- The OAuth 2.0 authorization framework enables a third-party application to obtain limited access to an HTTP service, either
- on behalf of a resource owner by orchestrating an approval interaction between the resource owner and the HTTP service, or
- by allowing the third-party application to obtain access on its own behalf.
- Replaces and obsoletes the OAuth 1.0 protocol described in RFC 5849.
- OAuth defines four roles:
- resource owner
- An entity capable of granting access to a protected resource. When the resource owner is a person, it is referred to as an end-user.
- resource server
- The server hosting the protected resources, capable of accepting and responding to protected resource requests using access tokens.
- client
- An application making protected resource requests on behalf of the resource owner and with its authorization.
- authorization server
- Server that authenticates the resource owner and issues access tokens after getting proper authorization.
- May be the same server as the resource server or a separate entity.
- A single authorization server may issue access tokens accepted by multiple resource servers.
- resource owner
- The OAuth 2.0 Authorization Framework supports several different flows (or grants).
- Flow are ways of retrieving an Access Token.
- In the case of machine-to-machine authorization, the Client is also the Resource Owner, so no end-user authorization is needed.
- E.g., a cron job that uses an API to import information to a database.
- See Client Credentials Flow.
- Use Authorization Code Flow.
- Considered the safest choice since the Access Token is passed directly to the web server hosting the Client, without going through the user's web browser and risking exposure.
- Use Resource Owner Password Credentials Grant when redirect-based flows (like the Authorization Code Flow) are not possible.
- The end-user is asked to fill in credentials (username/password), typically using an interactive form.
- There are 2 grant options:
- Authorization Code Flow with Proof Key for Code Exchange (PKCE)
- Recommended for most cases.
- Access Token is not exposed on the client side, and this flow can return Refresh Tokens.
- Implicit Flow with Form Post.
- If your SPA doesn't need an Access Token.
- Authorization Code Flow with Proof Key for Code Exchange (PKCE)
- Use Authorization Code Flow with Proof Key for Code Exchange (PKCE).
- "The OAuth 2.0 Authorization Framework." Ietf.org, 2023, www.ietf.org/rfc/rfc6749.txt. Accessed 30 Sept. 2023.
- Auth0. "Which OAuth 2.0 Flow Should I Use?" Auth0 Docs, 2023, auth0.com/docs/get-started/authentication-and-authorization-flow/which-oauth-2-0-flow-should-i-use. Accessed 30 Sept. 2023.
- Involves exchanging an authorization code for a token.
- Can only be used for confidential applications (such as regular web applications) because the application's authentication methods are included in the exchange and must be kept secure.
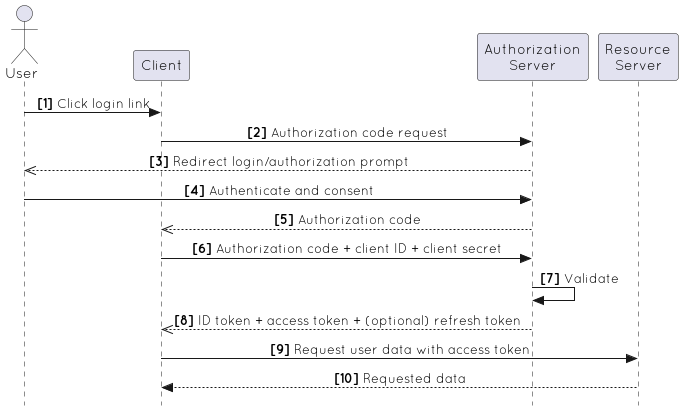
- A user tries to access the application (the client).
- The client application calls the authorization server's
authorizeendpoint. - The authorization server responds with the redirect URI to the login and authorization prompt.
- The user authenticates and gives their consent to provide permissions to the application.
- The authorization server issues an authorization code.
- The client application requests authentication to the token endpoint using the authorization code, application's client ID, and application's credentials such as client secret or Private Key JWT.
- The authorization server validates the authorization code, client ID, and application's credentials.
- The authorization server returns the ID token and access token (and optionally, a refresh token).
- The client application requests protected resources from the resource server with the access token.
- The resource server validates the token and responds with the requested resources.
- Auth0. "Authorization Code Flow." Auth0 Docs, 2023, auth0.com/docs/get-started/authentication-and-authorization-flow/authorization-code-flow. Accessed 30 Sept. 2023.
- "Authorization Code Flow." Cloudentity.com, 2023, cloudentity.com/developers/basics/oauth-grant-types/authorization-code-flow/. Accessed 1 Oct. 2023.