Configure the keys in the enviroment variables.
To get those variables:
-
Go to your project in firebase.
-
Then select the configuration icon:
-
Then select "configuracion del proyecto":
-
Scroll and take the keys from this object:
const firebaseConfig = { apiKey: "***********", authDomain: "***********", projectId: "***********", storageBucket: "***********", messagingSenderId: "***********", appId: "***********", measurementId: "***********", };
-
Paste them like this in the .env (create a file called .env):
FIREBASE_API_KEY="*******************" FIREBASE_AUTHDOMAIN="*******************" FIREBASE_PROJECTID="*******************" FIREBASE_STORAGEBUCKET="*******************" FIREBASE_MESSAGINGSENDERID="*******************" FIREBASE_APPID="*******************" FIREBASE_MEASUREMENTID="*******************"
-
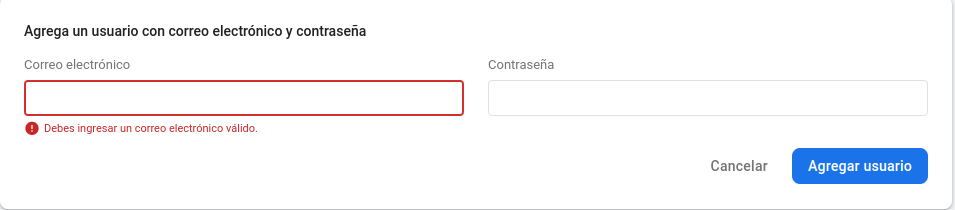
Create a user in the authentication field of firebase. This is to ignore the rules you have created.
6.1. Go to the authentication menu:
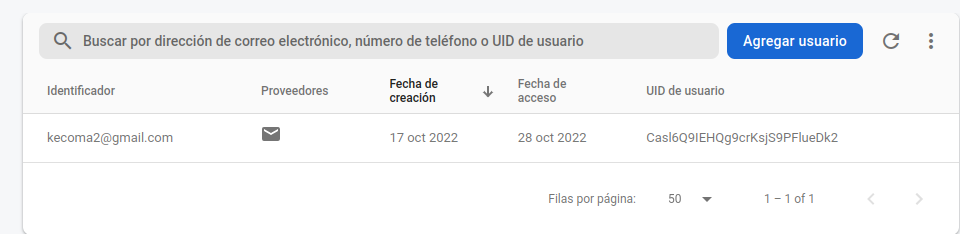
6.2. Click on add user and put an email and a password:
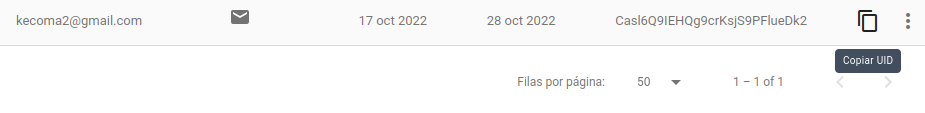
6.3. Take the userID.
6.4 Go to the storage, to the rules section and add the following rule (Do not forget to remove the rule after moving your files!!):
match /{allPaths=**} { allow read, write: if request.auth.uid == "<USER_ID_COPIED>"; }6.5. Add the user and the password into the .env:
FIREBASE_AUTH_EMAIL="*******************" FIREBASE_AUTH_PASSWORD="*******************"
Actions are simple. You just put the route from which you want to move something and the new route.
The actions are set in the actions.json file
There are several types of actions:
-
simple-move: Simply moves all the content from the takeFrom route and puts it in the moveTo route.
[ { "type": "simple-move", "takeFrom": "/test1", "moveTo": "/moveTest" }, ] -
firestore-update-route: Taking into account the collection, it takes all the elements in that collection, then it checks the routeField in the firestore element and finally it moves the file in the storage to the moveTo route while it updates the entry in the firestore object. You can add extra folders into de route by adding params (optional). Each param needs a name (name of the field in the firestore element) and a representation (string representing that field in the moveTo string). If you want to use this option, the same rule added to the storage must be added to the firestore.
[ { "type": "firestore-update-route", "collection": "collection_test", "routeField": "img", "params": [ {"name": "id", "representation": "{id}"} ], "moveTo": "/moveTest/{id}" }, { "type": "firestore-update-route", "collection": "collection_test", "routeField": "img", "moveTo": "/moveTest/" // Without params allowed }, ] -
firestore-update-route-name: The same as firestore-update-route but it changes the name of the file. The new name is common and it should be represented in the newName field (extension of the file is not changed). THE CODE ASSUMES THAT THERE ARE NOT '.' IN THE NAME. For example:
- Valid names: adjnajajnjad.gif, aidon42aiu12na.png.
- Invalid names: 123.23.gif, adicad.gadifa.png
[ { "type": "firestore-update-route-name", "collection": "collection_test", "routeField": "img", "params": [ {"name": "id", "representation": "{id}"} ], "moveTo": "/moveTest/{id}", "newName": "avatar" }, ] -
firestore-update-url: It updates the URL stored in a field in the firestore DB document. It looks for the object with a similar name to the objectName in the objectLocation. It updates the field in the collection documents. The objectLocation can be custom by using params.
{ "type": "firestore-update-url", "collection": "collection_test", "field": "avatarURL", "params": [ { "name": "id", "representation": "{id}" } ], "objectLocation": "/moveTest/{id}", "objectName": "avatar" } -
firestore-update-subcollection-file: It goes to the parentCollection and looks for the collection subcollection. Then in that subcollection it looks for the objectLocation by accessing the objectLocationField. With the use of params the objectLocation can be generic (the information used in the params is the one of the father).
{ "type": "firestore-update-subcollection-file", "parentCollection": "records_test", "collection": "files", "field": "file", "params": [ { "name": "id", "representation": "{pid}" } ], "objectLocation": "test1/{pid}", "objectLocationField": "file" }
Actions example:
[
{
"type": "simple-move",
"takeFrom": "/test1",
"moveTo": "/moveTest"
},
{
"type": "firestore-update-route",
"collection": "collection_test",
"routeField": "img",
"params": [
{"name": "id", "representation": "{id}"}
],
"moveTo": "/moveTest/{id}"
},
{
"type": "firestore-update-route",
"collection": "collection_test",
"routeField": "img",
"moveTo": "/moveTest/" // Without params allowed
},
,
{
"type": "firestore-update-route-name",
"collection": "collection_test",
"routeField": "img",
"params": [
{"name": "id", "representation": "{id}"}
],
"moveTo": "/moveTest/{id}",
"newName": "avatar"
},
{
"type": "firestore-update-url",
"collection": "collection_test",
"field": "avatarURL",
"params": [
{ "name": "id", "representation": "{id}" }
],
"objectLocation": "/moveTest/{id}",
"objectName": "avatar"
},
{
"type": "firestore-update-subcollection-file",
"parentCollection": "records_test",
"collection": "files",
"field": "file",
"params": [
{ "name": "id", "representation": "{pid}" },
{ "name": "id", "representation": "{newName}" }
],
"objectLocation": "test1/{pid}",
"objectLocationField": "file"
}
]The action is the object which is within a list, you can put as many actions as you want in the list, so that in one execution you move everything you want. DO NOT PUT ACTIONS OF DIFFERENT TYPES IN THE LIST, there may be issues.
node app