EnCLAP: Combining Neural Audio Codec and Audio-Text Joint Embedding for Automated Audio Captioning [ICASSP 2024]
Jaeyeon Kim, Jaeyoon Jung, Jinjoo Lee, Sang Hoon Woo @ MAUM AI Inc., SNU, SSU
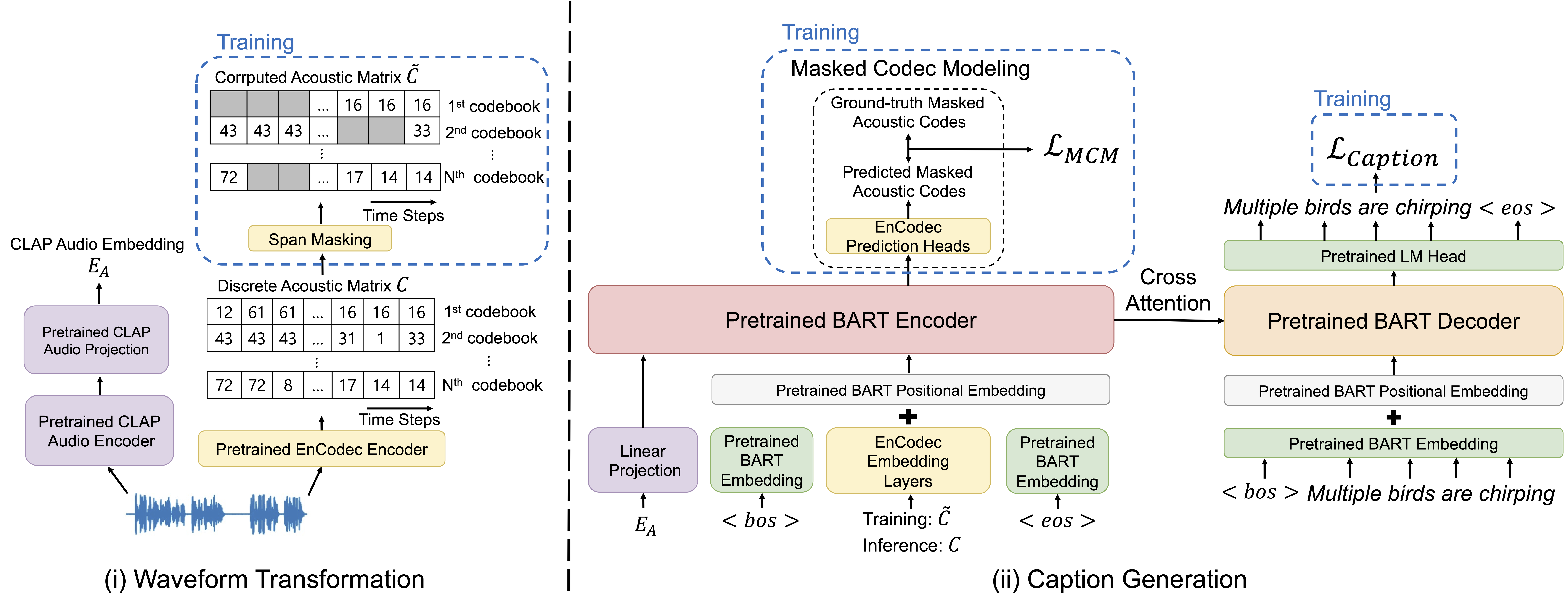
Abstract : We propose EnCLAP, a novel framework for automated audio captioning. EnCLAP employs two acoustic representation models, EnCodec and CLAP, along with a pretrained language model, BART. We also introduce a new training objective called masked codec modeling that improves acoustic awareness of the pretrained language model. Experimental results on AudioCaps and Clotho demonstrate that our model surpasses the performance of baseline models. Source code will be available at https://github.com/jaeyeonkim99/EnCLAP. An online demo is available at https://huggingface.co/spaces/enclap-team/enclap.
- We used
torch==1.13.0andpython==3.9.12for our experiment. - Please install required depedencies through
pip install -r requirements.txt. wget,java,unzipare required to useaac_metricslibrary. Please runaac-metrics-downloadafter installing the library.libsndfile1is required to usesoundfile.torchaudioversion should match the version oftorchandcuda. Check here for appropriate version.
- In our experiments, we used CLAP checkpoint trained on
LAION-audio-630kandAudioSet(630k-audioset-fusion-best.pt). See details of pretrained CLAP checkpoints in LAION-AI/CLAP.
- Preprocess the dataset: For training, you must first convert the audio files into their respective CLAP embeddings and EnCodec sequences. Once you have the converted data, you must write CSV files mapping each example to its CLAP embedding and EnCodec sequence files. The example CSV files for AudioCaps and Clotho are provided at csv. See data/README.md for further details.
- Setup the training config file: We included a number of training configuration files we used for our experiments at cfg. Feel free to modify them to fit your needs.
# Paths to save the experiment results
output_dir: /output
# Paths of the train csv file
train_file: csv/audiocaps/train.csv
# Paths of the validation csv file
validation_file: csv/audiocaps/valid.csv
# Root directory of the preprocessed EnCodec entries
encodec_base_path: /data/audiocaps/encodec
# Root directory of the preprocessed CLAP embeddings
clap_base_path: /data/audiocaps/clap
- Run the training script: Our training script is based on Accelerate, so you may need to setup Accelerate before running the training script. You can designate the path to the training config by modifying
CFG_PATHin the training script.
accelerate config # Set up Accelerate
sh train.sh # Run the training script
- The evaluation dataset may be either preprocessed CLAP embeddings and EnCodec sequences or raw wav files. Similarly to training, you must provide a CSV file containing the dataset. See csv for examples.
# From preprocessed data
python evaluate.py --ckpt checkpoint_directory_with_config --clap_ckpt clap_ckpt_path --test_csv test.csv --from_preprocessed --encodec_path data/encodec_embeddings --clap_path data/clap_embeddings
# From wav files
python evaluate.py --ckpt checkpoint_directory_with_config --clap_ckpt clap_ckpt_path --test_csv test.csv --audio_path data/wav_files
- You can save the predictions by adding CSV path with
--save_path. You can evaluate on other AAC metrics by modifyingmetric_liston the top ofevaluate.py. - To reproduce our results, we recommend you to evaluate several best checkpoints based on
valid/spiderscore (we evalauted 5). The score reported during the training is not 100% accurate due to DDP and dataloader padding.
- You can infer from wav files using the following code.
python inference.py --ckpt checkpoint_directory_with_config --clap_ckpt clap_ckpt_path --input input.wav
- You can also run the gradio demo with your own checkpoint.
python gradio_app.py --ckpt checkpoint_directory_with_config --clap_ckpt clap_ckpt_path --device cuda
Pretrained checkpoints are available here.
- Each folder contains both the configuration file (
config.json) and the weight file (pytorch_model.bin) required for inference. - The folders
audiocaps,clotho,clotho_finetune, andbothdenote the datasets on which each checkpoint is trained:clotho_finetunecontains checkpoints pretrained on AudioCaps and finetuned on Clotho.bothcontains checkpoints trained on both Clotho and AudioCaps, used for the official gradio demo.
- The labels
baseandlargeindicate the checkpoints for EnClap-base and EnClap-large, respectively.
@article{kim2024enclap,
title={EnCLAP: Combining Neural Audio Codec and Audio-Text Joint Embedding for Automated Audio Captioning},
author={Kim, Jaeyeon and Jung, Jaeyoon and Lee, Jinjoo and Woo, Sang Hoon},
journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:2401.17690},
year={2024}
}
@INPROCEEDINGS{10446672,
author={Kim, Jaeyeon and Jung, Jaeyoon and Lee, Jinjoo and Woo, Sang Hoon},
booktitle={ICASSP 2024 - 2024 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP)},
title={EnCLAP: Combining Neural Audio Codec and Audio-Text Joint Embedding for Automated Audio Captioning},
year={2024},
volume={},
number={},
pages={6735-6739},
keywords={Training;Codecs;Speech coding;Source coding;Signal processing;Acoustics;Task analysis;automated audio captioning;neural audio codec;audio-text joint embedding},
doi={10.1109/ICASSP48485.2024.10446672}}