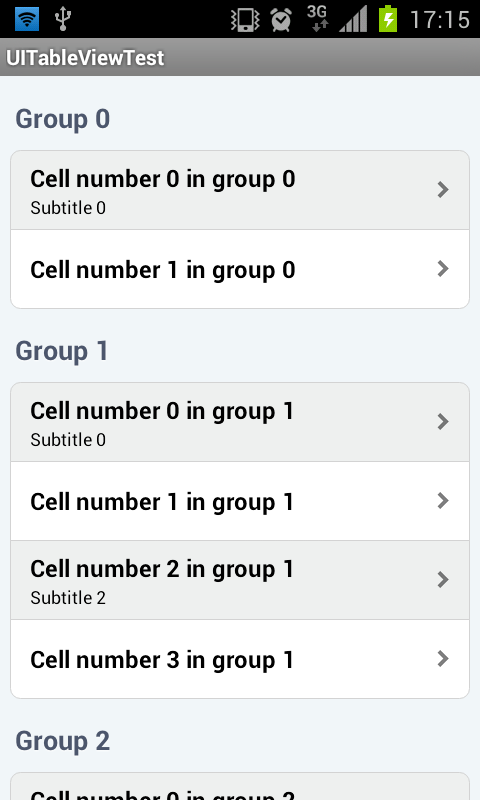
UITableView4Android is an Android library providing a customized ListView with the look & field and behavior of UITableView on iOS.
Some companies are asking for mobile applications that must have the same appearance both on Android and iOS. And of course, iOS is almost always the version to fit... List views are one the most difficult component to adapt on Android because of corners and borders to set correctly.
Add the UITableView in your layout :
<fr.days.android.uitableview.view.UITableView
android:id="@+id/listView"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_alignParentLeft="true"
android:layout_alignParentTop="true" >
</fr.days.android.uitableview.view.UITableView>This UITableView is a sub-class of Android ListView and need an implementation of UITableViewAdapter.
class SimpleUITableViewAdapter extends UITableViewAdapter {
private int[] color_line1_default;
private int[] color_line2_default;
private int[] color_line1_pressed;
private int[] color_line2_pressed;
public SimpleUITableViewAdapter() {
// Prepare two sets of colors for odd and even lines
color_line1_default = new int[] { getResources().getColor(R.color.base_start_color_line1_default), getResources().getColor(R.color.base_end_color_line1_default) };
color_line2_default = new int[] { getResources().getColor(R.color.base_start_color_line2_default), getResources().getColor(R.color.base_end_color_line2_default) };
color_line1_pressed = new int[] { getResources().getColor(R.color.base_start_color_line1_pressed), getResources().getColor(R.color.base_end_color_line1_pressed) };
color_line2_pressed = new int[] { getResources().getColor(R.color.base_start_color_line2_pressed), getResources().getColor(R.color.base_end_color_line2_pressed) };
}
@Override
public int numberOfGroups() {
return 4;
}
@Override
public int numberOfRows(int group) {
return (group + 1) * 2;
}
@Override
public UITableHeaderItem headerItemForGroup(Context context, IndexPath indexPath) {
return new UITableHeaderItem("Group " + indexPath.getGroup());
}
@Override
public UITableCellItem cellItemForRow(Context context, IndexPath indexPath) {
String title = "Cell number " + indexPath.getRow() + " in group " + indexPath.getGroup();
String subtitle = (indexPath.getRow() % 2 == 0) ? "Subtitle " + indexPath.getRow() : null;
return new UITableCellItem(title, subtitle);
}
@Override
public UITableHeaderView headerViewForGroup(Context context, IndexPath indexPath, UITableHeaderItem headerItem, UITableHeaderView convertView) {
UITableHeaderView headerView;
if (convertView == null) {
// If the recycled view is null, we just creating one
headerView = new UITableHeaderView(context, indexPath);
} else {
headerView = (UITableHeaderView) convertView;
}
headerView.setTitle(headerItem.title);
return headerView;
}
@Override
public UITableCellView cellViewForRow(Context context, IndexPath indexPath, UITableCellItem cellItem, UITableCellView convertView) {
UITableCellView cellView;
if (convertView == null) {
// If the recycled view is null, we just creating one with cell's commons parameters
cellView = new UITableCellView(context, indexPath);
cellView.setMinimumHeight(80);
cellView.setAccessory(AccessoryType.DISCLOSURE);
} else {
cellView = (UITableCellView) convertView;
}
cellView.setTitle(cellItem.title);
cellView.setSubtitle(cellItem.subtitle);
// Set alternated background color
if (indexPath.getRow() % 2 == 0) {
cellView.setBackgroundColor(color_line1_default, color_line1_pressed);
} else {
cellView.setBackgroundColor(color_line2_default, color_line2_pressed);
}
return cellView;
}
}Some listeners are avaible to handle click and long click on cells, headers and accessory's cells. Let's implement them all on our SimpleUITableViewAdapter.
@Override
public void onCellClick(IndexPath indexPath) {
Toast.makeText(getApplicationContext(), "Cell clicked : " + indexPath, 1000).show();
}
@Override
public boolean onCellLongClick(IndexPath indexPath) {
Toast.makeText(getApplication(), "Cell long clicked : " + indexPath, 1000).show();
return indexPath.getRow() % 2 == 0; // Consume the long click one row out of two
}
@Override
public void onCellAccessoryClick(IndexPath indexPath) {
Toast.makeText(getApplication(), "Cell accessory clicked : " + indexPath, 1000).show();
}
@Override
public void onHeaderClick(IndexPath indexPath) {
Toast.makeText(getApplicationContext(), "Header clicked : " + indexPath, 1000).show();
}
@Override
public boolean onHeaderLongClick(IndexPath indexPath) {
Toast.makeText(getApplicationContext(), "Header long clicked : " + indexPath, 1000).show();
return indexPath.getGroup() % 2 == 0; // Consume the long click one row out of two
}Now, we have an implementation of UITableViewAdapter with all listeners added. It only remains to configure the UITableView.
SimpleUITableViewAdapter tableViewAdapter = new SimpleUITableViewAdapter();
tableView = (UITableView) findViewById(R.id.listView);
tableView.setAdapter(tableViewAdapter);
tableView.setOnCellClickListener(tableViewAdapter);
tableView.setOnCellLongClickListener(tableViewAdapter);
tableView.setOnCellAccessoryClickListener(tableViewAdapter);
tableView.setOnHeaderClickListener(tableViewAdapter);
tableView.setOnHeaderLongClickListener(tableViewAdapter);And here is the result.