#Botan SDK
Botan is a telegram bot analytics system based on Yandex.Appmetrica. In this document you can find how to setup Yandex.Appmetrica account, as well as examples of Botan SDK usage.
- Go to Botaniobot https://telegram.me/botaniobot?start=src%3Dgithub
- Use Add bot command to get a token.
- Download lib for your language, and use it as described below. Don`t forget to insert your token!
- Come back to Botaniobot https://telegram.me/botaniobot?start=src%3Dgithub and use Statistics command to see your stats.
We have libraries for the following languages:
Alternatively, you can use Botan API via plain HTTP calls.
In case your preferred language is missed, you can make a contribution. It's easy — library usually contains 30 lines of code.
Also, pay attention to "what data to put into tracking data" section. 90% benefit from analytics usage lies in right integration;)
Install npm: npm install botanio
var botan = require('botanio')(token);
botan.track(message, 'Start');You need to install requests library to use python botan lib. You can do it with
pip install requests
Code:
import botan
token = 1
uid = 2
messageDict = {}
print botan.track(token, uid, messageDict, 'Search')
It's necessary to pass uid (user id you get from Telegram) into python lib calls.
You need to put the class in a convenient place.
private $token = 'token';
public function _incomingMessage($message_json) {
$messageObj = json_decode($message_json, true);
$messageData = $messageObj['message'];
$botan = new Botan($this->token);
$botan->track($messageData, 'Start');
}uid is a user id you get from Telegram.
require_relative 'botan'
token = 1111
uid = 1
message = { text: 'text' }
puts Botan.track(token, uid, message, 'Search')
extern crate rustc_serialize;
extern crate botanio;
use botanio::{Botan};
#[derive(Debug, RustcEncodable)]
struct Message {
some_metric: u32,
another_metric: u32,
}
fn main() {
let token = "1111";
let uid = 1;
let name = "Search";
let message = Message {some_metric: 100, another_metric: 500};
let botan = Botan::new(token);
botan.track(uid, name, &message).unwrap();
}try (CloseableHttpAsyncClient client = HttpAsyncClients.createDefault()) {
client.start();
Botan botan = new Botan(client, new ObjectMapper());
botan.track("1111", "1", ImmutableMap.of("some_metric": 100, "another_metric": 500), "Search").get();
}package main
import (
"fmt"
"github.com/botanio/sdk/go"
)
type Message struct {
SomeMetric int
AnotherMetric int
}
func main() {
ch := make(chan bool) // Channel for synchronization
bot := botan.New("1111")
message := Message{100, 500}
// Asynchronous track example
bot.TrackAsync(1, message, "Search", func(ans botan.Answer, err []error) {
fmt.Printf("Asynchonous: %+v\n", ans)
ch <- true // Synchronization send
})
// Synchronous track example
ans, _ := bot.Track(1, message, "Search")
fmt.Printf("Synchronous: %+v\n", ans)
<-ch // Synchronization receive
}The base url is: https://api.botan.io/track
You can put data to Botan using POST method.
The url should look like https://api.botan.io/track?token=BOTAN_TOKEN&uid=UID&name=EVENT_NAME
Please provide a json document as the post body.
API response is a json document:
- on success: {"status": "accepted"}
- on failure: {"status": "failed"} or {"status": "bad request", "info": "some_additional_info_about_error"}
###Basic integration
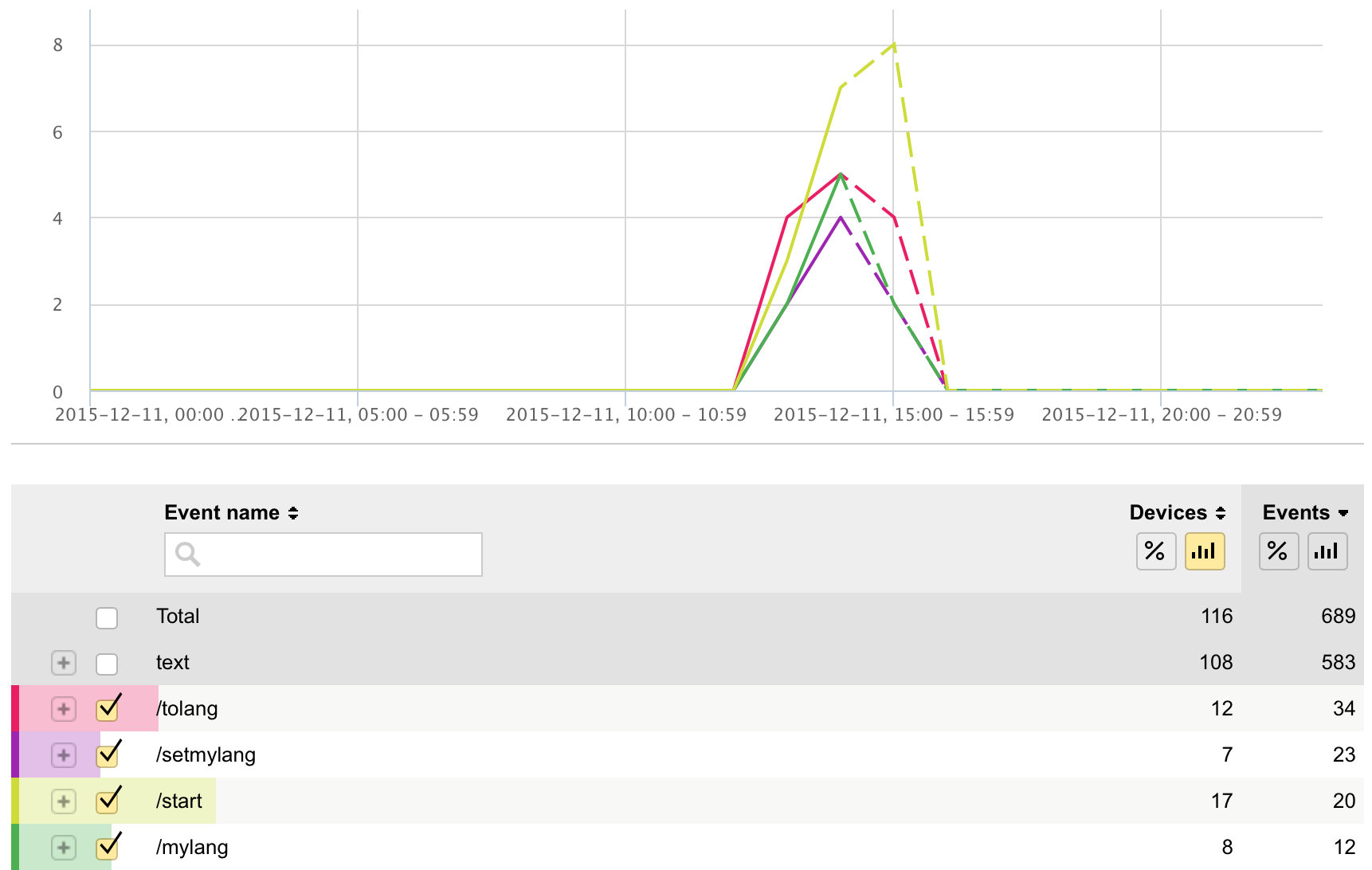
botan.track(<botan_token>, <user_who_wrote_to_bot>, <user_message_in_json_format>, <command_name>)- command_name - we recommend to put here not just message text, but command. Example: user wrote '/search californication', put to command_name 'Search'. This will help you to aggregate type of user's input and get such report:
- user_message_in_json_format - whole message got from Telegram. For example, using python-telegram-bot you can do it in such way: message.to_dict(). Passing whole message, you will be able to see nice data like number of group chats among all chats:
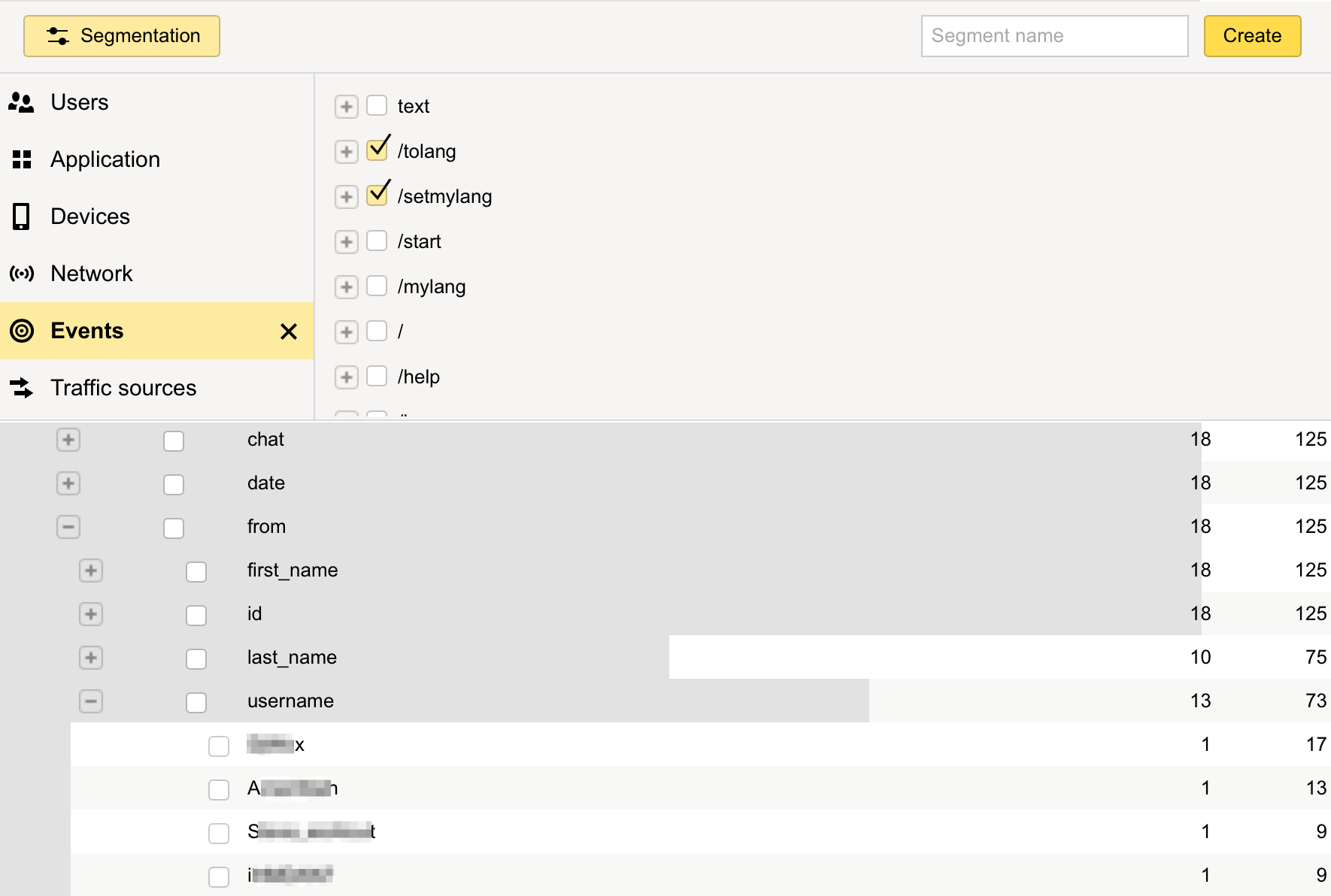
 Also you will be able to get userids who performed some particular action (through segmentation) or your most active users and contact them:
Also you will be able to get userids who performed some particular action (through segmentation) or your most active users and contact them:
###Advanced integration Actually, 70% benefit from analytics usage lies in sending right events with right data inside. Here is some ways of sending events, which we use. Feel free to contribute your ways or improve existing ones.
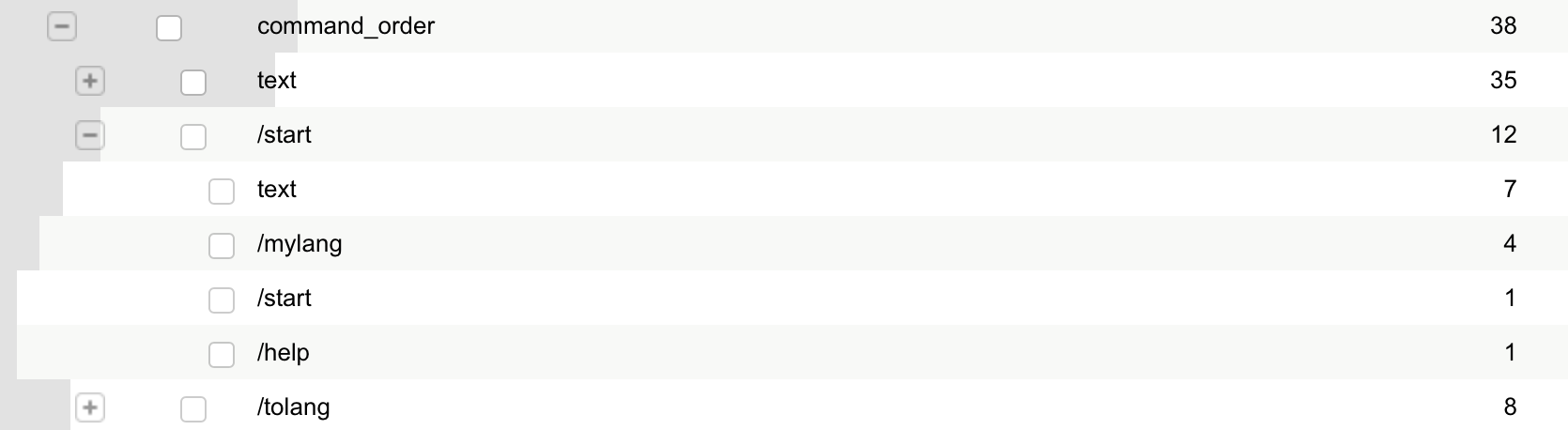
#####Commands order That's how you can see what command users execute after which:
botan.track(<botan_token>, <user_who_wrote_to_bot>, {last_command: current_command}, "command_order")Also you can send not pairs, but triples of commands:
botan.track(<botan_token>, <user_who_wrote_to_bot>, {before_last_command: {last_command: current_command}}, "command_order")Using this, we can see, for example, what commands users execute after /start:
 #####Date cohorts
Here is how you can tag every user with time cohort based on what was his first day at your service. Later you can use to see how your bot's performance has changed over time:
#####Date cohorts
Here is how you can tag every user with time cohort based on what was his first day at your service. Later you can use to see how your bot's performance has changed over time:
if this_is_first_occurence_of_user:
botan.track(<botan_token>,
<user_who_wrote_to_bot>,
{
'daily': message.date.strftime('%Y-%m-%d'),
'weekly': (message.date - datetime.timedelta(message.date.weekday())).strftime('%Y-%m-%d'),
'monthly': message.date.strftime('%Y-%m')
},
'cohorts')##Contribution We are welcome any contributions as pull-requests!
Feel free to write more libraries for the languages we are not supporting yet.