spectrum
Spectrum is a library containing signal analysis routines with a focus towards spectral routines.
Status
Documentation
The documentation can be found here.
Building Spectrum
CMakeThis library can be built using CMake. For instructions see Running CMake.
FPM can also be used to build this library using the provided fpm.toml.
fpm buildThe SPECTRUM library can be used within your FPM project by adding the following to your fpm.toml file.
[dependencies]
spectrum = { git = "https://github.com/jchristopherson/spectrum" }External Libraries
The FPLOT library depends upon the following libraries.
Spectrum contains a large selection of signal processing routines. The following examples illustrate some of the spectral capabilities in addition to some of the filtering options available.
Example 1
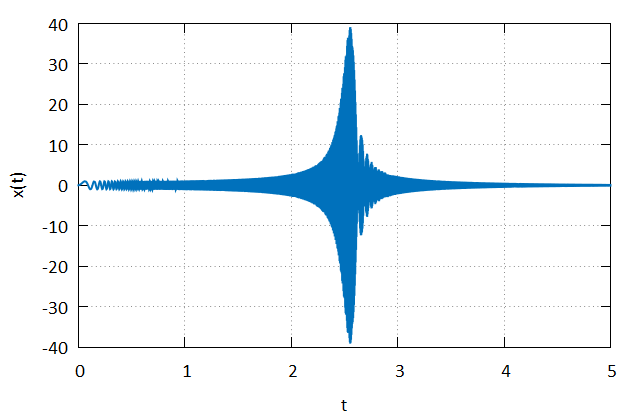
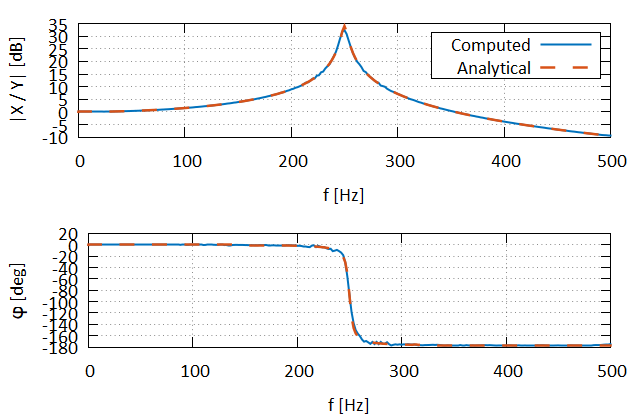
This example illustrates the calculation of a single-input/single-output (SISO) transfer function from a signal stored in a CSV file. This example utilizes the fplot library for plotting and the fortran-csv-module library for reading the CSV file.
program example
use iso_fortran_env
use spectrum
use fplot_core
use csv_module
implicit none
! Parameters
integer(int32), parameter :: winsize = 1024
integer(int32), parameter :: nxfrm = winsize / 2 + 1
real(real64), parameter :: pi = 2.0d0 * acos(0.0d0)
complex(real64), parameter :: j = (0.0d0, 1.0d0)
real(real64), parameter :: zeta = 1.0d-2
real(real64), parameter :: fn = 2.5d2
real(real64), parameter :: wn = 2.0d0 * pi * fn
! Local Variables
logical :: ok
integer(int32) :: i
real(real64) :: dt, fs, df, freq(nxfrm)
real(real64), allocatable, dimension(:) :: t, x, y, mag, phase, maga, pa
complex(real64), allocatable, dimension(:) :: tf, s, tfa
type(hamming_window) :: win
type(csv_file) :: file
! Plot Variables
type(multiplot) :: mplt
type(plot_2d) :: plt, plt1, plt2
type(plot_data_2d) :: pd, pda
class(plot_axis), pointer :: xAxis, yAxis
class(legend), pointer :: lgnd
! Import time history data
call file%read("files/chirp.csv", status_ok = ok)
call file%get(1, t, ok)
call file%get(2, y, ok)
call file%get(3, x, ok)
! Determine the sample rate
dt = t(2) - t(1)
fs = 1.0d0 / dt
print 100, "Sample Rate: ", fs, " Hz"
! Compute the transfer function
win%size = winsize
tf = siso_transfer_function(win, y, x)
! Compute the frequency, magnitude, and phase
df = frequency_bin_width(fs, winsize)
freq = (/ (df * i, i = 0, nxfrm - 1) /)
mag = 2.0d1 * log10(abs(tf)) ! Convert to dB
phase = atan2(aimag(tf), real(tf))
call unwrap(phase, pi / 2.0d0)
! Compare to the analytical solution
s = j * (2.0d0 * pi * freq)
tfa = (2.0d0 * zeta * wn * s + wn**2) / &
(s**2 + 2.0d0 * zeta * wn * s + wn**2)
maga = 2.0d1 * log10(abs(tfa))
pa = atan2(aimag(tfa), real(tfa))
call unwrap(phase, pi / 2.0d0)
! Set up the plot objects
call plt%initialize()
xAxis => plt%get_x_axis()
yAxis => plt%get_y_axis()
! Plot the time signal
call xAxis%set_title("t")
call yAxis%set_title("x(t)")
call pd%define_data(t, x)
call pd%set_line_width(2.0)
call plt%push(pd)
call plt%draw()
! Plot the transfer function
call mplt%initialize(2, 1)
call plt1%initialize()
call plt2%initialize()
! Plot the magnitude component
xAxis => plt1%get_x_axis()
yAxis => plt1%get_y_axis()
lgnd => plt1%get_legend()
call xAxis%set_title("f [Hz]")
call xAxis%set_autoscale(.false.)
call xAxis%set_limits(0.0d0, 5.0d2)
call yAxis%set_title("|X / Y| [dB]")
call lgnd%set_is_visible(.true.)
call pd%define_data(freq, mag)
call pd%set_name("Computed")
call plt1%push(pd)
call pda%define_data(freq, maga)
call pda%set_name("Analytical")
call pda%set_line_style(LINE_DASHED)
call pda%set_line_width(2.5)
call plt1%push(pda)
! Plot the phase component
xAxis => plt2%get_x_axis()
yAxis => plt2%get_y_axis()
call xAxis%set_title("f [Hz]")
call xAxis%set_autoscale(.false.)
call xAxis%set_limits(0.0d0, 5.0d2)
call yAxis%set_title("{/Symbol f} [deg]")
call pd%define_data(freq, phase * 1.8d2 / pi)
call plt2%push(pd)
call pda%define_data(freq, pa * 1.8d2 / pi)
call plt2%push(pda)
call mplt%set(1, 1, plt1)
call mplt%set(2, 1, plt2)
call mplt%draw()
! Formatting
100 format(A, F6.1, A)
end programThis example produces the following plots.
Example 2
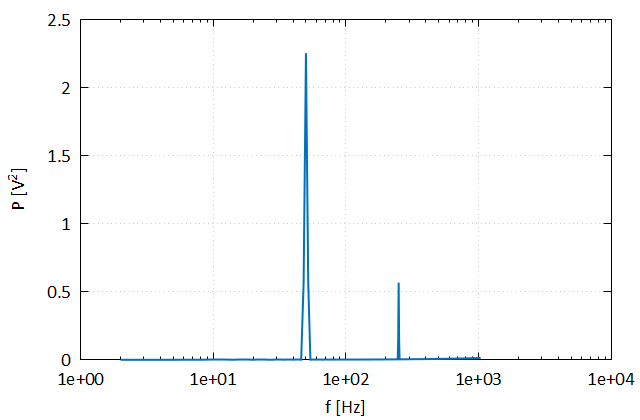
This example illustrates the calculation of the power-spectral-density (PSD) of a signal. This example also utilizes the fplot library for plotting.
program example
use iso_fortran_env
use spectrum
use fplot_core
implicit none
! Parameters
integer(int32), parameter :: npts = 20000
integer(int32), parameter :: winsize = 1024
real(real64), parameter :: sample_rate = 2.048d3
real(real64), parameter :: freq1 = 5.0d1
real(real64), parameter :: freq2 = 2.5d2
real(real64), parameter :: phase1 = 0.0d0
real(real64), parameter :: phase2 = 4.5d1
real(real64), parameter :: pi = 2.0d0 * acos(0.0d0)
real(real64), parameter :: amp1 = 1.5d0
real(real64), parameter :: amp2 = 7.5d-1
! Local Variables
integer(int32) :: i, nxfrm
real(real64) :: df, dt, t(npts), x(npts)
real(real64), allocatable, dimension(:) :: pwr, freq
type(hann_window) :: win
! Plot Variables
type(plot_2d) :: plt
type(plot_data_2d) :: pd
class(plot_axis), pointer :: xAxis, yAxis
! Build the signal - assume units of V
dt = 1.0d0 / sample_rate
t = (/ (dt * i, i = 0, npts - 1) /)
x = amp1 * sin(2.0d0 * pi * freq1 * t - pi * phase1 / 1.8d2) + &
amp2 * sin(2.0d0 * pi * freq2 * t - pi * phase2 / 1.8d2)
! Define the window
win%size = winsize
! Compute the PSD
pwr = psd(win, x)
! Build a corresponding array of frequency values
df = frequency_bin_width(sample_rate, winsize)
allocate(freq(size(pwr)))
freq = (/ (df * i, i = 0, size(pwr) - 1) /)
! Plot the spectrum
call plt%initialize()
xAxis => plt%get_x_axis()
yAxis => plt%get_y_axis()
call xAxis%set_title("f [Hz]")
call yAxis%set_title("P [V^{2}]")
call xAxis%set_is_log_scaled(.true.)
call xAxis%set_use_default_tic_label_format(.false.)
call xAxis%set_tic_label_format("%0.0e")
call pd%define_data(freq, pwr)
call pd%set_line_width(2.0)
call plt%push(pd)
call plt%draw()
end programThis example produces the following plots.
Example 3
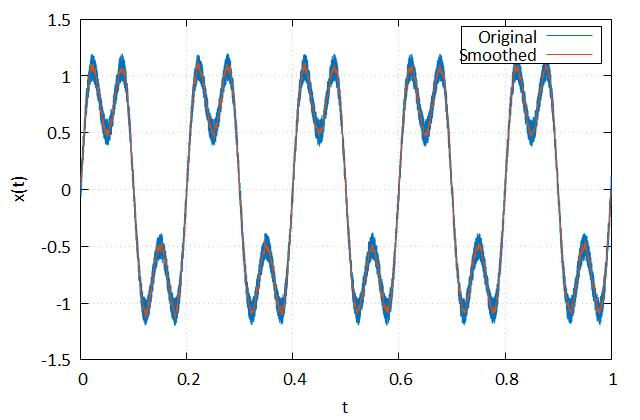
This example highlights some of the filtering capabilities; specifically, Gaussian filtering.
program example
use iso_fortran_env
use spectrum
use fplot_core
implicit none
! Parameters
integer(int32), parameter :: npts = 10000
real(real64), parameter :: pi = 2.0d0 * acos(0.0d0)
real(real64), parameter :: f1 = 5.0d0
real(real64), parameter :: f2 = 1.5d1
real(real64), parameter :: alpha = 3.0d0
! Local Variables
integer(int32) :: i, k
real(real64) :: t(npts), x(npts), y(npts)
! Plot Variables
type(plot_2d) :: plt
type(plot_data_2d) :: d1, d2
class(plot_axis), pointer :: xAxis, yAxis
class(legend), pointer :: lgnd
! Build the signal
t = linspace(0.0d0, 1.0d0, npts)
call random_number(x)
x = 0.25d0 * (x - 0.5d0) + sin(2.0d0 * pi * f1 * t) + &
0.5 * sin(2.0d0 * pi * f2 * t)
! Apply the filter
! - alpha = 3
! - kernel size = 21
y = gaussian_filter(x, 3.0d0, 21)
! Plot the results
call plt%initialize()
xAxis => plt%get_x_axis()
yAxis => plt%get_y_axis()
lgnd => plt%get_legend()
call xAxis%set_title("t")
call yAxis%set_title("x(t)")
call lgnd%set_is_visible(.true.)
call d1%define_data(t, x)
call d1%set_name("Original")
call plt%push(d1)
call d2%define_data(t, y)
call d2%set_name("Smoothed")
call plt%push(d2)
call plt%draw()
end programThis example produces the following plots.
References
- Welch, P.D. (1967). The Use of Fast Fourier Transform for the Estimation of Power Spectra: A Method Based on Time Averaging Over Short, Modified Periodograms. IEEE Transactions on Audio and Electroacoustics, AU-15 (2): 70-73.
- Stoica, Petre, and Randolph Moses. Spectral Analysis of Signals. Upper Saddle River, NJ: Prentice Hall, 2005.
- William H. Press, Saul A. Teukolsky, William T. Vetterling, and Brian P. Flannery. 2007. Numerical Recipes 3rd Edition: The Art of Scientific Computing (3rd. ed.). Cambridge University Press, USA.
- Millioz, Fabien & Martin, Nadine. (2011). Circularity of the STFT and Spectral Kurtosis for Time-Frequency Segmentation in Gaussian Environment. Signal Processing, IEEE Transactions on. 59. 515 - 524. 10.1109/TSP.2010.2081986.
- Wikipedia Contributors. (2022, February 9). Welch’s method. Wikipedia; Wikimedia Foundation. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Welch%27s_method
- Spectral density. (2023, April 9). Wikipedia. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Spectral_density#Cross-spectral_density
- Wikipedia Contributors. (2019, April 12). Short-time Fourier transform. Wikipedia; Wikimedia Foundation. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Short-time_Fourier_transform
- Window function. (2020, December 12). Wikipedia. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Window_function
- Wikipedia Contributors. (2019, March 22). Gaussian filter. Wikipedia; Wikimedia Foundation. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Gaussian_filter
- Selesnick Andilker Bayram, I. (2010). Total Variation Filtering. https://eeweb.engineering.nyu.edu/iselesni/lecture_notes/TV_filtering.pdf
- Unavane, T., & Panse. (2015). New Method for Online Frequency Response Function Estimation Using Circular Queue. INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL for RESEARCH in EMERGING SCIENCE and TECHNOLOGY, 2. https://ijrest.net/downloads/volume-2/issue-6/pid-ijrest-26201530.pdf