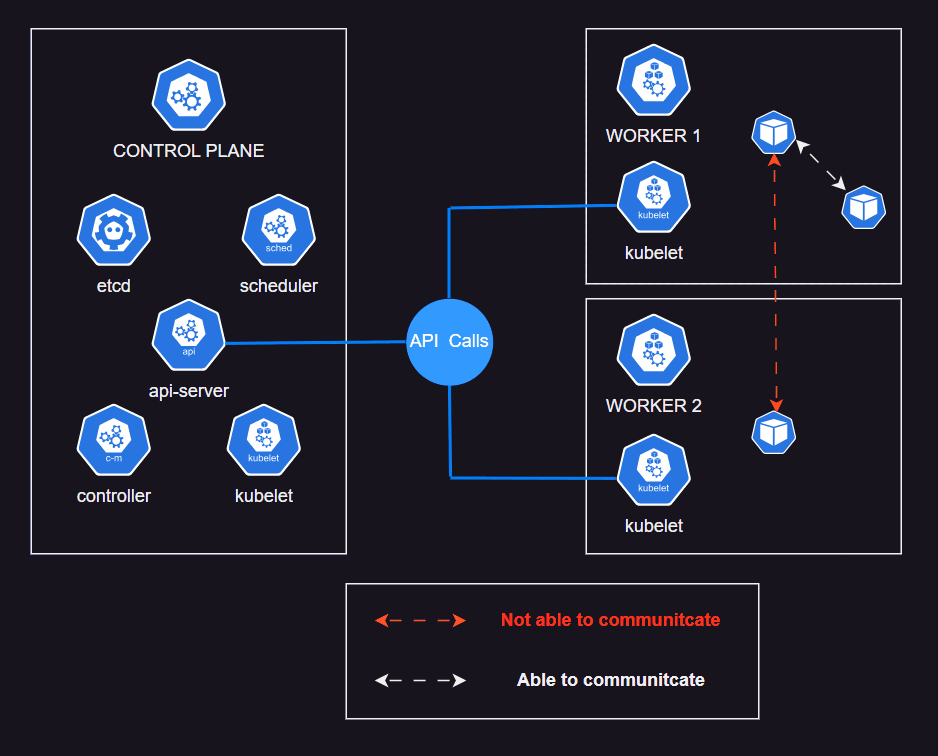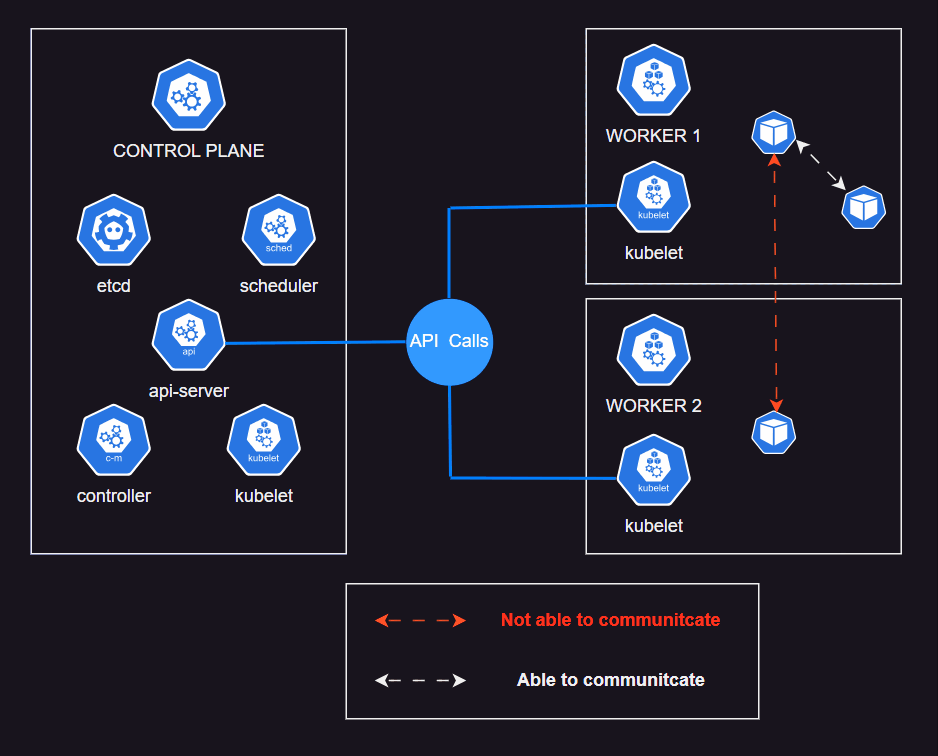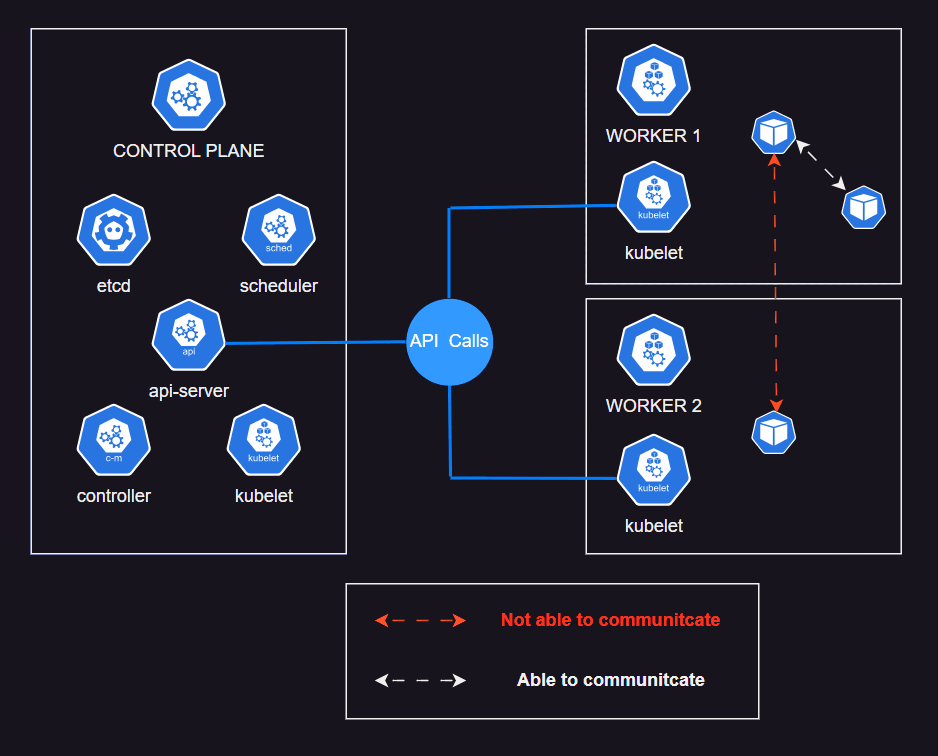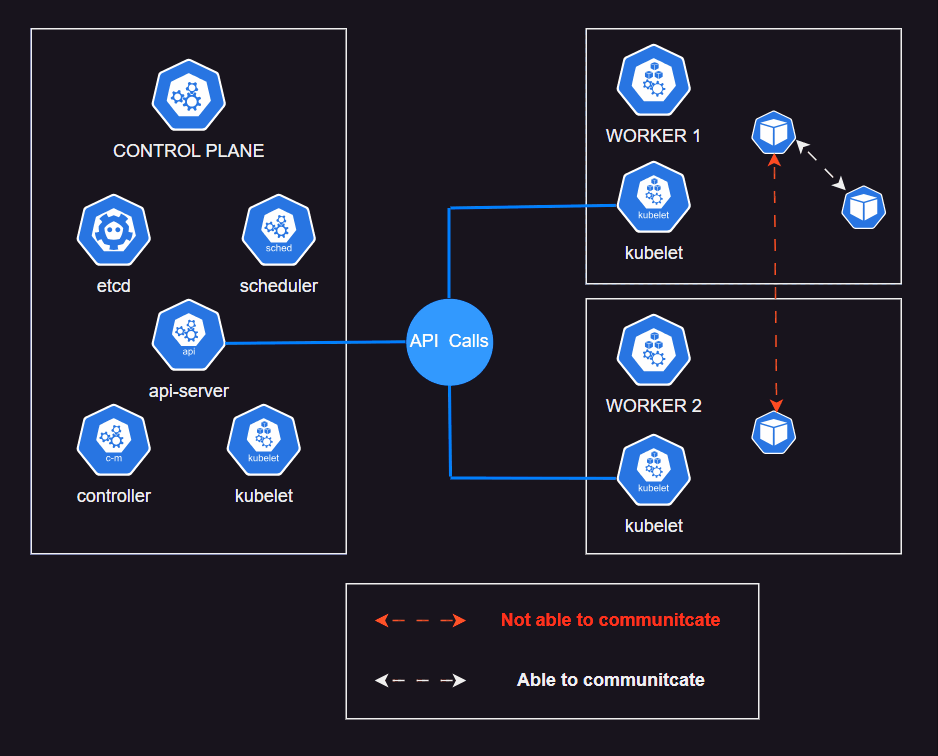
If you've already work with K8S Cluster. Move to Help Yourself
Deployment settings:
- K8S Cluster:
kubeadm - CNI Plugin: Calico
3 VMWare (Ubuntu 18.04 <Desktop version>)
- Control Plane (Master Node): NAT Network Mode, 4GB RAM, 2 CPU Processors. IP Address:
192.168.153.169 - Worker Node 1: NAT Network Mode, 2GB RAM, 1 CPU Processors. IP Address:
192.168.153.165 - Worker Node 2: NAT Network Mode, 2GB RAM, 1 CPU Processors. IP Address:
192.168.153.164
Note: You should set static IP Address, this instruction will not help you with this. If using dynamic IP (DHCP), don't turn on and off continually or IP may be changed.
Don't worry too much. When workers have joined cluster "beautifully", our cluster will update IP address according to changes to our nodes.
Kubernetes networking configuration:
- Cluster pod cidr: 10.48.0.0/16
- Cluster service cidr: 10.49.0.0/16
- Cluster kube-proxy mode: iptables
Calico networking configuration:
- Calico dataplane: Standard Linux networking
- Calico initial IP Pool cidr: 10.48.0.0/24
- Calico initial IP Pool block size: /26 (default)
- Calico initial IP Pool nat mode: enabled (default)
- Calico additional IP Pool cidr: 10.48.1.0/24
Change hostname rather than ubuntu. When a node is created and up, it will has a name with their hostname. Joining the cluster with same name will not work. Altering the hostname as following:
- Master: ubuntu (default)
- Worker1: knode1
- Worker2: knode2
Change hostname by :
hostnamectl set-hostname <host-name-you-want-to-set>At the same time, add these domain with specific IP above in /etc/hosts of each node. All nodes will be available to communicate with each other.
Master:
127.0.0.1 localhost
127.0.1.1 ubuntu
192.168.153.169 ubuntu
192.168.153.164 knode2
192.168.153.165 knode1
Worker1:
127.0.0.1 localhost
127.0.1.1 knode1
192.168.153.169 ubuntu
192.168.153.164 knode2
192.168.153.165 knode1
Worker2:
127.0.0.1 localhost
127.0.1.1 knode2
192.168.153.169 ubuntu
192.168.153.164 knode2
192.168.153.165 knode1
Now testing if 3 nodes can connect to each other by hostname:
ping knode1
ping knode2
ping ubuntuNow we are going to "play" with some installations.
- Always turn off swap partition whenever booting the virtual machine. Otherwise, this could be troubling in some steps
sudo swapoff -a- Install required tools, including docker used for containered environment.
curl -s https://packages.cloud.google.com/apt/doc/apt-key.gpg | sudo apt-key add
sudo apt-add-repository "deb http://apt.kubernetes.io/ kubernetes-xenial main"
sudo apt update -y
sudo apt install -y docker.io watch ipvsadm ipset tcpdump - Install main tools used for handling Kubernetes environment
sudo apt install -y kubeadm kubelet kubectl- Check versions:
docker --version
kubectl version
kubeadm version- Enable docker service:
sudo systemctl enable docker- Pull the image containing configurations for all needed services
sudo kubeadm config images pull- Initialize the kubernetes cluster with iptables mode kube-proxy. Configuration file:
nano kubeadm-config-iptables-mode.yaml---
apiVersion: kubeadm.k8s.io/v1beta2
kind: ClusterConfiguration
networking:
serviceSubnet: 10.49.0.0/16
podSubnet: 10.48.0.0/16
dnsDomain: cluster.local
---
apiVersion: kubeproxy.config.k8s.io/v1alpha1
kind: KubeProxyConfiguration
mode: iptables
- Create the cluster with config above:
sudo kubeadm init --config kubeadm-config-iptables-mode.yamlThere must be something like below at the end of output. This command will help your worker node join the cluster with exact credential in your output terminal.
Note that the hash key and K8s token would be different. Save this command immediately !
kubeadm join 192.168.153.169:6443 --token 0d3aqz.u2bmp0zwlfdh5pmt --discovery-token-ca-cert-hash sha256:726cf64d358aded6a6584271c5342178f10834e254bfe8ff08357dcc3c6af8771- Copy the kubectl config into
$HOME/.kube.
Kubectl interacts with the kubernetes cluster using the details available in the Kubeconfig file. By default, kubectl looks for the config file in the
$HOME/.kubelocation.
mkdir -p $HOME/.kube
sudo cp -i /etc/kubernetes/admin.conf $HOME/.kube/config
sudo chown $(id -u):$(id -g) $HOME/.kube/config- Monitor the K8S nodes's status:
watch kubectl get nodes
kubectl get pods -n kube-system Master's status should NOT be ready.
- Let 2 Worker nodes join cluster by command from above as i said before. The command will look like:
sudo kubeadm join 192.168.153.169:6443 --token 0d3aqz.u2bmp0zwlfdh5pmt --discovery-token-ca-cert-hash sha256:726cf64d358aded6a6584271c5342178f10834e254bfe8ff08357dcc3c6af8771Output if there is no errors:
This node has joined the cluster:
* Certificate signing request was sent to apiserver and a response was received.
* The Kubelet was informed of the new secure connection details.
Run 'kubectl get nodes' on the control-plane to see this node join the cluster
- Check the status from monitoring above in
Master node. 3 nodes'sSTATUSwould beNOT READY
kubectl get nodesIf workers don't join successfully. Remembering what we discussed above, nodes with same hostname won't work, rename them.
- Login to the other workers and repeat steps 1.
- Download Calico configuration files:
curl https://docs.projectcalico.org/manifests/calico.yaml -o calico.yaml- Edit the calico-node DaemonSet
nano calico.yaml- Change
CALICO_IPV4POOL_CIDRvalue to10.48.0.0/24;CALICO_IPV4POOL_IPIPtoNever
This section has 2 contents need to be substitute like below:
# Enable IPIP
- name: CALICO_IPV4POOL_IPIP
value: "Never"- name: CALICO_IPV4POOL_CIDR
value: "10.48.0.0/24"- Apply our config to cluster
calico.yaml
kubectl apply -f calico.yaml- Observe the control plane come completely
watch kubectl get nodesWait for a while (quite long :>) for step 4 to be completed. Then our cluster should be
READY
Every 2.0s: kubectl get nodes ubuntu: Tue Jun 14 06:53:46 2022
NAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSION
knode1 Ready <none> 5h18m v1.24.1
knode2 Ready <none> 5h23m v1.24.1
ubuntu Ready control-plane 5h27m v1.24.1
- Install and configure
calicoctl
curl -O -L https://github.com/projectcalico/calicoctl/releases/download/v3.14.0/calicoctl
chmod +x calicoctl
sudo mv calicoctl /usr/local/bin- Create a file
calicoctl.cfg:
nano calicoctl.cfg- Let's add config into :
apiVersion: projectcalico.org/v3
kind: CalicoAPIConfig
metadata:
spec:
datastoreType: "kubernetes"
kubeconfig: "/home/ubuntu/.kube/config"Note: the key
kubeconfigis the path$HOME/.kube/config
- Move our config to Calico'service in
/etcfolder.
sudo mkdir -p /etc/calico
sudo cp calicoctl.cfg /etc/calico- Check if Calico command is good to try:
calicoctl versionVideo demo link: https://youtu.be/EDbifjrOeKM
- Check out the Calico node status.
sudo calicoctl node statusOutput:
Calico process is running.
IPv4 BGP status
+-----------------+-------------------+-------+----------+-------------+
| PEER ADDRESS | PEER TYPE | STATE | SINCE | INFO |
+-----------------+-------------------+-------+----------+-------------+
| 192.168.153.164 | node-to-node mesh | up | 11:10:52 | Established |
| 192.168.153.165 | node-to-node mesh | up | 13:20:50 | Established |
+-----------------+-------------------+-------+----------+-------------+
IPv6 BGP status
No IPv6 peers found.
- Verify your IP pool settings
calicoctl get ippools default-ipv4-ippool -o yamlOutput:
apiVersion: projectcalico.org/v3
kind: IPPool
metadata:
creationTimestamp: "2022-06-14T08:45:55Z"
name: default-ipv4-ippool
resourceVersion: "2180"
uid: ece0af99-c0fa-4a46-bc49-0e5c9a9252bd
spec:
blockSize: 26
cidr: 10.48.0.0/24
ipipMode: Never
natOutgoing: true
nodeSelector: all()
vxlanMode: Never
- Check out our IP pool utilization
calicoctl ipam show+----------+--------------+-----------+------------+-----------+
| GROUPING | CIDR | IPS TOTAL | IPS IN USE | IPS FREE |
+----------+--------------+-----------+------------+-----------+
| IP Pool | 10.48.0.0/24 | 256 | 3 (1%) | 253 (99%) |
+----------+--------------+-----------+------------+-----------+
calicoctl ipam show --show-blocks+----------+--------------+-----------+------------+-----------+
| GROUPING | CIDR | IPS TOTAL | IPS IN USE | IPS FREE |
+----------+--------------+-----------+------------+-----------+
| IP Pool | 10.48.0.0/24 | 256 | 3 (1%) | 253 (99%) |
| Block | 10.48.0.0/26 | 64 | 3 (5%) | 61 (95%) |
+----------+--------------+-----------+------------+-----------+
- Inspect the global network policies
calicoctl get globalnetworkpolicies- Download a Firewall policy:
curl -LO https://raw.githubusercontent.com/xxradar/k8s-calico-oss-onprem-install/master/FirewallZonesPolicies.yaml- Deploy the zone-based segmentation policies:
calicoctl apply -f FirewallZonesPolicies.yaml- Verify the zone-based segmentation policies
calicoctl get networkpolicies --all-namespaces
- Going on running some tests. Deploy some pods:
kubectl run --image nginx nginx --port=80 -l fw-zone=trusted
kubectl get pods -o wideOutput:
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE IP NODE NOMINATED NODE READINESS GATES
nginx 1/1 Running 0 4m17s 10.48.0.128 knode1 <none> <none>
- This will run a container with image named
nginx, port80, just let it keep running. Carefully beware of label-valuefw-zone=trusted. - Master Node defaulty will auto create this pod into
knode1Worker.
- Try another container (fail to predefined policy):
kubectl run -it --rm --image xxradar/hackon hackon -- bashOnce we get into our container with -it options as illustrated. Check the running container nginx above by curl its content pages by its IP shown in pod above. Type:
curl 10.48.0.128There should be no respond from the container. This because our policy kicked in. You can open another terminal to view all current pods
kubectl get pods -o wide- Try another container (pass predefined policy):
kubectl run -it --rm --image xxradar/hackon -l fw-zone=dmz hackon -- bashRun again:
curl 10.48.0.128This should be successful. It prints out the contents of nginx's webpage.
calicoctl apply -f 10.48.1.0-ippool.yaml
kubectl create namespace internal-ns
kubectl annotate namespace internal-ns "cni.projectcalico.org/ipv4pools"="[\"new-pool\"]" --overwrite
kubectl run nginx --image nginx --namespace internal-nsYou can add more pods between Worker 1 and Worker 2 and set more rules/policies to observe the result. Happy testing !!!!
- If you need to reset cluster in below case:
- Redo
kubeadm init - Redo
kubeadm join
You could use the following command:
sudo kubeadm reset # --cri-socket=unix://var/run/cri-dockerd.sock
- If there are multiple CRI Socket, you must specify which socket you're using by
--cri-socket=YOUR_SOCKET.YOUR_SOCKETformat should beunix:/SOCKETPATH. AvailableYOUR_SOCKETare located in/var/run, you could use this to list the available:
sudo ls /var/run | grep -E ".sock$"
Main link: xxradar-k8s-calico-oss-onprem-deploy
- Kubeadm Install: https://docs.projectcalico.org/getting-started/kubernetes/quickstart
- Kube-Proxy Mode: https://www.projectcalico.org/comparing-kube-proxy-modes-iptables-or-ipvs/
- Calico IPAM: https://docs.projectcalico.org/networking/ipam
- Intro Calico eBPF dataplane: https://www.projectcalico.org/introducing-the-calico-ebpf-dataplane/
- CNCF Calico eBPF webinar: https://www.cncf.io/webinars/calico-networking-with-ebpf/
- Trying Calico eBPF dataplane: https://docs.projectcalico.org/getting-started/kubernetes/trying-ebpf