Egg Plan Transformer (eggplant)
This project introduces a query plan expression cost-based rewrite application, the Egg Plan Transformer (eggplant), that attempts to locate cardinality issues in execution plans, and provide improved query plan expressions. The Egg Plan Transformer is built using the Egg (E-graphs are Good) library that implements equality saturation to discover optimal rewrites. The optimizations implemented by eggplant are relatively simple, based on a small set of rewrite rules implemented with cardinality-driven cost functions. The rules focus on join algorithm, join ordering, expression tree shape, and access method.
The use-case for this project is as part of a query performance tuning workflow to automate the analysis of execution plans. The query plan graph would be translated into a query plan expression and processed by eggplant. Eggplant applies the rewrite rules with input metadata to find possible improvements on the plan. Commercial database management system query optimizers generate high-quality plans for most SQL statements given accurate statistics. The query rules in eggplant are similar to ones that are already better implemented in SQL Server for general cases, leaving no meaningful optimizations to be further applied. However, since eggplant will have the actual cardinalities it can improve plans where the DBMS choses suboptimal operators based on incorrect column statistics. The rewrites correspond to query hints that can be applied to the the original SQL statement to instruct the DBMS to build a potentially better plan.
The Egg Plan Transformer (eggplant) is implemented as a Rust console application that uses the Egg expression rewriter library. The application accepts a JSON input file that contains a query execution plan expression and metadata about the tables referenced in that expression. Eggplant uses the facilities provided by the Egg library to construct an e-graph and attach the query statistics metadata to e-nodes. There is also a cost function that evaluates various expression rewrite candidates to discover potentially beneficial transformations. The lowest cost equivalent expression is printed as output.
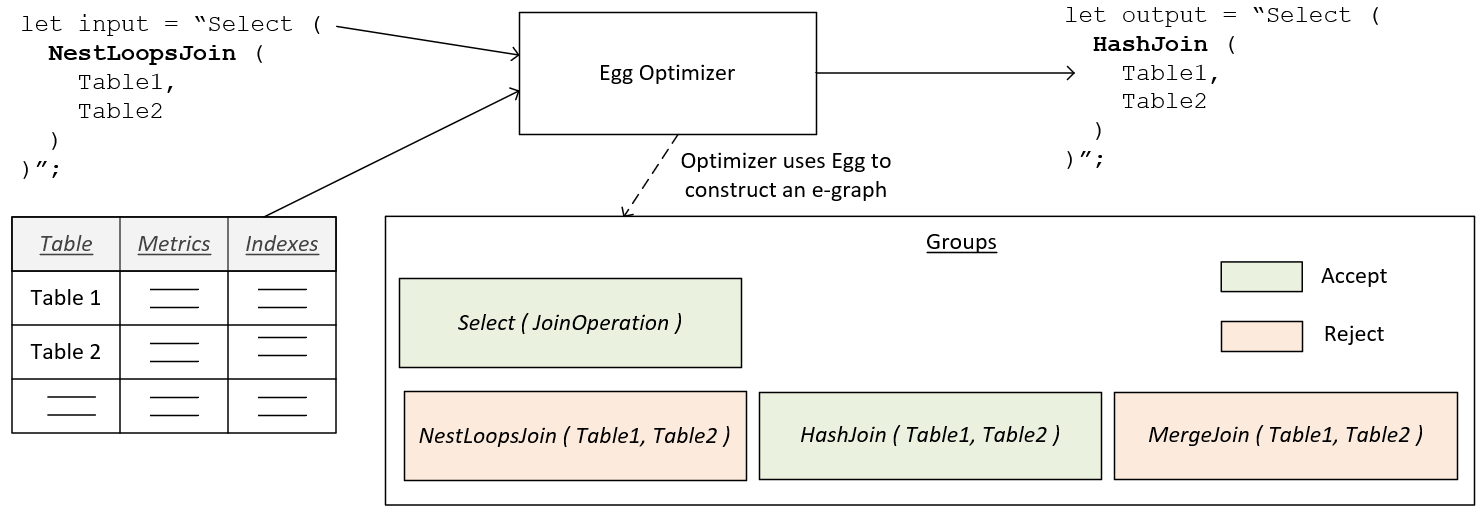
It is important to consider the purpose of the eggplant tool when assessing its design. Eggplant is a component that is intended to be in the inner-core of a query performance tuning workflow, where the input is based on query plans generated from commercial database systems. These database systems have extensive optimization rules, data distribution metrics, and other specialized algorithms. Eggplant is not trying to add new rules that the DBMS is missing. Instead its advantage is that the input metrics contain the actual metrics collected from running the query, not based on estimates from data distribution statistics. This allows eggplant to use the same rules as the DBMS but to produce a different, and potentially better plan, since differences between actual and estimated cardinalities are a common source of suboptimal query plans. The following diagram provides a high-level illustration of eggplant inputs and outputs.
For additional information please take a look at the Final Report and Final Presentation.
For information on the Egg library please take a look at https://egraphs-good.github.io.