In large enterprises, its not about how easy it is to build a new solution, but how easy it is to sustain, maintain, and scale a solution.
Notebooks may be the in-thing that every data scientist or data engineer, who is just getting started with the field, may use. Notebooks are a great tool for experimenting data analysis or project, but it is not designed as a scalable solution for production.
- Good for kaggle, MooCs
- Single notebook structure leads to Spaghetti Code and Big Ball of Mud
- Poor maintainability
- Poor scalability
- Poor testability
- Poor integrability
- Poor reusability
- In summary,
- Poor best practices for enterprise needs
- Kaggle, MooCs
- As a scratch pad
- Ad hoc analysis
- One time analysis
- Experiments
- Quick POC
- Team showcasing analysis results to others
But remember,
- Quick and easy to get started and begin prototyping with notebooks
- Transition to ‘coded with best practices’ with ease
- Get full features of IDE from integrated terminal, code debug, variable inspectors, tabbed environments, autocomplete, intellisense, etc.
- Natural workflows and integrations with SCM/Git
- Easy to build test scripts, integrate with CI/CD pipelines
- Uses battle tested SDLC practices with Object Oriented Principles
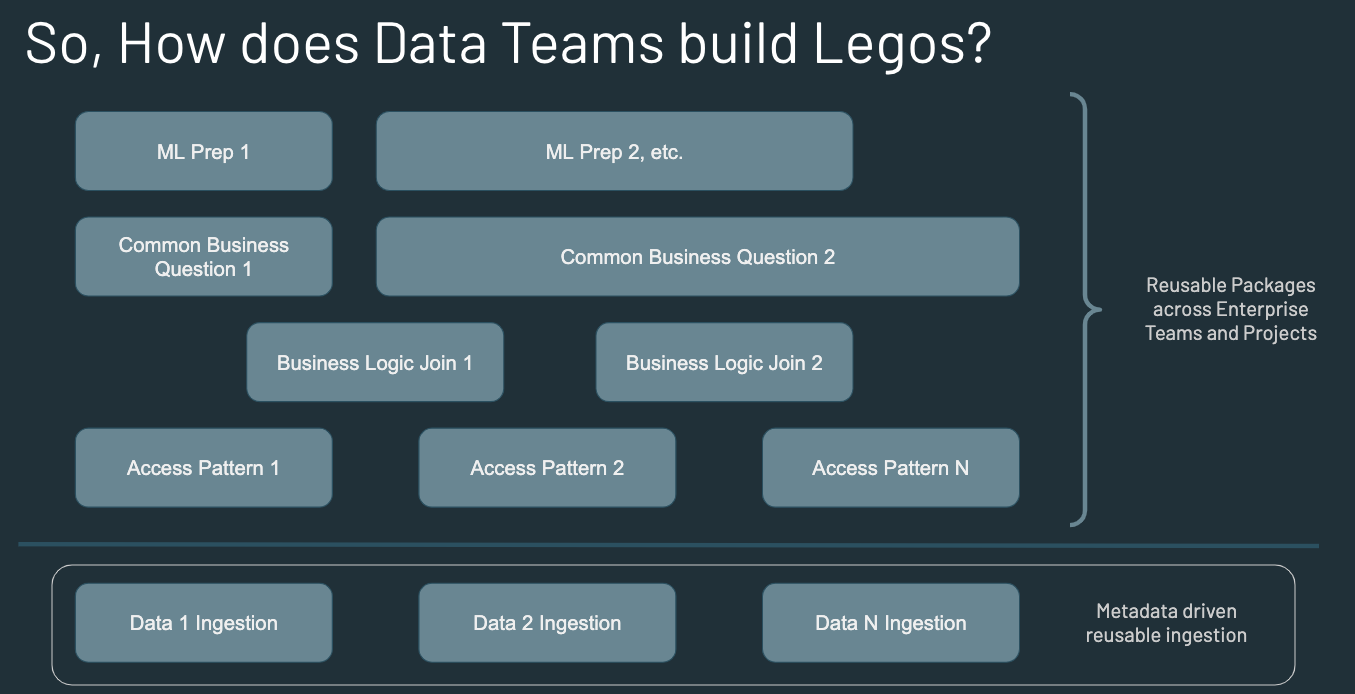
- Modular & Reusable package along with above benefits leads to macro productivity of Enterprise Data Teams that produce Sustainable & Scalable solutions
- Start with the general structure defined here. You can clone to get started.
example_project- main directory where notebooks and python files residesconfig- Make your project configurable and hostconfig.inienvandrequirements.yaml- Host python virtual env or preferably use conda to manage dedicated environment for each project.tests- Host test scriptsdocs- Host documentation of this project and package on how to use, extend, etc.buildanddist- To host files and artifacts generated while packagingsetup.py- Setup file for packagingpytest.ini- Pytest configurationsscheduler- Details or scripts on how this project is scheduled to run
- Setup a conda environment, and install any dependencies as needed.
- In the
example_projectdirectory start with ascratchordevnotebook to access and explore data. - As you develop small snippets of working code, organize them as functions, which can then be moved over as modules.
- Use relative reference to access newly created modules from notebook, while creating and testing new sections of the project.
- Continue above 2 steps interatively to add more features.
- If needed, create an entry python file that can take command line arguments to execute the project.
- As modules are developed, add test scripts in
testsdirectory. This will allow for easy and automated CICD process. - Update
requirements.yamlusing conda to ensure dependencies are captured prior to commit. - Use
setup.pyto setup on how to package the modules as a library, etc. - Host created artifacts within enterprise repo managers like artifactory or nexus to be accessed by other projects and teams with appropriate security measures. Also, use such tools to improve discoverability, etc.
- Repeat this process for different aspects of building the data science/engineering stack within the organization to have reproducible and reusable solutions.