Codes for "LOGIC-LM: Empowering Large Language Models with Symbolic Solvers for Faithful Logical Reasoning".
Authors: Liangming Pan, Alon Albalak, Xinyi Wang, William Yang Wang.
NLP Group, University of California, Santa Barbara
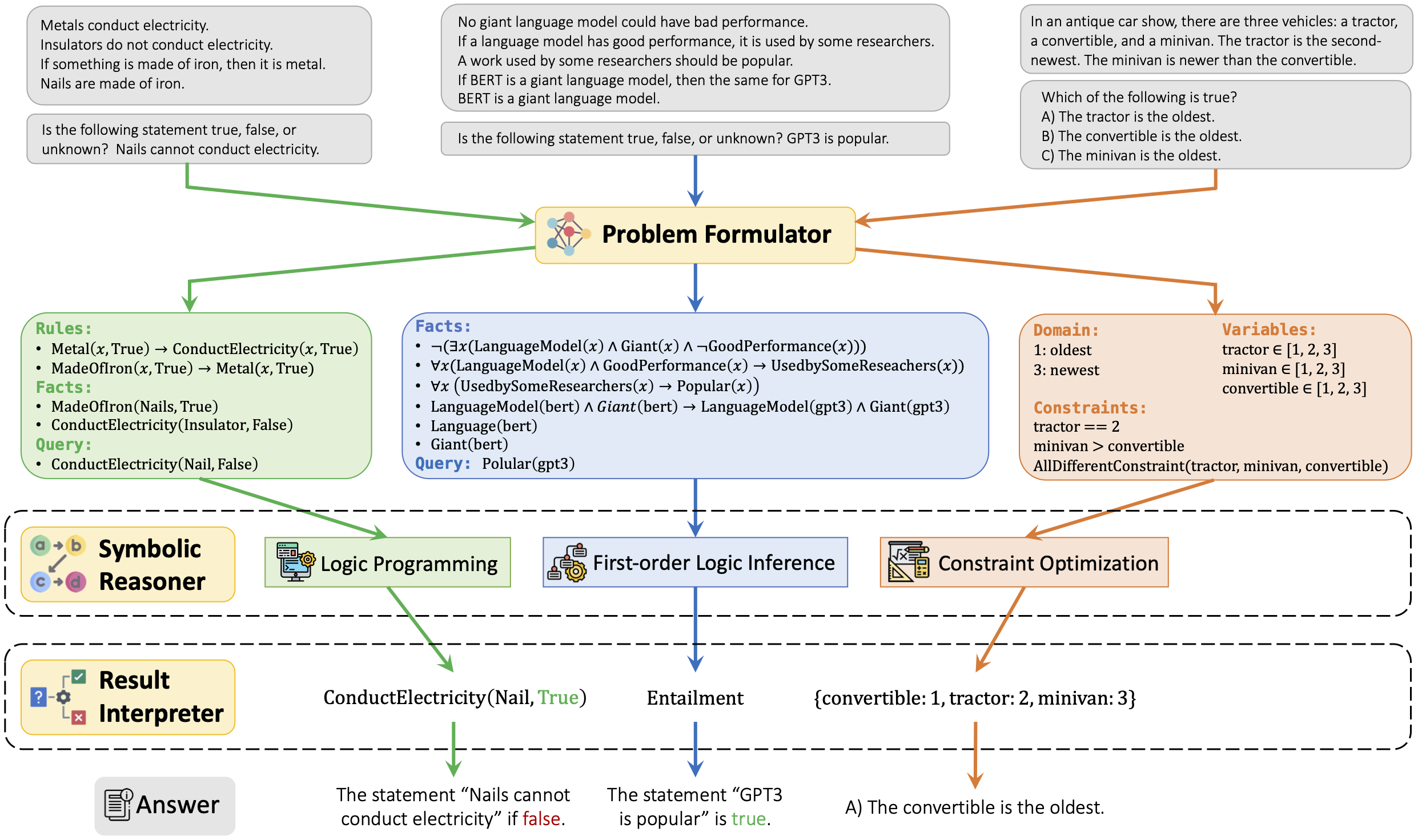
We introduce a novel framework, LOGIC-LM, which integrates LLMs with symbolic reasoning to improve logical problem-solving. Our method first utilizes LLMs to translate a natural language problem into a symbolic formulation. Afterward, a deterministic symbolic solver performs inference on the formulated problem. We also introduce a self-refinement stage, which utilizes the symbolic solver’s error messages to revise symbolic formalizations. We demonstrate LOGIC-LM’s effectiveness on four logical reasoning datasets: ProofWriter, PrOntoQA, FOLIO, and LogicalDeduction. Our results show significant improvement compared to LLMs alone, with an average performance boost of 62.6% over standard prompting and 23.5% over chain-of-thought prompting.
First, install all the required packages:
pip install -r requirements.txtThe datasets we used are preprocessed and stored in the ./data folder. We evaluate on the following datasets:
- ProntoQA: Deductive resoning dataset. We use the 5-hop subset of the fictional characters version, consisting of 500 testing examples.
- ProofWriter: Deductive resoning dataset. We use the depth-5 subset of the OWA version. To reduce overall experimentation costs, we randomly sample 600 examples in the test set and ensure a balanced label distribution.
- FOLIO: First-Order Logic reasoning dataset. We use the entire FOLIO test set for evaluation, consisting of 204 examples.
- LogicalDeduction: Constraint Satisfaction Problems (CSPs). We use the full test set consisting of 300 examples.
To replicate the Standard-LM (Direct) and the Chain-of-Thought (CoT) baselines, please run the following commands:
cd ./baselines
python gpt3_baseline.py \
--api_key "Your OpenAI API Key" \
--model_name "Model Name [text-davinci-003 | gpt-4]" \
--dataset_name "Dataset Name [ProntoQA | ProofWriter | FOLIO | LogicalDeduction]" \
--split dev \
--mode "Baseline [Direct | CoT]" \
--max_new_tokens "16 for Direct; 1024 for CoT" \The results will be saved in ./baselines/results. To evaluate the results, please run the following commands:
python evaluate.py \
--dataset_name "Dataset Name [ProntoQA | ProofWriter | FOLIO | LogicalDeduction]" \
--model_name "Model Name [text-davinci-003 | gpt-4]" \
--split dev \
--mode "Baseline [Direct | CoT]" \To generate logic programs for logical reasoning problems in each dataset, please run the following commands:
cd ./models
python logic_program.py \
--api_key "Your OpenAI API Key" \
--interpreter "The type of symbolic solver [pyke | fol | csp]" \
--dataset_name "Dataset Name [ProntoQA | ProofWriter | FOLIO | LogicalDeduction]" \
--split dev \
--model_name "Model Name [text-davinci-003 | gpt-4]"Note: use the right symbolic grammar (--interpreter) for each dataset:
pyke: Logic programming grammar; used for ProntoQA and ProofWriter.fol: First-Order Logic grammar; used for FOLIO.csp: Constraint Satisfaction Problem grammar; used for LogicalDeduction.
The generated logic programs will be saved in ./models/logic_programs.
After generating logic programs, we can perform inference with symbolic solvers.
For basic version that does not use self-refinement, please run the following commands:
cd ./models
python logic_inference.py \
--model_name "The logic programs are generated by which model? [text-davinci-003 | gpt-4]" \
--interpreter "The type of symbolic solver [pyke | fol | csp]" \
--dataset_name "Dataset Name [ProntoQA | ProofWriter | FOLIO | LogicalDeduction]" \
--split dev \
--save_path ./resultsThe logic reasoning results will be saved in ./models/results.
Note: in the basic version, if the generated logic program cannot be executed by the symbolic solver, we will use random guess as the prediction.
In this mode, if the generated logic program cannot be executed by the symbolic solver, we will back up to using LLMs to generate the prediction. To run this mode, you need to have the corresponding baseline LLM results stored in ./baselines/results. To make the inference more efficient, the model will just load the baseline LLM results and use them as the prediction if the symbolic solver fails.
For LLM-Symbolic collaboration mode, please run the following commands:
cd ./models
python logic_inference.py \
--model_name "The logic programs are generated by which model? [text-davinci-003 | gpt-4]" \
--interpreter "The type of symbolic solver [pyke | fol | csp]" \
--dataset_name "Dataset Name [ProntoQA | ProofWriter | FOLIO | LogicalDeduction]" \
--split dev \
--save_path ./results \
--backup_strategy LLM \
--backup_LLM_result_path ../baselines/resultsTo run the inference with self-refinement, please run the following commands:
cd ./models
python logic_inference.py \
--model_name "The logic programs are generated by which model? [text-davinci-003 | gpt-4]" \
--interpreter fol \
--dataset_name FOLIO \
--split dev \
--save_path ./results \
--backup_strategy LLM \
--backup_LLM_result_path ../baselines/results \
--self_debug \
--debug_api_key "Your OpenAI API Key" \(Note that relf-refinement is only available for FOL rightnow. We will release the code for other datasets soon.)
To evaluate the logic reasoning results, please run the following commands:
python evaluation.py \
--dataset_name "Dataset Name [ProntoQA | ProofWriter | FOLIO | LogicalDeduction]" \
--model_name "The logic programs are generated by which model? [text-davinci-003 | gpt-4]" \
--interpreter "The type of symbolic solver [pyke | fol | csp]" \
--split dev \
--backup "The basic mode (random) or LLM-Symbolic collabration mode (LLM)" \
--self_debug # Optional, only for self-refinementPlease cite the paper in the following format if you use this dataset during your research.
@article{PanLogicLM23,
author = {Liangming Pan and
Alon Albalak and
Xinyi Wang and
William Yang Wang},
title = {{Logic-LM:} Empowering Large Language Models with Symbolic Solvers for Faithful Logical Reasoning},
journal = {CoRR},
volume = {abs/2305.12295},
year = {2023},
url = {https://arxiv.org/abs/2305.12295}
}
If you encounter any problem, please either directly contact the Liangming Pan or leave an issue in the github repo.