CANU (CSM Automatic Network Utility) will float through a Shasta network and make switch setup and validation a breeze.
CANU can be used to:
- Check if switches (Aruba, Dell, or Mellanox) on a Shasta network meet the firmware version requirements
- Check network cabling status using LLDP
- Validate BGP status
- Validate that SHCD spreadsheets are configured correctly and pass a number of checks
- Validate an SHCD against actual network cabling status to check for mis-cabling
- Generate switch configuration for an entire network
- Convert SHCD to CCJ (CSM Cabling JSON)
- Use CCJ / Paddle to validate the network and generate network config
- Run tests against the mgmt network to check for faults/inconsistencies.
- Backup switch configs.
- Quickstart Guide
- Paddle / CCJ
- Versioning
- Installation and Usage
- Prerequisites
- Installation
- Usage
- Initialization
- Report Switch Firmware
- Report Network Firmware
- Report Switch Cabling
- Report Network Cabling
- Validate SHCD
- Validate Paddle
- Validate Network Cabling
- Validate SHCD and Cabling
- Validate Paddle and Cabling
- Validate Network BGP
- Generate Switch Config
- Generate Network Config
- Validate Switch Config
- Validate Network Config
- Cache
- Test the network
- Backup Network
- Send Command
- Report Network Version
- Using
canu-inventorywith Ansible - Uninstallation
- Testing
- Changelog
To checkout a fresh system using CSI:
- Make a new directory to save switch IP addresses
mkdir ips_folder
cd ips_folder-
Parse CSI files and save switch IP addresses
canu init --sls-file sls_input_file.json --out ips.txt` -
Check network firmware
canu report network firmware --csm 1.2 --ips-file ips.txt
-
Check network cabling
canu report network cabling --ips-file ips.txt
-
Validate BGP status
canu validate network bgp --ips-file ips.txt --verbose
-
Validate cabling
canu validate network cabling --ips-file ips.txt
If you have the system's SHCD, there are even more commands that can be run
-
Validate the SHCD
canu validate shcd --shcd SHCD.xlsx
-
Validate the SHCD against network cabling
canu validate shcd-cabling --shcd SHCD.xlsx --ips-file ips.txt
-
Generate switch config for the network
canu generate network config --shcd SHCD.xlsx --sls-file sls_input_file.json --folder configs
-
Convert the SHCD to CCJ
canu validate shcd --shcd SHCD.xlsx --json --out paddle.json
If you have the system's CCJ
-
Validate the Paddle / CCJ
canu validate paddle --ccj paddle.json
-
Validate the CCJ against network cabling
canu validate paddle-cabling --ccj paddle.json --ips-file ips.txt
-
Generate switch config for the network
canu generate network config --ccj paddle.json --sls-file sls_input_file.json --folder configs
The paddle or CCJ (CSM Cabling JSON) is a JSON representation of the network. There are many benefits of using the CCJ:
- The CCJ schema has been validated using
paddle-schema.json - The paddle has been architecturally validated to ensure all connections between devices are approved
- All port connections between devices have been checked using the CANU model to ensure speed, slot choice, and port availability has been confirmed
- The CCJ is machine-readable and therefore easy to build additional tooling around
- Less flags need to be used when reading the CCJ vs the SHCD
The SHCD can easily be converted into CCJ by using
canu validate shcd --shcd SHCD.xlsx --json --out paddle.jsonThe version is derived from Git by the setuptools_scm Python module and follows PEP0440's version identification
and dependency specification for final and pre releases.
The items below denote how stable, pre-release, and unstable versions are classified through version strings.
-
(stable) final release: A git-tag following the
X.Y.Zsemver format is considered a final release version.# Format: # {tag} # X.Y.Z # X - Major # Y - Minor # Z - Micro (a.k.a. patch) 0.1.2
-
(unstable) pre-release: A git-tag with an
a(lpha),b(eta), orr(elease)c(andidate) annotation and an identification numberNdenotes a pre-release/preview.For
canu, these are sometimes created before an official release (e.g. 1.7.0a1 might exist before 1.7.0 is released). Additionally the beta and release candidate tags may be skipped. Whether an alpha, beta, or release candidate pre-release is taken is entirely up to thecanurelease management team.# Format: # {tag}[{a|b|rc}N] 0.1.2a1 0.1.2b1 0.1.2rc1 -
(unstable) development: Development builds auto-increment the micro version (the
ZinX.Y.Z) or pre-release version (theNinX.Y.Z{[a|b|rc]N}), and then append a suffix based on whether the working directory was clean, dirty, or mixed.-
clean: When the version shows an appended
devN+{scm_letter}{revision_short_hash}, that means there have been commits made since the previous git-tag.# Format: # {next_version}.dev{distance}+{scm_letter}{revision_short_hash} # If the previous git-tag was 0.1.2: 0.1.3.dev4+g818da8a # If the previous get-tag was a pre-release of 0.1.3a1: 0.1.3a2.dev4+g818da8a -
dirty When the version shows an appended
.d{YYYYMMDD}datestamp, that means there were modified/uncommitted changes in the working directory when the application was built.# Format: # {next_version}.d(datestamp} # If the previous git-tag was 0.1.2: 0.1.3.d20230123 # If the previous get-tag was a pre-release of 0.1.3a1: 0.1.2a2.d20230123 -
mixed When the version shows a development tag with an appended datestamp, this means commits have been made but there were uncommitted changes present in the working directory when the application was built.
# Format: # {next_Version}.dev{distance}+{scm_letter}{revision_short_hash}.d{datestamp} # If the previous git-tag was 0.1.2: 0.1.3.dev3+g3071655.d20230123 # If the previous get-tag was a pre-release of 0.1.3a1: 0.1.3a2.dev3+g3071655.d20230123
-
The setuptools_scm module is configured by pyproject.toml.
For more information regarding configuration of setuptools_scm, see version number construction.
In order to run CANU, both python3 and pip3 need to be installed.
-
To run CANU inside a container:
-
Prerequisites:
- a container runtime (podman or docker)
There are a few ways to run
canuin a container:This builds (if necessary) and
execs into a container, where you can runcanuas normal.# launch an editable development container ./canuctl -d ARGS # launch a prod container ./canuctl -p ARGS # example: launch canu --version using the production container ./canuctl -p canu --version
# make a production image make image # exec into the container make dev # or make prod
# exec into the container docker run -it canu:<tag> sh # running a removeable container docker run -it --rm --net=host -v ${PWD}:/home/canu/mounted:rw canu:<tag> canu validate shcd /home/canu/mounted/myshcd.xlsx
-
-
To run CANU in a Python Virtualenv:
-
Prerequisites:
-
python3
-
pip3
-
Python Virtualenv
python3 -m venv .venv source ./.venv/bin/activate python3 -m pip install 'setuptools_scm[toml]' python3 -m pip install .
-
-
When you are done working in the Python Virtualenv. Use the following command to exit out of the Python Virtualenv:
deactivate
-
-
To install the development build of CANU type:
python3 -m pip install --editable . -
To install SLES RPM versions
To run, just type canu, it should run and display help. To see a list of commands and arguments, just append --help.
To help make switch setup a breeze. CANU can automatically parse SLS JSON data - including CSI sls_input_file.json output or the Shasta SLS API for switch IPv4 addresses.
- In order to parse CSI output, use the
--sls-file FILEflag to pass in the folder where an SLS JSON file is located.
The CSI sls_input_file.json file is generally stored in one of two places depending on how far the system is in the install process.
- Early in the install process, when running off of the LiveCD the CSI
sls_input_file.jsonfile is normally found in the the directory/var/www/ephemeral/prep/SYSTEMNAME/ - Later in the install process, the CSI
sls_input_file.jsonfile is generally in/mnt/pitdata/prep/SYSTEMNAME/ - The SLS file can also be obtained from an NCN that's in the k8s cluster by running
cray sls dumpstate list --format json - The switch IPs will be read from the 'NMN' network, if a different network is desired, use the
--networkflag to choose a different one e.g. (CAN, MTL, NMN).
To get the switch IP addresses from CSI output, run the command:
canu init --sls-file SLS_FILE --out output.txtPotential output:
8 IP addresses saved to output.txt
- To parse the Shasta SLS API for IP addresses, ensure that you have a valid token. The token file can either be passed in with the
--auth-token TOKEN_FILEflag, or it can be automatically read if the environmental variableSLS_TOKENis set. The SLS address is default set toapi-gw-service-nmn.local, if you are operating on a system with a different address, you can set it with the--sls-address SLS_ADDRESSflag.
To get the switch IP addresses from the Shasta SLS API, run the command:
canu init --auth-token ~./config/cray/tokens/ --sls-address 1.2.3.4 --out output.txtPotential output:
8 IP addresses saved to output.txt
The output file for the canu init command is set with the --out FILENAME flag.
CANU checks the switch firmware version against the standard in the canu.yaml file found in the root directory.
The CSM version is required to determine the firmware to validate against, you can pass it in with --csm like --csm 1.2.
To check the firmware of a single switch run: canu report switch firmware --csm 1.2 --ip 192.168.1.1 --username USERNAME --password PASSWORD
$ canu report switch firmware --csm 1.2 --ip 192.168.1.1 --username USERNAME --password PASSWORD
🛶 - Pass - IP: 192.168.1.1 Hostname:sw-spine-001 Firmware: GL.10.06.0010Multiple switches on a network (Aruba, Dell, or Mellanox) can be checked for their firmware versions. The IPv4 addresses of the switches can either be entered comma separated, or be read from a file. To enter a comma separated list of IP addresses to the ---ips flag. To read the IP addresses from a file, make sure the file has one IP address per line, and use the flag like --ips-file FILENAME to input the file.
The CSM version is required to determine the firmware to validate against, you can pass it in with --csm like --csm 1.2.
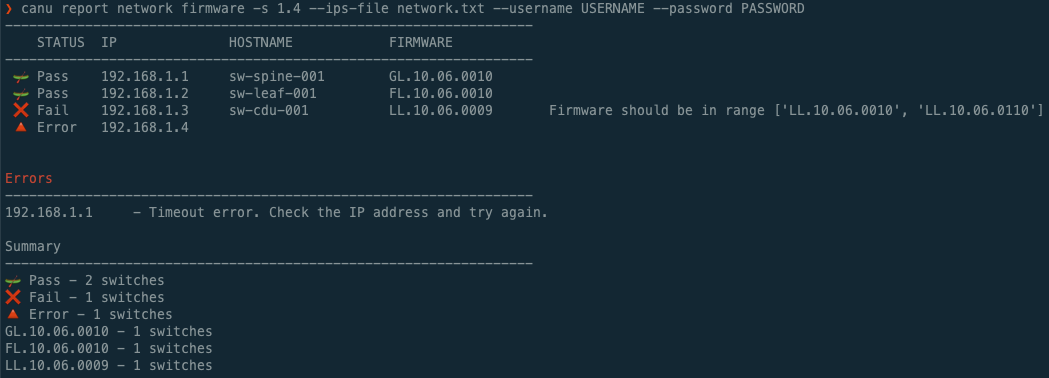
An example of checking the firmware of multiple switches: canu report network firmware --csm 1.2 --ips 192.168.1.1,192.168.1.2 --username USERNAME --password PASSWORD
canu report network firmware --csm 1.2 --ips 192.168.1.1,192.168.1.2,192.168.1.3,192.168.1.4 --username USERNAME --password PASSWORDPotential output:
------------------------------------------------------------------
STATUS IP HOSTNAME FIRMWARE
------------------------------------------------------------------
🛶 Pass 192.168.1.1 test-switch-spine01 GL.10.06.0010
🛶 Pass 192.168.1.2 test-switch-leaf01 FL.10.06.0010
❌ Fail 192.168.1.3 test-wrong-version FL.10.05.0001 Firmware should be in range ['FL.10.06.0001']
🔺 Error 192.168.1.4
Errors
------------------------------------------------------------------
192.168.1.4 - HTTP Error. Check that this IP is an Aruba switch, or check the username and password
Summary
------------------------------------------------------------------
🛶 Pass - 2 switches
❌ Fail - 1 switches
🔺 Error - 1 switches
GL.10.06.0010 - 1 switches
FL.10.06.0010 - 1 switches
FL.10.05.0010 - 1 switches
When using the network firmware commands, the table will show either: 🛶 Pass, ❌ Fail, or 🔺 Error. The switch will pass or fail based on if the switch firmware matches the canu.yaml.
To output the results of the switch firmware or network firmware commands to a file, append the --out FILENAME flag
To get the JSON output from a single switch, or from multiple switches, make sure to use the --json flag. An example json output is below.
canu network firmware --csm 1.2 --ips 192.168.1.1,192.168.1.2 --username USERNAME --password PASSWORD --jsonPotential output:
{
"192.168.1.1": {
"status": "Pass",
"hostname": "test-switch-spine01",
"platform_name": "8325",
"firmware": {
"current_version": "GL.10.06.0010",
"primary_version": "GL.10.06.0010",
"secondary_version": "GL.10.05.0020",
"default_image": "primary",
"booted_image": "primary",
},
},
"192.168.1.2": {
"status": "Pass",
"hostname": "test-switch-leaf01",
"platform_name": "6300",
"firmware": {
"current_version": "FL.10.06.0010",
"primary_version": "FL.10.06.0010",
"secondary_version": "FL.10.05.0020",
"default_image": "primary",
"booted_image": "primary",
},
},
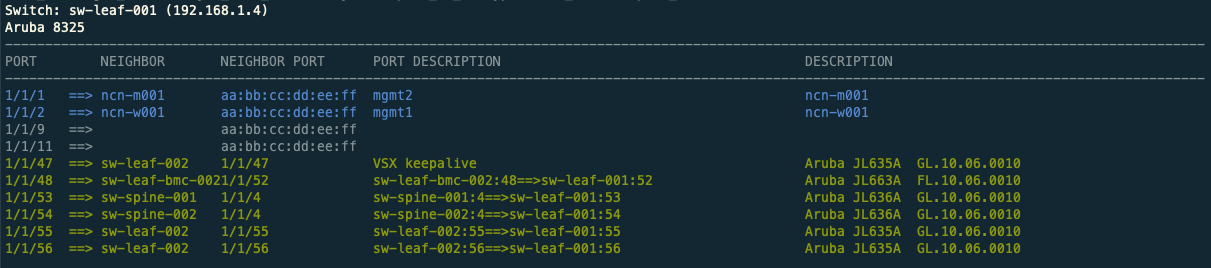
}CANU can also use LLDP to check the cabling status of a switch. To check the cabling of a single switch run: canu report switch cabling --ip 192.168.1.1 --username USERNAME --password PASSWORD
canu report switch cabling --ip 192.168.1.1 --username USERNAME --password PASSWORDPotential output:
Switch: test-switch-spine01 (192.168.1.1)
Aruba 8325
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
PORT NEIGHBOR NEIGHBOR PORT PORT DESCRIPTION DESCRIPTION
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1/1/1 ==> 00:00:00:00:00:01 No LLDP data, check ARP vlan info. 192.168.1.20:vlan1, 192.168.2.12:vlan2
1/1/3 ==> ncn-test2 00:00:00:00:00:02 mgmt0 Linux ncn-test2
1/1/5 ==> ncn-test3 00:00:00:00:00:03 mgmt0 Linux ncn-test3
1/1/7 ==> 00:00:00:00:00:04 No LLDP data, check ARP vlan info. 192.168.1.10:vlan1, 192.168.2.9:vlan2
1/1/51 ==> test-spine02 1/1/51 Aruba JL635A GL.10.06.0010
1/1/52 ==> test-spine02 1/1/52 Aruba JL635A GL.10.06.0010
Sometimes when checking cabling using LLDP, the neighbor does not return any information except a MAC address. When that is the case, CANU looks up the MAC in the ARP table and displays the IP addresses and vlan information associated with the MAC.
Entries in the table will be colored based on what they are. Neighbors that have ncn in their name will be colored blue. Neighbors that have a port labeled (not a MAC address), are generally switches and are labeled green. Ports that are duplicated, will be bright white.
The cabling of multiple switches (Aruba, Dell, or Mellanox) on a network can be checked at the same time using LLDP. The IPv4 addresses of the switches can either be entered comma separated, or be read from a file. To enter a comma separated list of IP addresses to the ---ips flag. To read the IP addresses from a file, make sure the file has one IP address per line, and use the flag like --ips-file FILENAME to input the file.
An example of checking the cabling of multiple switches: canu report network cabling --ips 192.168.1.1,192.168.1.2 --username USERNAME --password PASSWORD
There are two different --view options, switch and equipment.
- The
--view switchoption displays a table for every switch IP address passed in showing connections. This is the same view as shown in the above example of checking single switch cabling. - The
--view equipmentoption displays a table for each mac address connection. This means that servers and switches will both display incoming and outgoing connections.
An example of checking the cabling of multiple switches and displaying with the equipment view: canu network cabling --ips 192.168.1.1,192.168.1.2 --username USERNAME --password PASSWORD --view equipment
canu report network cabling --ips 192.168.1.1,192.168.1.2 --username USERNAME --password PASSWORD --view equipmentPotential output:
sw-spine01 Aruba JL635A GL.10.06.0010
aa:aa:aa:aa:aa:aa
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1/1/1 <==> sw-spine02 1/1/1 Aruba JL635A GL.10.06.0010
1/1/3 ===> 00:00:00:00:00:00 mgmt1
1/1/4 ===> ncn-test bb:bb:bb:bb:bb:bb mgmt1 Linux ncn-test
sw-spine02 Aruba JL635A GL.10.06.0010
bb:bb:bb:bb:bb:bb
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1/1/1 <==> sw-spine01 1/1/1 Aruba JL635A GL.10.06.0010
00:00:00:00:00:00
192.168.2.2:vlan3, 192.168.1.2:vlan1
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
00:00:00:00:00:00 mgmt1 <=== sw-spine01 1/1/3
ncn-test Linux ncn-test2
bb:bb:bb:bb:bb:bb
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
bb:bb:bb:bb:bb:bb mgmt1 <=== sw-spine01 1/1/4
CANU can be used to validate that an SHCD (SHasta Cabling Diagram) passes basic validation checks.
- The
--architecture / -aflag is used to set the architecture of the system, either TDS, Full, or V1.. - Use the
--tabsflag to select which tabs on the spreadsheet will be included. - The
--cornersflag is used to input the upper left and lower right corners of the table on each tab of the worksheet. The table should contain the 11 headers: Source, Rack, Location, Slot, (Blank), Port, Destination, Rack, Location, (Blank), Port. If the corners are not specified, you will be prompted to enter them for each tab.
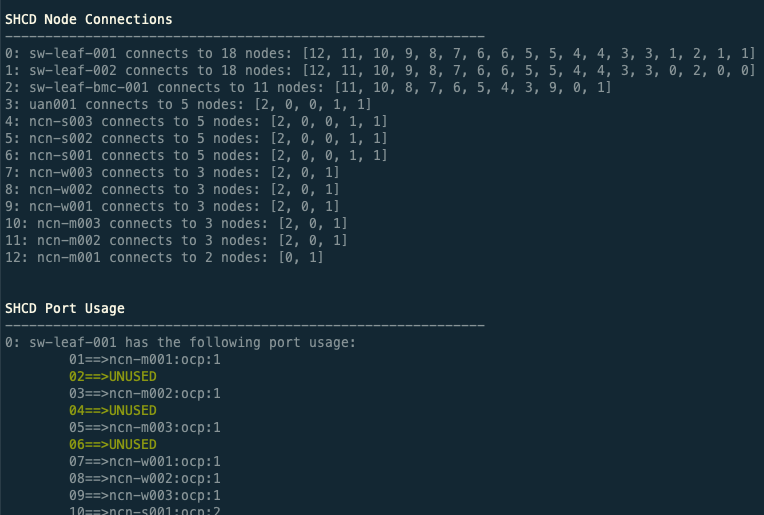
To check an SHCD run: canu validate shcd -a tds --shcd FILENAME.xlsx --tabs 25G_10G,NMN,HMN --corners I14,S25,I16,S22,J20,T39
canu validate shcd -a tds --shcd FILENAME.xlsx --tabs 25G_10G,NMN,HMN --corners I14,S25,I16,S22,J20,T39Potential output:
SHCD Node Connections
------------------------------------------------------------
0: sw-spine-001 connects to 6 nodes: [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6]
1: sw-spine-002 connects to 6 nodes: [0, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6]
2: sw-leaf-bmc-001 connects to 2 nodes: [0, 1]
3: uan001 connects to 2 nodes: [0, 1]
4: ncn-s001 connects to 2 nodes: [0, 1]
5: ncn-w001 connects to 2 nodes: [0, 1]
6: ncn-m001 connects to 2 nodes: [0, 1]
Warnings
Node type could not be determined for the following
------------------------------------------------------------
CAN switch
The SHCD can easily be converted into CCJ by using by using the --json flag and outputting to a file by canu validate shcd --shcd SHCD.xlsx --json --out paddle.json
CANU can be used to validate that a CCJ (CSM Cabling JSON) passes basic validation checks.
To validate a paddle CCJ run: canu validate paddle --ccj paddle.json
canu validate paddle --ccj paddle.jsonPotential output:
CCJ Node Connections
------------------------------------------------------------
0: sw-spine-001 connects to 6 nodes: [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6]
1: sw-spine-002 connects to 6 nodes: [0, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6]
2: sw-leaf-bmc-001 connects to 2 nodes: [0, 1]
3: uan001 connects to 2 nodes: [0, 1]
4: ncn-s001 connects to 2 nodes: [0, 1]
5: ncn-w001 connects to 2 nodes: [0, 1]
6: ncn-m001 connects to 2 nodes: [0, 1]
CANU can be used to validate that network cabling passes basic validation checks.
- The
--architecture / -aflag is used to set the architecture of the system, either TDS, Full, or V1. - To enter a comma separated list of IP addresses to the
---ipsflag. To read the IP addresses from a file, make sure the file has one IP address per line, and use the flag like--ips-file FILENAMEto input the file.
To validate the cabling run: canu validate network cabling -a tds --ips 192.168.1.1,192.168.1.2 --username USERNAME --password PASSWORD
canu validate network cabling -a tds --ips 192.168.1.1,192.168.1.2 --username USERNAME --password PASSWORDPotential output:
Cabling Node Connections
------------------------------------------------------------
0: sw-spine-001 connects to 10 nodes: [1, 2, 3, 4]
1: ncn-m001 connects to 2 nodes: [0, 4]
2: ncn-w001 connects to 2 nodes: [0, 4]
3: ncn-s001 connects to 2 nodes: [0, 4]
4: sw-spine-002 connects to 10 nodes: [0, 1, 2, 3 ]
Warnings
Node type could not be determined for the following
------------------------------------------------------------
sw-leaf-001
sw-spine-001 1/1/1 ===> aa:aa:aa:aa:aa:aa
sw-spine-001 1/1/2 ===> 1/1/1 CFCANB4S1 Aruba JL479A TL.10.03.0081
sw-spine-001 1/1/3 ===> 1/1/3 sw-leaf-001 Aruba JL663A FL.10.06.0010
sw-spine-002 1/1/4 ===> bb:bb:bb:bb:bb:bb
sw-spine-002 1/1/5 ===> 1/1/2 CFCANB4S1 Aruba JL479A TL.10.03.0081
sw-spine-002 1/1/6 ===> 1/1/6 sw-leaf-001 Aruba JL663A FL.10.06.0010
Nodes that show up as MAC addresses might need to have LLDP enabled.
The following nodes should be renamed
------------------------------------------------------------
sw-leaf01 should be renamed (could not identify node)
sw-spine01 should be renamed sw-spine-001
sw-spine02 should be renamed sw-spine-002
If there are any nodes that cannot be determined or should be renamed, there will be warning tables that show the details.
CANU can be used to validate an SHCD against the current network cabling.
- The
--csmflag is used to set the CSM version of the system. - The
--architecture / -aflag is used to set the architecture of the system, either TDS, Full, or V1. - Use the
--tabsflag to select which tabs on the spreadsheet will be included. - The
--cornersflag is used to input the upper left and lower right corners of the table on each tab of the worksheet. The table should contain the 11 headers: Source, Rack, Location, Slot, (Blank), Port, Destination, Rack, Location, (Blank), Port. If the corners are not specified, you will be prompted to enter them for each tab. - To enter a comma separated list of IP addresses to the
---ipsflag. To read the IP addresses from a file, make sure the file has one IP address per line, and use the flag like--ips-file FILENAMEto input the file.
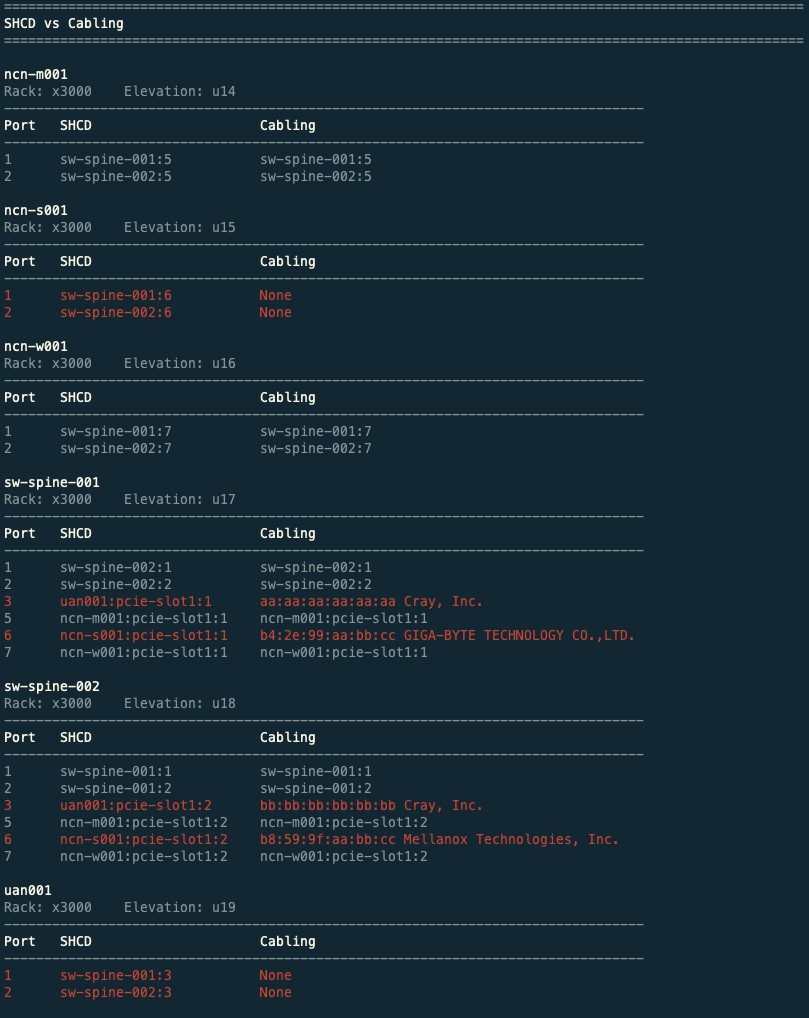
To validate an SHCD against the cabling run: canu validate shcd-cabling --csm 1.2 -a tds --shcd FILENAME.xlsx --tabs 25G_10G,NMN --corners I14,S49,I16,S22 --ips 192.168.1.1,192.168.1.2 --username USERNAME --password PASSWORD
canu validate shcd-cabling --csm 1.2 -a tds --shcd FILENAME.xlsx --tabs 25G_10G,NMN --corners I14,S49,I16,S22 --ips 192.168.1.1,192.168.1.2 --username USERNAME --password PASSWORDPotential output:
====================================================================================================
SHCD vs Cabling
====================================================================================================
ncn-m001
Rack: x3000 Elevation: u14
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Port SHCD Cabling
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 sw-spine-001:5 sw-spine-001:5
2 sw-spine-002:5 sw-spine-002:5
ncn-s001
Rack: x3000 Elevation: u15
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Port SHCD Cabling
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 sw-spine-001:6 None
2 sw-spine-002:6 None
ncn-w001
Rack: x3000 Elevation: u16
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Port SHCD Cabling
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 sw-spine-001:7 sw-spine-001:7
2 sw-spine-002:7 sw-spine-002:7
sw-spine-001
Rack: x3000 Elevation: u17
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Port SHCD Cabling
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 sw-spine-002:1 sw-spine-002:1
2 sw-spine-002:2 sw-spine-002:2
3 uan001:pcie-slot1:1 aa:aa:aa:aa:aa:aa Cray, Inc.
5 ncn-m001:pcie-slot1:1 ncn-m001:pcie-slot1:1
6 ncn-s001:pcie-slot1:1 b4:2e:99:aa:bb:cc GIGA-BYTE TECHNOLOGY CO.,LTD.
7 ncn-w001:pcie-slot1:1 ncn-w001:pcie-slot1:1
sw-spine-002
Rack: x3000 Elevation: u18
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Port SHCD Cabling
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 sw-spine-001:1 sw-spine-001:1
2 sw-spine-001:2 sw-spine-001:2
3 uan001:pcie-slot1:2 bb:bb:bb:bb:bb:bb Cray, Inc.
5 ncn-m001:pcie-slot1:2 ncn-m001:pcie-slot1:2
6 ncn-s001:pcie-slot1:2 b8:59:9f:aa:bb:cc Mellanox Technologies, Inc.
7 ncn-w001:pcie-slot1:2 ncn-w001:pcie-slot1:2
uan001
Rack: x3000 Elevation: u19
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Port SHCD Cabling
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 sw-spine-001:3 None
2 sw-spine-002:3 None
====================================================================================================
SHCD Warnings
====================================================================================================
Warnings
Node type could not be determined for the following
------------------------------------------------------------
Sheet: HMN
Cell: R21 Name: SITE
====================================================================================================
Cabling Warnings
====================================================================================================
Node type could not be determined for the following
------------------------------------------------------------
sw-spine-001 1/1/3 ===> aa:aa:aa:aa:aa:aa Cray, Inc.
sw-spine-002 1/1/3 ===> bb:bb:bb:bb:bb:bb Cray, Inc.
Nodes that show up as MAC addresses might need to have LLDP enabled.
The output of the validate shcd-cabling command will show a port by port comparison between the devices found in the SHCD and devices found on the network. If there is a difference in what is found connected to a devices port in SHCD and Cabling, the line will be highlighted in red.
CANU can be used to validate aCCJ paddle against the current network cabling.
- The
--csmflag is used to set the CSM version of the system. - The
--ccjflag is used to input the CCJ file. - To enter a comma separated list of IP addresses to the
---ipsflag. To read the IP addresses from a file, make sure the file has one IP address per line, and use the flag like--ips-file FILENAMEto input the file.
To validate an SHCD against the cabling run: canu validate paddle-cabling --csm 1.2 --ccj paddle.json --ips 192.168.1.1,192.168.1.2 --username USERNAME --password PASSWORD
canu validate paddle-cabling --csm 1.2 --ccj paddle.json --ips 192.168.1.1,192.168.1.2 --username USERNAME --password PASSWORDPotential output:
====================================================================================================
CCJ vs Cabling
====================================================================================================
ncn-m001
Rack: x3000 Elevation: u14
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Port CCJ Cabling
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 sw-spine-001:5 sw-spine-001:5
2 sw-spine-002:5 sw-spine-002:5
ncn-s001
Rack: x3000 Elevation: u15
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Port CCJ Cabling
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 sw-spine-001:6 None
2 sw-spine-002:6 None
ncn-w001
Rack: x3000 Elevation: u16
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Port CCJ Cabling
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 sw-spine-001:7 sw-spine-001:7
2 sw-spine-002:7 sw-spine-002:7
sw-spine-001
Rack: x3000 Elevation: u17
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Port CCJ Cabling
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 sw-spine-002:1 sw-spine-002:1
2 sw-spine-002:2 sw-spine-002:2
3 uan001:pcie-slot1:1 aa:aa:aa:aa:aa:aa Cray, Inc.
5 ncn-m001:pcie-slot1:1 ncn-m001:pcie-slot1:1
6 ncn-s001:pcie-slot1:1 b4:2e:99:aa:bb:cc GIGA-BYTE TECHNOLOGY CO.,LTD.
7 ncn-w001:pcie-slot1:1 ncn-w001:pcie-slot1:1
sw-spine-002
Rack: x3000 Elevation: u18
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Port CCJ Cabling
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 sw-spine-001:1 sw-spine-001:1
2 sw-spine-001:2 sw-spine-001:2
3 uan001:pcie-slot1:2 bb:bb:bb:bb:bb:bb Cray, Inc.
5 ncn-m001:pcie-slot1:2 ncn-m001:pcie-slot1:2
6 ncn-s001:pcie-slot1:2 b8:59:9f:aa:bb:cc Mellanox Technologies, Inc.
7 ncn-w001:pcie-slot1:2 ncn-w001:pcie-slot1:2
uan001
Rack: x3000 Elevation: u19
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Port CCJ Cabling
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 sw-spine-001:3 None
2 sw-spine-002:3 None
====================================================================================================
CCJ Warnings
====================================================================================================
====================================================================================================
Cabling Warnings
====================================================================================================
Node type could not be determined for the following
------------------------------------------------------------
sw-spine-001 1/1/3 ===> aa:aa:aa:aa:aa:aa Cray, Inc.
sw-spine-002 1/1/3 ===> bb:bb:bb:bb:bb:bb Cray, Inc.
Nodes that show up as MAC addresses might need to have LLDP enabled.
The output of the validate paddle-cabling command will show a port by port comparison between the devices found in the CCJ and devices found on the network. If there is a difference in what is found connected to a devices port in CCJ and Cabling, the line will be highlighted in red.
CANU can be used to validate BGP neighbors. All neighbors of a switch must return status Established or the verification will fail.
- The default asn is set to 65533 if it needs to be changed, use the flag
--asn NEW_ASN_NUMBERto set the new number
If you want to see the individual status of all the neighbors of a switch, use the --verbose flag.
To validate BGP run: canu validate network bgp --ips 192.168.1.1,192.168.1.2 --username USERNAME --password PASSWORD
canu validate network bgp --username USERNAME --password PASSWORDPotential output:
BGP Neighbors Established
--------------------------------------------------
PASS - IP: 192.168.1.1 Hostname: sw-spine01
PASS - IP: 192.168.1.2 Hostname: sw-spine01
If any of the spine switch neighbors for a connection other than Established, the switch will FAIL validation.
Details
To see all the lags that are generated, see lags
CANU can be used to generate switch config.
In order to generate switch config, a valid SHCD or CCJ must be passed in and system variables must be read in from any SLS data, including CSI output or the SLS API.
- In order to parse CSI output, use the
--sls-file FILEflag to pass in the folder where thesls_file.jsonfile is located.
The sls_input_file.json file is generally stored in one of two places depending on how far the system is in the install process.
-
Early in the install process, when running off of the LiveCD the sls_input_file.json file is normally found in the the directory
/var/www/ephemeral/prep/SYSTEMNAME/ -
Later in the install process, the sls_input_file.json file is generally in
/mnt/pitdata/prep/SYSTEMNAME/
- To parse the Shasta SLS API for IP addresses, ensure that you have a valid token. The token file can either be passed in with the
--auth-token TOKEN_FILEflag, or it can be automatically read if the environmental variable SLS_TOKEN is set. The SLS address is default set to api-gw-service-nmn.local, if you are operating on a system with a different address, you can set it with the--sls-address SLS_ADDRESSflag.
- The
--csmflag is used to set the CSM version of the system. - The
--ccjflag is used to input the CCJ file.
To generate switch config run: canu generate switch config --csm 1.2 --ccj paddle.json --sls-file SLS_FILE --name SWITCH_HOSTNAME --out FILENAME
- The
--csmflag is used to set the CSM version of the system. - The
--architecture / -aflag is used to set the architecture of the system, either TDS, Full, or V1.. - Use the
--tabsflag to select which tabs on the spreadsheet will be included. - The
--cornersflag is used to input the upper left and lower right corners of the table on each tab of the worksheet. The table should contain the 11 headers: Source, Rack, Location, Slot, (Blank), Port, Destination, Rack, Location, (Blank), Port. If the corners are not specified, you will be prompted to enter them for each tab.
To generate config for a specific switch, a hostname must also be passed in using the --name HOSTNAME flag. To output the config to a file, append the --out FILENAME flag.
To generate switch config run: canu generate switch config --csm 1.2 -a full --shcd FILENAME.xlsx --tabs 'INTER_SWITCH_LINKS,NON_COMPUTE_NODES,HARDWARE_MANAGEMENT,COMPUTE_NODES' --corners 'J14,T44,J14,T48,J14,T24,J14,T23' --sls-file SLS_FILE --name SWITCH_HOSTNAME --out FILENAME
canu generate switch config --csm 1.2 -a full --shcd FILENAME.xlsx --tabs INTER_SWITCH_LINKS,NON_COMPUTE_NODES,HARDWARE_MANAGEMENT,COMPUTE_NODES --corners J14,T44,J14,T48,J14,T24,J14,T23 --sls-file SLS_FILE --name sw-spine-001Potential output:
hostname sw-spine-001
user admin group administrators password plaintext
bfd
no ip icmp redirect
vrf CAN
vrf keepalive
...
Pass in a switch config file that CANU will inject into the generated config. A use case would be to add custom site connections. This config file will overwrite previously generate config.
The custom-config file type is YAML and a single file can be used for multiple switches. You will need to specify the switch name and what config inject. The custom-config feature is using the hierarchical configuration library, documentation can be found here https://netdevops.io/hier_config/.
custom config file examples
Aruba
sw-spine-001: |
ip route 0.0.0.0/0 10.103.15.185
interface 1/1/36
no shutdown
ip address 10.103.15.186/30
exit
system interface-group 3 speed 10g
interface 1/1/2
no shutdown
mtu 9198
description sw-spine-001:16==>ion-node
no routing
vlan access 7
spanning-tree bpdu-guard
spanning-tree port-type admin-edge
sw-spine-002: |
ip route 0.0.0.0/0 10.103.15.189
interface 1/1/36
no shutdown
ip address 10.103.15.190/30
exit
system interface-group 3 speed 10g
sw-leaf-bmc-001: |
interface 1/1/20
no routing
vlan access 4
spanning-tree bpdu-guard
spanning-tree port-type admin-edgeMellanox/Dell
sw-spine-001: |
interface ethernet 1/1 speed 10G force
interface ethernet 1/1 description "sw-spine02-1/16"
interface ethernet 1/1 no switchport force
interface ethernet 1/1 ip address 10.102.255.14/30 primary
interface ethernet 1/1 dcb priority-flow-control mode on force
ip route vrf default 0.0.0.0/0 10.102.255.13
sw-spine-002: |
interface ethernet 1/16 speed 10G force
interface ethernet 1/16 description "sw-spine01-1/16"
interface ethernet 1/16 no switchport force
interface ethernet 1/16 ip address 10.102.255.34/30 primary
interface ethernet 1/16 dcb priority-flow-control mode on force
ip route vrf default 0.0.0.0/0 10.102.255.33
sw-leaf-bmc-001: |
interface ethernet1/1/12
description sw-leaf-bmc-001:12==>cn003:2
no shutdown
switchport access vlan 4
mtu 9216
flowcontrol receive off
flowcontrol transmit off
spanning-tree bpduguard enable
spanning-tree port type edge
interface vlan7
description CMN
no shutdown
ip vrf forwarding Customer
mtu 9216
ip address 10.102.4.100/25
ip access-group cmn-can in
ip access-group cmn-can out
ip ospf 2 area 0.0.0.0To generate switch configuration with custom config injection.
canu generate switch config --csm 1.2 -a full --shcd FILENAME.xlsx --tabs INTER_SWITCH_LINKS,NON_COMPUTE_NODES,HARDWARE_MANAGEMENT,COMPUTE_NODES --corners J14,T44,J14,T48,J14,T24,J14,T23 --sls-file SLS_FILE --name sw-spine-001 --custom-config CUSTOM_CONFIG_FILE.yamlThis option allows you to generate swtich configs while preserving the lag #s of the previous running config.
The use case for this is if you have a running system and you don't want to take an outage to renumber the LAGs.
It requires a folder with the config/s backed up.
The recommended way to back these configs up is with Backup Network
canu generate switch config -a v1 --csm 1.0 --ccj ccj.json --sls-file sls_input_file.json --name sw-spine-001 --preserve ../backup_configs/
Details
To see all the lags that are generated, see lags
CANU can also generate switch config for all the switches on a network.
In order to generate network config, a valid SHCD or CCJ must be passed in and system variables must be read in from either CSI output or the SLS API. The instructions are exactly the same as the above Generate Switch Config except there will not be a hostname and a folder must be specified for config output using the --folder FOLDERNAME flag.
To generate switch config from a CCJ paddle run: canu generate network config --csm 1.2 --ccj paddle.json --sls-file SLS_FILE --folder FOLDERNAME
To generate switch config from SHCD run: canu generate network config --csm 1.2 -a full --shcd FILENAME.xlsx --tabs 'INTER_SWITCH_LINKS,NON_COMPUTE_NODES,HARDWARE_MANAGEMENT,COMPUTE_NODES' --corners 'J14,T44,J14,T48,J14,T24,J14,T23' --sls-file SLS_FILE --folder FOLDERNAME
canu generate network config --csm 1.2 -a full --shcd FILENAME.xlsx --tabs INTER_SWITCH_LINKS,NON_COMPUTE_NODES,HARDWARE_MANAGEMENT,COMPUTE_NODES --corners J14,T44,J14,T48,J14,T24,J14,T23 --sls-file SLS_FILE --folder switch_configPotential output:
sw-spine-001 Config Generated
sw-spine-002 Config Generated
sw-leaf-001 Config Generated
sw-leaf-002 Config Generated
sw-leaf-003 Config Generated
sw-leaf-004 Config Generated
sw-cdu-001 Config Generated
sw-cdu-002 Config Generated
sw-leaf-bmc-001 Config Generated
This option allows extension and maintenance of switch configurations beyond plan-of-record. A YAML file expresses custom configurations across the network and these configurations are merged with the plan-of-record configurations.
WARNING: Extreme diligence should be used applying custom configurations which override plan-of-record generated configurations. Custom configurations will overwrite generated configurations! Override/overwrite is by design to support and document cases where site-interconnects demand "nonstandard" configurations or a bug must be worked around.
The instructions are exactly the same as Generate Switch Config with Custom Config Injection
To generate network configuration with custom config injection run
canu generate network config --csm 1.2 -a full --shcd FILENAME.xlsx --tabs INTER_SWITCH_LINKS,NON_COMPUTE_NODES,HARDWARE_MANAGEMENT,COMPUTE_NODES --corners J14,T44,J14,T48,J14,T24,J14,T23 --sls-file SLS_FILE --folder switch_config --custom-config CUSTOM_CONFIG_FILE.yamlThis option allows you to generate swtich configs while preserving the lag #s of the previous running config.
The use case for this is if you have a running system and you don't want to take an outage to renumber the LAGs.
It requires a folder with the config/s backed up.
The recommended way to back these configs up is with Backup Network
canu generate network config --csm 1.0 -a full --shcd FILENAME.xlsx --tabs INTER_SWITCH_LINKS,NON_COMPUTE_NODES,HARDWARE_MANAGEMENT,COMPUTE_NODES --corners J14,T44,J14,T48,J14,T24,J14,T23 --sls-file SLS_FILE --folder switch_config --preserve FOLDER_WITH_SWITCH_CONFIGSAfter config has been generated, CANU can validate the generated config against running switch config. The running config can be from either an IP address, or a config file.
- To get running config from an IP address, use the flags
--ip 192.168.1.1 --username USERNAME --password PASSWORD. - To get running config from a file, use the flag
--running RUNNING_CONFIG.cfginstead.
After running the validate switch config command, you will be shown a line by line comparison of the currently running switch config against the config file that was passed in. You will also be given a list of remediation commands that can be typed into the switch to get the running config to match the config file. There will be a summary table at the end highlighting the most important differences between the configs.
- Lines that are red and start with a
-are in the running config, but not in the config file - Lines that are green and start with a
+are not in the running config, but are in the config file - Lines that are blue and start with a
?are attempting to point out specific line differences
To validate switch config run: canu validate switch config --ip 192.168.1.1 --username USERNAME --password PASSWORD --generated SWITCH_CONFIG.cfg
canu validate switch config --ip 192.168.1.1 --generated sw-spine-001.cfgPotential output:
hostname sw-spine-001
- ntp server 192.168.1.10
? ^
+ ntp server 192.168.1.16
? ^
vlan 1
vlan 2
- name RVR_NMN
? ----
+ name NMN
apply access-list ip nmn-hmn in
apply access-list ip nmn-hmn out
...
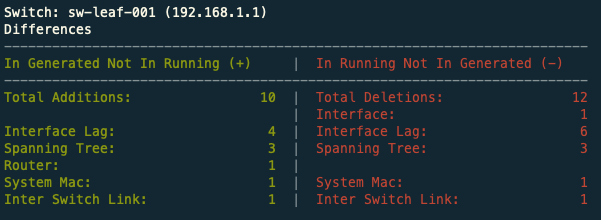
Switch: sw-leaf-001 (192.168.1.1)
Differences
-------------------------------------------------------------------------
In Generated Not In Running (+) | In Running Not In Generated (-)
-------------------------------------------------------------------------
Total Additions: 7 | Total Deletions: 7
Hostname: 1 | Hostname: 1
Interface: 2 | Interface: 1
Interface Lag: 1 | Interface Lag: 2
Spanning Tree: 2 | Spanning Tree: 3
Router: 1 |
Details
Aruba support only.
The validate network config command works almost the same as the above validate switch config command. There are three options for passing in the running config:
- A comma separated list of ips using
--ips 192.168.1.1,192.168.1. - A file of ip addresses, one per line using the flag
--ips-file ips.txt - A directory containing the running configuration
--running RUNNING/CONFIG/DIRECTORY
A directory of generated config files will also need to be passed in using --generated GENERATED/CONFIG/DIRECTORY. There will be a summary table for each switch highlighting the most important differences between the running switch config and the generated config files.
To validate switch config run: canu validate network config --ips-file ips.txt --username USERNAME --password PASSWORD --generated /CONFIG/FOLDER
canu validate network config --csm 1.2 --ips-file ips.txt --generated /CONFIG/FOLDERPotential output:
Switch: sw-leaf-001 (192.168.1.1)
Differences
-------------------------------------------------------------------------
In Generated Not In Running (+) | In Running Not In Generated (-)
-------------------------------------------------------------------------
Total Additions: 7 | Total Deletions: 7
Hostname: 1 | Hostname: 1
Interface: 2 | Interface: 1
Interface Lag: 1 | Interface Lag: 2
Spanning Tree: 2 | Spanning Tree: 3
Router: 1 |
Switch: sw-spine-001 (192.168.1.2)
Differences
-------------------------------------------------------------------------
In Generated Not In Running (+) | In Running Not In Generated (-)
-------------------------------------------------------------------------
Total Additions: 3 | Total Deletions: 2
Interface: 2 | Interface: 1
Interface Lag: 1 |
...
Errors
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
192.168.1.3 - Timeout error connecting to switch 192.168.1.3, check the entered username, IP address and password.
To output the results of the config validation command to a file, append the --out FILENAME flag. To get the results as JSON, use the --json flag.
There are several commands to help with the canu cache:
canu cache locationwill tell you the folder where your cache is locatedcanu cache printwill print a colored version of your cache to the screencanu cache deletewill delete your cache file, the file will be created again on the next canu command
CANU has the ability to run a set of tests against all of the switches in the management network. It is utilizing the nornir automation framework and additional nornir plugins to do this.
More info can be found at
- https://nornir.tech/2021/08/06/testing-your-network-with-nornir-testsprocessor/
- https://github.com/nornir-automation/nornir
- https://github.com/dmulyalin/salt-nornir
Required Input You can either use an SLS file or pull the SLS file from the API-Gateway using a token.
--sls-file--auth-token
Options
--logoutputs the nornir debug logs--network [HMN|CMN]This gives the user the ability to connect to the switches over the CMN. This allows the use of this tool from outside the Mgmt Network. The default network used is the HMN.--jsonoutputs the results in json format.--passwordprompts if password is not entered--usernamedefaults to admin
Additional tests can be easily added by updating the .yaml file at canu/test/*/test_suite.yaml
More information on tests and how to write them can be found at https://nornir.tech/2021/08/06/testing-your-network-with-nornir-testsprocessor/
Example test
- name: Software version test
task: show version
test: contains
pattern: "10.08.1021"
err_msg: Software version is wrong
device:
- cdu
- leaf
- leaf-bmc
- spineThis test logs into the cdu, leaf, leaf-bmc, and spine switches and runs the command show version and checks that 10.09.0010 is in the output. If it's not the test fails.
Canu can backup the running configurations for switches in the management network.
It backs up the entire switch inventory from SLS by defualt, if you want to backup just one switch use the --name flag.
Required Input You can either use an SLS file or pull the SLS file from the API-Gateway using a token.
--sls-file--folder"Folder to store running config files"
Options
--logoutputs the nornir debug logs--network [HMN|CMN]This gives the user the ability to connect to the switches over the CMN. This allows the use of this tool from outside the Mgmt Network. The default network used is the HMN.--passwordprompts if password is not entered--usernamedefaults to admin--unsanitizedRetains sensitive data such as passwords and SNMP credentials. The default is to sanitize the config.--nameThe name of the switch that you want to back up. e.g. 'sw-spine-001'
Example
canu backup network --sls-file ./sls_input_file.json --network CMN --folder ./ --unsanitizedPotential output:
Running Configs Saved
---------------------
sw-spine-001.cfg
sw-spine-002.cfg
sw-leaf-001.cfg
sw-leaf-002.cfg
sw-leaf-003.cfg
sw-leaf-004.cfg
sw-leaf-bmc-001.cfg
sw-leaf-bmc-002.cfg
sw-cdu-001.cfg
sw-cdu-002.cfg
Canu can send commands to the switches via the CLI.
This is primarily used for show commands since we do not elevate to configuration mode.
You can either use an SLS file or pull the SLS file from the API-Gateway using a token.
--sls-file--logoutputs the nornir debug logs--network [HMN|CMN]This gives the user the ability to connect to the switches over the CMN. This allows the use of this tool from outside the Mgmt Network. The default network used is the HMN.--commandcommand to send to the switch/switches.--passwordprompts if password is not entered--usernamedefaults to admin--nameThe name of the switch that you want to back up. e.g. 'sw-spine-001'
Examples
canu send command --sls-file ./sls_input_file.json --network cmn --command "show banner exec" --name sw-spine-001
-netmiko_send_command************************************************************
* sw-spine-001 ** changed : False **********************************************
vvvv netmiko_send_command ** changed : False vvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvv INFO
###############################################################################
# CSM version: 1.2
# CANU version: 1.3.2
###############################################################################
^^^^ END netmiko_send_command ^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^canu send command --command 'show version | include "Version :"'
\netmiko_send_command************************************************************
* sw-leaf-bmc-001 ** changed : False *******************************************
vvvv netmiko_send_command ** changed : False vvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvv INFO
Version : FL.10.09.0010
^^^^ END netmiko_send_command ^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^
* sw-spine-001 ** changed : False **********************************************
vvvv netmiko_send_command ** changed : False vvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvv INFO
Version : GL.10.09.0010
^^^^ END netmiko_send_command ^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^
* sw-spine-002 ** changed : False **********************************************
vvvv netmiko_send_command ** changed : False vvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvv INFO
Version : GL.10.09.0010
^^^^ END netmiko_send_command ^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^Canu reports the version of configuration on the switch. It reads the exec baner of all the switches and outputs to the screen.
Options
--sls-file--network [HMN|CMN]This gives the user the ability to connect to the switches over the CMN. This allows the use of this tool from outside the Mgmt Network. The default network used is the HMN.--passwordprompts if password is not entered--usernamedefaults to admin
Example
canu report network version --sls-file ../sls_input_file.json --network cmn
Password:
SWITCH CANU VERSION CSM VERSION
sw-spine-001 1.5.12 1.2
sw-spine-002 1.5.12 1.2
sw-leaf-bmc-001 1.5.12 1.2canu send command --command 'show version | include "Version :"'
\netmiko_send_command************************************************************
* sw-leaf-bmc-001 ** changed : False *******************************************
vvvv netmiko_send_command ** changed : False vvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvv INFO
Version : FL.10.09.0010
^^^^ END netmiko_send_command ^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^
* sw-spine-001 ** changed : False **********************************************
vvvv netmiko_send_command ** changed : False vvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvv INFO
Version : GL.10.09.0010
^^^^ END netmiko_send_command ^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^
* sw-spine-002 ** changed : False **********************************************
vvvv netmiko_send_command ** changed : False vvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvv INFO
Version : GL.10.09.0010
^^^^ END netmiko_send_command ^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^canu-inventory is a dynamic inventory script that queries a sls_input_file.json in the working directory, or an API gateway ($SLS_API_GW). It can be called directly to print the information or it can be passed as an argument to ansible-inventory.
$SLS_API_GWand$SLS_TOKEN(or$TOKEN) must be set in order to query the API.$SWITCH_USERNAMEand$SWITCH_PASSWORDmust be set in order to execute playbooks.ANSIBLE_HOST_KEY_CHECKING=Falsecan be set to ignore host key checking.-e config_foldershould be set to the directory containing the switch configs.
# examples
ansible-inventory -i canu-inventory --list
ansible-playbook -i canu-inventory aruba-aoscx.yml -e config_folder=/switch_configsWhen running the playbook you may need to input the full path to canu-inventory, the playbook, and the switch configs.
# example
ansible-playbook -i /Users/bin/canu-inventory /Users/bin/canu/inventory/plays/aruba-aoscx.yml -e config_folder=/Users/canuIf using the API, $TOKEN or $SLS_TOKEN need to be set.
If running this from outside the cluster over the CMN, $REQUESTS_CA_BUNDLE needs to be set
pip3 uninstall canu
To run the full set of tests, linting, coverage map, and docs building run:
python3 -m pip install .[ci]noxTo just run tests:
nox -s testsTo just run linting:
nox -s lintTo run a specific test file:
nox -s tests -- tests/test_report_switch_firmware.pyTo reuse a session without reinstalling dependencies use the -rs flag instead of -s.
- Create rootless
canucontainer image - Add a
canuctlwrapper command
- Fix link to generate switch configuration documentation.
- Add better LLDP data error handling for
canu report network cablingandcanu validate network cabling. - Refine error messaging for failed logins.
- Detect and respond to a rare condition where LLDP queries to Mellanox switches succeed, but the return data is not JSON.
- Bump netmiko version
- Bump nornir_netmiko version
- Fix canu test and canu validate bgp
- Add viz node to v2 TDS architecture.
- Modify ansible playbook to work with aruba 6300s.
- Updated Aruba ansible playbook and documentation.
- Added ansible play to retain mgmt interface configuration. This will help avoid lockouts.
- Added ansible play utilize the aruba checkpoint feature. This will revert the switch config after 1 minute if the switch becomes unresponsive.
- Modify nmn-hmn ACL to block traffic between the NMNLB and HMNLB networks.
- Add the ability to generate NMN configs for application nodes (v1 architecture).
- Added dynamic ansible inventory script, installed as
canu-inventory. - Added a playbook to validate/upload a config.
- Add viz node to v1 architecture
- Fix a bug where
bmcslots were allowed non-existent port3. - Remove confusing references to "bi-directional" in warnings and errors.
- Change versioning of flake8-commas to break dependency loop.
- Add logging to
validate paddle. - Begin refactoring the model to better validate and pick slot/port/speed requests.
- Enhance node connection exception messaging in the model.
- Fix login node shasta name for v1 architecture
- Added gpu and kvm node definitions to v1 architecture.
- Added logging to
canu generate switch/network configto clean up output. - Provided better messaging about next-step handling of missing configs in generated files.
- Fix the CANU model to allow "cable swapping" while using LLDP data.
- Add gpu node definitiions to v2 TDS architecture.
- Provide better guidance during SHCD validation if port re-use/change is attempted.
- Update generated docs from template changes.
- Fix sls_utils so that it works correctly when using a SLS.json file.
- Shutdown UAN CAN port when CHN is enabled.
- Remove Control Plane ACL for CSM 1.2 previousl missed.
- Update Arista BGP templates
- Add feature flag for CHN BGP control plane
- Fix ordering of switch configuration when using custom switch configs or
--reorder
- Change UAN port config to be a trunk port on mellanox (prevously hybrid port).
- Remove Control Plane ACL for CSM 1.3.
- Add BGP multipath to mellanox default VRF.
- Add Arista ISL to the Model
- Update MTN VLAN descriptions on CDU switches
- Update Arista configs to match slingshot docs
- Add datamover to canu model
- Add LNET, datamover to config generation
- Fix a bug where destination port reuse was incorrectly allowed for
validate shcdandvalidate paddle
- Fix switch firmware version for 1.2 and 1.3
- Fix JSON output with canu test
- Add canu test --ping
- Add additional tests for dellanox
- Remove CPU and memory, and ip helper test from aruba
- Add the ability to have multiple CSM versions for tests
- Add sls_utils
- Support SLS query in CANU container that works both in and out of Kubernetes
- Fix CSM 1.2 UAN template when CHN is used - do not produce None VLAN.
- Bump docs generated from code.
- Change exception-handling in
canu validate shcdand fromnetwork_modeling. - Provide better next steps from errors reported while validating SHCDs.
- canu test add ping test for KEA
- Update to release process
- Enabling 1.3 configuration templates.
- Ensure location rack and elevation strings are lower case.
- Add 4 port OCP to templates.
- Add GPU node to model.
- Use Scrapli instead of Netmiko to SSH to Aruba switches when using Nornir.
- Add additional tests to the aruba test suite.
- Add dell CDUs to test suite.
- Add CSM version flag to
canu test
- Fix 1.3 template links.
- Fix VLAN ordering of CMM ports.
- Add Customer ACLs back to 1.3 templates.
- Add SSH ACLs to dellanox.
- Fix Dell CMN-CAN ACL.
- Remove CMN from UAN 1.3 template.
- Add KVM to HPE model.
- Create initial CSM 1.3 configuration framework.
- Remove Metallb IP ranges from ACLs.
- Remove CAN-CMN ACLs from VLAN interfaces.
- Add CMN VLAN to UAN template for Mellanox & Aruba.
- Use full
show runcommands to retrieve running config fromcanu network backup - UAN CAN ports are now shutdown if CHN is enabled.
- Mellanox UAN CAN ports now only allow the CAN vlan.
- Added CMC subrack port configuration.
- Documentation updates to docs/network_configuration_and_upgrade
- Correct the 'slot warning' to specify more accurate options
- Disable load balacing configuration for Dell CDU/Leaf.
- Add
canu report network versionfeature. - Fix Errors in the output of
canu test
- Add route-map and prefixes to allow connection to UAI's from CAN network.
- Fix Dell4148 template to include correct port count
- Add netutils pyinstaller hook file.
- Create unique VSX system macs for each VSX cluster.
- Fixed Mellanox Customer ACL.
- Add VLAN 7 to Dellanox UAN for 1.0
- Fix canu paddle-file.json schema
- Change Rosetta/Columbia switch naming to be sw-hsn--<####> (as with PDU and CMM/CEC).
- Change switch port/interface descriptions to
dst:slot:port==>srcto avoid truncation. - Change gateway nodes to 4 port 1G OCP card definitions.
- Add dvs and ssn nodes as 4 port 1G OCP card definitions.
- Change large memory node common name from
lmtolmem. - Beta release of
--reorderfor switch/network config generation where custom-config is not used.
- Added shellcheck GitHub action
- Bump ipython to 7.16.3 to remediate CVE
- Clean up Jenkins build
- Add ACL to block CHN <> traffic for CSM 1.2
- Add Route-Map to CMN BGP peers to restrict routes to only CMN IPs
- More verbose instructions for generating switch configs
- Add the ability to generate BGP config for Arista edge switches.
canu backup networkandcanu testnow checks for connectivity before running commands against the switch.- Refactored canu
test.py. - Fixed mellanox backup config. It requires
show running-config expandedvsshow run - Add test for out of sync LAG on aruba.
- Fixed mellanox ping test.
- Update base packages required by Canu to function and fix known CVE from paramiko
- Fixed aruba and dell 1.2 templates so CAN config is only generated when it's detected in SLS.
- Fix
canu generate --customandcanu generate --preserveusage with RPM, this requried a new pyinstaller hook file. - Remove MTU from mellanox templates
- Add negate commands to templates to remove switch defaults.
- Fix a couple
canu validateissues - Bump ttp version
- Add DNS test to canu/test. remove folder "network configuration and upgrade"
- Add
canu send commandfeature.
- Added new guide for network install
- Add the ability to preserve LAG #s when generating switch configs.
- Fix hard coded LAG numbers in templates.
- Fix hard coded VLAN IDs in templates.
- Remove unused Dellanox TDS templates.
- Fix BGP output of canu validate
- Ignore
user adminandsnmpv3config during canu validate
- fixed PDU and sw-hsn ports being generated for sw-leaf-bmc switches
- Define warnings variable as defaultdict(list) to handle invalid key errors
- Fix aruba banner output during canu validate
- shutdown unused ports by default on aruba 6300+dell+mellanox
- Removed the override feature
- Add feature to inject custom configs into generated switch configs
- Change Aruba banner from motd to exec
- Reordered the configuration output so that vlans are defined before being applied to ports.
- Fix Leaf-bmc naming corner case: leaf-bmc-bmc to leaf-bmc
- Fix OSPF CAN vlan for 1.2 in full/tds
- Fixed bug to allow canu to exit gracefully with sys.exit(1)
- Add network test cases
- Add network test cases for DNS and site connectivity
- Fixed missing DNS from Aruba switches
- Add NMN network for 1.0 to ssh allowed into switches because of BGP DOCS in 1.0 allowing it.
- Remove router ospfv3 from 1.0/1.2
- Fixed ACL, OSPF, BGP config files
- Fixed test templates for ACL, OSPF, BGP
- Change Aruba banner to match running config.
- Fix Canu test --network
- Add OSPF to vlan 1.
- Add 'ip ospf passive' to vlan 1,4.
- Fix test cases: test_generate_switch_config_aruba_csm_1_2.py | test_generate_switch_config_dellanox_csm_1_2.py.
- Fix missing OSPF configuration from VLAN 7 in /network_modeling/configs/templates/dellmellanox/1.2/*.
- Fix descriptions for MTL
- Config backup create /running.
- Add SHCD filename to paddle/ccj JSON to obtain originating SHCD version.
- Remove
canu config bgp, there is no need for this as it's configured duringcanu generated switch/network config - Move Aruba CMN ospf instance from 1 to 2.
canu validateoutput enahncements & bug fixes.- Template fixes/enhancements.
- Add
canu backup network
canu validate BGPnow has an option to choose what network to run against.- Remove
'lacp-individualfrom mellanox spine02. - Generate unique MAC address for each Mellanox magp virtual router.
- Update canu validate to user heir config diff and cleaner output.
- Add --remediate option for canu validate
- bump heir config version
- Fix Mellanox web interface command
- Remove hard coded BGP ASN #
- Add CMN to CAN ACL
- Level set CSM 1.0 templates with CSM 1.2 minus CMN, VRF, etc..
- Add banner motd to all switch configs with CSM and CANU versions.
- Add documentation to install from RPM (for SLES).
- Remove CMN ip helper on mellanox.
- Remove broken tests.
- Fix Aruba OSPF process.
- Mellanox dns command fix.
- Mellanox loopback command fix.
- Mellanox NTP command fix.
- Add ACLs to VLAN interfaces.
- Add maximum paths to mellanox BGP template for customer VRF.
- Fix Mellanox ISL speed setting.
- Fix PDU node recognition and naming:
pdu<#>, <cabinet>pdu<#>, <cabinet>p<#> all map to a name pdu-<cabinet>-<####> - Add large memory UAN node definitions:
lm-<####> maps to lm-<####> - Add gateway:
gateway<#>, gw<#> map to gateway-<####>
- fix sls url
- validate BGP now reads IPs from the SLS API
- Added a feature to run tests against a live network. (Aruba only)
- Enabled webui for mellanox.
- Added speed commands to dell/mellanox templates.
1.1.1 2022-12-07
- Updated pull_request_template.md
- Adjusted the STP timeout to 4 seconds from the default of 15.
- Changed setup.py file glob to follow previously updated Jinja2 template locations.
- Command line option --csi-folder has changed to --sls-file. Any SLS JSON file can be used.
- Installation via pip now supports non-developer modes. Pyinstaller binary and RPM now work as advertised.
- The directory of canu_cache.yaml is now dynamically configured in the user's home directory (preferred), or the system temporary directory depending on filesystem permissions.
- Added
canu cache locationprint the folder where your cache is located - Added
canu cache printto print a colored version of your cache to the screen - Added
canu cache deleteto delete the cache file, the file will be created again on the next canu command - Added Dell and Mellanox support to the
canu validate switch configcommand - Added Dell and Mellanox support to the
canu validate network configcommand - Added ability to compare two config files with
canu validate switch config - Added ability to compare two config folders with
canu validate network config - Added an
--overrideoption tocanu generate switch configandcanu generate network config, this allows users to ignore custom configuration so CANU does not overwrite it. - Changed the
-s --shastaflag to--csm - Added Mellanox support to the
canu config bgpcommand - Added Dell/Mellanox support to the
canu generate network config&canu generate switch configcommands - Updated
canu validate shcd-cablingto show port by port differences. - Updated the docs in the
/docsfolder to build automatically with nox - Added support for CMN (Customer Management Network) on Aruba and Dellanox.
- Added mgmt plane ACL on Aruba Switches
- Added Metallb networks to ACLs
- Removed the hardcoded VLAN variables, these are now being pulled in from SLS.
- Added 1.2 Aruba templates
- Added CANU validate switch config support for dellanox.
- BGP is now generated during
canu generateswitch/network config. (aruba &Mellanox) - Computes/HSN-bmcs/VizNodes/LoginNodes/pdus now have their switch config generated.
- Added SubRack support for reading in all variations from the SHCD, and added sub_location and parent to the JSON output
- Added Paddle / CCJ (CSM Cabling JSON) support. Commands
canu validate paddleandcanu validate paddle-cablingcan validate the CCJ. Config can be generated using CCJ. - Added the
jqcommand to the Docker image. - Added
canu testto run tests against the network (aruba only).
0.0.6 - 2021-9-23
- Added alpha version of schema-checked JSON output in
validate shcdas a machine-readable exchange for SHCD data. - Add ability to run CANU in a container, and update Python virtual environment documentation.
- Added
canu generate switch configto generate switch configuration for Aruba systems. - Added
canu generate network configto generate network configuration for Aruba systems. - Added
canu validate switch configto compare running switch config to a file for Aruba systems. - Added
canu validate network configto compare running network config to files for Aruba systems. - Updated naming conventions to
canu <verb> switch/network <noun> - Added the ability to fully track device slot and port assignments.
- Mountain hardware (CMM, CEC) is now being generated in the switch configurations.
- Fixed multiple templates to match what is on the Aruba switch, these include, UANs, Loopbacks, VLAN interfaces, ACLs.
- Known Limitations:
- PDUs are not yet properly handled in the generated switch configurations.
- Switch and SNMP passwords have been removed from generated configurations until the handling code is secure.
0.0.5 - 2021-5-14
- Updated license
- Updated the plan-of-record firmware for the 8360 in Shasta 1.4 and 1.5
- Added
config bgpcommand to update bgp configuration for a pair of switches.
0.0.4 - 2021-05-07
- Added
verify shcdcommand to allow verification of SHCD spreadsheets - Added
verify cablingcommand to run verifications on network IPs - Added additional documentation for each command, added docstring checks to lint tests, and updated testing feedback
- Added
verify shcd-cablingcommand to run verifications of SHCD spreadsheets against network IPs - Added
validate bgpcommand to validate spine switch neighbors
0.0.3 - 2021-04-16
- Cache firmware API calls to canu_cache.yaml file.
- Able to check cabling with LLDP on a switch using the
canu switch cablingcommand. - Cache cabling information to canu_cache.yaml file.
- For the
canu initcommand the CSI input now comes from thesls_input_file.jsoninstead of theNMN.yamlfile. - Able to check cabling with LLDP on the whole network using the
canu network cablingcommand.
0.0.2 - 2021-03-29
- Added ability to initialize CANU by reading IP addresses from the CSI output folder, or from the Shasta SLS API by running
canu init. The initialization will output the IP addresses to an output file. - Added ability for the network firmware command to read IPv4 address from a file using the --ips-file flag
- Added the --out flag to the switch firmware and network firmware commands to output to a file.
- Added the --json output to the network firmware command
- Full coverage testing
- Added --version flag
- Docstring checks and improvements
0.0.1 - 2021-03-19
- Initial release!
- Ability for CANU to get the firmware of a single or multiple Aruba switches
- Standardized the canu.yaml file to show currently supported switch firmware versions.