- 바이트 단위 입력 스트림 최상위 추상 클래스
- 많은 추상 메서드가 선언되어 있고 이를 하위 스트림이 상속받아 구현함.
- 주요 하위 클래스
| 스트림 클래스 |
설명 |
| FileInputStream |
파일에서 바이트 단위로 자료를 읽습니다. |
| ByteArrayInputStream |
byte 배열 메모리에서 바이트 단위로 자료를 읽습니다. |
| FilterInputStream |
기반 스트림에서 자료를 읽을 때 추가 기능을 제공하는 보조 스트림의 상위 클래스 |
| 메서드 |
설명 |
| int read() |
입력 스트림으로부터 한 바이트의 자료를 읽습니다. 읽은 자료의 바이트 수를 반환합니다. |
| int read(byte b[]) |
입력 스트림으로부터 b[] 크기의 자료를 b[]에 읽습니다. 읽은 자료의 바이트 수를 반환합니다. |
| int read(byte b[], int off, int len) |
입력 스트림으로부터 b[] 크기의 자료를 b[]의 off 변수 위치부터 저장하면 len 만큼 읽습니다. 읽은 자료의 바이트 수를 반환합니다. |
| void close() |
입력 스트림과 연결된 대상 리소스를 닫습니다. |
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException; // FileNotFoundException으로 예외 처리를 하게 되면 FileInputStream의 예외 처리를 또 해야 하기 때문에 상위 클래스인 IOException으로 모두 잡아 준다.
import java.io.IOException;
public class FileInputStreamTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
FileInputStream fis = null;
try {
fis = new FileInputStream("input.txt");
System.out.println((char) fis.read());
System.out.println((char) fis.read());
System.out.println((char) fis.read());
} catch (IOException e) { // FileNotFoundException으로 예외 처리를 하게 되면 FileInputStream의 예외 처리를 또 해야 하기 때문에 상위 클래스인 IOException으로 모두 잡아 준다.
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
fis.close(); // FileInputStream을 닫을 때에도 input.txt 파일이 없다면 error가 나기 때문에 예외 처리를 해야 한다.
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (Exception e1) {
System.out.println(e1);
}
}
System.out.println("end");
// 결과
// A
// B
// C
// end
}
}import java.io.*;
public class FileInputStreamTest2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try (BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream("input.txt")))) { // 한글 깨짐 출력 방지를 위해서 InputStreamReader, BufferedReader 클래스 사용
int i;
while ((i = br.read()) != -1) {
System.out.print((char) i);
}
} catch (IOException e) { // FileNotFoundException으로 예외 처리를 하게 되면 FileInputStream의 예외 처리를 또 해야 하기 때문에 상위 클래스인 IOException으로 모두 잡아 준다.
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println();
System.out.println("end");
// 결과
// ABC hello 123 안녕하세요
// end
}
}import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException; // FileNotFoundException으로 예외 처리를 하게 되면 FileInputStream의 예외 처리를 또 해야 하기 때문에 상위 클래스인 IOException으로 모두 잡아 준다.
import java.io.IOException;
public class FileInputStreamTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
FileInputStream fis = null;
try {
fis = new FileInputStream("input.txt");
System.out.println((char) fis.read());
System.out.println((char) fis.read());
System.out.println((char) fis.read());
} catch (IOException e) { // FileNotFoundException으로 예외 처리를 하게 되면 FileInputStream의 예외 처리를 또 해야 하기 때문에 상위 클래스인 IOException으로 모두 잡아 준다.
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
fis.close(); // FileInputStream을 닫을 때에도 input.txt 파일이 없다면 error가 나기 때문에 예외 처리를 해야 한다.
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (Exception e1) {
System.out.println(e1);
}
}
System.out.println("end");
// 결과
// A
// B
// C
// end
}
}
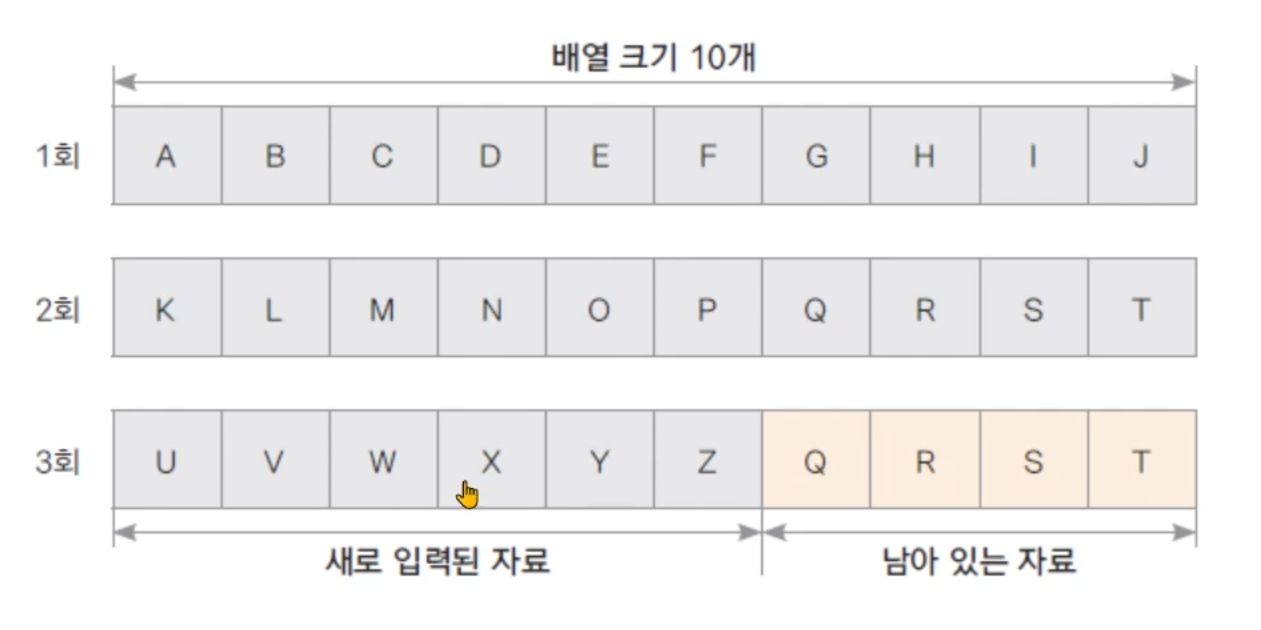
- 파일에서 바이트 배열로 자료 읽기 (배열에 남아 있는 자료가 있을 수 있으매 유의)
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
public class FileInputStreamTest3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int i;
try (FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("input2.txt")) { // try() 안에 I/O Stream을 설정하면 auto close가 되어서 catch나 finally에서 해당 스트림을 close(닫기)를 하지 않아도 된다.
byte[] bytes = new byte[10];
while((i = fis.read(bytes)) != -1){
for(int j = 0; j < i; j++) {
System.out.print((char)bytes[j]);
}
System.out.println(": " + i + "바이트 읽음");
}
} catch (IOException e) { // FileNotFoundException으로 예외 처리를 하게 되면 FileInputStream의 예외 처리를 또 해야 하기 때문에 상위 클래스인 IOException으로 모두 잡아 준다.
e.printStackTrace();
}
// 결과
// ABCDEFGHIJ: 10바이트 읽음
// KLMNOPQRST: 10바이트 읽음
// UVWXYZ: 6바이트 읽음
}
}
- 바이트 단위 출력 스트림 최상위 추상 클래스
- 많은 추상 메서드가 선언되어 있고 이를 하위 스트림이 상속받아 구현함.
- 주요 하위 클래스
| 스트림 클래스 |
설명 |
| FileOutputStream |
파일에서 바이트 단위로 자료를 씁니다. |
| ByteArrayOutputStream |
byte 배열 메모리에서 바이트 단위로 자료를 씁니다. |
| FilterOutputStream |
기반 스트림에서 자료를 쓸 때 추가 기능을 제공하는 보조 스트림의 상위 클래스 |
| 메서드 |
설명 |
| int write() |
한 바이트를 출력합니다. |
| int write(byte b[]) |
b[] 크기의 자료를 출력합니다. |
| int write(byte b[], int off, int len) |
b[] 배열에 있는 자료의 off 위치부터 len 개수만큼 자료를 출력합니다. |
| void flush() |
출력을 위해 잠시 자료가 머무르는 출력 버퍼를 강제로 비워 자료를 출력합니다. |
| void close() |
출력 스트림과 연결된 대상 리소스를 닫습니다. 출력 버퍼가 비워집니다. |
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
public class FileOutputStreamTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try (FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("output.txt")) {
fos.write(65);
fos.write(66);
fos.write(67);
}catch (IOException e) {
System.out.println(e);
}
System.out.println("end");
}
}
- byte[] 배열에 A-Z까지 넣고 배열을 한꺼번에 파일에 쓰기
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
public class FileOutputStreamTest2 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws FileNotFoundException {
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("output2.txt", true); // true로 설정하면 누적해서 입력한다.
try (fos) {
byte[] bytes = new byte[26];
byte data = 65;
for (int i = 0; i < bytes.length; i++) {
bytes[i] = data++;
}
fos.write(bytes);
} catch (IOException e) {
System.out.println(e);
}
System.out.println("end");
}
}
- 출력 버퍼를 비울 때 flush() 메서드를 사용
- close() 메서드 내부에서 flush()가 호출되므로 close() 메서드가 호출되면 출력 버퍼가 비워짐.
