🛠️ Command line tool for machine learning on AWS
awstrainer helps you run machine learning tasks (or any other long-running computations) on AWS. With one simple command, it spins up an AWS instance (from your own account), transfers your code & dataset, starts the training run, syncs all output files back to your computer, and terminates the instance after training has finished. It really shines when you need to quickly launch multiple, long-running jobs in parallel (e.g. for hyperparameter optimization).
-
pip install git+https://github.com/jrieke/awstrainer -
Install the AWS CLI from here and run
aws configureto connect your AWS account (alternatively, you can create a credentials file as described here).
First, you need to create a launch template for your AWS instance. This specifies which instance type should be used, how big the storage is, which packages should be installed, etc. You can either follow the instructions here or create a launch template from an existing instance.
Then, navigate into your project dir and run:
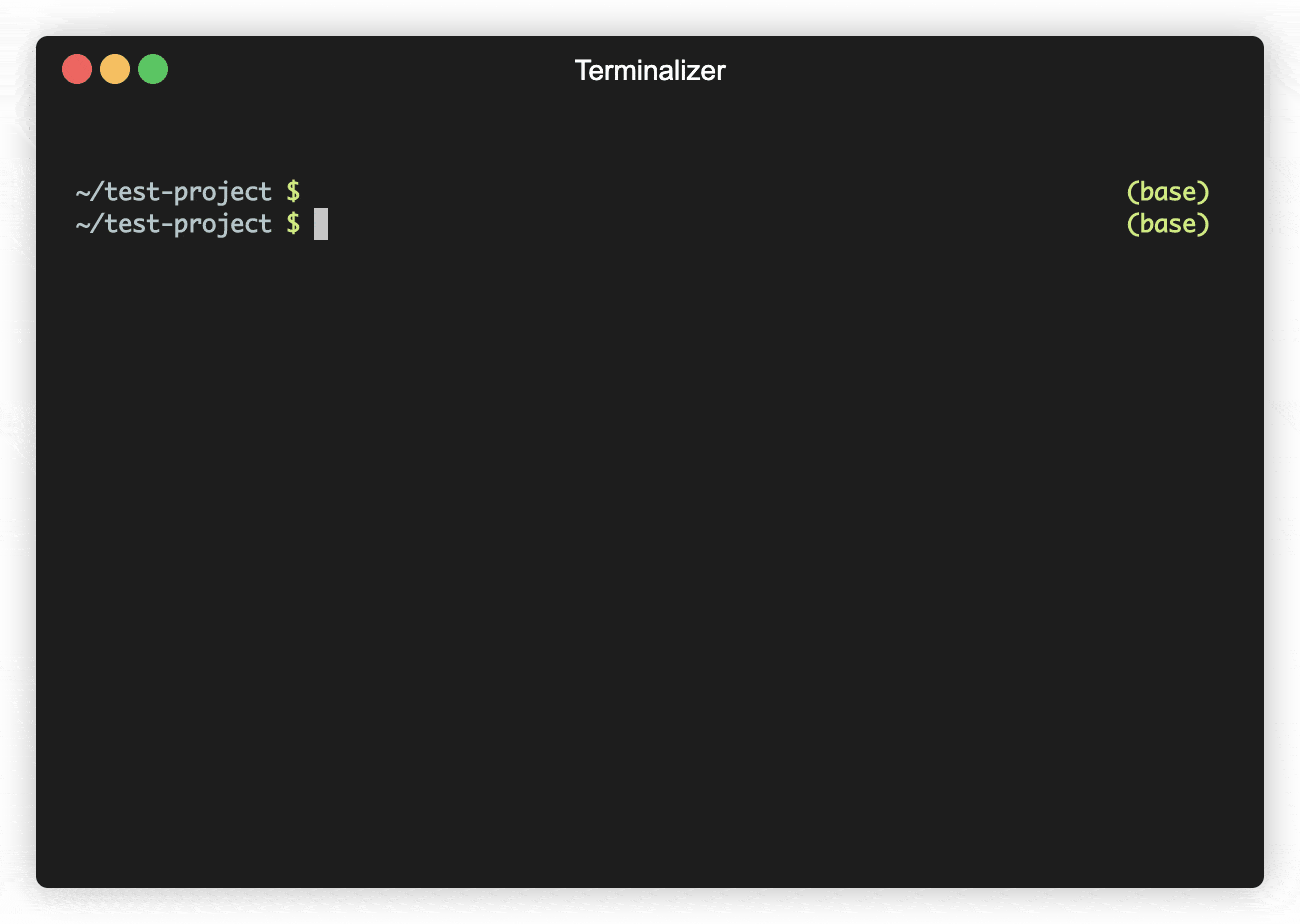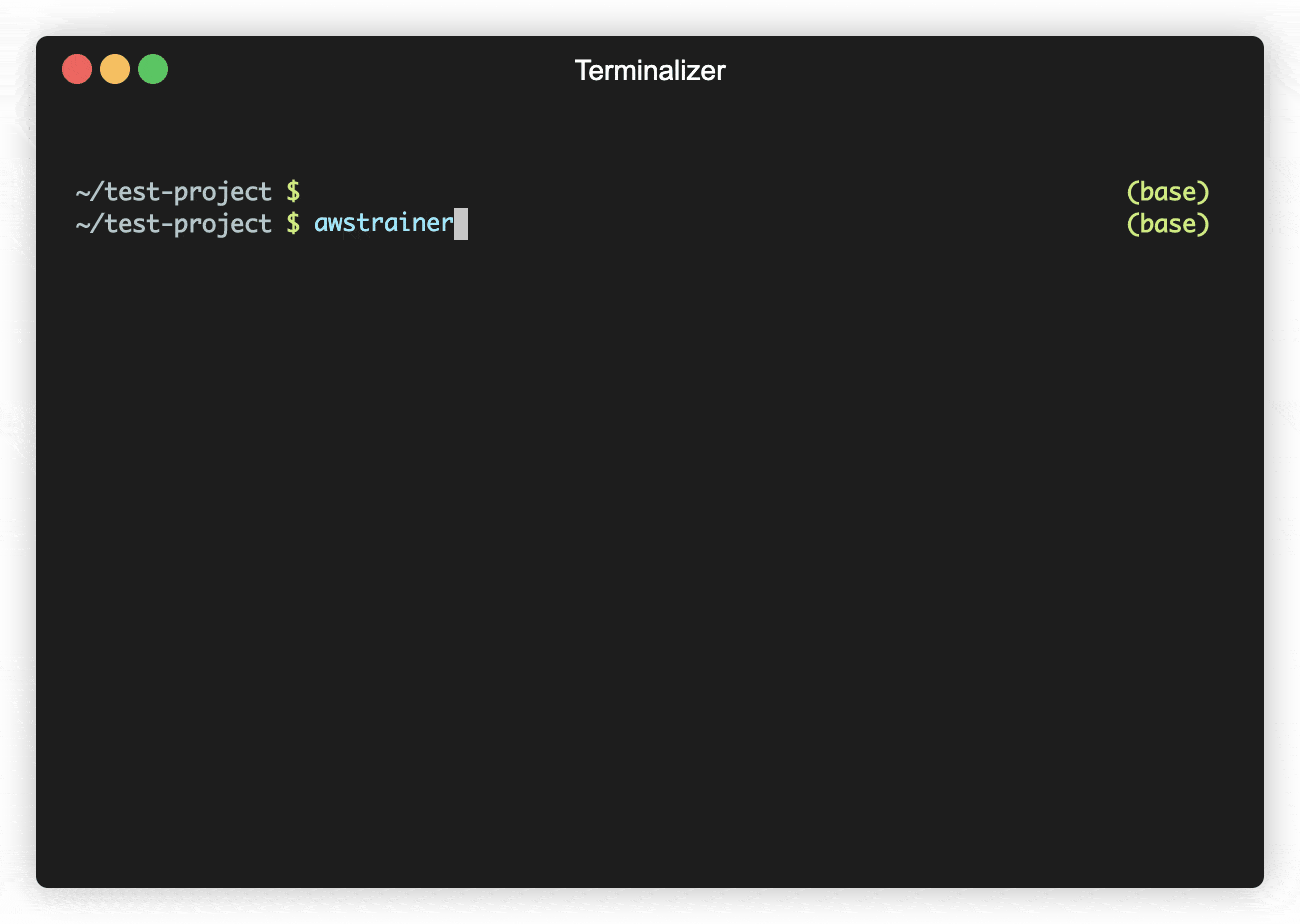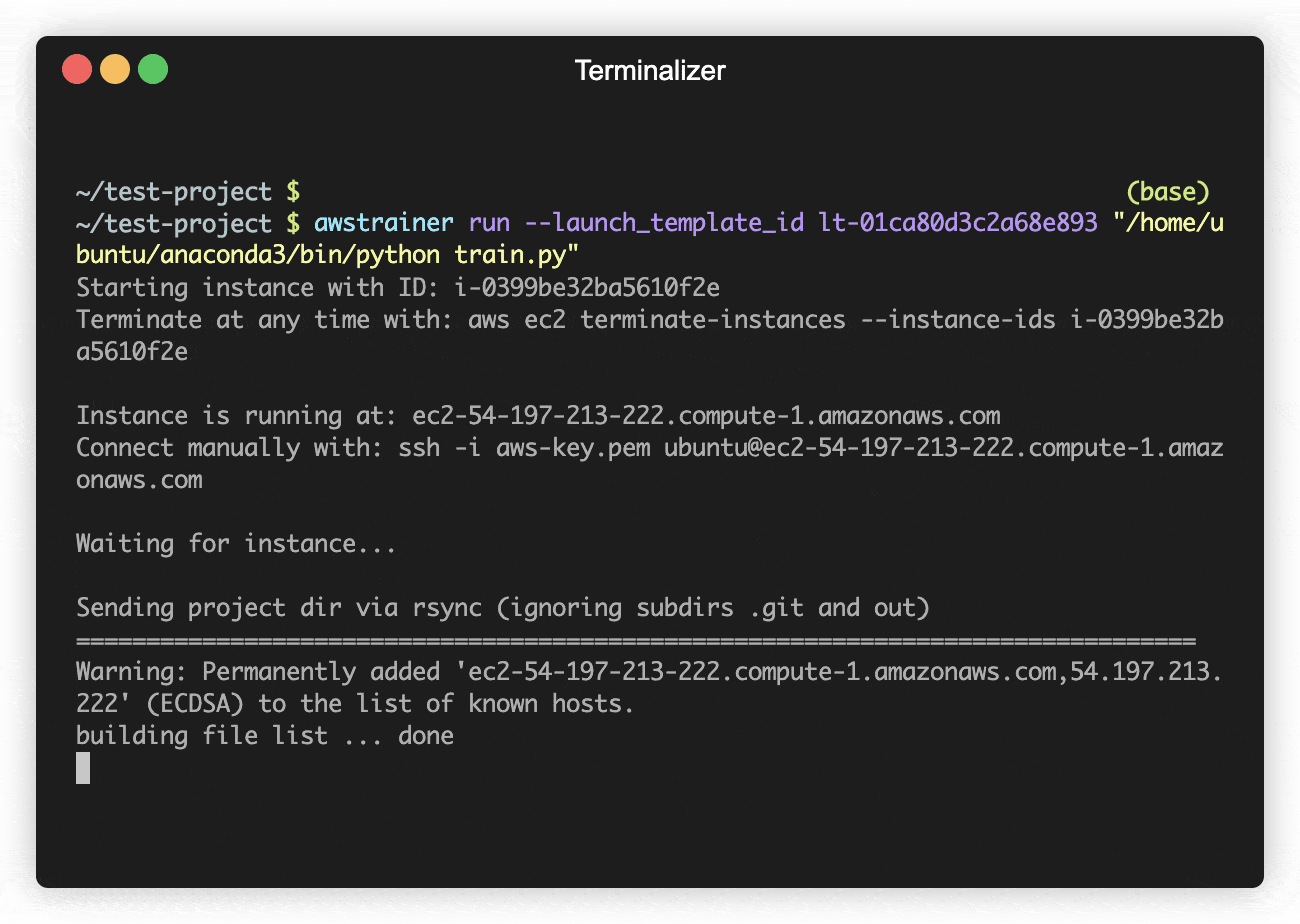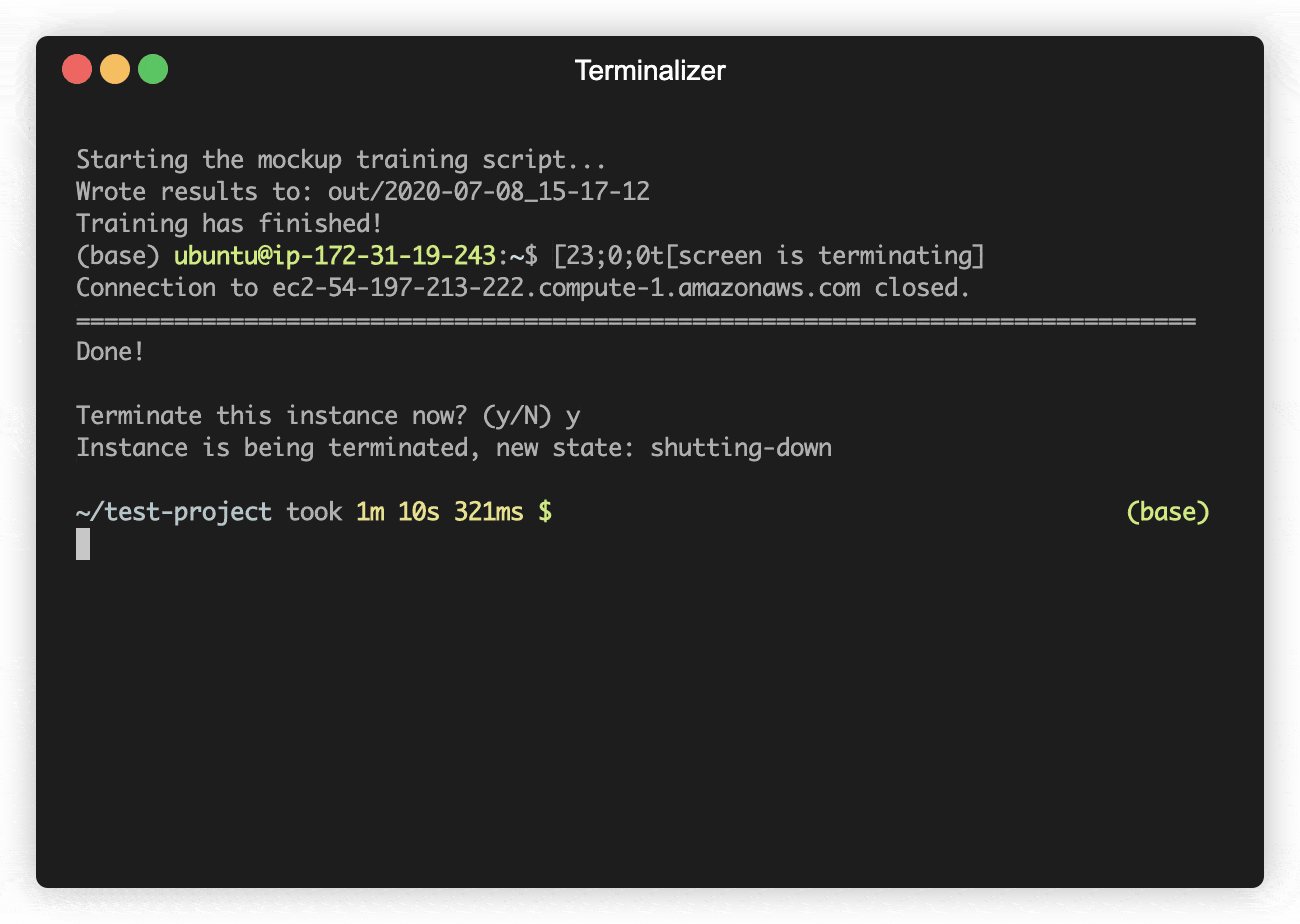
awstrainer run --launch_template_id <id> "/home/ubuntu/anaconda3/bin/python train.py"
This launches an AWS instance (based on your launch template), uploads the project dir
(excluding subdirs .git and out), executes a command via ssh (here it's starting a
training script, but this can be any command - note that you have to use absolute
paths because $PATH won't be available), and terminates the instance after
training has finished. Note that this assumes your private key file from AWS to be
stored as aws-key.pem in the project dir. To adapt this, set the --key_file option.
Based on which operating system your instance uses, you may also need to set the
--user option (default: ubuntu).
For a complete list of options, run awstrainer run --help.
awstrainer also allows you to sync any output files from the AWS instances back to your
local machine. For this to work, you need to write output files to a folder out.
Then, on your local machine, run:
awstrainer sync --every 60
This pulls output files from all running AWS instances every 60 seconds and syncs them
to a local dir aws-synced-out. You can also run awstrainer sync without the
--every option for a one-time sync.
For a complete list of options, run awstrainer sync --help.
If awstrainer run shows a "Connection refused" error, try increasing the
waiting time after instance launch via the --wait_time option (default: 20).
Sometimes, the instance doesn't allow a connection even though the AWS API reports it
as ready, which may lead to this error.