Notes for the course Azure Fundamentals. Both content and images are extracted from there.
Show content
- Common cloud computing services
- Benefits of cloud computing
- Cloud deployment model
It's a resource rental based on a pay per use approach, abstracting the hardware from the users.
It is the processing capability offered by cloud-based servers. Depending on our needs, we can chose among three different options:
-
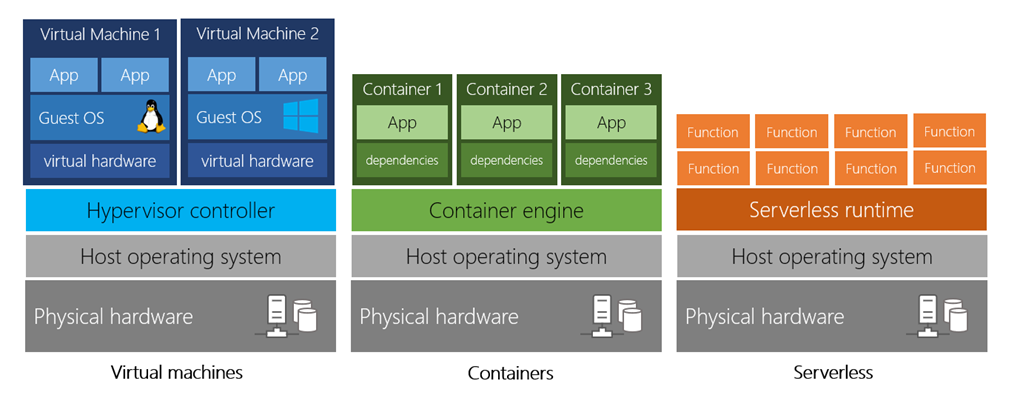
Virtual Machines (VM): You are provided the hardware and the OS, but have to control and maintain the rest of the software. This VM will run on a physical server based on a datacenter and overall resources will be shared with other VMs in an isolated and secure fashion.
-
Containers: Such as Docker, offer an independent, consistent and isolated execution environment for applications. They do not require any OS - as they just contain the minimum dependencies to run the app - they are easy and fast to spin up, move to a different machine and scale.
-
Serverless Computing: Is the ability to run an application without creating, configuring nor maintaining a server. By breaking the whole application into smaller pieces, we can define a workflow and a set of triggers to execute the different parts of the application.
As per pricing, with VMs and Containers, we pay for as long the server is up, eventhough the application is idle. With Serverless Computing though, you only pay for the processing time of each function.
If you either need to store a file or use a database, cloud providers offer the possibility to scale the storage as per your needs.
As requirements vary among all the processes and services business needs to offer, cloud computing is a flexible and cost-efficient solution to both small or big companies.
-
Cost-Effective: with a pay-as-you-go model you don't need to make huge upfronts investments to start offering your services. Moreover, you don't need to manage any kind of infrastructure, freeing people to focus on other tasks.
-
Scalable: It's easy to increase / decrease the resources used either manually or automatically.
- Vertical Scaling or scaling up can be used to increase the power of an existing machine.
- Horizontal Scaling or scaling out adds more servers to function together as a unit.
-
Elastic: Can automatically adapt to workload changes by adding or removing resources.
-
Current: By removing the need of managing hardware and other IT tasks, you can focus on just building and deploying your apps.
-
Reliable: As it offers backups, disaster recovery and data replication services to make sure that your data is always safe. If on top you follow redudancy on your architectures you can avoid single points of failure.
-
Global: With datacenters all over the globe, you can have presence close to your customers and reduce response time.
-
Secure: Offering policies, technologies and controls.
Cloud providers should also help when complying with regulations and standards such as GDPR.
The ability to do things at a lower cost per unit when operating at a larger scale.
-
Capital Expenditure (CapEx): Spending of money on physical infrastructure up front, and then deducting that expense from your tax bill over time. This is the example of on-premise servers, where one needs to pay for server, storage, network, backup, disaster recovery and general infrastructure costs for both software and hardware plus the technical personnel.
-
Operational Expenditure (OpEx): Spending money on services or products now and being billed for them now. With cloud computing we can access to more customized features as we're not sharing the same framework for everyone. Charges are scalable based on usage rather than having a fixed capacity and the billing can directly by focused to a user or organization level.
A cloud deployment model defines where the data is stored and how customers interact with it.
-
Public Cloud: No local hardware - everything runs on the cloud provider. It implies the following advantadges:
- Scalability and agility, as you just rent more hardware when needing it.
- Pay-as-you-go pricing: no CapEx.
- No need for hardware maintenance.
- Minimal technical knowledge to set up and use.
However, there also are some disadvantages:
- Maybe you are not able to manage the hardware as you'd want.
- It's possible that some security requirements, policies or standards that cannot be met.
- Unique business requirements - such as maintaining a legacy application - might be hard to meet.
-
Private Cloud: You set up the whole datacenter, access policies and resources in the organization. This has some advantages:
- You can configure it so that it's possible to maintain any legacy app.
- Full control (and responsability) over security.
- Easier to meet security, policy and standards.
The disadvantages would be:
- Initial CapEx costs.
- Limited agility.
- High IT skills.
-
Hybrid Cloud: Combination of Public and Private clouds, which brings both worlds advantages which may be benefitial for some applications or configurations but also can end up being more expensive and hard to manage.
-
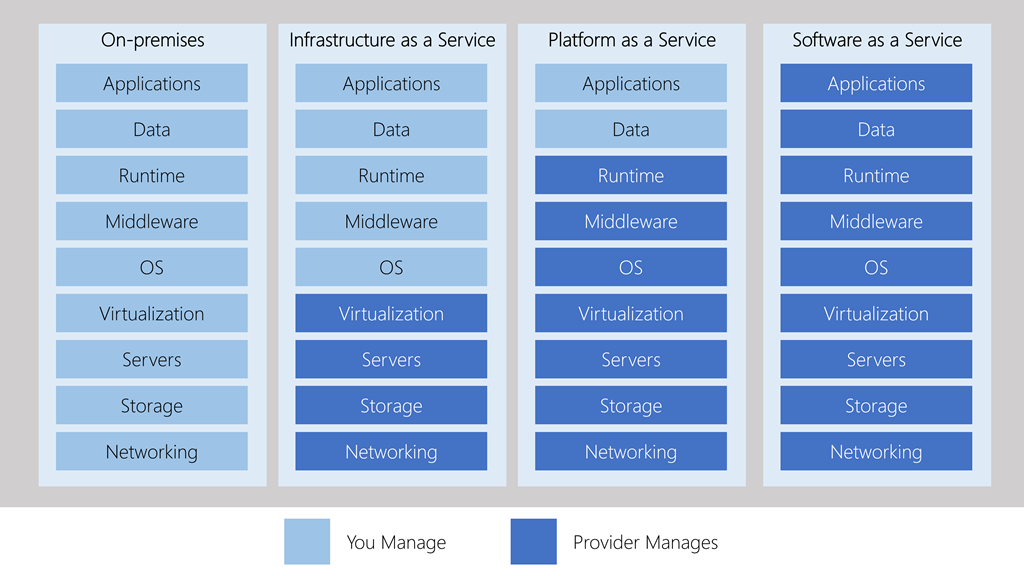
IaaS: Most flexible category, giving full control on the hardware that runs the app.
Shared repsonsibility model: Ensuring that a service is running is a shared responsibility between the cloud provider (in charge of the infrastructure) and the customer (who needs to set up the proper configurations). This is the usual scenario when migrating workloads - as you can mimic on-premise setup, testing and deployment for new apps and for storage, backup and recovery.
-
PaaS: Provides an environment for building, testing and deploying software applications, where one does not need to care about the underlying infrastructure. It is useful as it brings a framework that developers can work upon and also for analytics or BI tasks.
-
SaaS: Software hosted and managed for the customer, who acts as end user.
- Which term from the list below would be viewed as benefits of using cloud services?
-
Unpredictable costs
-
Elasticity
-
Local reach only
Answer
Elasticity: Elasticity, Agility and Economies of scale are the correct answers, and would be seen as benefits that you can gain from using cloud services.
- Suppose you have two types of applications: legacy applications that require specialized mainframe hardware and newer applications that can run on commodity hardware. Which cloud deployment model would be best for you?
-
Public cloud
-
Private cloud
-
Hybrid cloud
Answer
Hybrid cloud: A hybrid cloud is a public and private cloud combined. You can run your new applications on commodity hardware you rent from the public cloud and maintain your specialized mainframe hardware on-premises.
- You're developing an application and want to focus on building, testing, and deploying. You don't want to worry about managing the underlying hardware or software. Which cloud service type is best for you?
-
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
-
Platform as a Service (PaaS)
-
Software as a Service (SaaS)
Answer
Platform as a Service (PaaS): Platform as a Service is the best choice here because the PaaS services handle the IT management tasks for you, so you can focus on writing code.
Show content
- What Microsoft Azure is.
- Deploy and configure a web server.
- Learn how to scale up your server.
- Interact with the web server using Azure Cloud Shell.
Azure is Microsoft's cloud computing platform.
It offers a lot of services of different nature:
- Compute: helping in hosting applications and services.
- Networking: for linking resources and providing access to applications.
- Four main types of storage: Blob storage, File storage, Queue storage and Table storage (NoSQL store).
- Mobile: to create services for iOS, Android an Windows.
- Databases with global connectivity.
- Building and hosting Web applications.
- IoT data gathering and analysis.
- Analytics solutions for Big Data.
- AI: helping with creating and deploying ML models.
- DevOps services for building, testing and releasing your applications.
In this section, it is useful to directly access Azure course and work with the given sandbox. It does not charge your subscription.
-
App Service: HTTP-based service that enables you to build many types of web-based solutions without managing the infrastructure. With an App Service Plan we specify the compute resources and location for the web app.
-
Azure Marketplace: Online store that hosts certified and optimized applications to run in Azure, for example Wordpress in an App Service.
In this section, it is useful to directly access Azure course and work with the given sandbox. It does not charge your subscription.
By looking at the performance graphs we can check if we need to perform any changes on the configuration of our app. When scaling a webb app, we could add network bandwidth, memory, storage or compute power.
Azure Advisor and Azure Cost Management are two services that help you optimize cloud spend. You can use these services to identify where you're using more than you need, and then scale back to the capacity you're actually using.
Finally, notice that there are three categories of configurations plans to make it easier to define our setup for dev, prod or isolated workloads.
Isolated: This category is ideal for workloads that require advanced networking and fine-grained scaling.
In this section, it is useful to directly access Azure course and work with the given sandbox. It does not charge your subscription.
Azure Cloud Shell is a browser-based command-line experience for managing and developing Azure resources
- What is Azure?
-
Microsoft's cloud computing platform, which provides compute power, storage, and services over the Internet using a pay-as-you-go pricing model.
-
A single data center located in Redmond, Washington.
-
A hosting environment specifically for virtual machines
Answer
Microsoft's cloud computing platform, which provides compute power, storage, and services over the Internet using a pay-as-you-go pricing model: Azure provides raw compute power and storage, as well as services to help you explore new software paradigms such as intelligent bots and mixed reality.
- Which of the following is an example of an Azure application platform?
-
Azure App Service
-
Azure Load Balancer
-
Azure Table Storage
-
Azure Cache for Redis
Answer
Azure App Service: Azure App Service is an HTTP-based service that enables you to build and host many types of web-based solutions without managing infrastructure.
- When should you scale out your deployment?
-
When your application or service requires a more powerful CPU or more memory to run faster.
-
When you need additional virtual machines to speed up your application.
-
When you're using excess capacity that you don't need.
Answer
When you need additional virtual machines to speed up your application: Scaling out means adding additional systems, such as virtual machines. For example, you might create many virtual machines configured in the same way and use a load balancer to distribute work across them.
Show content
- Physical infrastructure of Azure.
- Understand the service level agreements provided by Azure.
- Learn how to provide your own service level agreement for your apps.
Cloud providers are built upon datacenters around the globe, where the physical hardware is located.
Regions are geographical areas on the planet containing +1 datacenter. This partition into regions gives flexibility to provide services which are close - and thus ensure lower latency - to the user.
Azure divides the world into geographies that are defined by geopolitical boundaries. Each geography preserve data residency and compliance needs required by those countries. Moreover, they are fault-tolerant to withstand complete region failure. We have the following geographies:
- Americas
- Europe
- Asia Pacific
- Middle East and Africa
Each region belongs to a single geography and has specific service availability, compliance, and data residency/sovereignty rules applied to it
To avoid single points of failure, cloud providers can help us create highly available applications through Availability Zones, which are separate datancenters within a region isolated from each other. If one zone goes down, the others keep working. The idea is that we can locate the resources in a zone and replicate in another.
There are two types of services that support AZs:
- Zonal Services: where the resource is pinned to a specific zone (e.g., a VM)
- Zone-redundant Services: where the platform automatically replicates services accross zones (e.g., zone-redundant storage or SQL databases)
Availability zones are created using 1+ datacenters, and there is a minimum of three zones within a single region. To ensure that services can still be provided even if two datacenters go down, Azure created Region Pairs.
Region Pairs are two region in the same geography but at least 300 miles away, which helps replicating resources accross the same geography and ensuring availabilty even in case of disaster. They are used to provide reliable services and data redudancy (geo-redundant).
Formal documents called Service-Level Agreements (SLAs) capture the specific terms that define the performance standards that apply to Azure. These documents are specific for individual services and define what happens if a products fails to perform.
There are three key characteristics of SLAs:
- Performance Targets: such as uptime guarantees or connectivity rates.
- Uptime and Connectivity Guarantees: which usually specify from 99.9% performance target commitment to 99.999%.
- Service Credits: describing how Microsoft will respond if a service fails to perform its governing SLA's specification.
Combining SLAs from different services results in a Composite SLA. We can calculate this with probability calculus.
For example having a Web App (99.95%) that redirects trafic to either a DB (99.99%) or a Queue (99.9%) gives us:
- If the probability that both DB and queue are up is
1.0 − (0.0001 × 0.001) = 99.99999% - Then, the composite SLA ends up as
99.95 × 99.99999 = ~99.95%Application SLA is the creation of your own SLA based on the workloads and services. We need to know our business requirements to provide a solution that best suits an overall SLA considering all components.
Although rare, we also need to plan for entire service disruption. Here we have important aspects such as Resiliency, the ability of a system to recover from failures and continue to function. High availability and disaster recovery are two crucial components of resiliency. Howeher, the higher availability we want our application to be, the more expensive it will get as it will require more resources. This will also make it more complex in the overall architecture.
- Deploying an app can be done directly to what level of physical granularity?
-
Region
-
Datacenter
-
Server rack
Answer
Region: Azure organizes infrastructure around regions, which include multiple datacenters. You can pick the region you want resources deployed into. You can't select a specific datacenter or location within a datacenter.
- To use Azure datacenters that are made available with power, cooling, and networking capabilities independent from other datacenters in a region, choose a region that supports _________?
-
Geography distribution
-
Service-Level Agreements (SLAs)
-
Availability Zones
Answer
Availability Zones: Availability Zones are datacenters set up to be an isolation boundary from others in the region, with their own power, cooling, and networking. If one zone in a region goes down, other Availability Zones in the region continue to work.
- Application availability refers to what?
-
The service level agreement of the associated resource.
-
Application support for an availability zone.
-
The overall time that a system is functional and working.
Answer
The time that a system is working is referred to as the application availability.
Show content
An Azure account is an identity in either Azure Active Directory (Azure AD), or a directory that is trusted by Azure AD, such as a work or school organization. It holds information such as:
- Name, email, and contact preferences
- Billing information such as a credit card
You use an Azure account to sign in to the Azure website and administer or deploy services. Every Azure account is associated with one or more subscriptions.
An Azure subscription is a logical container used to provision resources in Azure and is associated with Azure AD.
There are four different subcription types:
- Free
- Pay-As-You-Go
- Enterprise Agreement
- Student
Sometimes it is useful to separate resources at a subcription level, as billing and access control happen at the subscription. We could use this to separate DEV and PROD environments for billing and security reasons or even to isolate some resources for compliance.
Also, note that one could also transfer a subscription from one billing account to another.
Azure AD is a modern identity provider that supports multiple authentication protocols. It is partitioned into separate tenants, which are dedicated and isolated instances of the Azure Active Directory service, owned and managed by an organization. A tenant may have multiple subscriptions (in a trust relationship), but a subscription only belongs to one tenant.
![./assets/azure-account/4-azure-ad-tenant.png]
Notice that each Azure AD tenant has an account owner. This is the original Azure account that is responsible for billing. You can add additional users to the tenant, and even invite guests from other Azure AD tenants to access resources in subscriptions.
- Which of the following defines an Azure subscription correctly?
-
Using Azure does not require a subscription
-
All Azure subscriptions are always free
-
An Azure subscription is a logical unit of Azure services that is linked to an Azure account
-
An account cannot have more than one subscription
Answer
An Azure subscription is a logical unit of Azure services that is linked to an Azure account: Using Azure requires an Azure subscription. Azure offer free and paid subscription options to suit different customer needs and requirements, and an account can have one or more subscriptions, with different billing models and access-management policies applied to each . A subscription provides authenticated and authorized access to Azure products and services, and allows you to provision resources.
- True or False. Azure has free services you can use once you have an Azure subscription.
-
True - there are several free services available.
-
False - services are only free for the first 12 months.
Answer
True: Azure has several free services you can use including Azure App Services, Functions, and Azure Kubernetes containers.
- Billing in Azure is ______________
-
Annually for each Azure account based on usage.
-
Monthly for each Azure subscription based on usage.
-
Monthly for each Azure account based on usage.
-
Daily for each Azure subscription based on usage.
Answer
Billing is performed monthly for each subscription in the account, based on the resource usage.
Show content
There is a broad selection of tools that can be used to configure and manage Azure.
- Azure portal for interacting with Azure via a Graphical User Interface (GUI). It uses a blades model for navigation, where a blade is a slide-out panel containing the UI for a single level in a navigation sequence. The initial dashboard can be configured with a tile system to show the resources or metrics that the user is interested in the most. Dashboards can be created, cloned or deleted and configured using the dashboard.json file.
- Azure PowerShell and Azure Command-Line Interface (CLI) for command line and automation-based interactions with Azure.
- Azure Cloud Shell for a web-based command-line interface.
- Azure mobile app for monitoring and managing your resources from your mobile device.
Moreover, it is good to know that one can use preview resources (by searching for "preview") and get notified about General Availability (GA) releases in the "What's new" link.
- An Azure dashboard is stored as which type of file?
-
XML
-
JSON
-
PNG
Answer
Azure dashboards are stored as JSON files, which allow them to be uploaded and downloaded to share with other members of the Azure directory.
- Azure Advisor provides advice on which of these topics:
-
Creating an Azure account
-
Best practices and security for your services
-
Using the Azure portal effectively
Answer
Azure Advisor is a free service built into Azure that provides recommendations on high availability, security, performance, and cost.
- True or false: Azure Cloud Shell is an interactive, browser-accessible shell for managing Azure resources?
-
True
-
False
Answer
Azure Cloud Shell is an interactive shell for managing Azure resources. You can control and administer all of your Azure resources in the current subscription through a command-line interface built right into the portal.
Show content
- Identify compute options in Azure.
- Select compute options that are appropriate for your business.
Azure compute is an on-demand computing service for running cloud-based applications in the form of:
- Virtual Machines: software emulations of physical computers. They include a virtual processor, memory, storage and networking resources. They need to run on an OS.
- Containers: virtualization environment for running applications. They do not need any OS, instead they just include the minimum necessary dependencies to run the application and use the existing host OS running the container.
- App Service: PaaS offering in Azure designes to host web-oriented applications.
- Serverless Computing: is a cloud-hosted execution environment that runs your code but abstracts the underlying hosting environment.
They are a useful choice when we need
- Total control over the operating system (OS)
- The ability to run custom software, or
- To use custom hosting configurations
Some use examples could be during testing and development, when running applications in the cloud without the need of creating the infrastructure, when extending your datacenter to the cloud or during disaster recovery to being able to run business critical applications.
Moreover, when migrating to the cloud, you could use a full IaaS approach to "lift and shift" your applications, copying your physical server configurations.
Grouping VMs together can bring the benefits of high availability, scalability and redundancy:
-
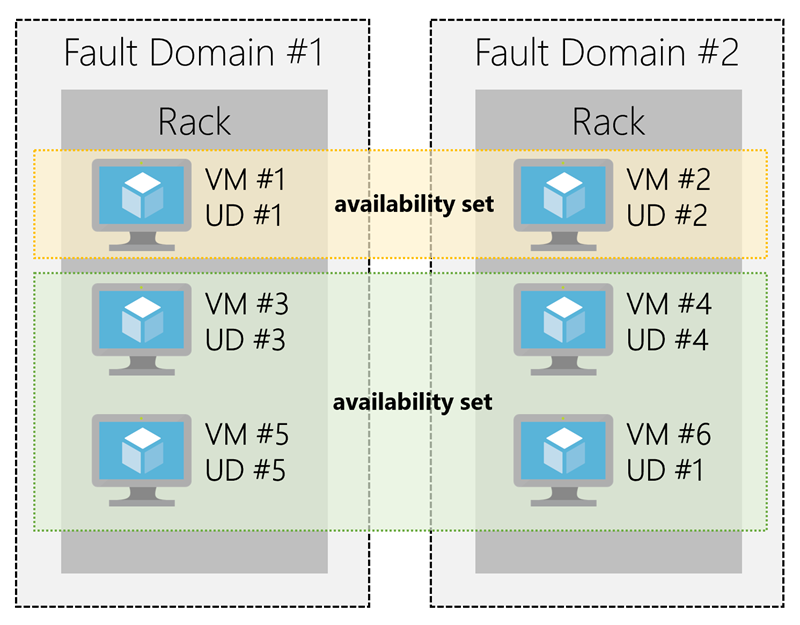
Availability sets: logical grouping of two or more VMs to keep applications up during maintenance. This could mean that some patches or upgrades needed to be done on the machine (planned maintenance) or due to hardware failure in the datacenter (unplanned maintenance). The group of VMs that share common hardware are in the same fault domain - rack of servers.
With an availability set you get up to three fault domains that each have a server rack with dedicated power and network resources and five logical update domains, which indicate the group of VMs that are being rebooted / patched at the same time.
-
Scale sets: let you create and manage a group of identical, load balanced VMs in order to provide high availability apps and increase / decrease the number of VMs depending on demand.
-
Azure Batch: enables large-scale job scheduling and compute management with the ability to scale to tens, hundreds or thousands of VMs. Batch starts a pool of VMs, installs applications and staging data, runs the jobs, identifies failures and requeues works, scales down the pool as work completes.
Azure supports Docker containers. There are several ways to manage containers in Azure:
- Azure Container Instances (ACI): PaaS offering that allows to upload the containers and execute them directly with automatic elastic scale.
- Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS): Complete orchestration service (automating, managing and interacting) for containers with distributes architectures with multiple containers.
Containers are often used to create solutions using a microservice architecture. This architecture is where you break solutions into smaller, independent pieces, which allows to scale and upgrade the differents parts independently.
PaaS service that allows you to focus on the website and API logic while Azure handles the infrastructure to run and scale your web applications. You pay for the resources used by processing depending on the App Service Plan chosen, which determines how much hardware is devoted to your host.
There are different types of web apps:
- Web Apps: which supports web app hosting.
- API Apps: you can build REAS-based Web APIs with Swagger support and the ability to package and publish your API in the Azure Marketplace.
- Web Jobs: allow you to run a program or scripts in the same context as a web app,API app or mobile app. They can be scheduled or run by a trigger.
- Mobile app back-ends: lets one quickly build the backend for iOS or Android apps. You can store mobile app data in cloud DBs, authenticate customers, send push notifications and execute custom backend logic.
Serverless computing encompasses three ideas:
- Abstraction of servers: where you simply deploy your code which then runs with high availability.
- Event-driven scale: Which is an excellent fit for workloads that respond to events. The platform automatically scales. Events can be defined by a variety of triggers.
- Micro-billing: Where you pay only for the time that your code is running.
Azure has two implementations of serverless compute:
- Azure Functions: which can execute code in almost any modern language. Furthermore, Azure Functions can be either stateless (the default) where they behave as if they're restarted every time they respond to an event), or stateful (called "Durable Functions") where a context is passed through the function to track prior activity.
- Azure Logic Apps: which execute workflows designed to automate business scenarios based on an event. They can be defined via UI or JSON files. While Azure Functions can run locally, Logic Apps only run in the cloud.
- Suppose you have an existing application running locally on your own server. You need additional capacity but prefer to move to Azure instead of buying upgraded on-premises hardware. Which compute option would likely give you the quickest route to getting your application running in Azure?
-
Serverless computing
-
Containers
-
Virtual machines
Answer
You have full control over the VM setup, so you can configure it to match your on-premises server. This control will allow your existing application to run on the Azure VM with little or no change.
- Imagine that you work on a photo-sharing application that runs on millions of mobile devices. Demand is unpredictable because you see a spike in usage whenever a locally or nationally significant event occurs. Which Azure compute resource is the best match for this workload?
-
Serverless computing
-
Containers
-
Virtual machines
Answer
The photo-sharing app is event driven and needs to handle unpredictable demand. Serverless computing is a good fit for this situation because it is event-based and can scale instantly to process spikes in traffic. It should also be a cost-effective choice because you will pay for compute time only when processing user data.
- The compute options give you different levels of control over the configuration of the environment in which your application runs. Which of the following lists the compute options in order from "most control" to "least control"?
-
Serverless computing, containers, virtual machines
-
Containers, serverless computing, virtual machines
-
Virtual machines, containers, serverless computing
Answer
Virtual machines give you full control over the environment. Containers give you limited control. Serverless computing does not allow you to do any infrastructure configuration.
Show content
- Survey the data storage options in Azure
- Discover how Azure data storage can meet your business demands
- Compare Azure data storage with on-premises storage
- Automated backup and recovery: mitigating the risk of losing data.
- Replication across the globe: protecting your data.
- Support for data analytics
- Encryption capabilities: making it secure. You also have control over who can access the data.
- Multiple data types: for both relational and NoSQL.
- Data storage in virtual disks: with up to 8TB capacity per disk.
- Storage Tiers: to prioritize access to data based on frequently used vs. rarely used information.
- Structured data: data that adhers to a schema so all of it has the same fields or properties. Also known as relational data.
- Semi-structured data: which does not neatly fit into tables, rows and columns. Uses keys to organize and provide a hierarchy. Also known as non-relational or NoSQL data.
- Unstructured data: No structure means no restrictions. For example, a blob can hold a PDF, JPG, JSON, video...
- Azure SQL: As a Database as a Service (DaaS), it gives the latest stable SQL server engine in a high performance, reliable, fully managed and secure way.
- Azure Cosmos DB: Distributed database service which supports schema-less data. This means that it supports applications with changing data.
- Azure Blob Storage: It is unstructured, so no restrictions applied. Blobs are scalable and it's easy to rowk with blobs with applications. They can manage thousands of simultaneous uploads and massive amounts of data.
- Azure Data Lake Storage: Large repository hosting both structured and unstructured data which allows to perform analytics on the data. Combines the scalability and cost benefits of object storage with the reliability and performance of the Big Data file system capabilities.
- Azure Files: Offers fully managed file shares in the cloud that are accessible via the industry standard Server Message Block (SMB) protocol. Machines can mount these to have access to the data.
- Azure Queue: Service for storing large numbers of message. It also can be used to help build flexible applications and separate functions for better durability across large workloads and provides asynchronous message queueing for communication between application components.
- Disk Storage: Disk storage provides disks for virtual machines, applications, and other services to access and use as they need, similar to how they would in on-premises scenarios.
- Storage Tiers: Azure offers three storage tiers for blob object storage:
- Hot storage tier: optimized for storing data that is accessed frequently.
- Cool storage tier: optimized for data that are infrequently accessed and stored for at least 30 days.
- Archive storage tier: for data that are rarely accessed and stored for at least 180 days with flexible latency requirements.
- Encryption and replication: Azure provides security and high availability to your data through encryption and replication features:
- Encryption for storage services: We can choose between SSE (Azure Storage Service Encryption) which encrypts data before writing and decrypts when reading transparently to the user or Client-side encryption, where the data is already encrypted by the client libraries.
- Replication for storage availability: ensuring that data is durable and available.
Storing data in the cloud gives the following benefits vs. on prem solutions:
- Cost effectiveness: as we don't need an upfront expense and just pay-as-you-go.
- Reliability: Azure data storage provides data backup, load balancing, disaster recovery, and data replication as services to ensure data safety and high availability without as much investment as in on premise.
- Multiple storage types depending on your needs.
- The agility to change the technologies used.
- Suppose you work at a startup with limited funding. Why might you prefer Azure data storage over an on-premises solution?
-
To ensure you run on a specific brand of hardware, which will let you form a marketing partnership with that hardware vendor.
-
The Azure pay-as-you-go billing model lets you avoid buying expensive hardware.
-
To get exact control over the location of your data store.
Answer
The Azure pay-as-you-go billing model lets you avoid buying expensive hardware: There are no large, up-front capital expenditures (CapEx) with Azure. You pay monthly for only the services you use (OpEx).
- Which of the following situations would yield the most benefits from relocating an on-premises data store to Azure?
-
Unpredictable storage demand that increases and decreases multiple times throughout the year.
-
Long-term, steady growth in storage demand.
-
Consistent, unchanging storage demand.
Answer
Unpredictable storage demand that increases and decreases multiple times throughout the year: Azure data storage is flexible. You can quickly and easily add or remove capacity. You can increase performance to handle spikes in load or decrease performance to reduce costs. In all cases, you pay for only what you use.
- A newly released mobile app using Azure data storage has just been mentioned by a celebrity on social media, seeing a huge spike in user volume. To meet the unexpected new user demand, what feature of pay-as-you-go storage will be most beneficial?
-
The ability to provision and deploy new infrastructure quickly
-
The ability to predict the service costs in advance
-
The ability to meet compliance requirements for data storage
Answer
The ability to provision and deploy new infrastructure quickly: As the user demand increases, the agility to deploy new servers or services as needed can help scale to meet the increased user load.
Show content
- How an Azure virtual network provides secure network communication among resources such as virtual machines and other networks
- What high availability and resiliency mean and how Azure Load Balancer can increase resiliency within a single geographic region
- What latency is and how Traffic Manager helps reduce network latency and provides resiliency across geographic locations
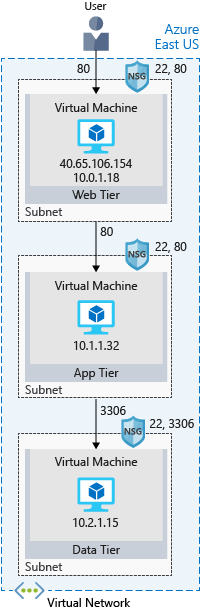
This approach divides an application into two or more logial tiers. A higher tier can access services from a lower tier, but a lower tier should never access a higher tier. It allows for reusability of the different pieces and simplifies maintenance.
A three-tier architecture is often used in web applications:
This also allows for fine-grained securization of the different pieces with inbound rules.
Let's break down some definitions:
- Region: one or more Azure datacenters within a specific geographic location.
- Virtual Network: logically isolated network on Azure, allowing resources to securely communicate with each other, to the internet and on-premise networks. A virtual network is scoped to a single region, but multiple networks from different regions can be connected together by peering.
- Subnets are an internal logical organization of a virtual network so that you can organize and secure your resources in discrete sections.
- Network Security Group or NSG allows or denies inbound network traffic to your Azure resources. It can be seen as a cloud-level firewall.
- Availability refers to how long your service is up and running without interruption. High Availability refers to a service that is up and running for a long period of time.
- Resiliency refers to a system's ability to stay operational during abnormal conditions such as natural disasters, maintenance (planned or unplanned), spikes in traffic and malicious threads.
- Load Balancer distributes traffic evenly among each system in a pool in order to achieve high availability and resiliency.
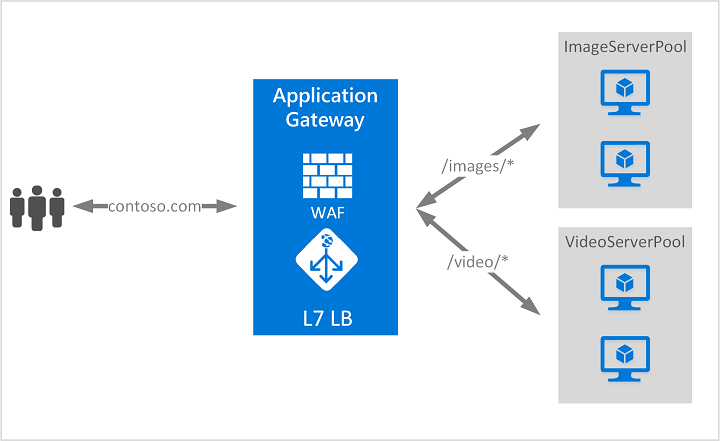
- Azure Application Gateway is a load balancer designed for web applications. It uses Load Balancer at the transport level (TCP) and applies sophisticated URL-based routing rules to support several advanced scenarios. The image below shows an application layer (OSI layer 7) load balancing, as it understands HTTP messages.
Some benefits of using an App Gateway over a LB are:
* Cookie affinity, when you want to keep a user session on the same backend server.
* SSL termination: pass uncrypted traffic to the backend. It also support full end-to-end encryption if you need it.
* Web application firewall, as it supports a sophisticated firewall (WAF).
* URL rule-based routes: allows you to route traffic based on URL patterns, source IP address and port to destination IP address and port. This is helpful when setting up a content delivery network.
* Rewrite HTTP headers to add or remove information of outbound HTTP headers.
-
A content delivery network (CDN) is a distributed network of servers that can efficiently deliver web content to users. It is useful to get content to users in their local region to minimize latency.
-
DNS or Domain Name System is a way to map user-friendly names to their IP addresses.
Latency is the time it takes for data to travel over the network (in ms). Contrary, bandwidth refers to the amount of data that can fir on the connection. One of the biggest factors affecting latency is distance.
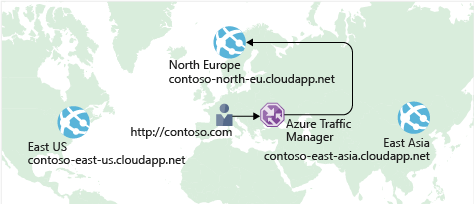
Thus, one way to reduce latency is to provide different copies of a Web App in different regions and then use Azure Traffic Manager to route users to the closest endpoint. It uses the DNS server that's closer to the user.
You could even connect Traffic Manager to an existing on-premise network.
- What is an Azure region?
-
One or more Azure data centers within a specific geographical location.
-
A way of breaking networks into smaller networks.
-
Firewall rules which define the flow of traffic in and out of Azure.
Answer
ne or more Azure data centers within a specific geographical location.: Azure regions help you deliver your apps and services closest to your users. West US and North Europe are examples.
- Which of the following is true about virtual networks?
-
You configure virtual networks through software.
-
A virtual network accepts network traffic on all ports. You configure the firewall through virtual machines.
-
Virtual networks are always reachable from the internet.
Answer
You configure virtual networks through software: Software enables you to treat a virtual network just like your own network. Azure maintains the physical hardware for you.
- Which is true about Azure Load Balancer?
-
You must use Azure Load Balancer if you want to distribute traffic among your virtual machines running in Azure.
-
Azure Load Balancer works with internet-facing traffic only.
-
Azure Load Balancer distributes traffic among similar systems, making your services more highly available.
Answer
Azure Load Balancer distributes traffic among similar systems, making your services more highly available: If one system is unavailable, Azure Load Balancer stops sending traffic to it. It then directs traffic to one of the responsive servers.
- What is network latency?
-
The amount of data that can fit on the connection.
-
The distance data must travel to reach its destination.
-
The time it takes for data to travel over the network.
Answer
Latency measures the time it takes for data to reach its destination. Latency is typically measured in milliseconds.
- How does Azure Traffic Manager reduce latency?
-
It chooses only the fastest networks between endpoints.
-
It chooses the endpoint that's closest to the user's DNS server.
-
It caches content, similar to how content delivery networks work.
Answer
Choosing the server that's closest to the user is a good way to reduce latency.
Show content
- Security responsibility is shared with Azure
- Identity management provides protection, even outside your network
- Encryption capabilities built into Azure can protect your data
- To protect your network and virtual networks
- In IaaS, you are responsible of patching and securing the OS, software and network.
- In PaaS, you need to secure your application but not the infrastructure.
- With SaaS, almost everything is outsourced.
However, you are always responsible for data, endpoints, accounts and access management.
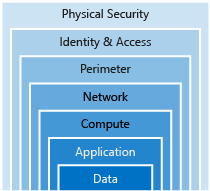
Defense in depth is a strategy that employs a series of mechanisms to slow the advance of an attack aimed at acquiring unauthorized access to information. After a layer is breached, the next is already in place to prevent further exposure. This way there is not just a single layer of protection.
- Data: Attackers usually are after data. It's the user's responsibility to control data access and security.
- Application: Development teams must ensure app security and avoid vulnerabilities.
- Compute: Secure access to VMs and implement endpoint protection.
- Networking: Secure the resources communication.
- Perimeter: Protect from network-based attacks such as DDoS. Use firewalls to identify and alert on malicious attacks.
- Identify and access: ensure identities are secure and grant access only to what is needed.
- Physical Security: Physical buildings and access control.
Is a monitoring service that provides threat protection across all of your services both in Azure, and on-premises, which continuously monitors services and resources and provides security recommendations. Has both free and standard tiers.
- You can use Security Center for incident response to detect (first indication of event investigation), asses (initial analysis to obtain information about the suspicious activity) and diagnose (to conduct a technical investigation and identify containment, mitigation and workaround strategies).
- Use Security Center recommendations to enhance security by configuring security policies, which define a set og controls to specified subscriptions or resource groups.
- Authentication is the process of establishing the identity of a person or service looking to access a resource.
- Authorization is the process of establishing what level of access an authenticated person or service has.
Azure AD is a cloud-based identity service. It provides services such as
- Authentication to identify access to applications and resources.
- Single-Sign-On (SSO), which enables users to remember only one ID and password accross multiple applications.
- Application Management, where you can manage your cloud and on-premise apps using Azure AD Application Proxy.
- Business to business (B2B) Identity services: Manage your guest users and external partners while maintaining control over your own corporate data Business-to-Customer (B2C) identity services.
- Device Management. Manage how your cloud or on-premises devices access your corporate data.
MFA provides addictional security for your identities by requiring two or more elements for full authentication. These elements fall into three categories:
- Something you know - password or the answer to a security question.
- Something you posses - mobile app that receives a notification or token.
- Something you are - biometric property.
Usually, and against best practices, services credentials are embedded into not securized configuration files, which is a risk to exposure. Azure AD addresses this problem through two methods: service principals and managed identities for Azure services.
- An Identity is just a thing that can be authenticated, such as users, applications or servers.
- A Principal is an identity acting with certain roles or claims (such as
sudo). - A Service Principal is an identity that is used by a service or applications. Like other identities, it can be assigned roles.
Creating Service Principals can be tedious. That's why Managed identites for Azure services are much easier and will do most of the work for you. A managed identity can be instantly created for any service supporting it, which automatically creates an account on AD and the infrastructure will automatically take care of authenticating the service and managing the account.
Roles are sets of permissions, like "Read-only" or "Contributor", that users can be granted to access an Azure service instance. Roles can be assigned at different levels and can be inherited:
Management Group > Subcription > Resource Group > Resource
It is an additional paid-on offering that provides oversight of role assignments, self-service and just-in-time role activiation and Azure AD and resources access reviews.
Encryption is the process of making data unreadable and unusable to unauthorized viewers.
- Symmetric Encryption uses the same key to encrypt and decrypt data.
- Asymmetric Encryption uses a public key and private key pair, for example in SSH connections.
Encryption is approached in two ways:
- Encryption at rest: stored data is encrypted (in a disk or db), which makes the data unreadable without the keys and secrets to decrypt it.
- Encryption in transit, such as HTTPS, ensures that data is safe while traveling from one location to another. This gives protection to outside observers.
- Azure Storage Service Encryption encrypts data at rest.
- Azure Disk Encryption helps encrypt VMs disks.
- Transparent data encryption (TDE) protects data in Azure SQL databases and Data Warehouses. It uses a symmetric encryption key.
Moreover, we need to makesure that keys themselves are secure. For this, Azure bring Azure Key Vault, which helps to manage both keys and secrets which are accessible via API. Also, it makes it easier to manage certificates (SSL/TSL) and sotre secrets backed by hardware security models (HSMs).
Some of the benefits of Azure KV are that you are centralizing application secrets which helps to control their distribution; secrets and keys are secure and you can monitor access and use; simplified administration of application secrets and is a service tightly integrated with other Azure services.
Transport Layer Security (TLS) is the basis for encryption of website data in transit. These certificates, though, have a lifecycle and require administration.
- Service Certificates used for cloud services and enable secure communication and from the service. They can be managed separately from the service itself.
- Management Certificates are used for authenticating with the management API. They can be used to automate configuration and deployment of various Azure services. These are not directly related to any cloud service.
All of these certificates can be stored in Azure Key Vault as any other secret.
A common theme is an emphasis of a layered approach to security.
A firewall is a service that grants server access based on the originating IP of the request. To provide inbound protection at the perimeter one can use:
- Azure Firewall which protects Azure Virtual Network resources.
- Azure Application Gateway which is a Load Balancer with a Web Application Firewall included. This protects from common, known vulnerabilities in websites. It is specifically designed to protect HTTP traffic.
- Network virtual appliances (NVAs) are ideal for non-HTTP services. Similar to hardware firewall appliances.
These attacks attemp to overwhelm a network resources by sending requests. Azure uses the scale and elasticity of Microsoft's global network to mitigate DDoS attacks.
Network Security Groups allow you to filter network traffic to and from Azure resources in an Azure virtual network. They can contain multiple inbound and outbound rules to filter traffic. You can even totally remove public internet access to some resources.
VPN (Virtual Private Network) can be used to integrate on-premises network with Azure networks with secure communication. One could even use Azure ExpressRoute to connect cloud services over a private circuit instead of the public internet.
Microsoft Azure Information Protection (sometimes referred to as AIP) is a cloud-based solution that helps organizations classify and optionally protect documents and emails by applying labels.
Azure Advanced Threat Protection (Azure ATP) is a cloud-based security solution that identifies, detects, and helps you investigate advanced threats, compromised identities,and malicious insider actions directed at your organization. Azure ATP is available as part of the Enterprise Mobility + Security E5 suite (EMS E5) and as a standalone license.
The Microsoft Security Development Lifecycle (SDL) introduces security and privacy considerations throughout all phases of the development process. It helps developers build highly secure software, address security compliance requirements, and reduce development costs. There are important security practices that should be followed:
- Provide training, as security is everyone's job.
- Define security Requirements including legal and industry requirements, internal standards and coding best practices.
- Define metrics and compliance reporting to ensure a minimum level of security quality.
- Perform threat modeling in environment with a meaningful security risk.
- Emable design requirements to help engineers implement more secure features.
- Define and use cryptography standards to ensure that all data is secure from unintended disclosure and alteration.
- Manage security risks from using third-party components, as they can be a possible vulnerability.
- Define a list of Approved tools.
- Perform Static Analysis Security Testing to test code before compilation.
- Perform Dynamic Analysis Security Testing to test the final packaged software.
- Perform penetration testing simulating the actions of a hacker.
- Establish a standard incident response process to address how to answer to new threats.
- Cloud security is a shared responsibility between you and your cloud provider. Which category of cloud services requires the greatest security effort on your part?
-
Infrastructure as a service (IaaS)
-
Platform as a service (PaaS)
-
Software as a service (SaaS)
Answer
IaaS: At this level, the cloud provider provides physical security to compute resources. However, it's your responsibility to patch and secure your operating systems and software, as well as configure your network to be secure.
- Which of these helps you most easily disable an account when an employee leaves your company?
-
Enforce multi-factor authentication (MFA)
-
Monitor sign-on attempts
-
Use single sign-on (SSO)
Answer
SSO centralizes user identity, so you can disable an inactive account in a single step.
- Which of these is the strongest way to protect sensitive customer data?
-
Encrypt data as it sits in your database
-
Encrypt data as it travels over the network
-
Encrypt data both as it sits in your database and as it travels over the network
Answer
Encrypting your data at all times, both as it sits in your database and as it travels over the network, minimizes the opportunity for an attacker to access your data in plain text.
- There has been an attack on your public-facing website, and the application's resources have been overwhelmed and exhausted, and are now unavailable to users. What service should you use to prevent this type of attack?
-
DDoS protection
-
Azure Firewall
-
Network Security Group
-
Application Gateway
Answer
DDoS protection is the correct answer, because it will help prevent DDoS attacks.
- You want to store certificates in Azure to centrally manage them for your services. Which Azure service should you use?
-
AIP
-
Azure AD
-
Azure Key Vault
-
Azure ATP
Answer
Azure Key Vault is the correct answer, because it is a centralized cloud service for storing application secrets, referred to as a secret store.
Show content
- Apply policies to control and audit resource creation
- Learn how role-based security can fine-tune access to your resources
- Understand Microsoft's policies and privacy guarantees
- Learn how to monitor your resources
Your policies will enforce your rules for created resources, so your infrastructure stays compliant with your corporate standards, cost requirements, and service-level agreements (SLAs) you have with your customers.
Azure Policy is an Azure service you use to create, assign and, manage policies. This service evaluates resources looking for noncompliance with assigned policies.
Azure Policies vs. RBAC: RBAC (role based access control) focuses on user actions at different scopes. Azure Policy focuses on resource properties during deployment and for already existing resources. It is a default-allow-and-explicit-deny system.
To create a policy you need to
- Create a policy definition: it expresses what to evaluate and what action to take. For example, ensure all public websites are secured with HTTPS. A policy definition is represented as a JSON file. This can be done via Azure portal or Powershell.
- Assign a definition to a scope of resources. The policy will then need to be assigned to a resource orgroup of resources (with child inheritance). This can be done by using Azure portal, Powershell or Azure CLI.
- View policy evaulation results: it can allow a resource to be created even if it doesn't pass validation.
Then, in the Policy resource in the portal we can check for non compliant resources.
OBS: Requests to create or update a resource through Azure Resource Manager are evaluated by Azure Policy first, evaluating all of them against each definition.
An initiative definition is a set or group of policy definitions to help track your compliance state for a larger goal. They are also assigned to a specific scope.
Access management occurs at the Azure subscription level. This allows an organization to configure each division of the company in a specific fashion based on their responsibilities and requirements.
Azure Management Groups are containers for managing access, policies, and compliance across multiple Azure subscriptions with child inheritance.
Azure Blueprints enables cloud architects and central information technology groups to define a repeatable set of Azure resources that implements and adheres to an organization's standards, patterns, and requirements. It is adeclarative way to orchestrate the deployment of resource templates and artifacts.
It is based on defining "What should be deployed" and then keeping an audit of "what was deployed".
The Azure Blueprints service is designed to help with environment setup. On the other hand, ARM templates are just a definition of resources that we may want to deploy that does not exist natively in Azure. Each blueprint can consist of zero or more ARM template artifacts.
A blueprint is a package of sets of standards, which can include policies in it. Policies are just used to audit and control resource usage.
Governing your own resources and how they are used is only part of the solution when using a cloud provider. You also have to understand how the provider manages the underlying resources you are building on. We have full transparency with four sources:
- Microsoft Privacy Statement: explains what personal data Microsoft processes, how Microsoft processes it, and for what purposes.
- Microsoft Trust Center: website resource containing information and details about how Microsoft implements and supports security, privacy, compliance, and transparency in all Microsoft cloud products and services. It includes information such as recommended resources, organizational roles and direct guidance, if needed.
- Service Trust Portal: hosts the Compliance Manager service, and is the Microsoft public site for publishing audit reports and other compliance-related information relevant to Microsoft’s cloud services. It helps your organization maintain track and compliance with standards such as ISO or GDPR, access Microsoft's audit reports, compliance guides and trust documents.
- Compliance Manager: dashboard that provides a summary of your data protection and compliance stature and recommendations for improvement.
Azure provides two primary services to monitor the health of your apps and resources.
-
Azure Monitor: helps you understand how your applications are performing and proactively identifies issues affecting them and the resources they depend on. It gets and analyzes data from your resources. Some of the data sources are Activity Logs of your applications, Event Logs, Application Insights, Azure monitor for containers or VMs... Moreover, it proactively notifies of critical conditions using Alerts. These can be configured based on metrics to have almost real-time responses. Also, Azure Monitor uses Autoscale to make sure that you always have enough resources to run your applications based on your rules and metrics. All of this information can be integrated with visualization tools.
-
Azure Service Health: suite of experiences that provide personalized guidance and support when issues with Azure services affect you. It is composed of the following views:
- Azure status provides a global view of the health state of Azure services.
- Service Health gives a customizable dashboard that tracks the state of your Azure services in the regions where you use them.
- Resource Health helps you diagnose and obtain support when a service issue affects your resources. It helps you understand if an SLA was violated.
- True or false: You can download published audit reports and other compliance-related information related to Microsoft’s cloud service from the Service Trust Portal
-
True
-
False
Answer
True: You can download published audit reports and other compliance-related information related to Microsoft’s cloud service from the Service Trust Portal.
- Which Azure service allows you to configure fine-grained access management for Azure resources, enabling you to grant users only the rights they need to perform their jobs?
-
Locks
-
Policy
-
Initiatives
-
Role-based Access Control
Answer
Role-based access control (RBAC) provides fine-grained access management for Azure resources, enabling you to grant users only the rights they need to perform their jobs. RBAC is provided at no additional cost to all Azure subscriber.
- Which Azure service allows you to create, assign, and, manage policies to enforce different rules and effects over your resources and stay compliant with your corporate standards and service-level agreements (SLAs)?
-
Azure Policy
-
Azure Blueprints
-
Azure Security Center
-
Role-based Access Control
Answer
Azure Policy is a service in Azure that you use to create, assign, and, manage policies. These policies enforce different rules and effects over your resources, so those resources stay compliant with your corporate standards and service-level agreements (SLAs).
- Which of the following services provides up-to-date status information about the health of Azure services?
-
Compliance Manager
-
Azure Monitor
-
Service Trust Portal
-
Azure Service Health
Answer
Azure Service Health is the correct answer, because it provides you with a global view of the health of Azure services. With Azure Status, a component of Azure Service Health, you can get up-to-the-minute information on service availability.
- Where can you obtain details about the personal data Microsoft processes, how Microsoft processes it, and for what purposes?
-
Microsoft Privacy Statement
-
Compliance Manager
-
Azure Service Health
-
Trust Center
Answer
You can obtain the details about how Microsoft uses personal data in the Microsoft Privacy Statement.
Show content
- Use resource groups to organize Azure resources
- Use tags to organize resources
- Apply policies to enforce standards in your Azure environments
- Use resource locks to protect critical Azure resources from accidental deletion
A resource group is a logical container for resources deployed on Azure. All resources must be in a resource group and a resource can only be a member of a single resource group. Resource groups can't be nested.
They help to organize services, so we are interested in created logical groups. Moreover, deleting a RG will delete all services that it contains. They are also a scope for applying role-based access control (RBAC) permissions.
It is important to apply naming conventions to both the RG and the contained services. We could organize resource groups by service, environment or authorization level, as they are a scope of RBAC. Furthemore, it may be useful organizing RG by life-cycle or billing.
Tags are name/value pairs of text data that you can apply to resources and resource groups. Tags allow you to associate custom details about your resource, in addition to the standard Azure properties a resource has:
- department (like finance, marketing, and more)
- environment (prod, test, dev),
- cost center
- life cycle and automation (like shutdown and startup of virtual machines).
Apart from organization utilities, tags could also be used to automate or schedule activies such as shutting down VMs. By adding the tag shutdown:6PM tag to a group of VMs, we could set up an activity that filters VMs by that.
For example, we could create policies that force the existance of a tag on a resource or restrict which types of VMs sizes can be deployed.
Here are some best practices you should use when setting up resources.
- Segregate duties within your team and grant only the amount of access to users that they need to perform their jobs. Instead of giving everybody unrestricted permissions in your Azure subscription or resources, allow only specific actions at a particular scope.
- When planning your access control strategy, grant users the lowest privilege level that they need to do their work.
- Use Resource Locks to ensure critical resources aren't modified or deleted.
Resource locks are a setting that can be applied to any resource to block modification or deletion. Resource locks can set to either Delete (all operations but delete are allowed) or Read-only (only allows read operations, blocking any modification).
- Tags can be applied to any type of resource on Azure
-
True
-
False
Answer
False
- Tags applied at a resource group level are propagated to resources within the resource group.
-
True
-
False
Answer
False
- Which of the following is not a feature of resource groups?
-
Resources can be in only one resource group.
-
Resources can be moved from one resource group to another resource group.
-
Resource groups can be nested.
-
Role-based access control can be applied to the resource group.
Answer
Resource groups can be nested.
- Which of the following might be a good usage of tags?
-
Using tags to associate a cost center with resources for internal chargeback
-
Using tags in conjunction with Azure Automation to schedule maintenance windows
-
Using tags to store environment and department association
-
All of the above are good ways to use tags
Answer
All of the above are good ways to use tags
- Which of the following would be the most efficient way to ensure a naming convention was followed across your subscription?
-
Send out an email with the details of your naming conventions and hope it is followed
-
Create a policy with your naming requirements and assign it to the scope of your subscription
-
Give all other users except for yourself read-only access to the subscription. Have all requests to create resources sent to you so you can review the names being assigned to resources, and then create them.
Answer
Create a policy with your naming requirements and assign it to the scope of your subscription
- Which of the following would be good to put a resource lock on?
-
An ExpressRoute circuit with connectivity back to your on-premises network
-
A non-production virtual machine used to test occasional application builds
-
A storage account used to temporarily store images processed in a development environment
Answer
An ExpressRoute circuit with connectivity back to your on-premises network
Show content
- Learn the different options you have to purchase Azure services
- Estimate costs with the Azure pricing calculator
- Predict and optimize costs with Azure Cost Management and Azure Advisor
- Apply best practices for saving on infrastructure costs
- Apply best practices for saving on licensing costs
There are three main customer types:
- Enterprise: Customers commit to spend a negotiated amount on services, usually paid annually. They also get customized pricings.
- Web direct: Customers pay general public prices and their monthly billing and payments occur through Azure website.
- Cloud Solution Provider: Microsoft partner companies that a customer hires to build solution on Azure. Payment and billing occur through the CSP.
Meters track the resource's usage used to calculate the bill. Usually they are compute hours, IP addresses, data transfer, Disk operations...
OBS: De-allocating a VM is not the same as deleting a VM. De-allocation means the VM is not assigned to a CPU or network in a datacenter. However, your persistent disks remain, and the resource is present in your subscription. It's similar to turning off your physical computer.
There are different aspects which affect on the costs:
- Resource type, as costs are resource specific, so the usage meter varies. The usage that a meter tracks correlates to a number of billable units.
- Services: Rates and billings vary depending on the customer types.
- Location, based on the resource popularity, demand, and local infrastructure costs.
- Azure Billing Zones: Most of the inbound data transfers (data going into Azure datacenters) are free, but different charges will be applied on outbound data based on Billing Zones. A Zone is a geographical grouping of Azure Regions for billing purposes, for example Zone 1 is US, Europe, Canada, UK and France.
Free web-based tool that allows you to input Azure services and modify properties and options of the services. It outputs the costs per service and total cost for the full estimate.
Azure Advisor is a free service built into Azure that provides recommendations on high availability, security, performance, and cost. Advisor analyzes your deployed services and looks for ways to improve your environment across those four areas.
- Reduce costs by eliminating unprovisioned Azure ExpressRoute circuits: Recommends deleting circuits not provisioned for more than 1 month.
- Buy reserved instances to save money over pay-as-you-go: This will review your virtual machine usage over the last 30 days and determine if you could save money in the future by purchasing reserved instances.
- Right-size or shutdown underutilized virtual machines: This monitors your virtual machine usage for 14 days and then identifies underutilized virtual machines.
Azure Cost Management is another free, built-in Azure tool that can be used to gain greater insights into where your cloud money is going. You can get historical breakdowns, set budgets, schedule reports and analyze cost areas.
If you are starting to migrate to the cloud, a useful tool you can use to predict your cost savings is the Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) calculator. You'll need to define your workloads, such as the details of current servers and databases infrastructure, then adjust some assumptions on storage, hardware and network costs among others and finally view the report. The report allows to compare cloud vs. on-premises costs.
There are some ways in which customers can save on costs:
- Azure Credits, which can be obtained for specific subscription levels.
- Use spending limits prevent you from exhausting the credit on your account within each billing period. The spending limit feature is specific to subscriptions that include a monthly Azure credit allotment. It is not available on pay-only subscriptions.
- Use reserved instances purchased in one-year or three-year terms, with payment required for the full term up front.
- Choose low-cost locations and regions
- Research available cost-saving offers
- Right-size underutilized virtual machines by getting insights from Azure Cost Management and Azure Advisor.
- Deallocate virtual machines in off hours
- Delete unused virtual machines
- Migrate to PaaS or SaaS services, which provide substantial savings in both resources and operational costs.
- Linux vs. Windows: Costs can vary depending on the OS you use.
- Azure Hybrid Benefit for Windows Server: letting customers repurpose their Windows licenses.
- Azure Hybrid Benefit for SQL Server
- Use Dev/Test subscription offers to save cost on non-production environments.
- Bring your own SQL Server license
- Use SQL Server Developer Edition
- Use constrained instance sizes for database workloads
- Which tab of the Azure pricing calculator will you use to put together your estimate?
-
Estimate
-
Products
Answer
Products: This tab has all the Azure services listed and is where you'll add or remove services to get your estimate.
- True or false: You can share your estimate through an Excel spreadsheet or through a URL.
-
True
-
False
Answer
Clicking Export at the bottom of the estimate will export an Excel spreadsheet that you can share, or you can click Share to get a URL link that you can share with your team.
- Azure Advisor provides recommendations for _________.
-
Costs only
-
High availability, security, performance, and cost
-
High availability, performance, and cost
Answer
Azure Advisor provides recommendations on high availability, security, performance, and cost.
- Azure Cost Management allows you to _________.
-
See historical breakdowns of what services you are spending your money on.
-
See estimates of what your services might cost if you make a change.
Answer
Cost Management analyzes where you are historically spending your money and can track it against budgets you have set.
- Which one of these is not a cost-saving solution?
-
Deallocate virtual machines during off hours.
-
Use Azure Reserved Virtual Machine Instances.
-
Load balance your virtual machines for incoming messages.
-
Right-size underutilized virtual machines.
Answer
Load balancing is used for performance optimization not cost savings.
- True or false: PaaS is generally less expensive than IaaS.
-
True
-
False
Answer
IaaS requires Azure to dedicate resources while PaaS give Azure more flexibility in how services are delivered. This means Azure can fill and operate hardware efficiently and therefore offer PaaS services at a savings over IaaS.
- True or false: If you already have Windows Server licenses, you have to pay for them again on Azure.
-
True
-
False
Answer
False: Under certain circumstances, you can utilize the hybrid benefit for Windows Server and pay only the Linux rate.
- True or false: Azure has money-saving options for test and development servers.
-
True
-
False
Answer
The Azure Enterprise Dev/Test and Azure Pay-As-You-Go Dev/Test benefits give you several discounts, most notably for Windows workloads, eliminating license charges and billing you only at the Linux rate for virtual machines. This also applies to SQL Server and any other Microsoft software that is covered under a Visual Studio subscription.
- Which one of the following is used to determine Azure costs for each billing period?
-
The Azure website
-
Number of created virtual machines
-
The Azure pricing calculator
-
Usage meters
Answer
Azure is billed according to your consumption based on monthly usage meters.
- Which of the following is a factor affecting costs?
-
Global infrastructure
-
Location
-
Availability zone
Answer
The location you place your resources will vary the price for the resource.
- Complete the following sentence. As an Azure customer, Azure Reservations offer discounted prices if you _________
-
Pay in advance
-
Provision many resources
-
Have a free account
-
Set Spending Limits
Answer
Azure Reservations offer discounted prices on certain Azure products and resources. To get a discount, you reserve products and resources by paying in advance. You can prepay for one or three year's of usage of certain Azure resources.