Robust and effective logging for Python 2 and 3.
- Documentation: https://logzero.readthedocs.io
- GitHub: https://github.com/metachris/logzero
- Easy logging to console and/or (rotating) file.
- Provides a fully configured standard Python logger object.
- No dependencies (except on Windows colorama for color output)
- Pretty formatting, including level-specific colors in the console.
- Windows color output supported by colorama
- Robust against str/bytes encoding problems, works with all kinds of character encodings and special characters.
- Multiple loggers can write to the same logfile (also across multiple Python files).
- Global default logger with logzero.logger and custom loggers with logzero.setup_logger(..).
- Compatible with Python 2 and 3.
- All contained in a single file.
- Licensed under the MIT license.
- Heavily inspired by the Tornado web framework.
from logzero import logger
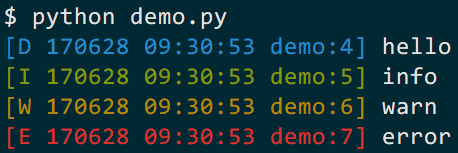
logger.debug("hello")
logger.info("info")
logger.warn("warn")
logger.error("error")
# This is how you'd log an exception
try:
raise Exception("this is a demo exception")
except Exception as e:
logger.exception(e)Adding a rotating logfile is that easy:
import logzero
from logzero import logger
# Setup rotating logfile with 3 rotations, each with a maximum filesize of 1MB:
logzero.logfile("/tmp/rotating-logfile.log", maxBytes=1e6, backupCount=3)
# Log messages
logger.info("This log message goes to the console and the logfile")Here are more examples which show how to use logfiles, custom formatters and setting a minimum loglevel:
import logging
import logzero
from logzero import logger
# This log message goes to the console
logger.debug("hello")
# Set a minimum log level
logzero.loglevel(logging.INFO)
# Set a logfile (all future log messages are also saved there)
logzero.logfile("/tmp/logfile.log")
# You can also set a different loglevel for the file handler
logzero.logfile("/tmp/logfile.log", loglevel=logging.ERROR)
# Set a rotating logfile (replaces the previous logfile handler)
logzero.logfile("/tmp/rotating-logfile.log", maxBytes=1000000, backupCount=3)
# Disable logging to a file
logzero.logfile(None)
# Set a custom formatter
formatter = logging.Formatter('%(name)s - %(asctime)-15s - %(levelname)s: %(message)s');
logzero.formatter(formatter)
# Log some variables
logger.info("var1: %s, var2: %s", var1, var2)Take a look at the documentation for more information and examples:
- Documentation: https://logzero.readthedocs.io.
Install logzero with pip:
$ pip install -U logzeroIf you don't have pip installed, this Python installation guide can guide you through the process.
Alternatively, if you use the Anaconda distribution:
$ conda config --add channels conda-forge
$ conda install logzeroYou can also install logzero from the public Github repo:
$ git clone https://github.com/metachris/logzero.git
$ cd logzero
$ python setup.py installOn openSUSE you can install the current version from repos: python2-logzero, python3-logzero. In the newest openSUSE release you can install it with zypper: sudo zypper in python2-logzero.
Note: this project is using pytest. CI is run with Github actions.
# Activate virtualenv
$ python3 -m venv venv
$ . venv/bin/activate
# Install main and dev dependencies
$ pip install -e .
$ pip install -r requirements_dev.txt
# Run the tests
$ make test
# Run the linter
$ make lint
# Generate the docs (will auto-open in Chrome)
$ make docsSee the changelog here: https://github.com/metachris/logzero/blob/master/HISTORY.rst
All kinds of feedback and contributions are welcome.
- Create an issue
- Create a pull request
- @metachris // chris@linuxuser.at