DataTalksClub
cd ML_Zoomcamp_Midterm_Project
pip install -r requirements.txt
python -m streamlit run ./src/app.pyYou will get this as a output:
Local URL: http://localhost:8501
Network URL: http://192.168.1.137:8501If you don't want to run the app locally, you can also check this DEMO
To install the app, you need to have Docker, and Docker-Compose installed on your system. You have a perfect installation guide in this link
Open a terminal or command prompt, navigate to the directory containing Dockerfile
docker build -t your_image_name:tag .and then
docker run -p 4000:80 your_image_name:tagCustomer segmentation is a pivotal strategy employed across various industries, enabling businesses to understand their diverse customer base more comprehensively Christy et al. (2021). In the field of banking, where customer needs and behaviors vary widely, effective segmentation holds huge significance. By grouping customers with similar attributes, banks can tailor their services and marketing efforts, ultimately enhancing customer satisfaction and loyalty Ernawati et al. 2021.
Techniques like RFM (Recency, Frequency, Monetary) analysis simplify this complexity, offering deep insights into how often customers engage, how much they spend, and when they last made a transaction. RFM's power shines brightly when predicting Customer Lifetime Value (CLV), essentially foretelling the revenue a customer is likely to generate over their relationship with a business Wu, J. et al. (2020).
In this machine learning Midterm project, a bank harnessed the power of RFM and advanced algorithms to forecast CLV. Armed with a dataset encompassing a million rows, featuring vital customer information such as date of birth, transaction timestamps, transaction amounts, and account balances, the bank embarked on creating a robust ML model. This project aims to perform a model to predict customer lifetime value accurately. By doing so, the bank aimed to deepen its understanding of customers, optimize marketing strategies, and offer tailored financial products and services. This strategic approach not only enhances customer experiences but also augments the bank's profitability, solidifying its position in an increasingly competitive market.
- Develop a machine learning model to accurately predict customer lifetime value (CLV) for a dataset from an Indian bank to optimize marketing strategies, enhance customer experiences, and improve profitability for the bank.
- Cleanse and prepare the dataset, perform exploratory data analysis (EDA) to gain insights into customer behavior
- Build a robust predictive model for customer lifetime value by using Scikit-Learn and appropriate machine learning algorithms.
- Experiment with different algorithms, feature combinations, and hyperparameters to enhance the model's accuracy
- Visualize customer segments, CLV predictions, and key metrics to facilitate a comprehensive understanding of the model's insights.
- Leverage Microsoft PowerBI and Streamlit to create interactive visualizations and dashboards.
In the dynamic field of modern banking, the Indian banking sector confronts a pivotal challenge: comprehensively understanding its diverse clientele. India, with its diverse populace encompassing various languages, traditions, and financial habits, presents a unique tapestry for segmentation. The existing banking segmentation methods often lack the cultural depth required to resonate with the diverse Indian consumer base. This research aims to bridge this gap by developing a sophisticated segmentation framework that not only considers the typical socio-economic variables but also delves deeply into cultural nuances and regional preferences.
Dataset is about Customer demographics and transactions data from an Indian Bank. This dataset consists of 1 Million+ transaction by over 800K customers for a bank in India. The data contains information such as - customer age (DOB), location, gender, account balance at the time of the transaction, transaction details, transaction amount, etc. Based on the features of this dataset we can develop a customer segmentation based in groups on shared traits.
| Tool | Explanation | Icon |
|---|---|---|
Google Colab |
Develop entire solution, including EDA and model training | |
Microsoft PowerQuery |
ETL process, cleaning, and type formatting | |
Python 3.10 |
Main programming language and dependencies (Pandas, Numpy, Matplotlib, Plotly) | |
Scikit-Learn |
Machine Learning library used for model creation | |
Microsoft PowerBI |
Visualization tool for interactive dashboards | |
Miniconda |
Environment library for isolating the system | |
Streamlit |
Web-based tool for sharing model implementation |
| Features | Target |
|---|---|
account_balance |
RF_segment |
transaction_amount |
|
gender_int |
|
R_score |
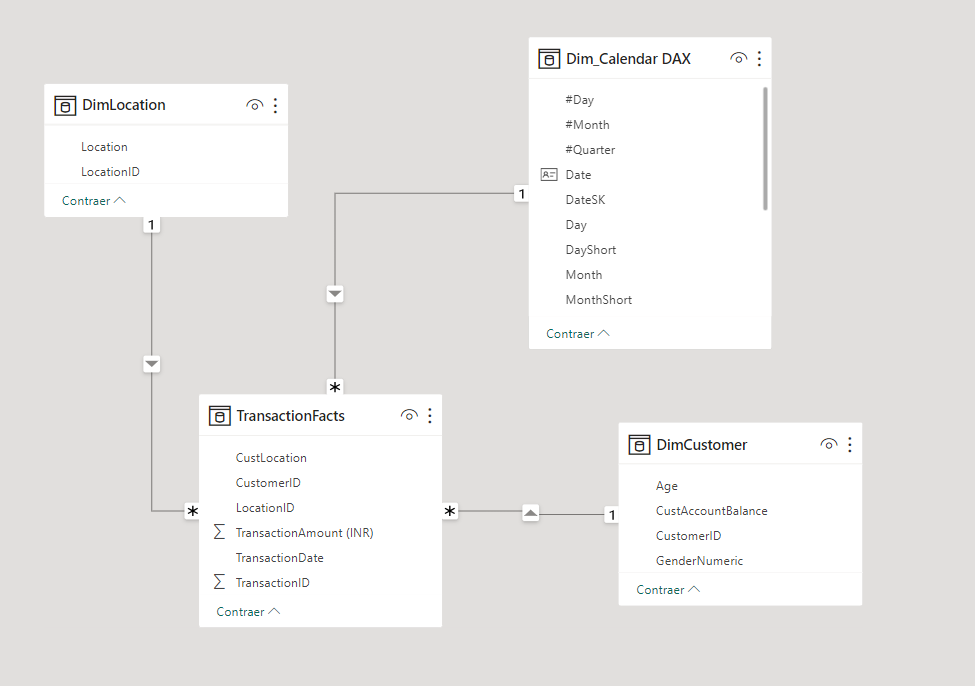
Data Model was performed in PowerBI and it could be found here
All related to Exploratory Data Analysis can be found thin this notebook
XGBoost is a powerful machine learning algorithm renowned for its efficiency and accuracy in various data science tasks, especially in the realm of supervised learning. It belongs to the ensemble learning methods and is based on decision trees. Moreover, XGBClassifier is an implementation of XGBoost specifically designed for classification tasks. This method is used to train a predictive model that can classify input data points into different categories or segments based on their features.
Therefore, XGBClassifier is particularly valuable for customer segmentation projects due to its ability to handle nonlinear relationships and capture intricate patterns within customer data. By identifying nuanced patterns in customer behavior, businesses can tailor marketing strategies, improve customer engagement, and enhance overall customer satisfaction.
hyperparameters = {
'n_estimators': [100, 300, 400],
'max_depth': [3, 4, 5],
'learning_rate': [0.1, 1, 0.01],
'subsample': [0.7, 0.9],
} model = xgb.XGBClassifier(max_depth=10,
learning_rate=0.1,
n_stimators = 400,
objective='multi:softmax',
subsample = 0.7,
num_classes=3)
with open('./src/model/xgboost_model.pkl', 'wb') as model_file:
pickle.dump(model, model_file) In this project, an approach to data preprocessing was adopted, entailing rigorous data cleansing and transformation techniques executed through the PowerQuery editor within PowerBI. Simultaneously, comprehensive Exploratory Data Analysis (EDA) was conducted, enabling a nuanced understanding of the dataset's intricacies. Subsequently, a judicious feature selection process was undertaken, aligned with the observed data behavior.
Advanced machine learning methodologies, notably the XGBOOST classifier, were leveraged to enhance predictive accuracy. Systematic feature engineering encompassed the calculation of essential metrics, including Recency, Frequency, Recency Score, and Frequency Score. Hyperparameter optimization strategies were meticulously implemented to refine the model's performance.
The resultant model exhibited notable prowess, enabling precise customer segmentation with an impressive accuracy of 82%, precision of 85%, and a recall score of 83%. However, it is imperative to acknowledge a limitation: the inability to estimate Customer Lifetime Value (CLV) due to the absence of Return on Investment (ROI) metrics within the dataset. Specifically, the dataset lacked transaction fee metrics and profit-related data from banking entities, essential for accurate CLV estimation.
Looking forward to the capstone project, a more sophisticated segmentation approach is anticipated. Techniques such as K-Nearest Neighbors (KNN) or K-means clustering will be explored, moving beyond percentile-based divisions (25th, 50th, and 75th percentiles). Moreover, enriching the dataset with additional features, such as transaction fees, educational background, and customer occupation, is planned. These enhancements aim to elevate the granularity and depth of analysis, providing a more nuanced understanding of customer behavior and fostering robust predictive models.
- Ernawati, E., Baharin, S. S. K., & Kasmin, F. (2021). A review of data mining methods in RFM-based customer segmentation. In Journal of Physics: Conference Series (Vol. 1869, No. 1, p. 012085). IOP Publishing.
- Wu, J., Shi, L., Lin, W. P., Tsai, S. B., Li, Y., Yang, L., & Xu, G. (2020). An empirical study on customer segmentation by purchase behaviors using a RFM model and K-means algorithm. Mathematical Problems in Engineering, 2020, 1-7.
- Christy, A. J., Umamakeswari, A., Priyatharsini, L., & Neyaa, A. (2021). RFM ranking–An effective approach to customer segmentation. Journal of King Saud University-Computer and Information Sciences, 33(10), 1251-1257.
let
Origen = Csv.Document(File.Contents("C:\Users\javie\Documents\ML_Zoomcamp_Midterm_Project\dataset\bank_transactions.csv"),[Delimiter=",", Columns=9, Encoding=1252, QuoteStyle=QuoteStyle.None]),
#"Encabezados promovidos" = Table.PromoteHeaders(Origen, [PromoteAllScalars=true]),
#"Tipo cambiado" = Table.TransformColumnTypes(#"Encabezados promovidos",{{"TransactionID", type text}, {"CustomerID", type text}, {"CustomerDOB", type text}, {"CustGender", type text}, {"CustLocation", type text}, {"CustAccountBalance", Int64.Type}, {"TransactionDate", type date}, {"TransactionTime", Int64.Type}, {"TransactionAmount (INR)", Int64.Type}}),
#"Tipo cambiado1" = Table.TransformColumnTypes(#"Tipo cambiado",{{"CustomerDOB", type date}}),
#"Errores quitados" = Table.RemoveRowsWithErrors(#"Tipo cambiado1", {"CustomerDOB"}),
#"Antigüedad insertada" = Table.AddColumn(#"Errores quitados", "Antigüedad", each Date.From(DateTime.LocalNow()) - [CustomerDOB], type duration),
#"Columnas con nombre cambiado" = Table.RenameColumns(#"Antigüedad insertada",{{"Antigüedad", "Age"}}),
#"Total de años calculados" = Table.TransformColumns(#"Columnas con nombre cambiado",{{"Age", each Duration.TotalDays(_) / 365, type number}}),
#"Redondeado a la baja" = Table.TransformColumns(#"Total de años calculados",{{"Age", Number.RoundDown, Int64.Type}}),
#"Filas filtradas" = Table.SelectRows(#"Redondeado a la baja", each [Age] >= 0 and [Age] < 75),
#"Valor reemplazado" = Table.ReplaceValue(#"Filas filtradas","F","Female",Replacer.ReplaceText,{"CustGender"}),
#"Valor reemplazado1" = Table.ReplaceValue(#"Valor reemplazado","M","Male",Replacer.ReplaceText,{"CustGender"}),
#"Columna condicional agregada" = Table.AddColumn(#"Valor reemplazado1", "AgeNumeric", each if [CustGender] = "Male" then 0 else 1),
#"Columnas con nombre cambiado1" = Table.RenameColumns(#"Columna condicional agregada",{{"AgeNumeric", "GenderNumeric"}}),
#"Columnas quitadas" = Table.RemoveColumns(#"Columnas con nombre cambiado1",{"CustomerDOB", "CustGender", "TransactionTime"}),
#"Filas filtradas1" = Table.SelectRows(#"Columnas quitadas", each [CustLocation] <> null and [CustLocation] <> ""),
#"Filas filtradas2" = Table.SelectRows(#"Filas filtradas1", each [CustAccountBalance] <> null and [CustAccountBalance] <> ""),
#"Texto extraído después del delimitador" = Table.TransformColumns(#"Filas filtradas2", {{"TransactionID", each Text.AfterDelimiter(_, "T"), type text}}),
#"Columnas reordenadas" = Table.ReorderColumns(#"Texto extraído después del delimitador",{"TransactionID", "TransactionDate", "CustomerID", "TransactionAmount (INR)", "CustAccountBalance", "Age", "GenderNumeric", "CustLocation"}),
#"Conservar filas superiores" = Table.FirstN(#"Columnas reordenadas",587657),
#"Tipo cambiado2" = Table.TransformColumnTypes(#"Conservar filas superiores",{{"TransactionID", Int64.Type}}),
#"Texto extraído después del delimitador1" = Table.TransformColumns(#"Tipo cambiado2", {{"CustomerID", each Text.AfterDelimiter(_, "C"), type text}}),
#"Tipo cambiado3" = Table.TransformColumnTypes(#"Texto extraído después del delimitador1",{{"CustomerID", Int64.Type}}),
#"Columnas quitadas1" = Table.RemoveColumns(#"Tipo cambiado3",{"CustAccountBalance", "Age", "GenderNumeric"})
in
#"Columnas quitadas1"let
Origen = Csv.Document(File.Contents("C:\Users\javie\Documents\ML_Zoomcamp_Midterm_Project\dataset\bank_transactions.csv"),[Delimiter=",", Columns=9, Encoding=1252, QuoteStyle=QuoteStyle.None]),
#"Encabezados promovidos" = Table.PromoteHeaders(Origen, [PromoteAllScalars=true]),
#"Tipo cambiado" = Table.TransformColumnTypes(#"Encabezados promovidos",{{"TransactionID", type text}, {"CustomerID", type text}, {"CustomerDOB", type text}, {"CustGender", type text}, {"CustLocation", type text}, {"CustAccountBalance", Int64.Type}, {"TransactionDate", type date}, {"TransactionTime", Int64.Type}, {"TransactionAmount (INR)", Int64.Type}}),
#"Tipo cambiado1" = Table.TransformColumnTypes(#"Tipo cambiado",{{"CustomerDOB", type date}}),
#"Errores quitados" = Table.RemoveRowsWithErrors(#"Tipo cambiado1", {"CustomerDOB"}),
#"Antigüedad insertada" = Table.AddColumn(#"Errores quitados", "Antigüedad", each Date.From(DateTime.LocalNow()) - [CustomerDOB], type duration),
#"Columnas con nombre cambiado" = Table.RenameColumns(#"Antigüedad insertada",{{"Antigüedad", "Age"}}),
#"Total de años calculados" = Table.TransformColumns(#"Columnas con nombre cambiado",{{"Age", each Duration.TotalDays(_) / 365, type number}}),
#"Redondeado a la baja" = Table.TransformColumns(#"Total de años calculados",{{"Age", Number.RoundDown, Int64.Type}}),
#"Filas filtradas" = Table.SelectRows(#"Redondeado a la baja", each [Age] >= 0 and [Age] < 75),
#"Valor reemplazado" = Table.ReplaceValue(#"Filas filtradas","F","Female",Replacer.ReplaceText,{"CustGender"}),
#"Valor reemplazado1" = Table.ReplaceValue(#"Valor reemplazado","M","Male",Replacer.ReplaceText,{"CustGender"}),
#"Columna condicional agregada" = Table.AddColumn(#"Valor reemplazado1", "AgeNumeric", each if [CustGender] = "Male" then 0 else 1),
#"Columnas con nombre cambiado1" = Table.RenameColumns(#"Columna condicional agregada",{{"AgeNumeric", "GenderNumeric"}}),
#"Columnas quitadas" = Table.RemoveColumns(#"Columnas con nombre cambiado1",{"CustomerDOB", "CustGender", "TransactionTime"}),
#"Filas filtradas1" = Table.SelectRows(#"Columnas quitadas", each [CustLocation] <> null and [CustLocation] <> ""),
#"Filas filtradas2" = Table.SelectRows(#"Filas filtradas1", each [CustAccountBalance] <> null and [CustAccountBalance] <> ""),
#"Texto extraído después del delimitador" = Table.TransformColumns(#"Filas filtradas2", {{"TransactionID", each Text.AfterDelimiter(_, "T"), type text}}),
#"Columnas reordenadas" = Table.ReorderColumns(#"Texto extraído después del delimitador",{"TransactionID", "TransactionDate", "CustomerID", "TransactionAmount (INR)", "CustAccountBalance", "Age", "GenderNumeric", "CustLocation"}),
#"Conservar filas superiores" = Table.FirstN(#"Columnas reordenadas",587657),
#"Tipo cambiado2" = Table.TransformColumnTypes(#"Conservar filas superiores",{{"TransactionID", Int64.Type}}),
#"Columnas quitadas1" = Table.RemoveColumns(#"Tipo cambiado2",{"TransactionID", "TransactionDate", "CustLocation"}),
#"Duplicados quitados" = Table.Distinct(#"Columnas quitadas1", {"CustomerID"}),
#"Duplicados quitados1" = Table.Distinct(#"Duplicados quitados", {"CustomerID"}),
#"Texto extraído después del delimitador1" = Table.TransformColumns(#"Duplicados quitados1", {{"CustomerID", each Text.AfterDelimiter(_, "C"), type text}}),
#"Tipo cambiado3" = Table.TransformColumnTypes(#"Texto extraído después del delimitador1",{{"CustomerID", Int64.Type}}),
#"Duplicados quitados2" = Table.Distinct(#"Tipo cambiado3", {"CustomerID"})
in
#"Duplicados quitados2"