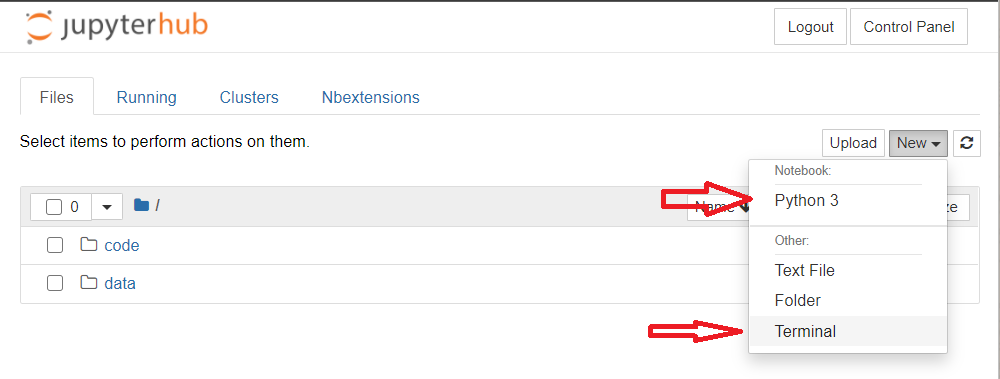
The Networks Data Science (NDS) group has 3 DELL Servers.
They operate inside a VLAN only for the NDS group which is 172.16.26.0/24, and the specifications are:
| Server name | OS | RAM | CPU | Hard Drive | GPU | IPs |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| santiago.networks.imdea.org | Ubuntu Server 20.04 LTS | 126GB | 96 | 1 x 480GB (OS) 1 x 3.6TB | NO | 172.16.26.2 |
| munez.networks.imdea.org | Ubuntu Server 20.04 LTS | 126GB | 96 | 1 x 480GB (OS) 1 x 3.6TB | NO | 172.16.26.3 |
| skynet.networks.imdea.org | Ubuntu Server 20.04 LTS | 62.6GB | 64 | 1 x 480GB (OS) 1 x 4.2TB | 2 x A100 40GB | 172.16.26.4 |
The default way of access the server is trough ssh.
However, all the servers exposes a JupyterHub platform where it possible to open jupyter notebooks and a terminal.
Each user can change their own password
- For JupyterHub platform
https://<server>/hub/auth/change-password - For
sshaccesssudo passwd <username>
It's possible to download and upload files using scp command
# Download
scp -r <username>@<server_name>:<remote_file> <local_dest>
# Upload
scp -r <local_file> <username>@<server_name>:<remote_dest>For avoid software conflict, is requested that each user has their own python virtual environments. By default, a python environment was created for each user, and is accessible through Jupyter Notebook. For create another virtual environment, it's recommended to run these commands in the terminal:
conda init bash
source .bashrc
conda deactivate
conda create --name <vitual_env_name>
conda activate <vitual_env_name>
conda install -y <some_package> # eg: numpy
conda install -cy anaconda ipykernel
python -m ipykernel install --user --name=<vitual_env_name>where <vitual_env_name> is the name of your virtual environment.
This environment is installed in the user home folder's and appear in the new notebook kernels lists.
By default the terminal and JupyterHub load automatically the default virtual environment.
It's possible to overwrite this behavior modifying the end of the /home/<jupyter-user_name>/.bashrc file.
conda deactivate
conda activate <venv_name>The amount of CPU and RAM memory for the Jupyter Notebooks are limited:
| Server | Resources |
|---|---|
| santiago | up to 30GB RAM & up to 30 CPUs |
| munez | up to 30GB RAM & up to 30 CPUs |
| skynet | up to 20GB RAM & up to 20 CPUs |
For the specific case of Skynet server, to limit the use of the GPU the only method know so far is to set a value on the machine learning python library. Eg: for tensorflow
import tensorflow as tf
init = tf.global_variables_initializer()
gpu_options = tf.GPUOptions(per_process_gpu_memory_fraction=<percentage>)
with tf.Session(config=tf.ConfigProto(gpu_options=gpu_options)) as sess:
sess.run(init)
############
#Training happens here#
############If you know another way to limit the usage for each user please let us know.
The previous solution was extracted from https://stackoverflow.com/questions/54912579/is-it-possible-to-threshold-the-maximum-gpu-usage-per-user
where is a float between (0, 1) that represents the GPU percentage that the library have access.
The Jupyter Notebooks will disconnects after 5 hours with out user interactions and for long running projects this is not the recommended way.
Instead the users are encouraged to use the tmux command (https://www.hamvocke.com/blog/a-quick-and-easy-guide-to-tmux/).
With tmux, users can create virtual terminals that keeps alive when the ssh connection is over and allow to attach or detached when they need it.
Some useful commands are:
# create a new tmux terminal
tmux
# run some command
python my_long_script.py
# press ctrl+b, and then press the "d" key for detached
# for list tmux terminal and ids
tmux ls
# for attach to a terminal
tmux attach -t <id>Jupyter Notebook offers extensions for simplify the workflow.
This is the list of available plugins:
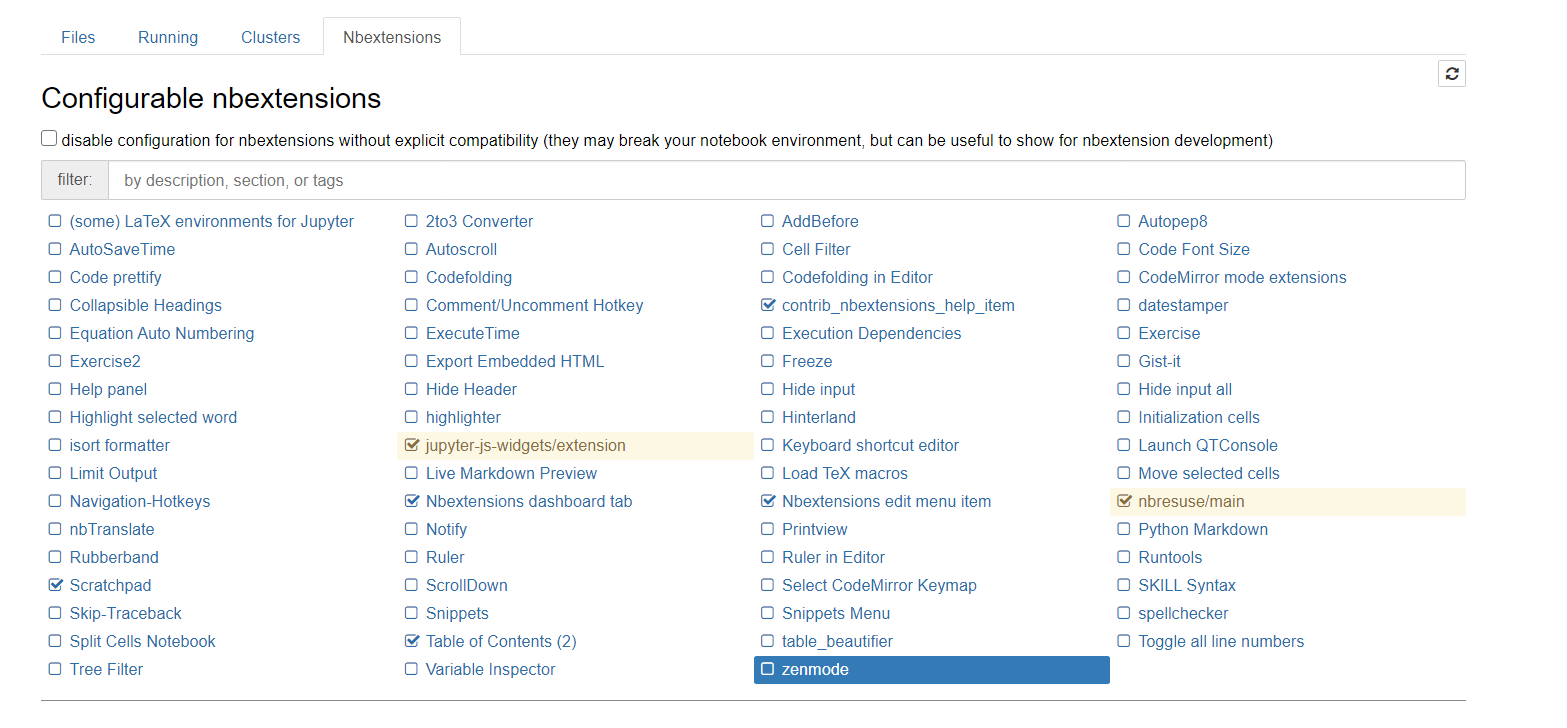
The recommend "getting started" extensions are:
- Table of content: that show an outline of the content based on markdown headlines.
- Scratchapd: a float cell that allows you to write small test code without adding more cells in the notebook.
- Nbresuse: that show the consume of RAM memory (enabled by default)
For more information: https://medium.com/@maxtingle/10-jupyter-notebook-extensions-making-my-lyfe-easier-f40139a334ce
For backup important files like code or Notebook, etc., each user have in their home folder a folder called code. This folder is a backup in the case of hardware failure, but it is not a repository of changes. For saving large files there is also, a folder called data. Is mandatory that each user saves the larger files inside data and not in the root of the home folder due to limited space.
There is a Spark cluster accessible through spark://munez.networks.imdea.org:7077,
and a Hadoop cluster at hdfs://munez.networks,imdea.org:9000 respectively.
For connecting to the Spark cluster using python it need the pyspark python package.
hdfs dfs -ls /