This tutorial walks you through using the Cloud Functions minimal instances feature to mitigate cold starts.
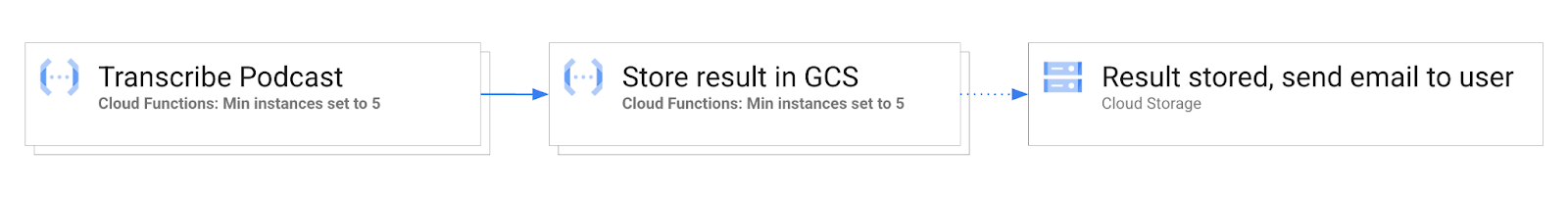
Let’s take a deeper look at min instances using a real-world use case: transcribing a podcast. The demo application takes a "recorded" podcast, transcribes the "audio", writes the text into a Cloud Storage bucket, and then emails a link to the transcribed file.
The recorded podcast is just a text file in order to keep the code simple.
This tutorial also aims to highlight the end-to-end latency differences between running functions with and without the min instances configuration set.
This tutorial assumes you have access to the Google Cloud Platform. You'll also need to clone this repository and use it as your working directory.
git clone https://github.com/kelseyhightower/cloud-functions-min-instances-tutorial.git
cd cloud-functions-min-instances-tutorial
In this approach, we use Cloud Functions and Google Cloud Workflows to chain together three individual cloud functions. The first function (transcribe), transcribes the podcast, the second function (store-transcription) consumes the result of the first function in the workflow and stores it in Cloud Storage , and the third function (send-email), is triggered by Cloud Storage after the transcribed file is writen, and sends an email to the user to inform them that the workflow is complete.
This is the function which takes in an audio podcast and transcribes it into a text file.
PROJECT_ID=$(gcloud config get-value core/project)
Create the transcribe-function IAM service account:
TRANSCRIBE_SERVICE_ACCOUNT_EMAIL="transcribe-function@${PROJECT_ID}.iam.gserviceaccount.com"
gcloud iam service-accounts create transcribe-function
Deploy the transcribe function:
gcloud functions deploy transcribe \
--allow-unauthenticated \
--entry-point Transcribe \
--runtime go113 \
--trigger-http \
--service-account ${TRANSCRIBE_SERVICE_ACCOUNT_EMAIL} \
--source transcribe
Post the podcast.wav file to the transcribe function using curl:
TRANSCRIBE_URL=$(gcloud functions describe transcribe \
--format='value(httpsTrigger.url)')
curl -X POST ${TRANSCRIBE_URL} \
-o podcast.txt \
--data-binary @podcast.wav
Results
Review the contents of the returned podcast.txt file:
cat podcast.txt
What's up YouTube? I'm Kelsey and welcome to my channel. Before we dive in please be sure to smash that like button and subscribe so you don't miss future videos.
This is the function which writes the transcribed podcast obtained from the transcribe function into a cloud storage bucket. Once the file is stored in cloud storage, an event is fired to invoke a function which sends an email to the user.
PROJECT_ID=$(gcloud config get-value project)
Create the store-transcription-function IAM service account:
STORE_TRANSCRIPTION_SERVICE_ACCOUNT_EMAIL="store-transcription-function@${PROJECT_ID}.iam.gserviceaccount.com"
gcloud iam service-accounts create store-transcription-function
Create a storage bucket to hold text files:
TRANSCRIPTION_UPLOAD_BUCKET_NAME="${PROJECT_ID}-transcriptions"
gsutil mb gs://${TRANSCRIPTION_UPLOAD_BUCKET_NAME}
gsutil iam ch \
serviceAccount:${STORE_TRANSCRIPTION_SERVICE_ACCOUNT_EMAIL}:objectAdmin \
gs://${TRANSCRIPTION_UPLOAD_BUCKET_NAME}
Deploy the store-transcription function:
gcloud functions deploy store-transcription \
--allow-unauthenticated \
--entry-point StoreTranscription \
--runtime go113 \
--trigger-http \
--service-account ${STORE_TRANSCRIPTION_SERVICE_ACCOUNT_EMAIL} \
--set-env-vars="TRANSCRIPTION_UPLOAD_BUCKET_NAME=${TRANSCRIPTION_UPLOAD_BUCKET_NAME}" \
--source store-transcription
List the files in the transcription upload bucket:
gsutil ls gs://${TRANSCRIPTION_UPLOAD_BUCKET_NAME}
At this point the storage bucket should be empty.
Post the podcast.txt file to the store-transcription function using curl:
STORE_TRANSCRIPTION_URL=$(gcloud functions describe store-transcription \
--format='value(httpsTrigger.url)')
curl -X POST ${STORE_TRANSCRIPTION_URL} \
--data-binary @podcast.txt
List the files in the transcription upload bucket:
gsutil ls gs://${TRANSCRIPTION_UPLOAD_BUCKET_NAME}
Output
gs://hightowerlabs-transcriptions/podcast.txt
At this point we have verified both the transcribe and store-transcription functions are working.
This is a function which sends an email to a user notifying the user that the transcription of the podcast has been completed.
PROJECT_ID=$(gcloud config get-value project)
Create the sendemail-function IAM service account:
SEND_EMAIL_FUNCTION_SERVICE_ACCOUNT_EMAIL="sendemail-function@${PROJECT_ID}.iam.gserviceaccount.com"
gcloud iam service-accounts create sendemail-function
Deploy the send-email function:
gcloud functions deploy send-email \
--allow-unauthenticated \
--entry-point SendEmail \
--runtime go113 \
--trigger-resource ${TRANSCRIPTION_UPLOAD_BUCKET_NAME} \
--trigger-event google.storage.object.finalize \
--service-account ${SEND_EMAIL_FUNCTION_SERVICE_ACCOUNT_EMAIL} \
--source send-email
STORE_TRANSCRIPTION_URL=$(gcloud functions describe store-transcription \
--format='value(httpsTrigger.url)')
Post the podcast.txt file to the store-transcription function using curl:
curl -X POST ${STORE_TRANSCRIPTION_URL} \
--data-binary @podcast.txt
Review the send-email function logs:
gcloud functions logs read send-email
Output
LEVEL NAME EXECUTION_ID TIME_UTC LOG
D send-email lhbh4r703djk 2021-07-14 17:17:32.665 Function execution took 3006 ms, finished with status: 'ok'
send-email lhbh4r703djk 2021-07-14 17:17:32.664 Email sent successfully
send-email lhbh4r703djk 2021-07-14 17:17:29.663 Sending email...
send-email lhbh4r703djk 2021-07-14 17:17:29.663 Processing send email request
D send-email lhbh4r703djk 2021-07-14 17:17:29.661 Function execution started
Notice the timestamps which help you track the functions end-to-end processing time.
In this section you will create a Cloud Workflow to automate the execution of the podcast transcription pipeline.
You can review the
workflow.yamlfile to see the details of the pipeline.
Deploy the transcribe workflow:
gcloud workflows deploy transcribe \
--source workflow.yaml
Execute the transcribe workflow:
gcloud workflows run transcribe
Review each of the function logs to see the end to end execution of the pipeline:
gcloud functions logs read transcribe
LEVEL NAME EXECUTION_ID TIME_UTC LOG
D transcribe 6k258ardszq7 2021-08-13 06:26:05.026 Function execution took 6737 ms, finished with status code: 200
D transcribe 6k258ardszq7 2021-08-13 06:25:58.290 Function execution started
gcloud functions logs read store-transcription
LEVEL NAME EXECUTION_ID TIME_UTC LOG
D store-transcription kunzo4g724ui 2021-08-13 06:26:08.075 Function execution took 2383 ms, finished with status code: 200
D store-transcription kunzo4g724ui 2021-08-13 06:26:05.692 Function execution started
gcloud functions logs read send-email
Output
LEVEL NAME EXECUTION_ID TIME_UTC LOG
D send-email e0sdnt52vlcf 2021-08-13 06:26:22.532 Function execution took 3013 ms, finished with status: 'ok'
send-email e0sdnt52vlcf 2021-08-13 06:26:22.529 Email sent successfully
send-email e0sdnt52vlcf 2021-08-13 06:26:19.528 Sending email...
Review the start and end timestamps of the entire transcription pipeline. The total runtime of Approach 1 took 17 seconds to complete.
Each function is hardcoded with a 2 second delay during function initialization. When combined with the Cloud Functions average cold start time, almost half the time is spend starting each function.
In this approach, we follow all the same steps as in Approach 1, with the addition of setting the --min-instances flag for each function transcribe workflow.
Redeploy the transcribe function with the --min-instances flag set:
gcloud beta functions deploy transcribe \
--allow-unauthenticated \
--entry-point Transcribe \
--runtime go113 \
--trigger-http \
--service-account ${TRANSCRIBE_SERVICE_ACCOUNT_EMAIL} \
--source transcribe \
--min-instances 5
Redeploy the store-transcription function with the --min-instances flag set:
gcloud beta functions deploy store-transcription \
--allow-unauthenticated \
--entry-point StoreTranscription \
--runtime go113 \
--trigger-http \
--service-account ${STORE_TRANSCRIPTION_SERVICE_ACCOUNT_EMAIL} \
--set-env-vars="TRANSCRIPTION_UPLOAD_BUCKET_NAME=${TRANSCRIPTION_UPLOAD_BUCKET_NAME}" \
--source store-transcription \
--min-instances 5
Redeploy the send-email function with the --min-instances flag set:
gcloud beta functions deploy send-email \
--allow-unauthenticated \
--entry-point SendEmail \
--runtime go113 \
--trigger-resource ${TRANSCRIPTION_UPLOAD_BUCKET_NAME} \
--trigger-event google.storage.object.finalize \
--service-account ${SEND_EMAIL_FUNCTION_SERVICE_ACCOUNT_EMAIL} \
--source send-email \
--min-instances 5
At this point each function in the transcribe workflow has been redeployed with the --min-instances flag set.
Re-run the transcribe workflow to warm up the functions. This ensures all functions have been initialized and ready to receive requests.
gcloud workflows run transcribe
Run the transcribe workflow again. You should see a significant improvement in the end-to-end runtime of the transcription pipeline.
gcloud workflows run transcribe
Review the function logs:
gcloud functions logs read transcribe
Output
LEVEL NAME EXECUTION_ID TIME_UTC LOG
D transcribe yu0magytxdyb 2021-08-13 06:26:17.843 Function execution took 5005 ms, finished with status code: 200
D transcribe yu0magytxdyb 2021-08-13 06:26:12.839 Function execution started
gcloud functions logs read store-transcription
Output
LEVEL NAME EXECUTION_ID TIME_UTC LOG
D store-transcription ci24ipm9d1c9 2021-08-13 06:26:18.345 Function execution took 397 ms, finished with status code: 200
D store-transcription ci24ipm9d1c9 2021-08-13 06:26:17.948 Function execution started
gcloud functions logs read send-email
Output
LEVEL NAME EXECUTION_ID TIME_UTC LOG
D send-email f0gtxaktn5ce 2021-08-13 06:26:22.527 Function execution took 3009 ms, finished with status: 'ok'
send-email f0gtxaktn5ce 2021-08-13 06:26:22.526 Email sent successfully
send-email f0gtxaktn5ce 2021-08-13 06:26:19.525 Sending email...
Now we can compare the total runtime between Approach 1 and 2. The total runtime of Approach 2 is 6 seconds, which is 11 seconds faster than Approach 1, which does not leverage the min instances feature. Approach 2 avoids cold starts and the additional function initialization overhead, and should provide a more constant runtime experience.