mlflow Demonstration
IMPORTANT: The master branch represents work-in-progress. Stable functionality are designated by
tags, e.g., v0.1.0, v0.2.0, etc, identified in
Releases section.
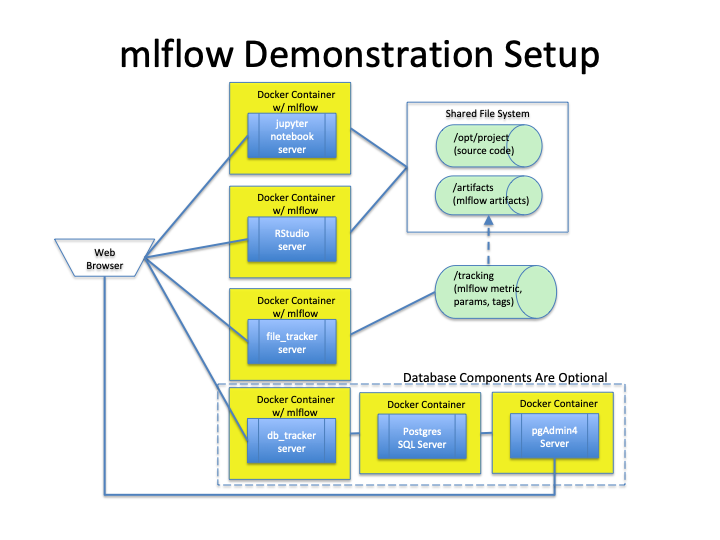
This repo demonstrates the use of the open source project mlflow, which is used to record and manage results of machine learning experiments. Docker containers provide the run-time environment for this demonstration.
Code used in this demonstration is based on these mflow examples:
examples/sklearn_elasticnet_wine
and examples/r_wine
Demonstration Environment
System Requirements
Work performed with Docker for Mac Version 2.0.0.3 (31259)
Environment Setup
Setup described in this section does not consider security requirements and is suitable only for demonstration purposes with non-sensitive data. Changes are required for any production deployment.
Set up local storage
- Clone repo to local computer. Note directory for the local repo, e.g.,
/home/userid/mlflow_demo - Create directory to hold mlflow server tracking data and artifacts, e.g.,
/home/userid/mlflow_server. Within this
directory create these subdirectories
/home/userid/mlflow_server/tracking
/home/userid/mlflow_server/artifacts
/home/userid/mlflow_server/postgres/postgres/data
/home/userid/mlflow_server/postgres/postgres/admin
Setup required environment variables
- Change working directory to
run_demo - Update contents of
./setup_environment_variablesto specify values for the required environment variables.
MLFLOW_VERSION
MLFLOW_VERSION_TO_INSTALL
MFLOW_DEMO_DIRECTORY
MLFLOW_TRACKING_DIRECTORY
MLFLOW_TRACKER_URL
Specify version of mlflow package. See example below.
###
# Set up environment variables to control building and
# running demonstration mlflow Docker containers
###
# mlflow version to install
export MLFLOW_VERSION=0.9.0
# directory containing demonstration source code
export MLFLOW_DEMO_DIRECTORY=/path/to/directory/for/local/repo
# directory to hold mlflow tracking and artifacts
export MLFLOW_TRACKING_DIRECTORY=/path/to/directory/for/tracking-artifacts
# mflow tracking server URL: file_tracker or db_tracker
# use MLFLOW_TRACKER_URL=http://file_tracker:5000 for file-based tracker server
# use MLFLOW_TRACKER_URL=http://db_tracker:5001 for Postgres SQL database tracker server
export MLFLOW_TRACKER_URL=http://db_tracker:5001
###
# EXAMPLES
# MLFLOW_VERSION_TO_INSTALL="mlflow" Current version in PyPi
# MLFLOW_VERSION_TO_INSTALL="mlflow==${MLFLOW_VERSION}" Specific version from PyPi
# MLFLOW_VERSION_TO_INSTALL="git+https://github.com/mlflow/mlflow.git@vx.y.z#egg=mlflow" specific version from github
###
# uncomment following to install mlflow from pypi
#export MLFLOW_VERSION_TO_INSTALL="mlflow==${MLFLOW_VERSION}"
# uncomment following to install mlflow from github
export MLFLOW_VERSION_TO_INSTALL="git+https://github.com/mlflow/mlflow.git@v${MLFLOW_VERSION}#egg=mlflow" specific version from github
Build the required mlflow Docker images
-
After updating
setup_environment_variables, execute following command to set
environment variables:. ./setup_environment_variables -
Run the following command to initially build the required Docker images.
bash ./build_images
Note: On a MacbookPro with 16GB RAM, it takes 10 to 13 minutes for the initial build of the images.
Postgres SQL database tracker components
Database Docker components:
Web-based Postgres Administration Tool
Perform only one of the following two tasks.
-
To disable the database tracker components, open
docker-compose.ymlfile and find this string# TO DISABLE DATABASE TRACKER COMPONENTS REMOVEand follow instructions.
Skip the next step. -
To make use of the database tracker components, run the following command to pull PostgresSQL database related images from dockerhub.com
bash ./pull_images
Note: This will take about one to two minutes to pull down the PostgresSQL images.
Start demonstration containers
After building the Docker images, navigate to ./run_demo. Ensure the required
environment variables are defined by running . ./setup_environment_variables.
- To start the Docker containers for the demonstration environment:
docker-compose up --detach
- To stop the Docker containers:
docker-compose down
Connecting to containers
Open a browser and enter the following URL for the respective service.
- Jupyter Notebook Python Container:
http://0.0.0.0:8888 - RStudio Container:
http://0.0.0.0:8787 - mlflow file-based tracking server:
http://0.0.0.0:5000 - mfllow PostgresSQL-based tracking server:
http://0.0.0.0:5001 - Postgres SQL pgAdmin Server:
http://0.0.0.0:80, login id:mlflow@gmail.com, passwordpgadmin4
Demonstration Programs
- mlflow_demo1.ipynb: Jupyter notebook runs a single machine learning experiment.
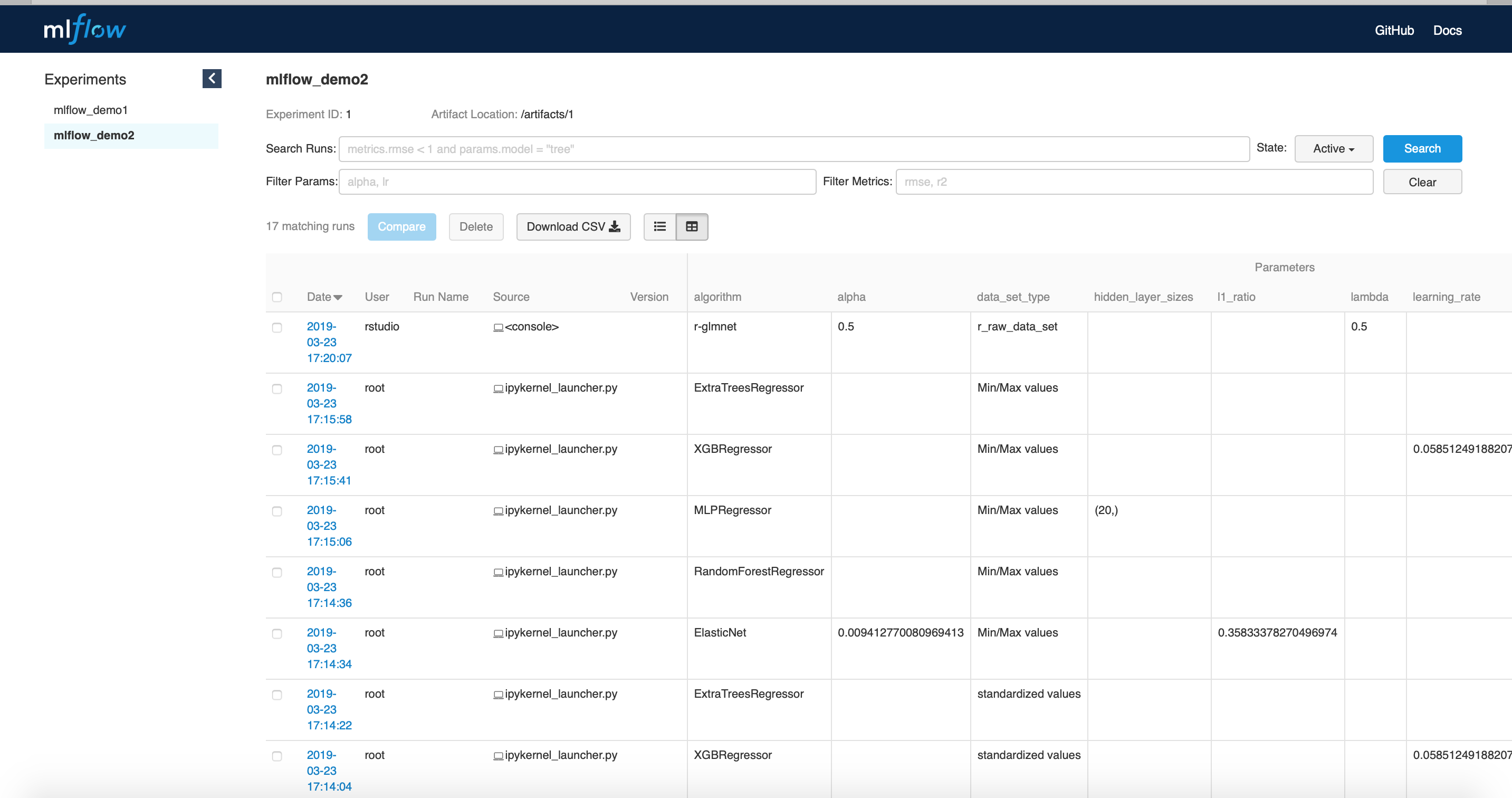
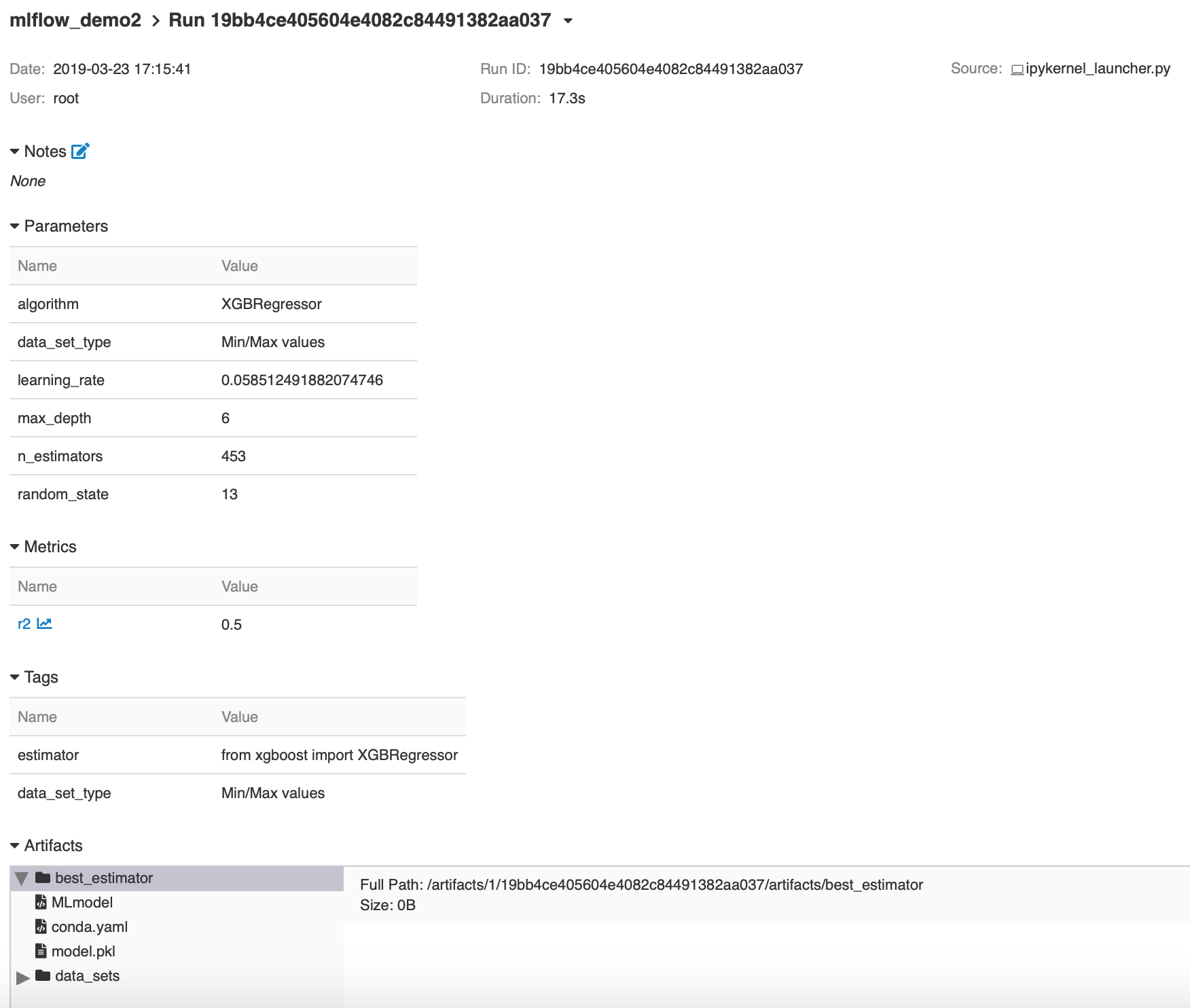
- mlflow_demo2.ipynb: Jupyter notebook performs hyper-parameter optimization.
- mlflow_demo2_r.Rmd: Rmarkdown notebook runs a single machine learning experiment.
- mlflow_api_demo.ipynb: Jupyter notebook creates pandas dataframe from mlflow experiment results.
- mlflow_reproducibility.ipynb: Jupyter notebook that creates results from an earlier experiment.