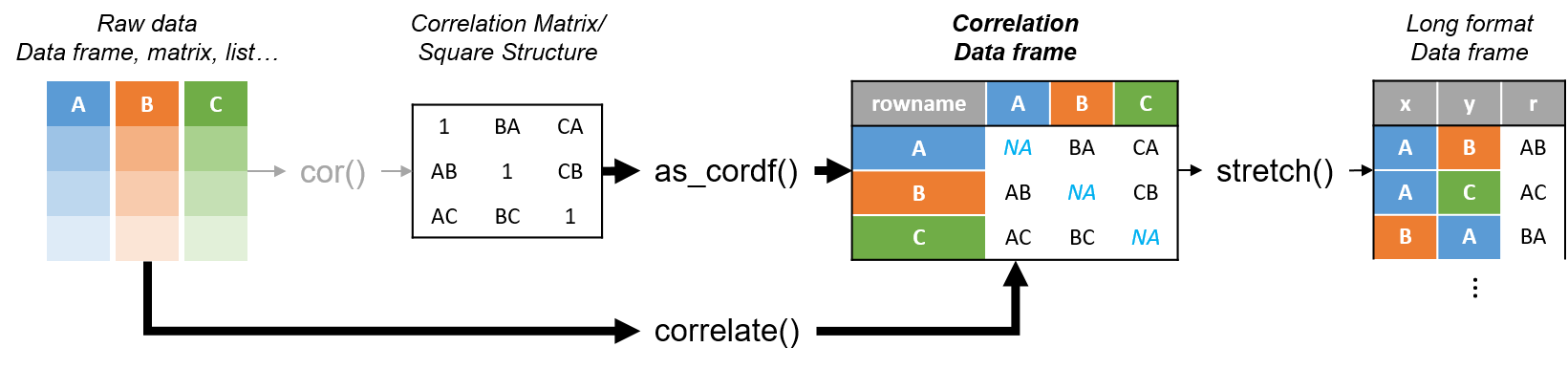
corrr is a package for exploring correlations in R. It focuses on creating and working with data frames of correlations (instead of matrices) that can be easily explored via corrr functions or by leveraging tools like those in the tidyverse. This, along with the primary corrr functions, is represented below:
You can install:
- the latest released version from CRAN with
install.packages("corrr")- the latest development version from github with
install.packages("devtools") # run this line if devtools is not installed
devtools::install_github("drsimonj/corrr")Using corrr typically starts with correlate(), which acts like the base correlation function cor(). It differs by defaulting to pairwise deletion, and returning a correlation data frame (cor_df) of the following structure:
- A
tblwith an additional class,cor_df - An extra "rowname" column
- Standardised variances (the matrix diagonal) set to missing values (
NA) so they can be ignored.
The corrr API is designed with data pipelines in mind (e.g., to use %>% from the magrittr package). After correlate(), the primary corrr functions take a cor_df as their first argument, and return a cor_df or tbl (or output like a plot). These functions serve one of three purposes:
Internal changes (cor_df out):
shave()the upper or lower triangle (set to NA).rearrange()the columns and rows based on correlation strengths.
Reshape structure (tbl or cor_df out):
focus()on select columns and rows.stretch()into a long format.
Output/visualisations (console/plot out):
fashion()the correlations for pretty printing.rplot()the correlations with shapes in place of the values.network_plot()the correlations in a network.
library(MASS)
library(corrr)
set.seed(1)
# Simulate three columns correlating about .7 with each other
mu <- rep(0, 3)
Sigma <- matrix(.7, nrow = 3, ncol = 3) + diag(3)*.3
seven <- mvrnorm(n = 1000, mu = mu, Sigma = Sigma)
# Simulate three columns correlating about .4 with each other
mu <- rep(0, 3)
Sigma <- matrix(.4, nrow = 3, ncol = 3) + diag(3)*.6
four <- mvrnorm(n = 1000, mu = mu, Sigma = Sigma)
# Bind together
d <- cbind(seven, four)
colnames(d) <- paste0("v", 1:ncol(d))
# Insert some missing values
d[sample(1:nrow(d), 100, replace = TRUE), 1] <- NA
d[sample(1:nrow(d), 200, replace = TRUE), 5] <- NA
# Correlate
x <- correlate(d)
class(x)
#> [1] "cor_df" "tbl_df" "tbl" "data.frame"
x
#> # A tibble: 6 × 7
#> rowname v1 v2 v3 v4 v5
#> <chr> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl>
#> 1 v1 NA 0.70986371 0.709330652 0.0001947192 0.021359764
#> 2 v2 0.7098637068 NA 0.697411266 -0.0132575510 0.009280530
#> 3 v3 0.7093306516 0.69741127 NA -0.0252752456 0.001088652
#> 4 v4 0.0001947192 -0.01325755 -0.025275246 NA 0.421380212
#> 5 v5 0.0213597639 0.00928053 0.001088652 0.4213802123 NA
#> 6 v6 -0.0435135083 -0.03383145 -0.020057495 0.4424697437 0.425441795
#> # ... with 1 more variables: v6 <dbl>As a tbl, we can use functions from data frame packages like dplyr, tidyr, ggplot2:
library(dplyr)
# Filter rows by correlation size
x %>% filter(v1 > .6)
#> # A tibble: 2 × 7
#> rowname v1 v2 v3 v4 v5
#> <chr> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl>
#> 1 v2 0.7098637 NA 0.6974113 -0.01325755 0.009280530
#> 2 v3 0.7093307 0.6974113 NA -0.02527525 0.001088652
#> # ... with 1 more variables: v6 <dbl>corrr functions work in pipelines (cor_df in; cor_df or tbl out):
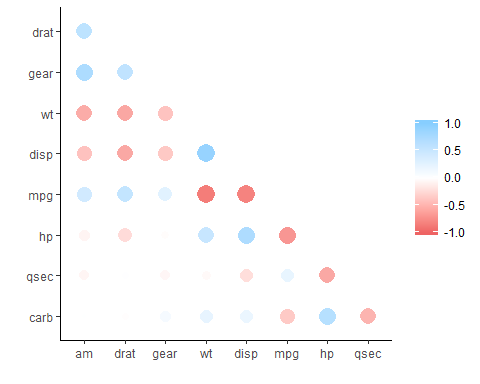
x <- datasets::mtcars %>%
correlate() %>% # Create correlation data frame (cor_df)
focus(-cyl, -vs, mirror = TRUE) %>% # Focus on cor_df without 'cyl' and 'vs'
rearrange() %>% # rearrange by correlations
shave() # Shave off the upper triangle for a clean result
#>
#> Correlation method: 'pearson'
#> Missing treated using: 'pairwise.complete.obs'
fashion(x)
#> rowname am drat gear wt disp mpg hp qsec carb
#> 1 am
#> 2 drat .71
#> 3 gear .79 .70
#> 4 wt -.69 -.71 -.58
#> 5 disp -.59 -.71 -.56 .89
#> 6 mpg .60 .68 .48 -.87 -.85
#> 7 hp -.24 -.45 -.13 .66 .79 -.78
#> 8 qsec -.23 .09 -.21 -.17 -.43 .42 -.71
#> 9 carb .06 -.09 .27 .43 .39 -.55 .75 -.66
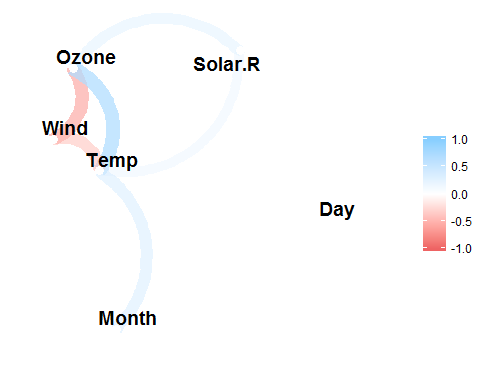
rplot(x)datasets::airquality %>%
correlate() %>%
network_plot(min_cor = .2)
#>
#> Correlation method: 'pearson'
#> Missing treated using: 'pairwise.complete.obs'