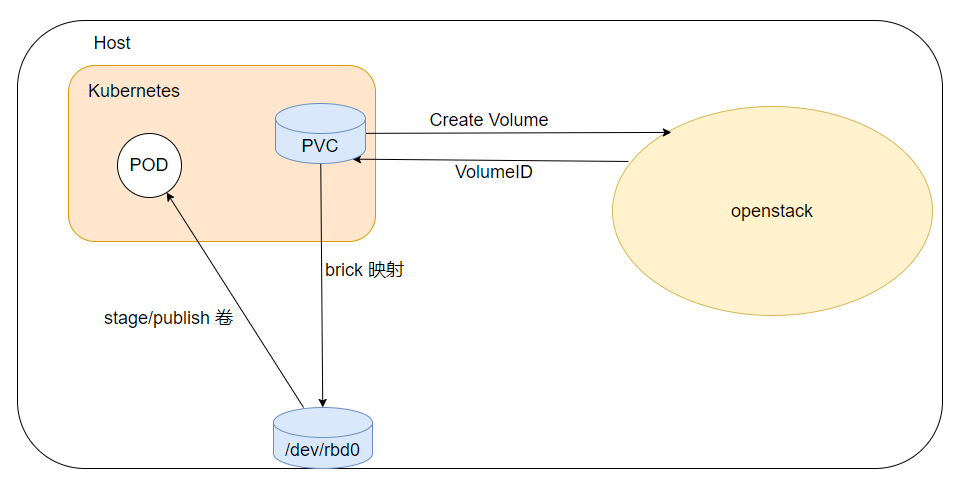
The Cinder CSI Driver is a CSI Specification compliant driver used by Container Orchestrators to manage the lifecycle of OpenStack Cinder Volumes.
The Cinder Metal CSI driver let openstack create cinder volume, map to the host, become the host a block device, and mount the block device to the pod.
You can either use the manifests under manifests file to deploy the cinder metal csi driver.
cinder-metal-csi accepts the following command-line arguments:
- --nodeid
- The kubernetes node IP.
- --endpoint
- The endpoint of the gRPC server agents will use to connect to this CSI plugin, typically a local unix socket.
- The manifests default this to unix:///csi/csi.sock, which is supplied via the CSI_ENDPOINT environment variable.
- --cloud-config
- The path to a driver config file. The format of this file is specified in Driver Config.
- The manifests default this to /etc/config/cloud.conf, which is supplied via the CLOUD_CONFIG environment variable.
For Driver configuration, parameters must be passed via configuration file specified in $CLOUD_CONFIG environment variable.
The following sections are supported in configuration file.
- username Keystone username. If you are using Keystone application credential, this option is not required.
- password Keystone user password. If you are using Keystone application credential, this option is not required.
- user-domain-name Keystone user domain name.
- project-domain-name Keystone project domain name.
- tenant-name Keystone project name.
- auth-url Keystone service URL.
- region Keystone region name.
- endpoint-type Specify which type of endpoint to use from the service catalog. If not set, public endpoints are used.
- auth-strategy Auth strategy. Support keystone and noauth mode.
- cinder-listen-addr Noauth mode config the cinder service listen addr.
- node-volume-attach-limit To configure maximum volumes that can be attached to the node. Its default value is 256
- lvm-volume-type The lvm volume type name, default lvm. Consistent with the type parameters in the dynamic storage class.
- ceph-volume-type The ceph volume type name, default rbd. Consistent with the type parameters in the dynamic storage class.
- local-volume-type The local volume type name, default local. Consistent with the type parameters in the dynamic storage class.
All the manifests required for the deployment of the plugin are found at manifests/
Configuration file specified in $CLOUD_CONFIG is passed to cinder CSI driver via kubernetes secret.
To create a secret:
- Encode your
$ClOUD_CONFIGfile content using base64.
$ base64 -w 0 $CLOUD_CONFIG
-
Update
cloud.confconfiguration inmanifests/csi-secret-cinderplugin.yamlfile by using the result of the above command. -
Create the secret.
$ kubectl create -f manifests/csi-secret-cinderplugin.yaml
-
If the cinder backend storage type is ceph, you need to config ceph config file and ceph keyring file.
-
Encode your
$CEPH_CONFIGfile content using base64.$ base64 -w 0 $CEPH_CONFIG -
Update
ceph.confconfiguration inmanifests/cinder-config.yamlfile by using the result of the above command. -
Create the configmap.
$ kubectl create -f manifests/cinder-config.yaml -
Encode your
$CEPH_ADMIN_KEYRINGfile content using base64.$ base64 -w 0 $CEPH_ADMIN_KEYRING -
Update
keyconfiguration inmanifests/cinder-volume-rbd-keyring.yamlfile by using the result of the above command. -
Create the Secrets.
$ kubectl create -f manifests/cinder-volume-rbd-keyring.yaml
Once the secret is created, Controller Plugin and Node Plugins can be deployed using respective manifests.
$ kubectl -f manifests/ apply
This creates a set of cluster roles, cluster role bindings, and statefulsets etc to communicate with openstack(cinder). For detailed list of created objects, explore the yaml files in the directory. You should make sure following similar pods are ready before proceed:
$ kubectl get pods -n kube-system
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
cinder-metal-csi-controller-plugin-7ff586b8f5-fvb88 6/6 Running 0 2d22h
cinder-metal-csi-nodeplugin-58mwv 4/4 Running 0 2d22h
To get information about CSI Drivers running in a cluster
kubectl get csidrivers.storage.k8s.io
NAME ATTACHREQUIRED PODINFOONMOUNT STORAGECAPACITY TOKENREQUESTS REQUIRESREPUBLISH MODES AGE
cinder.metal.csi true true false <unset> false Persistent 2d22h
For dynamic provisoning , create StorageClass, PersistentVolumeClaim and pod to consume it. Checkout rbd volume definition fore reference.
Notes: Add the type parameter to create the storage class.
kubectl apply -f example/nginx-rbd.yamlView the PVC status, Check the pvc is in Bound state which claims one volume from cinder
$ kubectl get pvc
NAME STATUS VOLUME CAPACITY ACCESS MODES STORAGECLASS AGE
cinder-pvc-rbd Bound pvc-444feb52-3e38-4a7f-962f-0f23de10b7a9 2Gi RWO cinder-metal-csi-rbd 3s
$ cinder list
+--------------------------------------+-----------+------------------------------------------+------+-------------+----------+-------------+
| ID | Status | Name | Size | Volume Type | Bootable | Attached to |
+--------------------------------------+-----------+------------------------------------------+------+-------------+----------+-------------+
| fcb80e1b-5525-4bea-a552-443f73a97ca1 | in-use | pvc-444feb52-3e38-4a7f-962f-0f23de10b7a9 | 2 | rbd | false | None |
+--------------------------------------+-----------+------------------------------------------+------+-------------+----------+-------------+
To Check the volume created and attached to the pod
$ ls /dev/rbd2
/dev/rbd2
$ mount |grep rbd2
/dev/rbd2 on /var/lib/kubelet/plugins/kubernetes.io/csi/pv/pvc-444feb52-3e38-4a7f-962f-0f23de10b7a9/globalmount type ext4 (rw,relatime,stripe=16)
/dev/rbd2 on /var/lib/kubelet/pods/4a9dae22-2e0f-4813-aaea-4376d934d3c7/volumes/kubernetes.io~csi/pvc-444feb52-3e38-4a7f-962f-0f23de10b7a9/mount type ext4 (rw,relatime,stripe=16)
Then try to add a file in the pod's mounted position (in our case, /var/lib/www/html)
$ kubectl exec -it nginx-rbd bash
kubectl exec [POD] [COMMAND] is DEPRECATED and will be removed in a future version. Use kubectl exec [POD] -- [COMMAND] instead.
root@nginx-rbd:/# df -Th
Filesystem Type Size Used Avail Use% Mounted on
overlay overlay 549G 29G 499G 6% /
tmpfs tmpfs 64M 0 64M 0% /dev
tmpfs tmpfs 252G 0 252G 0% /sys/fs/cgroup
/dev/sdx1 ext4 549G 29G 499G 6% /etc/hosts
shm tmpfs 64M 0 64M 0% /dev/shm
/dev/rbd2 ext4 2.0G 24K 1.9G 1% /var/lib/www/html
tmpfs tmpfs 504G 12K 504G 1% /run/secrets/kubernetes.io/serviceaccount
tmpfs tmpfs 252G 0 252G 0% /proc/acpi
tmpfs tmpfs 252G 0 252G 0% /proc/scsi
tmpfs tmpfs 252G 0 252G 0% /sys/firmware
root@nginx-rbd:/# touch /var/lib/www/html/index.html
root@nginx-rbd:/# exitNext, make sure the pod is deleted so that the persistent volume will be freed
$ kubectl delete pod nginx-rbd
$ cinder list
+--------------------------------------+-----------+------------------------------------------+------+-------------+----------+-------------+
| ID | Status | Name | Size | Volume Type | Bootable | Attached to |
+--------------------------------------+-----------+------------------------------------------+------+-------------+----------+-------------+
| fcb80e1b-5525-4bea-a552-443f73a97ca1 | available | pvc-444feb52-3e38-4a7f-962f-0f23de10b7a9 | 2 | rbd | false | |
+--------------------------------------+-----------+------------------------------------------+------+-------------+----------+-------------+