UNet is a popular architecture in computer vision for image segmentation tasks. Its name comes from its U-shaped architecture, which consists of a contracting path (encoder) and an expansive path (decoder). UNet is widely used because it effectively captures both local and global information, making it suitable for tasks like medical image segmentation and object detection. Its symmetric design helps in preserving spatial information and addressing the challenge of class imbalance in segmentation tasks
UNet is commonly used for medical image analysis due to several reasons:
UNet has demonstrated high performance in medical image segmentation tasks. Its architecture allows it to capture intricate details in images, making it suitable for identifying structures or abnormalities in medical images.
Medical image analysis often involves segmenting specific structures or regions of interest within an image. UNet's architecture, with its contracting and expanding paths, is well-suited for semantic segmentation tasks where precise delineation of structures is crucial.
Medical datasets are often limited in size, and UNet performs well with small datasets. Transfer learning and data augmentation techniques can be effectively applied to boost performance even when training data is scarce.
UNet can be adapted to different medical imaging modalities, such as MRI, CT scans, or X-rays. Its flexibility makes it applicable to various medical image analysis scenarios.
The skip connections in UNet enable the model to retain high-resolution details during the downsampling and upsampling processes. This helps in preserving spatial information, which is essential in medical imaging.
There are numerous open-source implementations of UNet available, making it easier for researchers and practitioners in the medical field to access and implement the architecture in their work.
Deploying a UNet model involves several steps. Here's a general guide:
Train and Save the Model:
Save the trained model weights and architecture to a file. Common formats include TensorFlow's SavedModel format or the HDF5 format.
Decide where you want to deploy your model. Options include cloud platforms like AWS, Azure, or Google Cloud, or on-premises servers.
Create an inference pipeline to process input data and obtain predictions from your UNet model. This may involve pre-processing steps to prepare input data for the model.
Choose a deployment framework suitable for your chosen platform. TensorFlow Serving, ONNX Runtime, and Flask are popular choices for deployment.
Containerize your model using Docker. This allows you to encapsulate your model, its dependencies, and the inference pipeline into a container that can be easily deployed and run consistently across different environments.
If using a cloud platform, follow the platform-specific instructions for deploying machine learning models. Many cloud providers offer specialized services for deploying and serving machine learning models, such as AWS SageMaker, Azure Machine Learning, or Google AI Platform.
Expose your model through a REST API if you want to make predictions over HTTP. Flask or FastAPI are commonly used for creating API endpoints.
Implement monitoring to keep track of the model's performance and usage. Consider scaling solutions based on your deployment requirements, such as load balancing for high demand. Security Considerations:
Implement security measures to protect your deployed model, especially if it involves handling sensitive medical data. Use authentication and encryption where necessary.
Thoroughly test the deployed model to ensure that it works as expected in the production environment. Remember that deployment specifics may vary depending on the platform and tools you choose. Always refer to the documentation provided by the deployment framework and platform for the most accurate and up-to-date instructions.
- Architecture
- Results
The block diagram of the UNET architecture taken from the original paper.
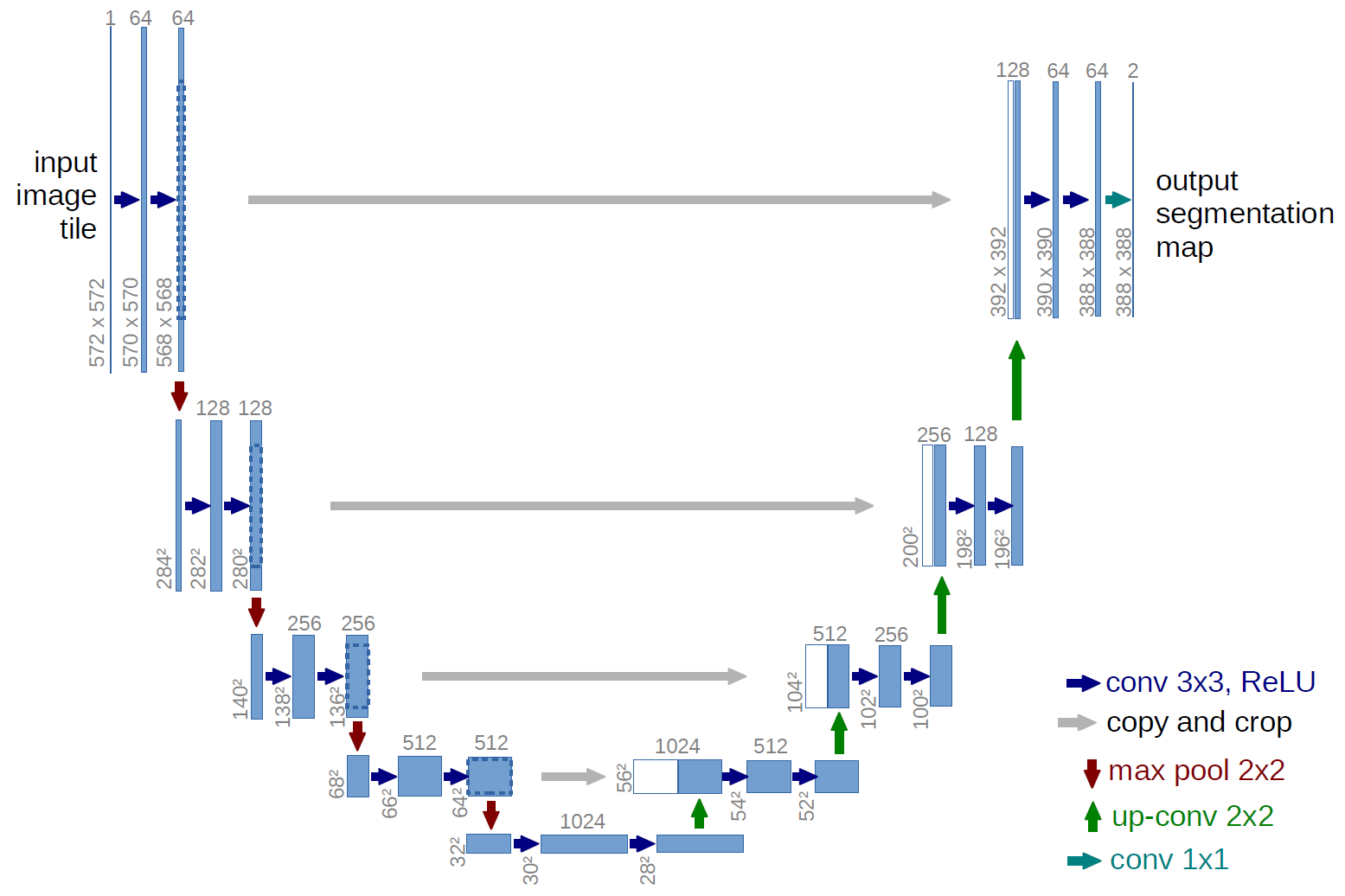 |
|---|
| U-Net Architecture |
The install following libraries: tensorflow glop Panda Numpy sk-learn
-
Clone this repository to your local machine.
git clone https://github.com/kartikshastrakar/UNET cd UNET -
Create a Python virtual environment (optional but recommended):
python -m venv venv source venv/bin/activate On Windows, use: venv\Scripts\activate ``
-
Run python Scripts
python train.py python model.py
The images below contains:
- Input image
- Ground truth
- Predicted mask
 |
|---|
 |
 |
 |