Data version Control (DVC) is a version control system that tracks large data sets and machine learning models with the aim to make ML models shareable and reproducible.
More information about DVC can be found on the official webpage https://dvc.org/
This repository shows you how to integrate dvc in your projects and hopefully you will not need to worry about where to store your data sets and models because github does not support more than 100mb.
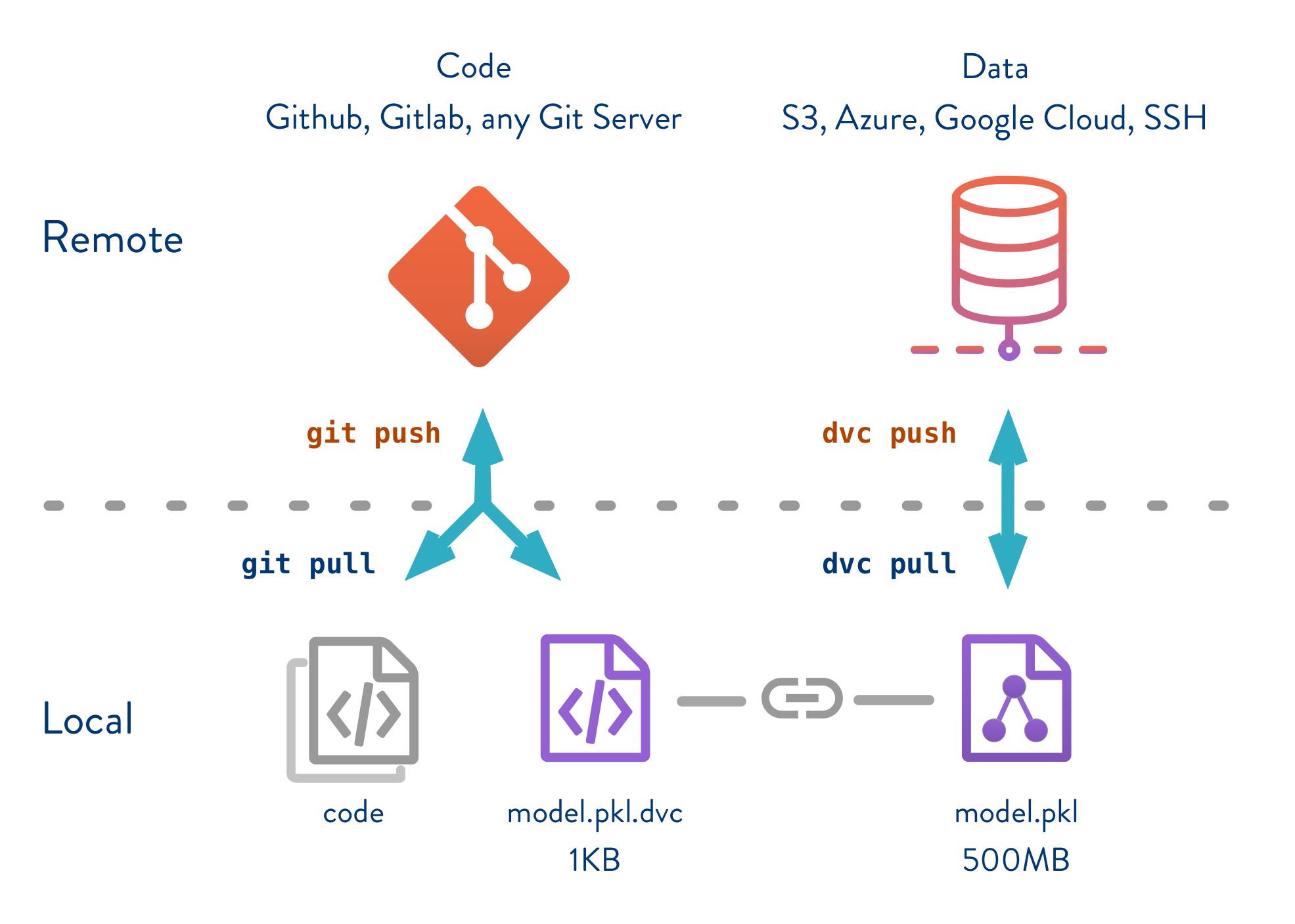 source: image taken from dvc
source: image taken from dvc
In this guide we are going to focus on dataset/model versioning in simple steps, reproducibility will be released later in this guide, so stay tunned.
First clone this or any other repository, because dvc works on top of git repositories.
git clone https://github.com/jwilliamn/dvcML.git
cd dvcMLIf you cloned this repository please remove .dvc/ and SQuAD.dvc to reproduce the following steps.
Once we have our repo, we install DVC. It is a good practice to install in an isolated environment i.e. virtualenv or conda.
pip install dvcor from a requirements file
pip install -r requirements.txtOn the fresh repository, we initialize as follows.
dvc init
git commit -m "DVC initialized"You can start working right away in its local setup, however to share data and models the way you share code using github, we need to setup a remote storage. You can find the configuration for several storage types here.
This guide shows a configuration with azure blob storage.
First we need to install dvc azure dependencies (If you installed from requirements.txt in step 1, skip the following line.)
pip install "dvc[azure]"dvc remote add myazure azure://my-container-name/path
dvc config core.remote myazure
dvc remote modify myazure connection_string my-connection-string --local
myazureis the name of the remote storage,my-container-nameis the name of the azure blob container i.e. dvcData. In order to get a connection with azure we need a connection string that should be placed instead ofmy-connection-stringwith the--localoption to write in a non traceable config file.
First we have to download some data to our repository. Here I am downloading SQuAD V1 data set (to train a question answering model, more info here)
mkdir SQuAD
wget https://rajpurkar.github.io/SQuAD-explorer/dataset/train-v1.1.json -P SQuAD/
wget https://rajpurkar.github.io/SQuAD-explorer/dataset/dev-v1.1.json -P SQuAD/Now we run the dvc add command to take the data under DVC control.
dvc add SQuAD/or
dvc add -f path/to/SQuAD.dvc SQuAD/This creates a data.dvc file that can be commited to track versions of the data. It also includes the data directory in the git ignore file.
git add SQuAD.dvc
git commit -m "data added to DVC"Now that DVC manages the data, we can push to our configured remote storage and share with the team.
dvc pushIf you make important changes to the data it is useful to run first dvc commit before dvc push.
dvc commit
dvc pushTo save changes of the dvc files and code we run the normal git commands.
git add .
git commit -m "dvc files changed"
git push origin masterIf you clone a repository make sure you have the dvc files or configure following steps 1 to 3. Then run the following command.
dvc pullThis will retrieve all data under DVC control. If you want just one part of the data add the dvc file corresponding to that data.
dvc pull path/to/SQuAD.dvc