a am I”。后来才意识到,这家伙原来把句子单词的顺序翻转了,正确的句子应该是“I am a student.”。Cat对一一的翻转这些单词顺序可不在行,你能帮助他么?
标签:字符串,时间换空间。
- 和上题类似,若不借用额外空间,abcd = (dT cT bT aT)T。
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
class Solution:
def ReverseSentence(self, s):
# write code here
res, length, last = list(s), len(s), -1
for i in range(len(res)):
if res[i] == ' ':
self.reverse(res, last + 1, i)
last = i
self.reverse(res, 0, length)
return "".join(res)
def reverse(self, res, l, r):
while l < r:
res[l], res[r-1] = res[r-1], res[l]
l += 1
r -= 1LL今天心情特别好,因为他去买了一副扑克牌,发现里面居然有2个大王,2个小王(一副牌原本是54张^_^)...他随机从中抽出了5张牌,想测测自己的手气,看看能不能抽到顺子,如果抽到的话,他决定去买体育彩票,嘿嘿!!“红心A,黑桃3,小王,大王,方片5”,“Oh My God!”不是顺子.....LL不高兴了,他想了想,决定大\小 王可以看成任何数字,并且A看作1,J为11,Q为12,K为13。上面的5张牌就可以变成“1,2,3,4,5”(大小王分别看作2和4),“So Lucky!”。LL决定去买体育彩票啦。 现在,要求你使用这幅牌模拟上面的过程,然后告诉我们LL的运气如何, 如果牌能组成顺子就输出true,否则就输出false。为了方便起见,你可以认为大小王是0。
标签:模拟。
- 先排序,统计王joker的数量;
- 在剩下的牌中计算需要多少王可以填充,若王全部用完或出现对子,则返回False。
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
class Solution:
def IsContinuous(self, numbers):
# write code here
numbers.sort()
joker = 0
for n in numbers[:4]:
if not n: joker += 1
for i in range(joker, len(numbers) - 1):
tmp = numbers[i+1] - numbers[i] - 1
joker -= tmp
if joker < 0 or tmp < 0: return False
return True if numbers else False每年六一儿童节,牛客都会准备一些小礼物去看望孤儿院的小朋友,今年亦是如此。HF作为牛客的资深元老,自然也准备了一些小游戏。其中,有个游戏是这样的:首先,让小朋友们围成一个大圈。然后,他随机指定一个数m,让编号为0的小朋友开始报数。每次喊到m-1的那个小朋友要出列唱首歌,然后可以在礼品箱中任意的挑选礼物,并且不再回到圈中,从他的下一个小朋友开始,继续0...m-1报数....这样下去....直到剩下最后一个小朋友,可以不用表演,并且拿到牛客名贵的“名侦探柯南”典藏版(名额有限哦!!^_^)。请你试着想下,哪个小朋友会得到这份礼品呢?(注:小朋友的编号是从0到n-1)。
标签:模拟。
- 纯模拟这个过程。
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
class Solution:
def LastRemaining_Solution(self, n, m):
# write code here
if not n: return -1
res = list(range(n))
length, index = len(res), 0
while length > 1:
index = (index + m - 1) % length
res.pop(index)
length = len(res)
return res[0]求1+2+3+...+n,要求不能使用乘除法、for、while、if、else、switch、case等关键字及条件判断语句(A?B:C)。
标签:发散思维,熔断机制。
- 使用递归计算n+n-1+...+1,使用and的阻断性质实现递归终止条件。
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
class Solution:
def __init__(self):
self.sum = 0
def Sum_Solution(self, n):
# write code here
n and self.Sum_Solution(n-1)
self.sum += n
return self.sum写一个函数,求两个整数之和,要求在函数体内不得使用+、-、*、/四则运算符号。
标签:位运算。
- 对于a + b, a ^ b异或相当于不算进位地将ab相加,如0011 ^ 0101 = 0110
- a & b << 1 相当于计算了a + b产生的进位,如 0011 & 0101 << 1 = 0001 << 1 = 0010
- 循环计算,直到进位项为0;
- 由于python长整数可以表示无限位,因此需要人工& 0xFFFFFFFF设置边界判断;
- 结果num1是无符号数,和0x7FFFFFFF作比较判断数字正负,若为负则求反码再转原码。
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
class Solution:
def Add(self, num1, num2):
# write code here
while num2:
num1, num2 = (num1 ^ num2) & 0xFFFFFFFF, (num1 & num2) << 1 & 0xFFFFFFFF
return num1 if num1 <= 0x7FFFFFFF else ~(num1 ^ 0xFFFFFFFF)将一个字符串转换成一个整数(实现Integer.valueOf(string)的功能,但是string不符合数字要求时返回0),要求不能使用字符串转换整数的库函数。 数值为0或者字符串不是一个合法的数值则返回0。
标签:字符串。
- 提取字符串每位依次添加进数字res;
- 遇非数字字符返回0;
- 判断首位是否是符号+ -,返回对应正负数。
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
class Solution:
def StrToInt(self, s):
# write code here
if not s: return 0
res, bit = 0, 1
end = -1 if s[0] != '+' and s[0] != '-' else 0
for i in range(len(s)-1, end, -1):
num = ord(s[i]) - 48
if num > 9 or num < 0: return 0
res += num * bit
bit *= 10
return -res if s[0] == "-" else res在一个长度为n的数组里的所有数字都在0到n-1的范围内。 数组中某些数字是重复的,但不知道有几个数字是重复的。也不知道每个数字重复几次。请找出数组中任意一个重复的数字。 例如,如果输入长度为7的数组{2,3,1,0,2,5,3},那么对应的输出是第一个重复的数字2。
标签:哈希表Hash。
- 建立长度为n的hash table,用于存储每个数字的出现次数;
- 遇到第一个出现两个的数字,记录并返回True。
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
class Solution:
# 这里要特别注意~找到任意重复的一个值并赋值到duplication[0]
# 函数返回True/False
def duplicate(self, numbers, duplication):
# write code here
table = [0 for _ in range(len(numbers))]
for n in numbers:
if table[n] > 0:
duplication[0] = n
return True
table[n] += 1
return False给定一个数组A[0,1,...,n-1],请构建一个数组B[0,1,...,n-1],其中B中的元素B[i]=A[0]A[1]...*A[i-1]A[i+1]...*A[n-1]。不能使用除法。
标签:
- 根据以下矩阵规律,先算下三角,再算上三角;
| B[0] | 1 | A[1] | ... | A[N] |
| B[1] | A[0] | 1 | ... | A[N] |
| ... | A[0] | A[1] | ... | A[N] |
| B[N] | A[0] | A[1] | ... | 1 |
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
class Solution:
def multiply(self, A):
# write code here
B, tmp = [1], 1
for i in range(len(A)-1):
B.append(B[i]*A[i])
for i in range(len(A)-1, 0, -1):
tmp *= A[i]
B[i-1] *= tmp
return B请实现一个函数用来匹配包括'.'和''的正则表达式。模式中的字符'.'表示任意一个字符,而''表示它前面的字符可以出现任意次(包含0次)。 在本题中,匹配是指字符串的所有字符匹配整个模式。例如,字符串"aaa"与模式"a.a"和"abaca"匹配,但是与"aa.a"和"ab*a"均不匹配。
标签:字符串,正则。
- 基本思路是按位匹配,但 * 较难处理,因为其前面的字符可以为任意数量(包括0),所以就会有多种情况。
- 例如:a a a和a * a匹配,* 前面的a出现两次正好匹配,但如果一直遍历a出现三次,则反而匹配失败。
- 根据以上案例,自然会想到return情况1 or 情况2的递归模式,这样只要匹配成功一种,就会返回True;
- 设s, p指针分别为i, j,按照p[j+1]是否为‘*’来分成两种情况:
- 不为*比较简单:
- 若s[i]等于p[j]或p[j]为‘.',则两指针同时+1继续递归;
- 否则匹配失败,返回False;
- 为*分成两种情况:
- 若s[i]等于p[j]或p[j]为‘.',说明此*前字符至少出现一次,则递归i+1 or j+2;
- 否则,说明*前的字符出现0次,j+2递归。
- 不为*比较简单:
- 中止条件为:两指针同时走过末尾则匹配成功,若j单独走过末尾则匹配失败(匹配字符串已经遍历完毕,无法继续匹配)。
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
class Solution:
# s, pattern都是字符串
def match(self, s, pattern):
# write code here
return self.match_str(s, pattern, 0, 0)
def match_str(self, s, p, i, j):
ls, lp = len(s), len(p)
if not j < lp:
if not i < ls: return True
return False
if j+1 < lp and p[j+1] == '*':
if i < ls and (s[i] == p[j] or p[j] == '.'):
return self.match_str(s, p, i+1, j) or self.match_str(s, p, i, j+2)
return self.match_str(s, p, i, j+2)
if i < ls and (s[i] == p[j] or p[j] == '.'):
return self.match_str(s, p, i+1, j+1)
return False请实现一个函数用来判断字符串是否表示数值(包括整数和小数)。例如,字符串"+100","5e2","-123","3.1416"和"-1E-16"都表示数值。 但是"12e","1a3.14","1.2.3","+-5"和"12e+4.3"都不是。
标签:字符串,问题分解。
- 首位字符必须为+或-或数字;
- 在e(E)之前,匹配数字or小数点;
- 在e(E)之后,首位匹配+或-或数字,后面匹配数字。
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
class Solution:
# s字符串
def isNumeric(self, s):
# write code here
ls, i, dot = len(s), 1, 0
# 首位必须为“+/-/number”
if s[0] != '+' and s[0] != '-' and (s[0] < '0' or s[0] > '9'): return False
# 遍历1~(len-1)位,如果发现E or e就跳到下一个while
while i < ls - 1:
if s[i] == 'E' or s[i] == 'e':
i += 1
break
elif s[i] == '.':
if dot: return False
dot += 1
elif s[i] < '0' or s[i] > '9': return False
i += 1
# e后面首位必须为“+/-/number”
if s[i] != '+' and s[i] != '-' and (s[i] < '0' or s[i] > '9'): return False
i += 1
# e不能出现两次,并且e后面的数字组合不能有小数点,其余和前面一样
while i < ls:
if s[i] < '0' or s[i] > '9': return False
i += 1
return True请实现一个函数用来找出字符流中第一个只出现一次的字符。例如,当从字符流中只读出前两个字符"go"时,第一个只出现一次的字符是"g"。当从该字符流中读出前六个字符“google"时,第一个只出现一次的字符是"l"。
标签:哈希表Hash,设计。
- 建立长度为256的hash table,用于统计字符出现次数。
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
class Solution:
# 返回对应char
def __init__(self):
self.s = ''
self.dic = {}
def FirstAppearingOnce(self):
# write code here
for c in self.s:
if self.dic[c] == 1: return c
return '#'
def Insert(self, char):
# write code here
self.s += char
if char in self.dic: self.dic[char] += 1
else: self.dic[char] = 1给一个链表,若其中包含环,请找出该链表的环的入口结点,否则,输出null。
标签:链表,双指针。
- 使用两个指针,p1步长为1,p2步长为2,同时出头结点出发一起向前走,则走k步后p1、p2相差距离为k;当p1和p2第一次重合时,p2比p1多走了一个环的周长;
- 声明两指针p1、p2在头结点,p1先走环周长的步数,然后两个节点一起向前走,下次两节点重合位置一定是环的入口节点。
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.next = None
class Solution:
def EntryNodeOfLoop(self, pHead):
# write code here
p1, p2, step= pHead, pHead, 0
while p1 != p2 or step == 0:
if not p1.next or not p2.next.next: return None
p1, p2 = p1.next, p2.next.next
step += 1
p1, p2 = pHead, pHead
for _ in range(step):
p1 = p1.next
while p1 != p2:
p1, p2 = p1.next, p2.next
return p1在一个排序的链表中,存在重复的结点,请删除该链表中重复的结点,重复的结点不保留,返回链表头指针。 例如,链表1->2->3->3->4->4->5 处理后为 1->2->5
标签:链表,双指针。
- 基本思路是创建两指针h1, h2确定list中只出现一次的数字,并将这些数字链起来;
- 指针的设定和边界的处理是此题关键:
- 设pre指针指向只出现一次的数字,当找到下一个只出现一次的数字时pre指针移动;
- h1指向每个数字第一次出现的位置,h2指针循环前进直到找到h1 != h2的第一个数字;
- 遇到几组连续出现的数字时,不要修改pre指针。
- 添加一个节点至头节点前,以处理左方越界问题;
- 在返回前,最后一个pre需置为None,以处理右方越界问题。
- 例如:以下是pre = 2时各指针位置。
| 1 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pre | n1,tmp | n2 |
class Solution:
def deleteDuplication(self, pHead):
# write code here
if not pHead: return
pre, h1, h2 = ListNode(pHead.val - 1), pHead, pHead
res, pre.next = pre, h2
while h2:
while h2 and h1.val == h2.val:
tmp, h2 = h2, h2.next
if tmp == h1: pre.next, pre = tmp, h1
h1 = h2
pre.next = None
return res.next给定一个二叉树和其中的一个结点,请找出中序遍历顺序的下一个结点并且返回。注意,树中的结点不仅包含左右子结点,同时包含指向父结点的指针。
标签:二叉树,中序遍历。
- 此节点有右分支,则输出right子节点一路left到底的节点;
- 此节点有父节点:
- 此节点为父节点的左节点,则返回父节点;
- 此节点是父节点右节点,则继续向上找父节点,直到找到为左节点的;
- 以上都不满足,返回None
class Solution:
def GetNext(self, pNode):
# write code here
if pNode.right: # 1
node = pNode.right
while node.left: node = node.left
return node
while pNode.next: # 2
if pNode == pNode.next.left: return pNode.next
pNode = pNode.next
return # 3请实现一个函数,用来判断一颗二叉树是不是对称的。注意,如果一个二叉树同此二叉树的镜像是同样的,定义其为对称的。
标签:二叉树,深度优先搜索DFS。
- 对称满足的性质:设置两个指针left,right从root根节点开始,一个向左一个向右,遇到的子节点值恒相等,且子节点同时存在或同时越过叶子节点;
- 根据此性质使用递归进行判断。
class Solution:
def isSymmetrical(self, pRoot):
if not pRoot: return True
return self.match(pRoot.left, pRoot.right)
def match(self, lef, rig):
if not lef and not rig: return True
if not lef or not rig or lef.val != rig.val: return False
return self.match(lef.left, rig.right) and self.match(lef.right, rig.left)请实现一个函数按照之字形打印二叉树,即第一行按照从左到右的顺序打印,第二层按照从右至左的顺序打印,第三行按照从左到右的顺序打印,其他行以此类推。
标签:二叉树,广度优先搜索BFS。
- 先解决一个基础问题:按层打印,这个前面的题中已经解决;
- 偶数层保持不变,对奇数层倒置再添加至结果。
class Solution:
def Print(self, pRoot):
# write code here
if not pRoot: return []
res, roots, reverse = [], [pRoot], False
while roots:
tmp = []
for _ in range(len(roots)):
r = roots.pop(0)
tmp.append(r.val)
if r.left: roots.append(r.left)
if r.right: roots.append(r.right)
if reverse: tmp.reverse()
reverse = not reverse
res.append(tmp)
return res从上到下按层打印二叉树,同一层结点从左至右输出。每一层输出一行。
标签:二叉树,广度优先遍历BFS。
- 仍然是按层打印,本次使用递归方法解。
class Solution:
# 返回二维列表[[1,2],[4,5]]
def Print(self, pRoot):
# write code here
res = []
self.line(res, [pRoot])
return res
def line(self, res, roots):
if not roots or not roots[0]: return
tmp, re = [], []
for r in roots:
re.append(r.val)
if r.left: tmp.append(r.left)
if r.right: tmp.append(r.right)
res.append(re)
self.line(res, tmp)请实现两个函数,分别用来序列化和反序列化二叉树。
标签:二叉树,设计,深度优先遍历DFS。
- 序列化:本解答使用前序遍历序列化,通过递归完成。
- 叶子节点的左右节点需要填充'#'。
- 反序列化:以前序遍历重构二叉树,返回根节点。
- '#'代表叶子节点底下的None。
class Solution:
def Serialize(self, root):
# write code here
return self.serialize(root)[:-1]
def serialize(self, root):
res = ""
if not root: return '#,'
res += str(root.val) + ','
res += self.serialize(root.left)
res += self.serialize(root.right)
return res
def Deserialize(self, s):
root, i = self.deserialize(s.split(","),0)
return root
def deserialize(self, s, i):
if i >= len(s) or s[i] == '#':
return None, i + 1
root = TreeNode(int(s[i]))
root.left, i = self.deserialize(s, i+1)
root.right, i = self.deserialize(s, i)
return root, i给定一棵二叉搜索树,请找出其中的第k小的结点。例如, (5,3,7,2,4,6,8) 中,按结点数值大小顺序第三小结点的值为4。
标签:二叉搜索树,中序遍历。
- 二叉搜索树的中序遍历即是排序list;
- 输出二叉搜索树的中序遍历,当输出到第k个节点时记录结果并return。
class Solution:
# 返回对应节点TreeNode
def KthNode(self, pRoot, k):
# write code here
self.res, self.k, self.count = None, k - 1, 0
self.recur(pRoot)
return self.res
def recur(self, root):
if not root: return
self.recur(root.left)
if self.res: return
if self.count == self.k: self.res = root
self.count += 1
self.recur(root.right)如何得到一个数据流中的中位数?如果从数据流中读出奇数个数值,那么中位数就是所有数值排序之后位于中间的数值。如果从数据流中读出偶数个数值,那么中位数就是所有数值排序之后中间两个数的平均值。我们使用Insert()方法读取数据流,使用GetMedian()方法获取当前读取数据的中位数。
标签:堆,设计。
- 采用一个大顶堆、一个小顶堆,并保证:
- 大顶堆内的所有数字小于小顶堆的所有数字;
- 允许大顶堆的长度==小顶堆长度+1;
- 当大顶堆长度==小顶堆长度时,中位数为大顶堆和小顶堆的顶元素的平均值;否则等于小顶堆的顶元素值(小顶堆长度>=大顶堆长度);
- python使用heapq直接实现小顶堆q。而大顶堆p的实现方法是将push的所有元素取负。顶元素为小顶堆/大顶堆的首个元素p[0]和q[0]。
import heapq
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
class Solution:
def __init__(self):
self.q = []
self.p = []
def Insert(self, num):
# write code here
if not self.p or num <= -self.p[0]: heapq.heappush(self.p, -num)
else: heapq.heappush(self.q, num)
if len(self.p) == len(self.q) + 2: heapq.heappush(self.q, -heapq.heappop(self.p))
elif len(self.p) + 1 == len(self.q): heapq.heappush(self.p, -heapq.heappop(self.q))
def GetMedian(self, data):
# write code here
return (self.q[0] - self.p[0]) / 2.0 if len(self.q) == len(self.p) else -self.p[0]- 二分法:
- Insert方法内用二分法插入数据,保持arr排序状态;
- GetMedian方法根据数组长度奇偶性返回中位数。
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
class Solution:
def __init__(self):
self.arr = []
def Insert(self, num):
# write code here、
i, j = 0, len(self.arr)-1
while i <= j:
m = (i+j) // 2
if self.arr[m] < num: i = m + 1
else: j = m - 1
self.arr = self.arr[:i] + [num] + self.arr[i:]
def GetMedian(self, data):
# write code here
m = len(self.arr)//2
return (self.arr[m]+self.arr[m-1])/2.0 if not len(self.arr) % 2 else self.arr[m]给定一个数组和滑动窗口的大小,找出所有滑动窗口里数值的最大值。例如,如果输入数组{2,3,4,2,6,2,5,1}及滑动窗口的大小3,那么一共存在6个滑动窗口,他们的最大值分别为{4,4,6,6,6,5}; 针对数组{2,3,4,2,6,2,5,1}的滑动窗口有以下6个: {[2,3,4],2,6,2,5,1}, {2,[3,4,2],6,2,5,1}, {2,3,[4,2,6],2,5,1}, {2,3,4,[2,6,2],5,1}, {2,3,4,2,[6,2,5],1}, {2,3,4,2,6,[2,5,1]}。
标签:队列。
- 建立一个队列存储窗口最大值,遍历整个list,按照以下规则处理队列:
- 循环判断队列尾部值是否小于等于num[i],若小于等于则pop此值(后面窗口最大值一定用不到这个值了,因为num[i]更大);
- 循环判断队列首部是否超出滑动窗口的范围,若超出则pop;
- 将当前指针位置i添加到队列尾部;
- 当滑动窗口范围大于0且形成窗口(i + 1 >= size),则添加队首值,队首值满足:
- 在窗口内;
- 大于窗口内的所有值。
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
class Solution:
def maxInWindows(self, num, size):
# write code here
queue, res = [], []
for i in range(len(num)):
while queue and num[queue[-1]] <= num[i]: queue.pop()
while queue and queue[0] <= i - size: queue.pop(0)
queue.append(i)
if size and i > size: res.append(num[queue[0]])
return res请设计一个函数,用来判断在一个矩阵中是否存在一条包含某字符串所有字符的路径。路径可以从矩阵中的任意一个格子开始,每一步可以在矩阵中向左,向右,向上,向下移动一个格子。如果一条路径经过了矩阵中的某一个格子,则之后不能再次进入这个格子。 例如 a b c e s f c s a d e e 这样的3 X 4 矩阵中包含一条字符串"bcced"的路径,但是矩阵中不包含"abcb"路径,因为字符串的第一个字符b占据了矩阵中的第一行第二个格子之后,路径不能再次进入该格子。
标签:深度优先搜索DFS,回溯法,记忆化。
- 深度优先搜索(DFS)/回溯法典型题,主体逻辑如下:
- 从当前节点出发,有上下左右四种情况,任意一种情况能走对应路径即可,递归使用or;
- 失败的终止条件:矩阵越界 or 已经走过 or 字符匹配失败;
- 成功的终止条件:不失败 and 已经匹配完字符串最后一位;
- 建立flags标志矩阵,记录已经走过的点位:
- 如果遇到走过的点位直接返回False;
- 如果当前点上下左右四个方向都匹配失败,需要将当前点Flag释放,以防止影响其他路线走此点。
- 题目中matrix输入的是一个一维list,因此index = self.cols * i + j。
- hasPath要对rows和cols进行遍历,将所有点作为起点进行DFS,只要其中一种找到就返回True。
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
class Solution:
def hasPath(self, matrix, rows, cols, path):
# write code here
self.flags = [0 for _ in range(len(matrix))]
self.matrix, self.rows, self.cols, self.path = matrix, rows, cols, path
for i in range(rows):
for j in range(cols):
if self.search(i, j, 0): return True
return False
def search(self, i, j, k):
index = self.cols * i + j
if not 0 <= i < self.rows or not 0 <= j < self.cols or \
self.flags[index] or self.matrix[index] != self.path[k]:
return False # 越界 or 已经走过 or 不是所需节点
if k == len(self.path) - 1:
return True # 已经找完,不需要继续递归
self.flags[index] = 1 # 走过这个点,寻找下个点
if self.search(i+1, j, k+1) or self.search(i-1, j, k+1) or \
self.search(i, j+1, k+1) or self.search(i, j-1, k+1):
return True # 四条路中有一条可以走通
self.flags[index] = 0 # 如果无法走通,要释放这个点,以防影响其他路线中走此点
return False地上有一个m行和n列的方格。一个机器人从坐标0,0的格子开始移动,每一次只能向左,右,上,下四个方向移动一格,但是不能进入行坐标和列坐标的数位之和大于k的格子。 例如,当k为18时,机器人能够进入方格(35,37),因为3+5+3+7 = 18。但是,它不能进入方格(35,38),因为3+5+3+8 = 19。请问该机器人能够达到多少个格子?
标签:深度优先搜索DFS,记忆化。
- 深度优先搜索DFS思路:
- 从矩阵某节点开始,可以向上下左右走,每个方向的格子数量都需要统计,因此递归将几个结果+;
- 不能走的终止条件:矩阵越界、已经统计过、不满足题中的加和条件;
- 建立matrix统计此格子是否已被统计。
- 可以理解为机器人按照以下优先级:向右、向左、向下、向上前进,其实此题下只需要�������右向左向下即可,由于上面的点都已经走过,self.moving(i, j-1)始终会return 0
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
class Solution:
def movingCount(self, threshold, rows, cols):
# write code here
self.matrix, self.k, self.rows, self.cols = \
[[0 for _ in range(cols)] for _ in range(rows)], threshold, rows, cols
return self.moving(0, 0)
def moving(self, i, j):
if not 0 <= i < self.rows or not 0 <= j < self.cols or \
self.matrix[i][j] or self.k < self.sums(i) + self.sums(j):
return 0
self.matrix[i][j] = 1
return 1 + self.moving(i+1, j) + self.moving(i-1, j) + \
self.moving(i, j+1) + self.moving(i, j-1) # still pass without self.moving(i, j-1).
def sums(self, i):
m = 0
while i:
i, b = i // 10, i % 10
m += b
return m数组 排序
位运算
字符串 双指针
二分查找 分治算法
队列 栈 堆 哈希表 链表 贪心算法
树 深度优先搜索 DFS 广度优先搜索 BFS 二叉搜索树 BST 平衡二叉树 BBT 递归 记忆化
动态规划 回溯算法
图 拓扑排序
极小化极大 蓄水池抽样 几何 并查集
等待申精 6. 26. 63. 122.