| About WAX Creator | API Documentation for WAX Creator | WAX Collectible Creator | Buy & Sell Collectibles | Trade Collectibles |
- Overview
- PHP
- Node.js
- Related APIs
The WAX Creator API allows developers to create NFTs (WAX Collectible Cards, WAX Stickers & WAX Digital Art) on the WAX Blockchain for free via external sources. NFTs must be approved by the OPSkins support team, before minted on the WAX Blockchain, and sent to the issuer's WAX Trade Inventory. A NFT can be Verified Authentic, meaning proof of ownership can be provided for that NFT. Verified Authentic NFTs can be assigned an Instant-Sell value opposed to non-Verified Authentic NFTs. Additionally, NFTs can also be assigned Attributes (this can be useful for card games, for example).
Note:
Verified AuthenticNFTs take longer to approve than non-Verified AuthenticNFTs. TheVerified Authenticstatus of an NFT is shown on WAX Trade and OPSkins.
Note: You need WAX Points to create a collectible with
Instant-Sellenabled.
- (None)
- (None)
Know of an extension that isn't listed above? Open an issue and it will be added to the list!
Note: Although there are many different extensions you can use (not limited to the list above) to invoke the WAX Creator API, the first extension under
Recommendedin each category will be the extension used in this tutorial.
Before anything, you will need to install a Web Server and PHP. If you already know how to do this and you're not interested in registering a domain alongside the configuration that comes with it, skip to the next step; otherwise, you can click here for information related to registering a domain and its configuration.
Note: Instructions related to setting up a MySQL Server won't be addressed in this tutorial; however, it's recommended that you go forward with the process if you plan on creating a website that serves user accounts, saves their settings and/or stores any other data in general.
If you aren't interested in setting up an environment for local development, you can skip directly to setting up a production environment (where you can publish your website so anyone can visit it).
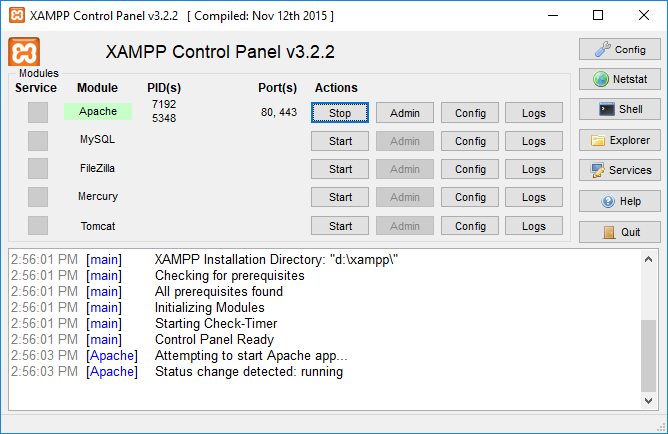
A Web Server and PHP can be installed by many different means, although XAMPP is an all-in-one package that's incredibly easy to install and use; hence, it's a highly recommended option and you should definitely consider using it!
After installing XAMPP (or the above by any other mean), start Apache (a.k.a Web Server):
Any website you create should be placed in the htdocs folder where you installed XAMPP. You can access one of your websites at http://localhost/some-website via a web browser, where some-website is the path to the website you wish to render.
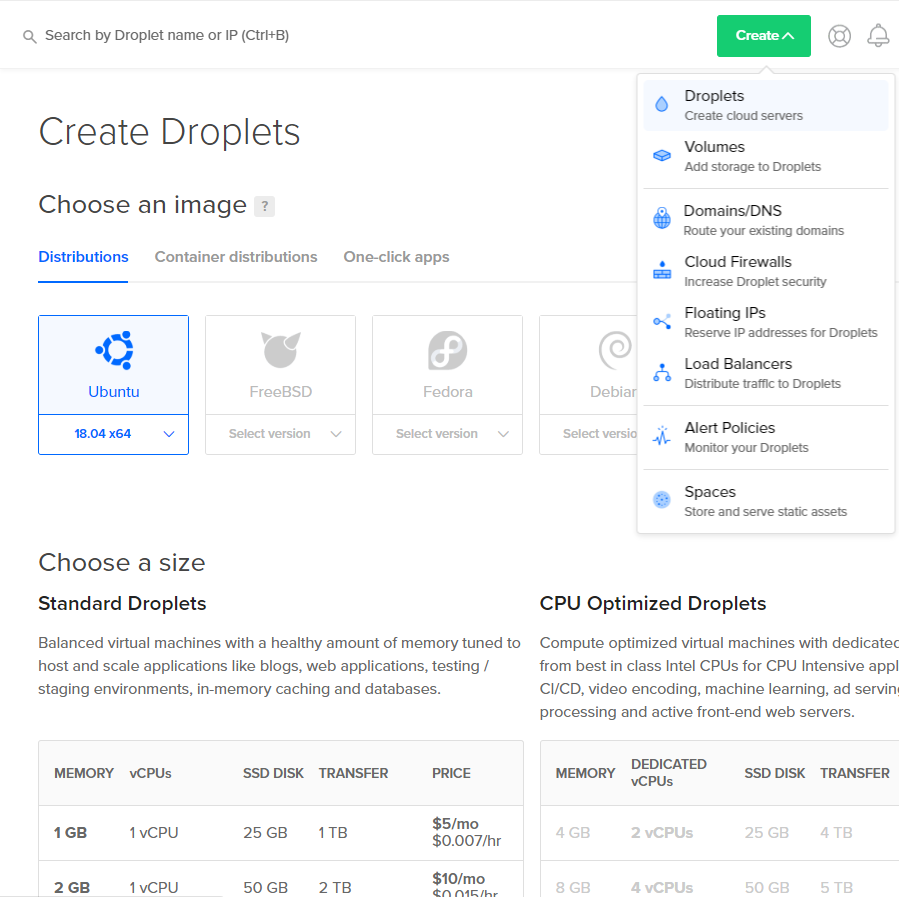
Hosting a website implies that you rent a VPS (Virtual Private Server) from a company of choice to keep it accessible 24/7. There are many companies you can rent a VPS from, although some may require that you submit a whitelist application beforehand (such as OVH). If you're looking for a decent VPS that's also quick to set up, DigitalOcean is an excellent option!
Note: You can alternatively host your website with a dedicated web hosting provider (such as HostGator), this would simplify the process a bit and can be a better option if your VPS provider doesn't provide strong protection against attacks using the default configuration. However, many dedicated web hosting providers disable certain features for security reasons - so if you want to be in complete control and/or plan on hosting more than one website while paying the same amount per month, a VPS would be the more convenient option!
Regardless of the company you decide to rent a VPS from, you must get it online with the OS (Operating System) of your choice installed. Ubuntu is recommended for beginners.
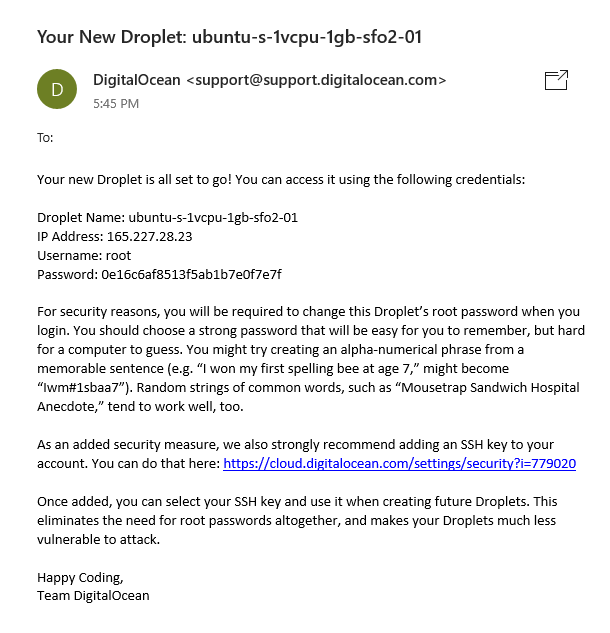
Typically after creating a VPS, its log in credentials are sent via email - have them ready as you'll need them in the next step!
Note: Hosting a website on a Windows Server is possible; however, it isn't recommended for beginners - many network adjustments must be applied to prevent attacks by third parties.
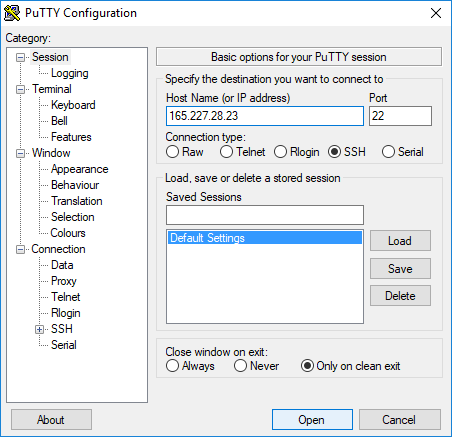
You will need an SSH Client in order to log into your VPS. PuTTY is vastly recommended!
Run PuTTY (or the SSH client of your choice) and connect to your VPS:
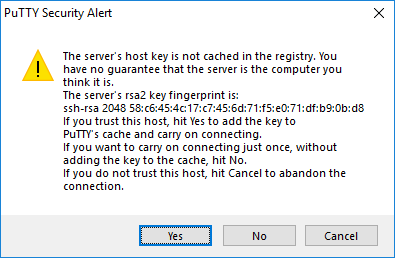
A dialog titled PuTTY Security Alert will prompt, hit Yes:
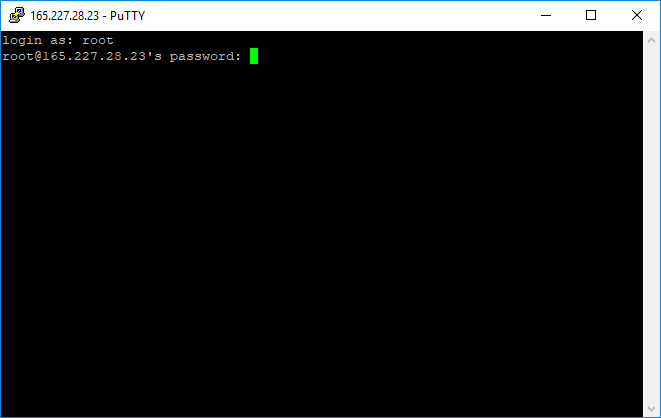
Enter the username and password sent to you via email:
Note: Passwords in the SSH client don't show whatsoever, not even as hidden characters (e.g. ••••••).
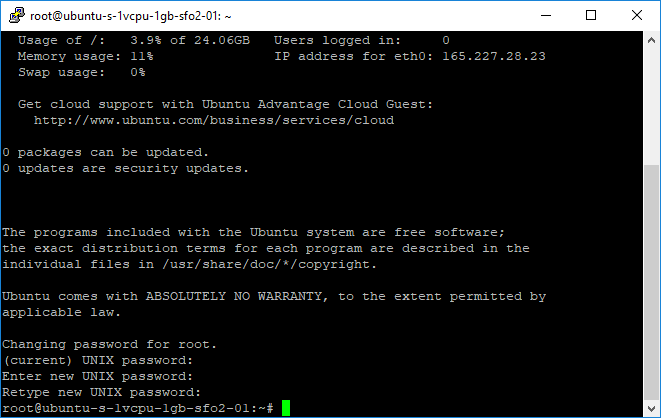
As stated in the email from DigitalOcean, you must change your password upon initially logging into your VPS for security reasons:
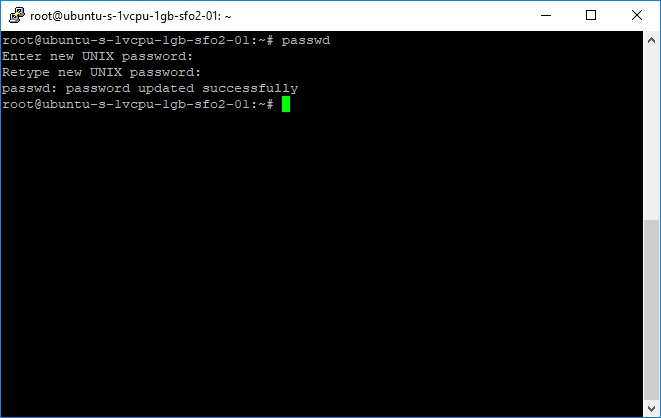
(Optional) Not all providers force you to change your password upon initially logging into your VPS, although it's recommended! You can alternatively change your password with the passwd command:
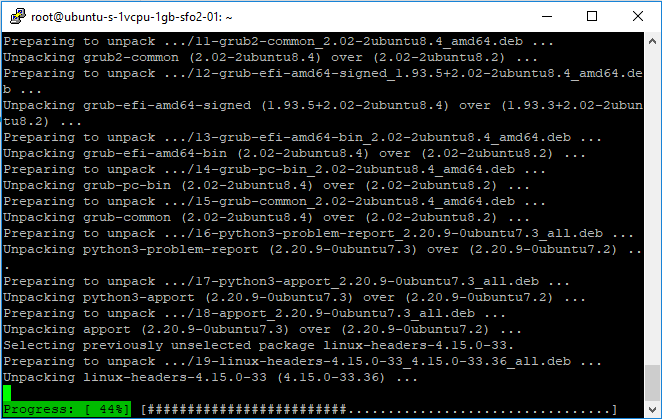
Check for and install all system updates by executing apt update && apt upgrade:
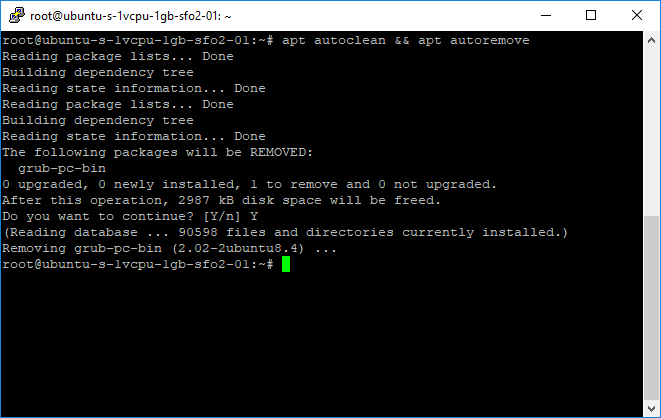
Remove any residue files by executing apt autoclean && apt autoremove:
No other command in this tutorial should be executed as root (about) (besides the ones below to create a new user).
Note: It's good practice to run your applications on a user level (as they were meant to) and leave administrative tasks to the
rootuser. Your system is vulnerable to exploits and attacks when running applications asroot, in consequence this can lead to files being deleted, breach of therootuser's credentials, or complete loss of your system. For even more security (e.g. preventing brute-force attacks), look into configuring SSH key based secure authentication.
Create a new user and add it to the sudo (about) group so you'll have administrative privileges:
- Create the user, replacing
example_userwith a username of your choice:adduser example_user(you'll be prompt to assign a password and enter information about the user) - Add the user to the
sudogroup, replacingexample_userwith the username of the user you previously created:adduser example_user sudo - Switch to the user, again by replacing
example_user:su example_user
Note: Log into your VPS with the credentials you previously created from here on out (add
sudoto the beginning of a command if administrative privileges is required); although, you can always use thesucommand to switch to the user.
If you're using Ubuntu 18.04, use Tasksel to install a LAMP Stack (Linux, Apache, MySQL, PHP):
sudo tasksel install lamp-server
(Optional) Otherwise, you can install Apache and PHP separately (or if you don't want MySQL to be installed altogether):
- Install Apache:
sudo apt install apache2 - Install the base PHP package and the PHP Extension and Application Repository:
sudo apt install php php-pear - Add the PHP module for Apache:
sudo apt install libapache2-mod-php
Any website you create should be placed in /var/www/html. You can access one of your websites at http://IP/some-website via a web browser, where IP is your VPS' IP address and some-website is the path to the website you wish to render.
Your website (or at least the Apache2 Ubuntu Default Page) should be accessible at this point. It's recommended that you assign a domain to your website if you plan on having visitors from all around the world; however, it isn't technically necessary - your visitors would just have trouble remembering your VPS' IP address! If you do not wish to assign a domain to your website, skip to the next step.
There are many companies you can register a Domain Name with. NameCheap & GoDaddy are excellent domain name providers, and both have an active support team! Either one is highly recommended.
Before you go ahead and purchase a domain, decide whether you want an SSL Certificate or not since purchasing one after you register a domain is often more expensive (you must pay the full price as no discount will be applied)! An SSL certificate will encrypt your visitors' information, thus improving the security of your website - it is recommended that you install one!
Note: You aren't forced to pay for a domain as there are free options (such as .tk), but you are limiting the array of extensions available to you. It's important to note that some people tend to stay away from websites with free domains, so go with a paid domain if you're aiming for success!
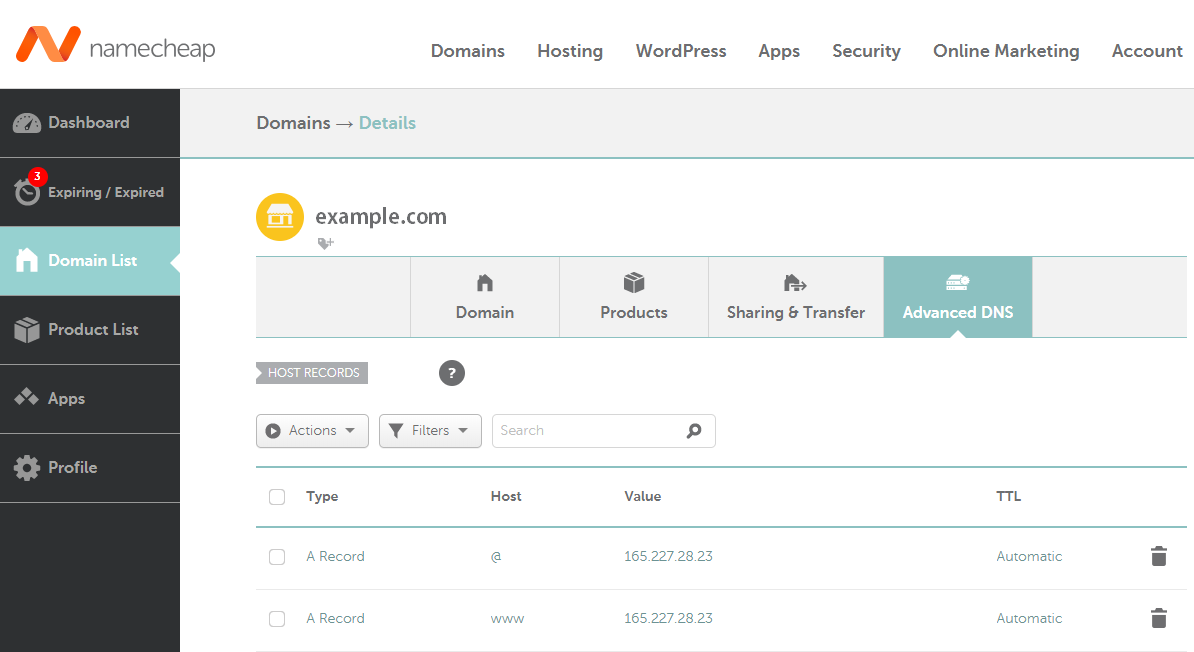
After registering a domain of your choice, modify its Host Records, replacing 165.227.28.23 with your VPS' IP address:
- Type: A Record, Host: @, Value: 165.227.28.23, TTL: Automatic
- Type: A Record, Host: www, Value: 165.227.28.23, TTL: Automatic
Note: @ is a shortcut for the name defined as $ORIGIN - basically your domain name which also represents the root directory. The second host record will accept requests with the www subdomain attached.
Note: When a domain is newly registered, or DNS changes are made, you can expect a propagation time up to 24 hours.
If you didn't purchase an SSL certificate, click here to continue.
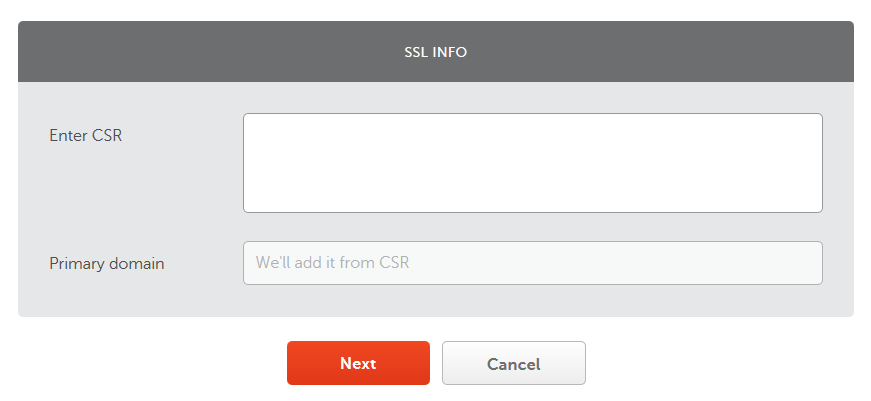
It's great that you have decided to install an SSL certificate to ensure that the information of your visitors is protected (such as passwords) - now you need to activate it! For that, you will need to generate a CSR:
openssl req -new -newkey rsa:2048 -nodes -keyout server.key -out server.csr (you'll be prompt to enter information)
Once you have entered all of the requested information, you should have a .csr and .key file in the path where you executed the command - download the .key file as you'll need it later! Open the .csr file with nano (install it by executing sudo apt install nano if it doesn't come pre-installed), copy its content, then go to your provider's dashboard and start the process of activating your SSL certificate (you can find your SSL certificate listed under Products on NameCheap).
Enter what you copied from the .csr file:
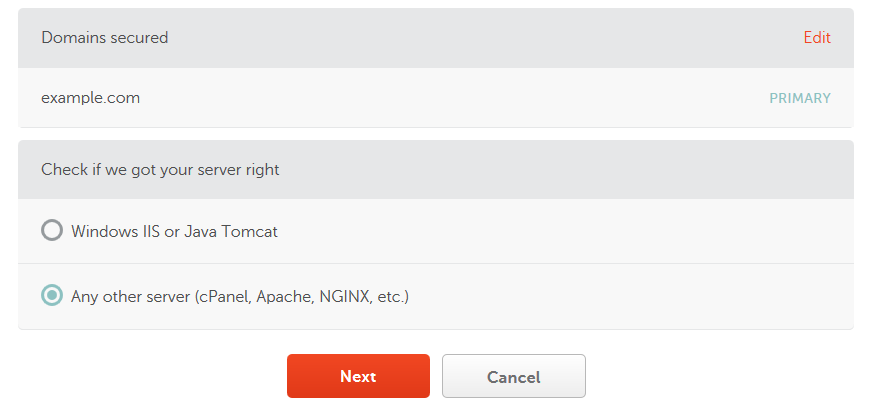
Confirm that the selected server is correct (it should include Apache):
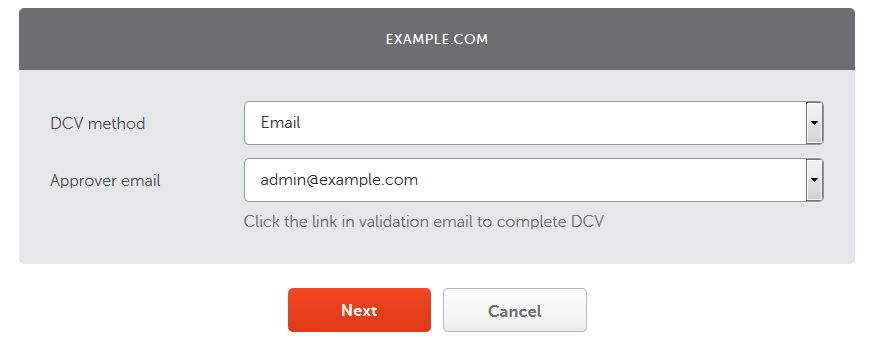
Select your preferred validation method:
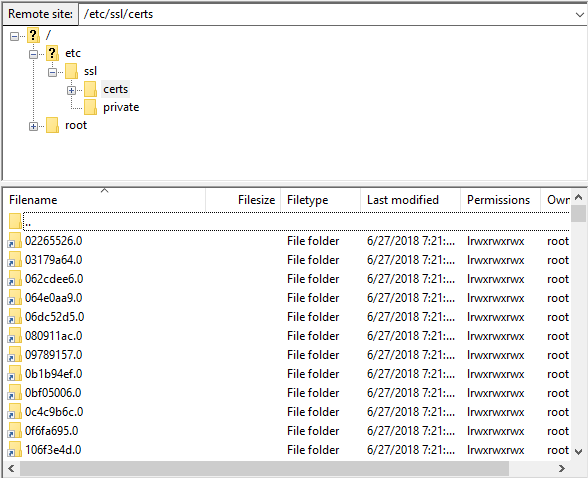
Go forward with the selected domain ownership validation process. At the end, typically two files in a compressed archive will be sent to you via email - download & extract it! With a FTP Client (FileZilla is highly recommended) connected through the sftp protocol (sftp://IP, where IP is your VPS' IP address - this is the value of Host on FileZilla), upload the files in the compressed archive (.crt & .ca-bundle) to /etc/ssl/certs and upload the .key file that was generated alongside the .csr file to /etc/ssl/private. See the following screenshots for reference:
Note: The
UsernameandPasswordfield on FileZilla correspond to your VPS log in credentials.
You will then need to enable SSL Mode so that Apache is able to run an encrypted HTTPS connection:
sudo a2enmod ssl
Moving forward, it's now time to configure the Name-based Virtual Hosts so that your system knows what to do when someone visits your domain! For that:
-
Disable the default Apache virtual host:
sudo a2dissite *default -
Create the necessary folders for your website, replacing
example.comwith your domain name:sudo mkdir -p /var/www/html/example.com/{includes,public_html} -
Create the virtual host file for your website, replacing
example.comwith your domain name:sudo nano /etc/apache2/sites-available/example.com.conf(the text editor will prompt, follow the step of your choice below) -
Paste the following configuration, replacing
example.comwith your domain name,example_com_keywith the name of your.keyfile,example_com_crtwith the name of your.crtfile, andexample_com_ca_bundlewith the name of your.ca-bundlefile:<VirtualHost *:80> ServerName example.com ServerAlias www.example.com Redirect permanent / https://www.example.com/ </VirtualHost> <VirtualHost *:443> ServerName example.com SSLEngine on SSLCertificateKeyFile /etc/ssl/private/example_com_key.key SSLCertificateFile /etc/ssl/certs/example_com_crt.crt SSLCACertificateFile /etc/ssl/certs/example_com_ca_bundle.ca-bundle Redirect permanent / https://www.example.com/ </VirtualHost> <VirtualHost *:443> ServerName www.example.com SSLEngine on SSLCertificateKeyFile /etc/ssl/private/example_com_key.key SSLCertificateFile /etc/ssl/certs/example_com_crt.crt SSLCACertificateFile /etc/ssl/certs/example_com_ca_bundle.ca-bundle DirectoryIndex index.html index.php DocumentRoot /var/www/html/example.com/public_html </VirtualHost>
-
(Optional) The previous configuration will redirect requests to the root directory (
example.com) to thewwwsubdomain (www.example.com) while enforcing theHTTPSprotocol. If you'd like the previous reversed (www.example.comredirects toexample.com), paste the following instead (just remember to make the same replacements):<VirtualHost *:80> ServerName example.com ServerAlias www.example.com Redirect permanent / https://example.com/ </VirtualHost> <VirtualHost *:443> ServerName www.example.com SSLEngine on SSLCertificateKeyFile /etc/ssl/private/example_com_key.key SSLCertificateFile /etc/ssl/certs/example_com_crt.crt SSLCACertificateFile /etc/ssl/certs/example_com_ca_bundle.ca-bundle Redirect permanent / https://example.com/ </VirtualHost> <VirtualHost *:443> ServerName example.com SSLEngine on SSLCertificateKeyFile /etc/ssl/private/example_com_key.key SSLCertificateFile /etc/ssl/certs/example_com_crt.crt SSLCACertificateFile /etc/ssl/certs/example_com_ca_bundle.ca-bundle DirectoryIndex index.html index.php DocumentRoot /var/www/html/example.com/public_html </VirtualHost>
-
Save the changes to the virtual host configuration file by pressing
CTRL+X, hittingYfor Yes, and then pressingENTERto confirm. -
Enable your website by creating a symbolic link to your virtual host configuration file, replacing
example.comwith your domain name:sudo a2ensite example.com.conf
Finally, restart Apache for the changes to take effect:
sudo systemctl restart apache2
If you purchased an SSL certificate, click here to continue.
Configure the Name-based Virtual Hosts so that your system knows what to do when someone visits your domain! For that:
-
Disable the default Apache virtual host:
sudo a2dissite *default -
Create the necessary folders for your website, replacing
example.comwith your domain name:sudo mkdir -p /var/www/html/example.com/{includes,public_html} -
Create the virtual host file for your website, replacing
example.comwith your domain name:sudo nano /etc/apache2/sites-available/example.com.conf(the text editor will prompt, follow the step of your choice below) -
Paste the following configuration, replacing
example.comwith your domain name:<VirtualHost *:80> ServerName example.com Redirect permanent / http://www.example.com/ </VirtualHost> <VirtualHost *:80> ServerName www.example.com DirectoryIndex index.html index.php DocumentRoot /var/www/html/example.com/public_html </VirtualHost>
-
(Optional) The previous configuration will redirect requests to the root directory (
example.com) to thewwwsubdomain (www.example.com). If you'd like the previous reversed (www.example.comredirects toexample.com), paste the following instead (just remember to make the same replacement):<VirtualHost *:80> ServerName www.example.com Redirect permanent / http://example.com/ </VirtualHost> <VirtualHost *:80> ServerName example.com DirectoryIndex index.html index.php DocumentRoot /var/www/html/example.com/public_html </VirtualHost>
-
Save the changes to the virtual host configuration file by pressing
CTRL+X, hittingYfor Yes, and then pressingENTERto confirm. -
Enable your website by creating a symbolic link to your virtual host configuration file, replacing
example.comwith your domain name:sudo a2ensite example.com.conf
Finally, restart Apache for the changes to take effect:
sudo systemctl restart apache2
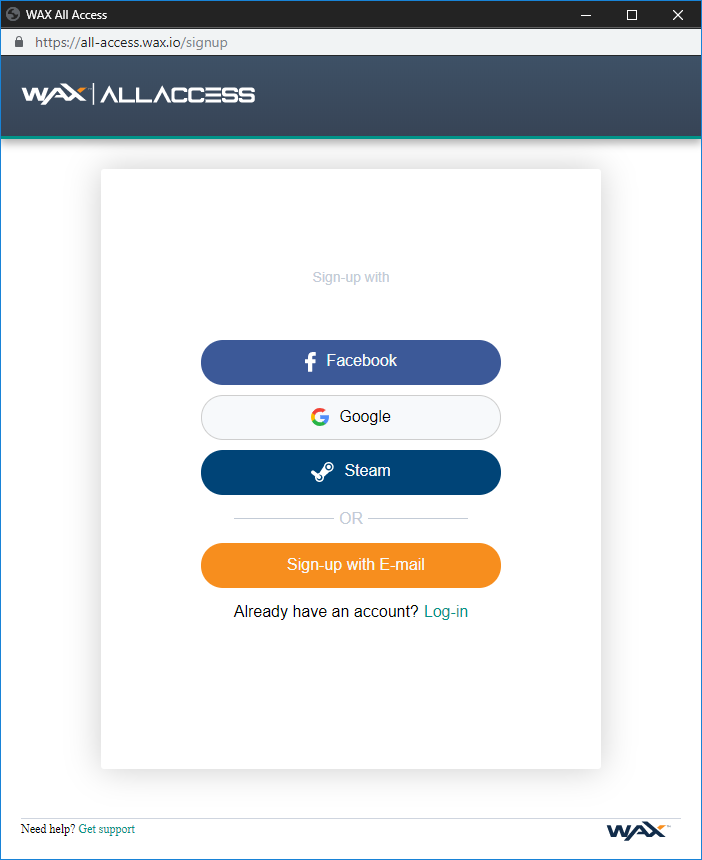
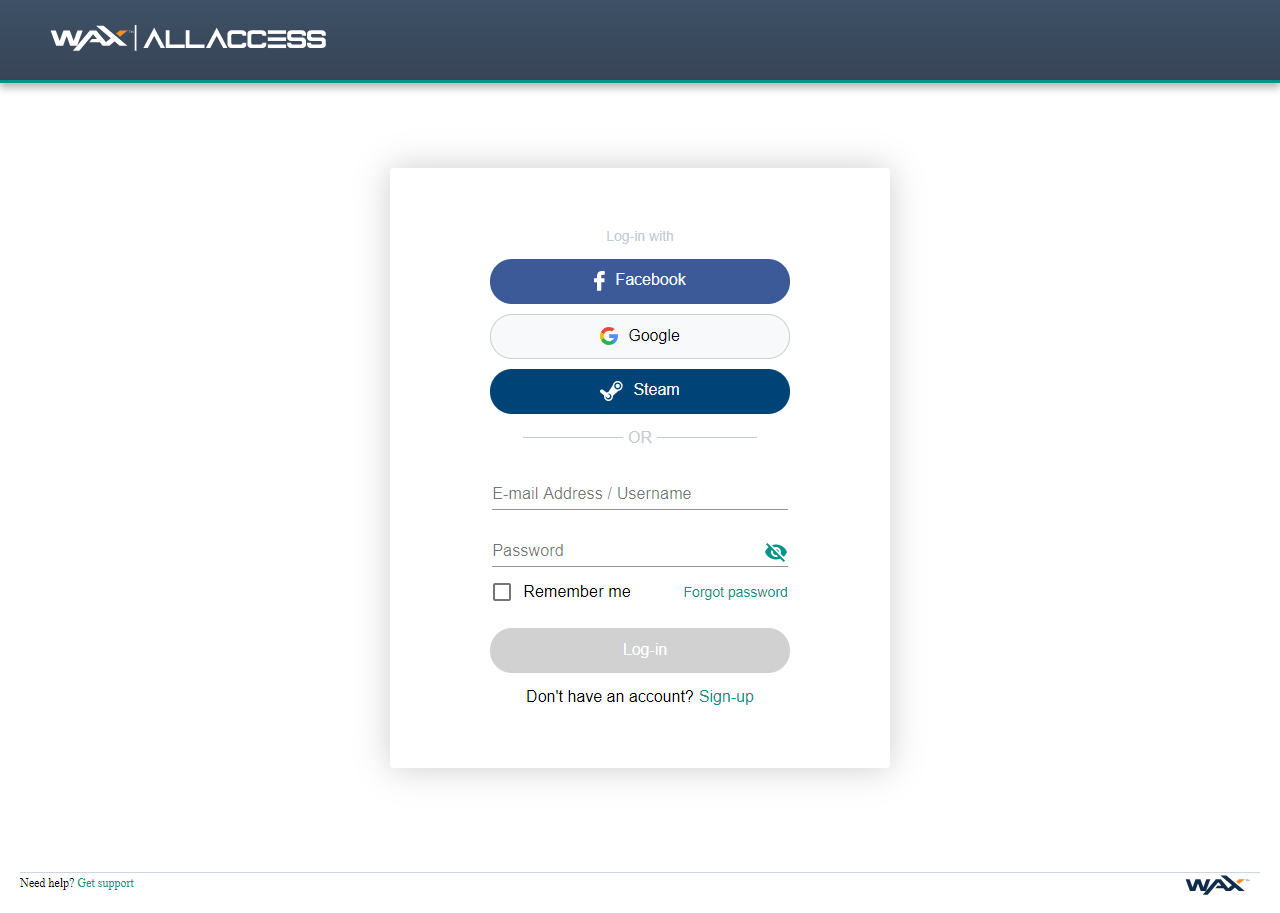
OPSkins is pretty much the main platform for all WAX services that require authentication, being interconnected through WAX AllAccess. You'll find yourself using OPSkins a lot, so it's recommended that you start by creating an account there!
You can create an OPSkins account by signing up with Facebook, Google, Steam, or Email:
2FA (Two-Factor Authentication) is required to request a WAX Creator API Key, use services such as WAX Trade, and more. You can activate 2FA with the help of your mobile device and the Google Authenticator app; however, it is recommended that you use a different app (this could also be an extension for your desktop browser, such as Authenticator - highly recommended!) that shows your secret as you may need it at times.
Note: Your 2FA
secretisn't needed for this tutorial; however, it can come in handy at times it's required!
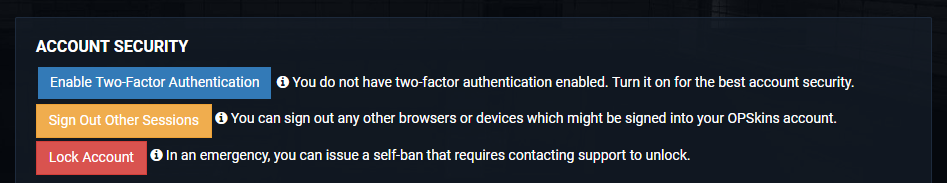
Go to your OPSkins account security page and hit the Enable Two-Factor Authentication button:
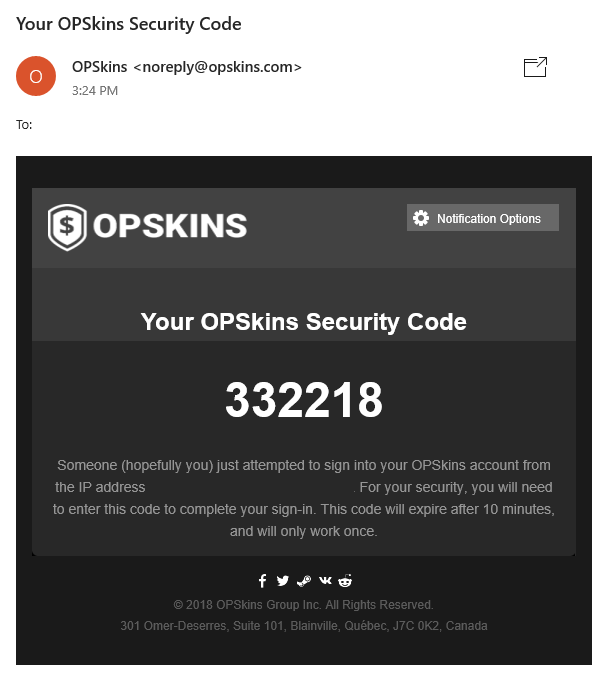
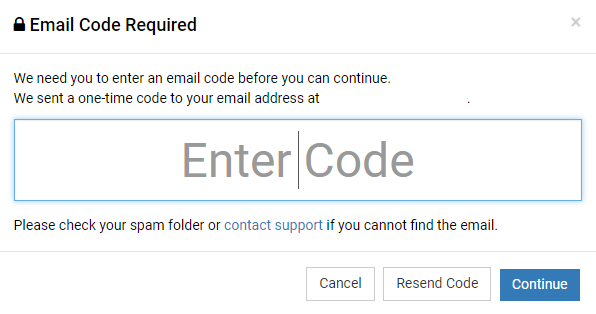
A modal will prompt asking you to enter a one-time code that was sent to your email. Get the code and enter it:
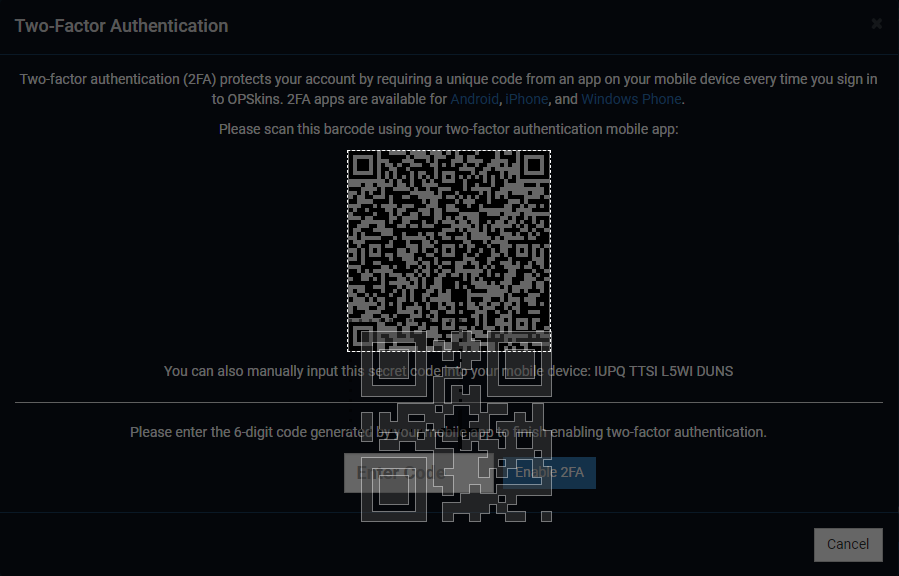
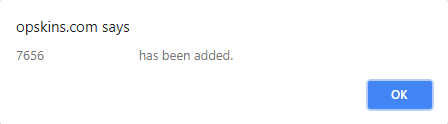
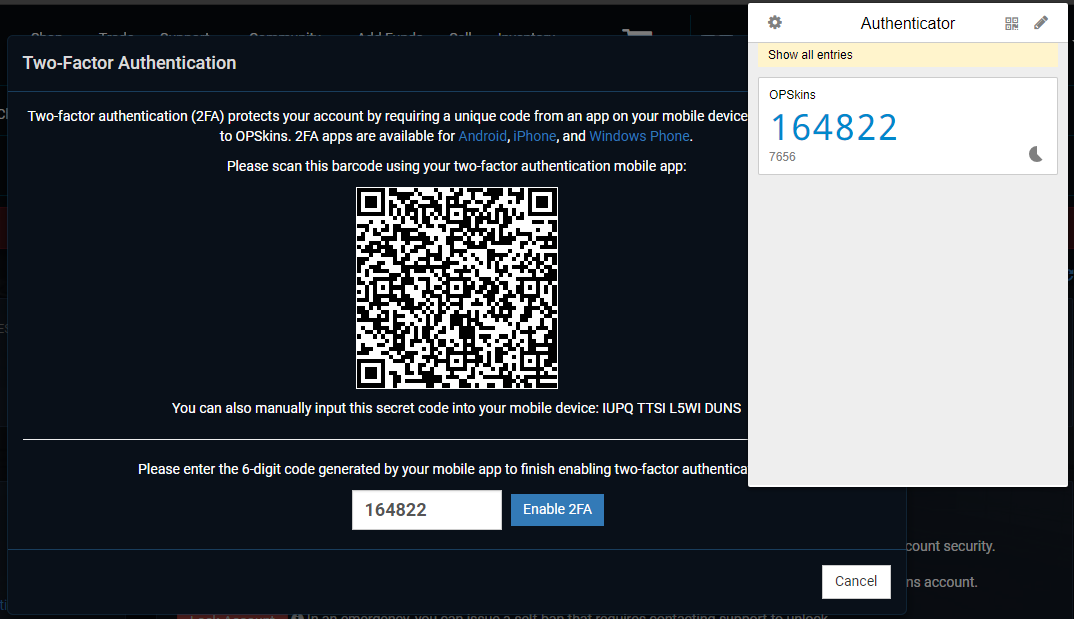
After submitting the one-time code, another modal will prompt. On the Authenticator browser extension (or with the 2FA app/extension of your choice - instructions may vary), click on the Scan QR Code icon located on the top right corner, select the barcode with your cursor by holding down left click on your mouse, and then let go:
If the selection of the barcode was successful, a browser alert should prompt stating that your account has been added:
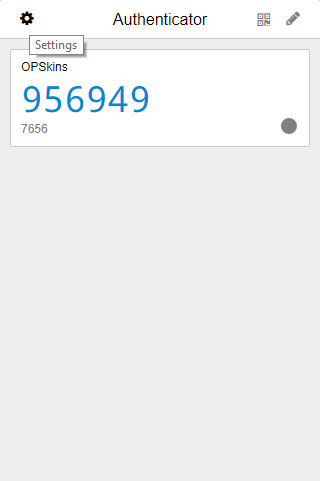
Note: You can alternatively add your account by entering the secret shown on the second modal on Authenticator, this can be done by clicking on the
Editicon - it's located on the top far right corner.
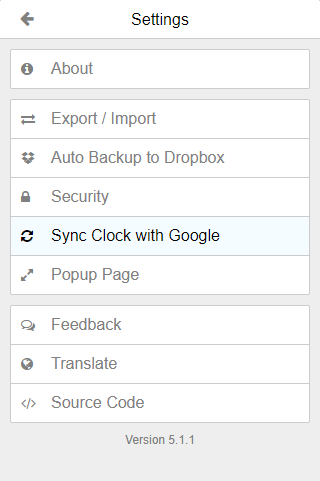
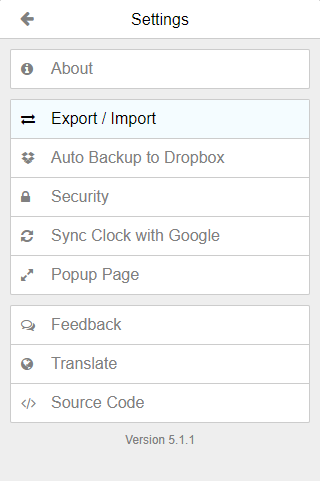
On Authenticator, click on the Settings icon located on the top left corner and hit Sync Clock with Google:
Note: This step is vital, the shown two-factor authentication code may be invalid otherwise.
Enter the current valid two-factor authentication code shown on Authenticator:
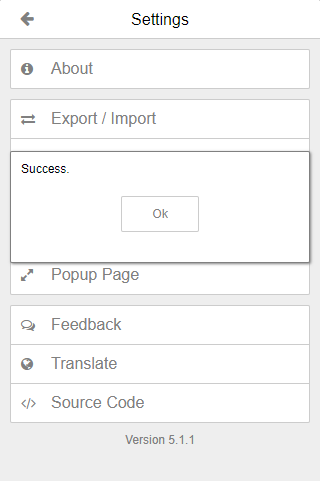
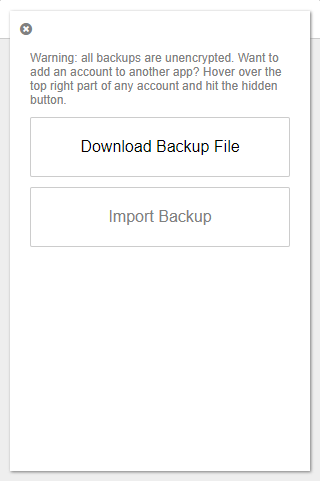
After successfully enabling 2FA for your OPSkins account, you can now obtain your secret from the Authenticator extension! Click on the Settings icon, hit the Export / Import option, and then press the Download Backup File button:
A .json file will begin to download. If you open it you'll see a similar multidimensional JSON Array as to the one below:
{
"3e44a51d4b5cad98c34f5f3658e35c73": {
"account": "76569192284382175",
"counter": 0,
"encrypted": false,
"hash": "3e44a51d4b5cad98c34f5f3658e35c73",
"index": 0,
"issuer": "OPSkins",
"secret": "IUPQTTSIL5WIDUNS",
"type": "totp"
}
}The only value you need from this .json file is secret (in case of the example above, that value is IUPQTTSIL5WIDUNS). Keep your secret in a safe place, and use it to restore your account or for development purposes such as programmatically generating 2FA codes (not required for this tutorial)!
(Optional) If you are unfamiliar with JSON arrays and have more than one account added to Authenticator, you'll see more entires as shown below:
{
"3e44a51d4b5cad98c34f5f3658e35c73": {
"account": "76569192284382175",
"counter": 0,
"encrypted": false,
"hash": "3e44a51d4b5cad98c34f5f3658e35c73",
"index": 0,
"issuer": "OPSkins",
"secret": "IUPQTTSIL5WIDUNS",
"type": "totp"
},
"313b6cb61386cb8f535cd74f2a5ea17c": {
"account": "76561147468942173",
"counter": 0,
"encrypted": false,
"hash": "313b6cb61386cb8f535cd74f2a5ea17c",
"index": 0,
"issuer": "OPSkins",
"secret": "BVXFQ1S7YCDP71J4",
"type": "totp"
}
}Simply find the right entry, make sure the issuer is OPSkins, and get your secret from the array.
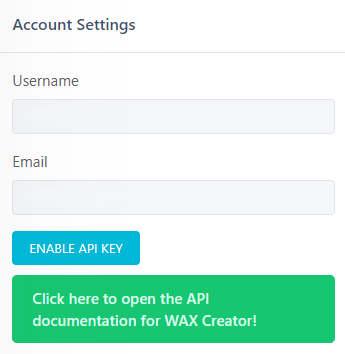
A WAX Creator API Key is required to invoke the WAX Creator API, you should request one!
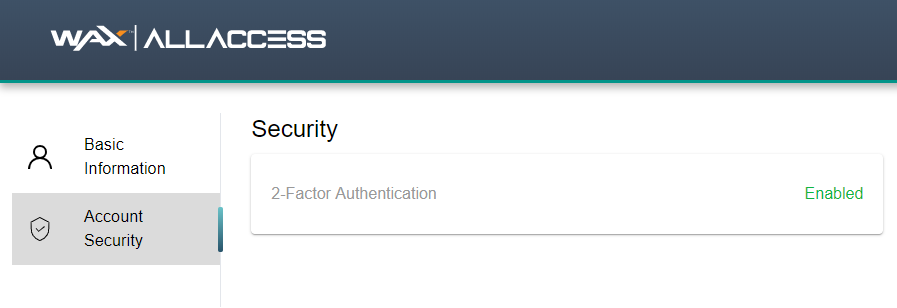
Go to your WAX AllAccess account security page and make sure 2FA is enabled for your account:
Log into the WAX Creator with your WAX AllAccess account:
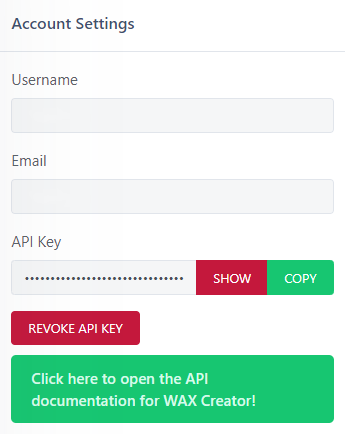
Go to your WAX Creator account page and hit ENABLE API KEY to request a WAX Creator API Key:
Copy your WAX Creator API Key and keep it in hand as you'll need it later!
Warning! If you give your WAX Creator API Key to anyone, they can invoke the WAX Creator API on your behalf without your consent.
Note: If you ever lose your WAX Creator API Key or if you think it has been breached, you can always retrieve it or generate a new one on your WAX Creator account page.
As stated in the Overview at the beginning of this tutorial, the first extension under Recommended will be used; although, you are free to use any other extension!
Download Execute API Call and place it inside your includes directory.
Note: If you skipped the part of the tutorial where the
includesfolder was created, simply create the folder outside of yourpublic_htmldirectory. You should place any file that can be dynamically included from yourpublic_htmldirectory inside theincludesfolder.
Note: If you are integrating the WAX Creator API directly into a production environment and you didn't install an SSL certificate, you will need an FTP client (FileZilla is highly recommended) to upload files to your VPS (click here and read the part addressing the use of an FTP client if you're having trouble connecting). If your website is hosted with a dedicated web hosting provider, you can use their web-based FTP client instead.
Create a .php file, name it index.php, place it inside of your public_html directory, open the file with a text editor (Sublime Text is recommended) and include execute_api_call.php (or you can download the index.php file in this repository and simply place it inside of your public_html folder). Your index.php file should contain the following:
<?php
include_once "../includes/execute_api_call.php";
?>Note: The
index.html/index.phpfile is the entry point of any website.
Calling the WAX Creator API implies that you either send a GET or POST request to https://api-icm.wax.io/api, this will tell the server to perform an action on its end and return a response. The extension of choice handles all this for you.
Note: Calls to
https://api-icm.wax.io/apishould always be executed over theHTTPSprotocol; otherwise, your calls will be redirected and you will receive erroneous responses.https://api-icm.wax.io/apiis the default value for theurlparameter in theExecuteAPICallfunction (loaded from theexecute_api_call.phpfile).
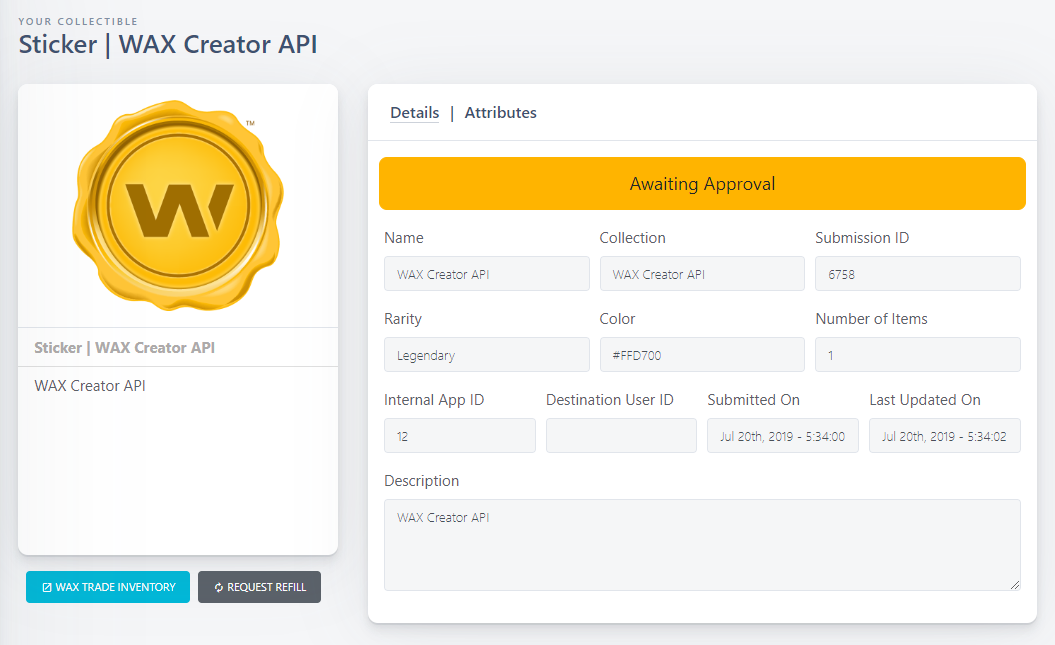
All endpoints of the WAX Creator API can be called using the same base structure. For instance, the create endpoint can be called as followed:
<?php
include_once "../includes/execute_api_call.php"; // include the extension used to invoke the WAX Creator API
$response = ExecuteAPICall("POST", "IItemSubmission/create", array( // method, endpoint, data (optional), url (optional - used to call any other API besides the WAX Creator API)
"api_token" => "Your WAX Creator API Key", // your WAX Creator API Key
"internal_app_id" => 12, // WAX App ID: 12 for WAX Stickers, 14 for WAX Digital Art, or 32 for WAX Collectible Cards
"name" => "WAX Creator API", // item name (simpler/shorter version of `market_name`)
"market_name" => "Sticker | WAX Creator API", // full market name (must be unique per `internal_app_id`)
"image_generic" => "https://static.wax.io/d-img/dynamic-apps/img/php5cfizh-9137032131.png", // item image url (must be a `static.wax.io` URL)
"amount" => 1, // number of items to be generated (copies)
"color" => "#FFD700", // color hex (#AA0000), related with rarity
"rarity_name" => "Legendary", // rarity name (Legendary, Rare, etc).
"collection_name" => "WAX Creator API", // name of the collection this item belongs to
"json_attributes" => '{"markdown_description": "WAX Creator API"}' // description of the item
));
if($response != NULL) // check if the WAX Creator API responded (it may be offline or under maintenance)
{
$response_data = json_decode($response, true); // return an array to easily process the response
echo "success: " . (($response_data['success']) ? ("true") : ("false")) . "<br><br>"; // example on how to access data in the array
var_dump($response_data); // output the response for debugging purposes
}
else
{
echo "The WAX Creator API didn't respond, it may be offline or under maintenance. Please try again later."; // output a message on the user's browser
}
?>As you can see in the screenshots above, the request was successfully received by the WAX Creator API and the collectible has been submitted by verifying on the WAX Creator!
Note: Your
WAX Creator API keyshould be passed asapi_token(as shown above).
Note: You can view all the parameters the
createendpoint supports by clicking here. Documentation for all other endpoints can be found on the same repository.
The data parameter in the ExecuteAPICall function should be structured differently when sending requests to endpoints that use the GET method:
<?php
include_once "../includes/execute_api_call.php"; // include the extension used to invoke the WAX Creator API
$response = ExecuteAPICall("GET", "IItemSubmission/read", "api_token=Your WAX Creator API Key&submission_id=6758"); // api_token - your WAX Creator API Key, submission_id - ID of the submission to retrieve info of | method, endpoint, data (optional), url (optional - used to call any other API besides the WAX Creator API
if($response != NULL) // check if the WAX Creator API responded (it may be offline or under maintenance)
{
$response_data = json_decode($response, true); // return an array to easily process the response
echo "success: " . (($response_data['success']) ? ("true") : ("false")) . "<br><br>"; // example on how to access data in the array
var_dump($response_data); // output the response for debugging purposes
}
else
{
echo "The WAX Creator API didn't respond, it may be offline or under maintenance. Please try again later."; // output a message on the user's browser
}
?>As you can see in the screenshot above, the request was successfully received by the WAX Creator API and information of the previously submitted collectible was returned!
Note: An & separates each parameter when using the
GETmethod (you may have seen this in an URL of a website).
When you receive an error, it may typically look like this:
{
"success": false,
"error":" The amount must be an integer."
}See the API Documentation for the WAX Creator to view all the other interfaces/endpoints you can call in the same manner as the create & read endpoint (as shown above).
If you are building a dApp, a website or a game using the WAX Creator, you can make use of other WAX services to power up your application:
- OAuth Implementation - Allows you to add a 'Login via WAX' button in your application and interact with the user's account using WAX Trade and OPSkins APIs.
- WAX Trade API - May be used to retrieve a user's inventory, manage trade offers, see meta-data of WAX NFTs, and much more.
- OPSkins API - May be used to purchase or sell items on OPSkins, check lowest prices of items, handle cashouts, and much more.