Few tools for a Tor relay.
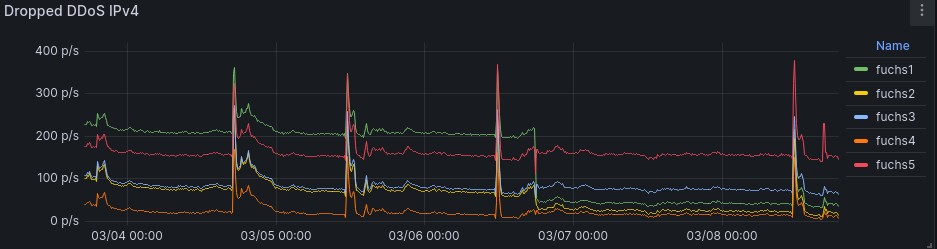
The scripts ipv4-rules.sh and ipv6-rules.sh protect a Tor relay against DDoS attacks¹ at the IP network layer, as seen in this metrics:
An older example is here.
¹ see ticket 40636 and ticket 40093 of the Tor project.
Install packages for jq, ipset and iptables, e.g. for Ubuntu 22.04:
sudo apt update
sudo apt install -y jq ipset iptables
wget -q https://raw.githubusercontent.com/toralf/torutils/main/ipv4-rules.sh -O ipv4-rules.sh
chmod +x ./ipv4-rules.shMake a backup of the current iptables filter table and run a quick test:
sudo /usr/sbin/iptables-save > ./rules.v4
sudo /usr/sbin/ip6tables-save > ./rules.v6
sudo ./ipv4-rules.sh testBest is to stop the Tor service(s) now. Flush the connection tracking table
sudo /usr/sbin/conntrack -Fand (re-)start the Tor service. Check that your ssh login and other services are still working. Watch the iptables live statistics by:
sudo watch -t ./ipv4-rules.shIf all works fine then run the script with the parameter start instead of test.
sudo ./ipv4-rules.sh startand create the following 2 cron jobs (via crontab -e):
# start firewall
@reboot /root/ipv4-rules.sh start; /root/ipv6-rules.sh start
# save ips to be blocked, helps at reboot
@hourly /root/ipv4-rules.sh save; /root/ipv6-rules.sh saveHowever, if something failed then restore the previous state:
sudo ./ipv4-rules.sh stop
sudo /usr/sbin/iptables-restore < ./rules.v4
sudo /usr/sbin/ip6tables-restore < ./rules.v6More hints are in the Installation section.
I do appreciate issue reports and GitHub PR.
- never touch established connections
- try to not overblock
Generic filter rules for the local network, ICMP, ssh and additional services are created. Then the following rules are applied:
- trust connection attempt to any port from trusted Tor authorities/Snowflake servers
- block the source² for 24 hours if the connection attempt rate to the ORPort exceeds > 9/min¹ within last 2 minutes
- ignore the connection attempt if there are already 9 established connections to the ORPort
- accept the connection attempt to the ORPort
¹ the value is derived from calculations given in ticket 40636 ² for IPv4 "source" is a regular ip, but for IPv6 the corresponding /80 CIDR block
If parsing of the Tor config (getConfiguredRelays()) and/or of the SSH config fails (addCommon()) then:
-
define the local running relay/s explicitely at the command line after the keyword
start, e.g.:sudo ./ipv4-rules.sh start 1.2.3.4:443 5.6.7.8:9001
-
-or- define them as environment variables, e.g.:
sudo CONFIGURED_RELAYS="5.6.7.8:9001 1.2.3.4:443" ./ipv4-rules.sh start(use
CONFIGURED_RELAYS6for the IPv6 case).
Specifying command line argument/s takes precedence over an environment variable. Please use the same syntax to allow inbound traffic to additional address:port destinations, e.g.:
export ADD_LOCAL_SERVICES="2.71.82.81:828 3.141.59.26:53"(use ADD_LOCAL_SERVICES6 appropriatly) before running the script.
Similar ADD_REMOTE_SERVICES and its IPv6 variant can be used to allow inbound traffic
from an address to the local port, e.g.:
export ADD_LOCAL_SERVICES="4.3.2.1:4711"allows traffic from the (remote) address "4.3.2.1" to local port "4711".
The script sets few sysctl values (following line). If not wanted then please comment out that call. If Hetzners system monitor isn't used, then comment out the call addHetzner() too.
To append (overwrite is the default) all rules onto existing iptables rule set please comment out the call clearRules() (near the end of the script at start)).
An implementation example using Ansible is seen here.
Before a reboot (or hourly via cron) run
sudo /etc/conf.d/ipv6-rules.sh save
sudo /etc/conf.d/ipv4-rules.sh saveto keep the list of blocked address between restarts.
The script metrics.sh exports data for Prometheus. The upload of DDoS metrics is done by node_exporter. Details and Grafana dashboards are here.
Graphs¹ of rx/tx packets, traffic and socket counts from 5th, 6th and 7th of Nov show the results for few DDoS attacks over 3 days for 2 relays. A more heavier attack was observed at 12th of Nov. A periodic drop down of the socket count metric, vanishing over time, appeared at 5th of Dec. Current attacks e.g. at the 7th of March are still handled well. Few more helper scripts were developed to analyze the attack vector. Look here for details.
¹ using sysstat
I used this Ansible role to deploy and configure Tor relays (server, bridges, snowflake). Take a look here for dashboards.
info.py gives a summary of all connections, e.g.:
sudo ./info.py --address 127.0.0.1 --ctrlport 9051
ORport 9051 0.4.8.0-alpha-dev uptime: 02:58:04 flags: Fast, Guard, Running, Stable, V2Dir, Valid
+------------------------------+-------+-------+
| Type | IPv4 | IPv6 |
+------------------------------+-------+-------+
| Inbound to our OR from relay | 2304 | 885 |
| Inbound to our OR from other | 3188 | 68 |
| Inbound to our ControlPort | | 1 |
| Outbound to relay OR | 2551 | 629 |
| Outbound to relay non-OR | | |
| Outbound exit traffic | | |
| Outbound unknown | 16 | 4 |
+------------------------------+-------+-------+
| Total | 8059 | 1587 |
+------------------------------+-------+-------+
relay OR connections 6369
relay OR ips 5753
3 inbound v4 with > 2 connections eachIf your Tor relay is running as an Exit then ps.py gives live statistics:
sudo ./ps.py --address 127.0.0.1 --ctrlport 9051orstatus.py prints the reason to stdout. orstatus-stats.sh prints/plots statistics (example) from that.
orstatus.py --ctrlport 9051 --address ::1 >> /tmp/orstatus &
sleep 3600
orstatus-stats.sh /tmp/orstatuskey-expires.py helps to maintain Tor offline keys. It returns the expiration time in seconds of the mid-term signing key, e.g.:
seconds=$(sudo ./key-expires.py /var/lib/tor/keys/ed25519_signing_cert)
days=$((seconds / 86400))
[[ $days -lt 23 ]] && echo "Tor signing key expires in less than $days day(s)"If Tor metrics are enabled then this 1-liner works too (replace 9052 with the actual metrics port if needed):
date -d@$(curl -s localhost:9052/metrics | grep "^tor_relay_signing_cert_expiry_timestamp" | awk '{ print $2 }')An open Tor control port is needed to query the Tor process via API. Configure it in torrc, e.g.:
ControlPort 127.0.0.1:9051
ControlPort [::1]:9051The python library Stem is needed. Install it either by your package manager -or- use the git sources, e.g.:
git clone https://github.com/torproject/stem.git
export PYTHONPATH=$PWD/stemThe script watch.sh helps to monitor a host or its Tor relay. It sends alarms via SMTP email.
log=/tmp/${0##*/}.log
# watch syslog
/opt/torutils/watch.sh /var/log/messages /opt/torutils/watch-messages.txt &>>$log &
# watch Tor
/opt/torutils/watch.sh /var/log/tor/notice.log /opt/torutils/watch-tor.txt -v &>>$log &