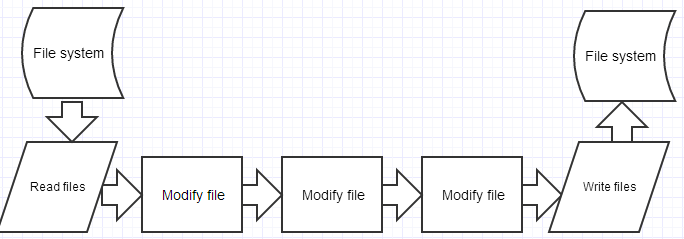
Gulp is an automation tool to help you streamline your build process and automate time-consuming tasks in a modular and clearly-controlled manner.
- Automation: Automation is Gulp's core concept. Instead of individually running linters, minifiers, and other build scripts, Gulp allows you to chain these together into a single process stream.
- Simplicity: Gulp has a "minimal API surface" -- you won't have to memorize a billion different methods in order to do what you want to do.
- Modularity: Instead of having one plugin that does many things, Gulp has many plugins that do one thing, allowing you to separate and pinpoint actions you want to have in your build process.
- Glob: A set of files compiled using a matching pattern, sort of like a RegExp but using the same patterns as a bash shell. "Like stars and stuff", say the Glob docs
- For example: the glob
'*.js', '!b*.js', 'bad.js'means "All the Javascript files except the ones that start withbbut includingglob.js. - And the glob
'client/templates/*.jade'is all thejadefiles in thetemplatesdirectory.
- For example: the glob
- Stream: Stream programming is a UNIX concept that describes a way of managing a control flow -- data (in the form of files or whatever else) is passed from one function to the next, being read or modified as it goes. You may have heard of Input/Output streams. Gulp works on this same concept. (Check out this stackoverflow answer to get more into streams.)
Gulp's API -- the methods that are available to use from Gulp -- is very light. There are only a few that you'll need to memorize.
gulp.task(name, fn)
- Registers the function with a name -- can also specify other task dependencies
- The task is available to the command line
gulp.run(tasks...)
- Accepts named tasks as arguments
- Runs them all with maximum concurrency
gulp.watch(glob, fn)
- Watches a glob for changes and runs when the file changes.
gulp.src(glob)
- Returns a file system glob and returns the files that match.
- The output can be piped to other streams.
gulp.dest(folder)
- Returns a writable stream that's saved to the specified folder.
gulp.src('./client/templates/*.jade')
// grabs a glob of jade files in the template directories
.pipe(jade())
// runs the jade method on all of the files
.pipe(gulp.dest('./build/templates'))
// saves that result in the build/templates folder
.pipe(minify())
// runs the minify function on the original post-jade-method glob of files
.pipe(gulp.dest('./build/minified_templates'));
// saves the minify result in the build/minified_templates folderHere's Gulp's official opinion of Grunt:
A six-line Gulp function can accomplish the same thing as a twenty-line Grunt file.
Webpack includes hot reloading but as a much steeper learning curve to really understand.