This document will guide you through the steps required to modify an existing Ubuntu package and upload it to your Personal Package Archive (PPA). The steps are:
-
Set up your system and your Launchpad account
-
Retrieve the source code of an existing Ubuntu package
-
Add a "testing.sh" script to the package and install it to
/usr/bin/ -
Add a "post-install" script
-
Re-package it as a
deband test it -
Host the package using your PPA on Launchpad to distribute it
I'm running Ubuntu 20.04 (focal) in a VM.
Make sure you have all the required software installed:
$ sudo apt install gnupg pbuilder ubuntu-dev-tools apt-file debhelperThen you need to set up pbuilder:
$ pbuilder-dist focal createI'm running Ubuntu 20.04 so I'm using focal. Make sure you have the
right release name here.
You need a GPG key to sign your packages. Running the command and follow the instruction to generate one:
$ gpg --gen-keyAt last you should see a message similar to this:
pub rsa3072 2020-11-14 [SC] [expires: 2022-11-14]
2734D5090EEC923C2FAB20373EAFB4567F851F68
uid John Liu <johnliu55tw@gmail.com>
sub rsa3072 2020-11-14 [E] [expires: 2022-11-14
- Note: You can also run
gpg --full-generate-keyto fine-tune the key (encryption algorithm, expiration of the key, ...).
You will need a Launchpad account to host a PPA on Launchpad. Click the link to register if you don't have one. After you got an account, upload your GPG key to Launchpad.
Retrieve the fingerprint of your GPG key with the following command:
$ gpg --fingerprint <Your email>It will print out the GPG fingerprint:
pub rsa3072 2020-11-14 [SC] [expires: 2022-11-14]
2734 D509 0EEC 923C 2FAB 2037 3EAF B456 7F85 1F68
uid [ultimate] John Liu <johnliu55tw@gmail.com>
sub rsa3072 2020-11-14 [E] [expires: 2022-11-14]
The hexadecimal digits in the second line are Key fingerprint (
2734 D509 0EEC 923C 2FAB 2037 3EAF B456 7F85 1F68), and the last
eight digits are key ID (7F851F68). Run the following command to submit your
key to Ubuntu keyserver:
$ gpg --keyserver keyserver.ubuntu.com --send-keys <Key ID> In my case the command is:
$ gpg --keyserver keyserver.ubuntu.com --send-keys 7F851F68Then head to https://launchpad.net/~/+editpgpkeys and copy the Key fingerprint into the text box. Now click "Import Key", and you should see a prompt on the page similar to this:
A message has been sent to
johnliu55tw@gmail.com, encrypted with the key3072R/2734D5090EEC923C2FAB20373EAFB4567F851F68. To confirm the key is yours, decrypt the message and follow the link inside.
Launchpad will send you an email with a message encrypted by the key you just
uploaded, and you must decrypt the message in order to finish the import
process. If your email client doesn't decrypt it automatically, you can still
decrypt it using gpg command:
-
Copy the message started from
-----BEGIN PGP MESSAGE-----to-----END PGP MESSAGE-----(including these two lines) into a text file (let's say it'smsg.txt). -
Run the command:
$ gpg -d msg.txtThen you will see the decrypted message prints on the screen. Follow the instruction to finish the import process.
After you imported your key, you can create a PPA now. Head to https://launchpad.net/~ and click "Create a new PPA". Enters URL and Display Name, then click "Activate".
First, you need to know the name of the package you want to modify. You could use Ubuntu Package Search to search for it. I will be using hello, an example package based on GNU hello, as an example.
The ubuntu-dev-tools has a tool called pull-lp-source that we could
use to download the source code of the package:
- Note: The command will download multiple files into current working
directory. I would recommend creating a new directory and
cdinto it before you run the command.
$ pull-lp-source hello focalNow you should see several files appeared:
$ ls -l
drwxrwxr-x 13 johnliu johnliu 4096 Nov 14 01:09 hello-2.10
-rw-rw-r-- 1 johnliu johnliu 6560 Nov 13 23:37 hello_2.10-2ubuntu2.debian.tar.xz
-rw-rw-r-- 1 johnliu johnliu 1847 Nov 13 23:37 hello_2.10-2ubuntu2.dsc
-rw-rw-r-- 1 johnliu johnliu 725946 Nov 13 23:32 hello_2.10.orig.tar.gzThe source code locates in folder hello-2.10. cd into it and let's make
some changes.
First, we need to use quilt to create a new patch:
$ quilt new johnliu.patchwhere johnliu.patch is the name of the patch.
Because we're adding a new file testing.sh instead of changing an existed
file, we need to create an empty file first so quilt can track it:
$ touch testing.shNow adding the file to quilt:
$ quilt add testing.shNow you can change the file. Here's a simple script that prints my name:
#!/bin/sh
echo 'this is a test from John Liu'
Update the patch after you made some change (you can do this as often as you like):
$ quilt refreshYou can also add a description to the patch using quilt:
$ quilt header --dep3 -eAfter you've finished, run the command:
$ quilt pop -aAnd that's it. You can check the patch file in debian/patches/.
There are many files under debian/ that control how a package should be
installed. To specify additional files to be installed to the system, we could
use
debian/install.
Create the file and put the following content into it:
testing.sh usr/bin
One-liner:
$ echo 'testing.sh usr/bin' >> debian/installIt's convenient to run custom scripts at different stages during the
installation process, and we can also create special files under debian/
folder for the purpose. To run a script after the package is installed, create
a file named postinst under debian/ and make sure it's executable. I will
add a simple script that prints my name:
#!/bin/sh
echo 'this is a test from John Liu'
See Package maintainer scripts and installation procedure for more information.
Every Debian and Ubuntu package source includes a file debian/changelog which
records version changes. Other than manually modifying the file, you could use dch
command to help you document your change:
$ dch -iThis will add a boilerplate changelog entry for you and launch an editor where you can fill in the blanks. Here's an example:
hello (2.10-2ubuntu2ppa2) focal; urgency=medium
* Add `testing.sh` and install it to /usr/bin.
* Add `postinst` script
-- John Liu <johnliu55tw@gmail.com> Sat, 14 Nov 2020 12:57:35 +0800
Three important things to note while you're editing the change log:
-
Version number (
2.10-2ubuntu2ppa2): If you're creating an alternative version of a package already available in Ubuntu's repositories, you should ensure that:- Your package supersedes the official Ubuntu version
- Future Ubuntu versions will supersede your package
I've added a suffix
ppa2to the original version number to achieve this. See https://help.launchpad.net/Packaging/PPA/BuildingASourcePackage#Versioning for more detail about versioning your package. -
Upload Ubuntu release (
focal): The default value isUNRELEASED, which would cause the build to fail. I'm using 20.04 so I changed it tofocal. -
Name and email address (
John Liu <johnliu55tw@gmail.com>): Make sure the email address is identical to the one you used to create the GPG key, or the build process can't sign thesource.changesfile automatically, which would cause the upload PPA process to fail.
See https://packaging.ubuntu.com/html/fixing-a-bug.html#documenting-the-fix for more about how to document your change.
To build a test package with your changes, run these commands:
$ debuild -S -d -us -uc
$ pbuilder-dist focal build ../<package>_<version>.dscIn my case the name of the dsc file is hello_2.10-2ubuntu2ppa2.dsc:
$ pbuilder-dist focal build ../hello_2.10-2ubuntu2ppa2.dscThe pbuilder-dist command will generate a deb under
~/pbuilder/<Ubuntu release>_result/ folder. I'm running 20.04 so it's
focal_result:
$ ls ~/pbuilder/focal_result/*.deb
/home/johnliu/pbuilder/focal_result/hello_2.10-2ubuntu2ppa2_amd64.debThen you can install it with dpkg command:
$ sudo dpkg -i ~/pbuilder/focal_result/hello_2.10-2ubuntu2ppa2_amd64.debYou should see the effect of postinst script:
$ sudo dpkg -i ~/pbuilder/focal_result/hello_2.10-2ubuntu2ppa2_amd64.deb
Selecting previously unselected package hello.
(Reading database ... 175934 files and directories currently installed.)
Preparing to unpack .../hello_2.10-2ubuntu2ppa2_amd64.deb ...
Unpacking hello (2.10-2ubuntu2ppa2) ...
Setting up hello (2.10-2ubuntu2ppa2) ...
this is a test from John Liu # <- This is what postinst did
Processing triggers for install-info (6.7.0.dfsg.2-5) ...
Processing triggers for man-db (2.9.1-1) ...
And the testing.sh we have installed into /usr/bin/:
$ dpkg -S testing.sh; testing.sh
hello: /usr/bin/testing.sh
this is a test from John Liu
After you finished testing, run debuild again to generate the source package
and sign it:
$ debuild -S -dNow you can use dput command to upload the *.changes file:
$ dput ppa:<Your Launchpad ID>/<Your PPA URL> <source.changes>In my case it's:
$ dput ppa:johnliu55tw/ppa ../hello_2.10-2ubuntu2ppa2_source.changes- Note: Launchpad builds the pacakges onsite, and does not accept deb files!
You will receive an email telling you whether the package is successfully uploaded and accepted. Be sure to check for the email. If your upload failed, check Package upload errors chapter of launchpad help for common issues.
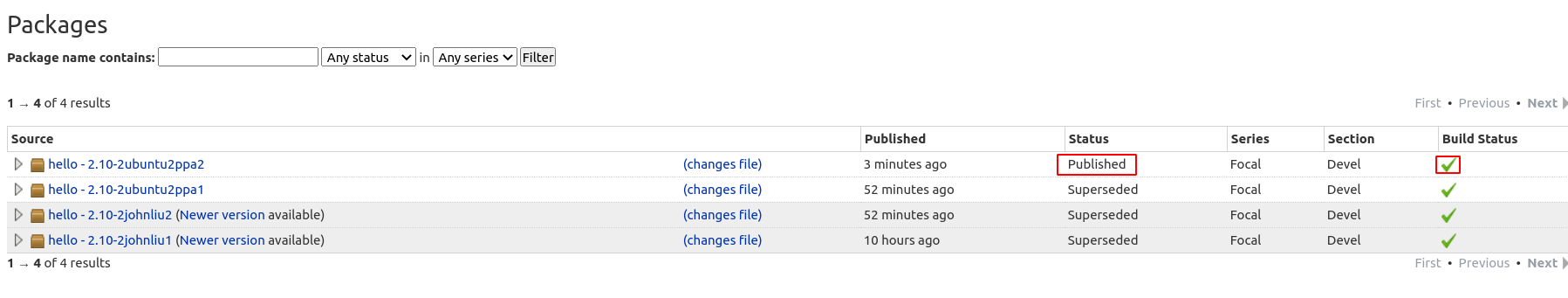
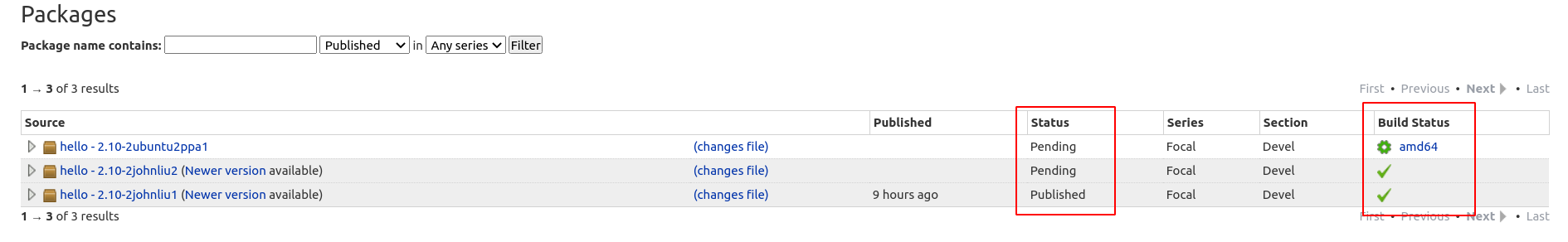
Notice that after it's uploaded, it takes some time for your source package to be built and published on Launchpad. Go to your PPA page, check the Status and Build Status of your package and make sure they are all finished.
- Note: Make sure your packages are built and published!
In order to install the package from your PPA, you have to add it to your system:
$ sudo add-apt-repository ppa:johnliu55tw/ppa
$ sudo apt-get updateThen you can install your package by apt. In my case I want to install
hello:
$ sudo apt install helloNotice that if your package's version does not supersede the official Ubuntu
version (i.e., your package is not newer), apt will install the official
package, not yours. See
https://help.launchpad.net/Packaging/PPA/BuildingASourcePackage#Versioning
for more about versioning.
Here are some issues and questions I have during the process.
I got an error when I try to run debuild -S -d -us -uc for the first time:
johnliu@johnliu-ubuntu-2004-vm:~/hello/hello-2.10$ debuild -S -d -us -uc
dpkg-buildpackage -us -uc -ui -S -d
dpkg-buildpackage: info: source package hello
dpkg-buildpackage: info: source version 2.10-2johnliu1
dpkg-buildpackage: info: source distribution focal
dpkg-buildpackage: info: source changed by John Liu <johnliu@johnliu-ubuntu-2004-vm>
dpkg-source --before-build .
debian/rules clean
dh clean
make: dh: Command not found
make: *** [debian/rules:3: clean] Error 127
dpkg-buildpackage: error: debian/rules clean subprocess returned exit status 2
debuild: fatal error at line 1182:
dpkg-buildpackage -us -uc -ui -S -d failed
The dh command is provided by package debhelper, but is not listed in
required package in the
Getting Set Up page.
I installed that package then it works. I installed Ubuntu in minimal setup,
not quite sure if it's related.
I got some error when I try to run dput for the first time:
Checking signature on .changes
gpg: /home/johnliu/repackage-htop/htop_2.2.0-2ubuntu1_source.changes: error 58: gpgme_op_verify
gpgme_op_verify: GPGME: No data
The file *.changes is not signed. I have to correct debian/changelog:
UNRELEASED->focal- User and email
Following the article
Fixing a bug in Ubuntu,
when I try to create a new patch using command edit-patch 99-new-patch, some
error occurred:
Normalizing patch path to 99-new-patch
Normalizing patch name to 99-new-patch.patch
No series file foundThe hello package does not have any patches so there's no
debian/patches/series. Need to use quilt new to initialize and
create a new patch.
johnliu@johnliu-ubuntu-2004-vm:~/hello/hello-2.10$ sudo add-apt-repository ppa:johnliu55tw/ppa
More info: https://launchpad.net/~johnliu55tw/+archive/ubuntu/ppa
Press [ENTER] to continue or Ctrl-c to cancel adding it.
Hit:1 http://tw.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu focal InRelease
Get:2 http://tw.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu focal-updates InRelease [111 kB]
Get:3 http://tw.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu focal-backports InRelease [98.3 kB]
Get:4 http://tw.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu focal amd64 Contents (deb) [40.9 MB]
Err:5 http://ppa.launchpad.net/johnliu55tw/ppa/ubuntu focal InRelease
403 Forbidden [IP: 91.189.95.83 80]
Get:6 http://security.ubuntu.com/ubuntu focal-security InRelease [107 kB]
Get:7 http://security.ubuntu.com/ubuntu focal-security i386 Contents (deb) [8,320 kB]
Get:8 http://tw.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu focal i386 Contents (deb) [32.2 MB]
Get:9 http://security.ubuntu.com/ubuntu focal-security amd64 Contents (deb) [16.6 MB]
Get:10 http://tw.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu focal-updates/main amd64 Packages [655 kB]
Get:11 http://tw.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu focal-updates/main i386 Packages [370 kB]
Get:12 http://tw.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu focal-updates/main amd64 DEP-11 Metadata [232 kB]
Get:13 http://tw.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu focal-updates amd64 Contents (deb) [20.4 MB]
Get:14 http://tw.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu focal-updates i386 Contents (deb) [11.0 MB]
Get:15 http://tw.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu focal-updates/main amd64 c-n-f Metadata [11.0 kB]
Get:16 http://tw.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu focal-updates/universe amd64 Packages [689 kB]
Get:17 http://tw.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu focal-updates/universe i386 Packages [512 kB]
Get:18 http://tw.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu focal-updates/universe amd64 DEP-11 Metadata [205 kB]
Get:19 http://tw.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu focal-updates/universe amd64 c-n-f Metadata [13.0 kB]
Get:20 http://tw.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu focal-updates/multiverse amd64 DEP-11 Metadata [2,468 B]
Get:21 http://tw.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu focal-backports amd64 Contents (deb) [7,720 B]
Get:22 http://tw.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu focal-backports i386 Contents (deb) [6,243 B]
Get:23 http://tw.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu focal-backports/universe amd64 DEP-11 Metadata [1,768 B]
Reading package lists... Done
E: Failed to fetch http://ppa.launchpad.net/johnliu55tw/ppa/ubuntu/dists/focal/InRelease 403 Forbidden [IP: 91.189.95.83 80]
E: The repository 'http://ppa.launchpad.net/johnliu55tw/ppa/ubuntu focal InRelease' is not signed.
N: Updating from such a repository can't be done securely, and is therefore disabled by default.
N: See apt-secure(8) manpage for repository creation and user configuration details.
You can see that when it's updating my PPA, it received 403 Forbidden.
Err:5 http://ppa.launchpad.net/johnliu55tw/ppa/ubuntu focal InRelease
403 Forbidden [IP: 91.189.95.83 80]
I googled and found this issue might be caused by the PPA has no package. I then realized receiving the "Accepted" email doesn't mean your package is ready to ship via PPA. You have to wait until it's built and published.
I ran apt update after it's built and published, then the PPA is updated
without any error.
The file's permission is 644 in the source, but after it's installed to
/usr/bin, it becomes 755. I've tested changing it to install the file to
/etc and the permission became 644, not 755. Maybe some rules automatically
changed the permission because I want it in /usr/bin? I wasn't able to find
documents so far.