An Android application that uses Estimote beacons to help the user navigate an indoor environment.
Developed at Cossette in July-August 2016 and demonstrated to representatives from SickKids.
| Discovery | Search | Navigation |
|---|---|---|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
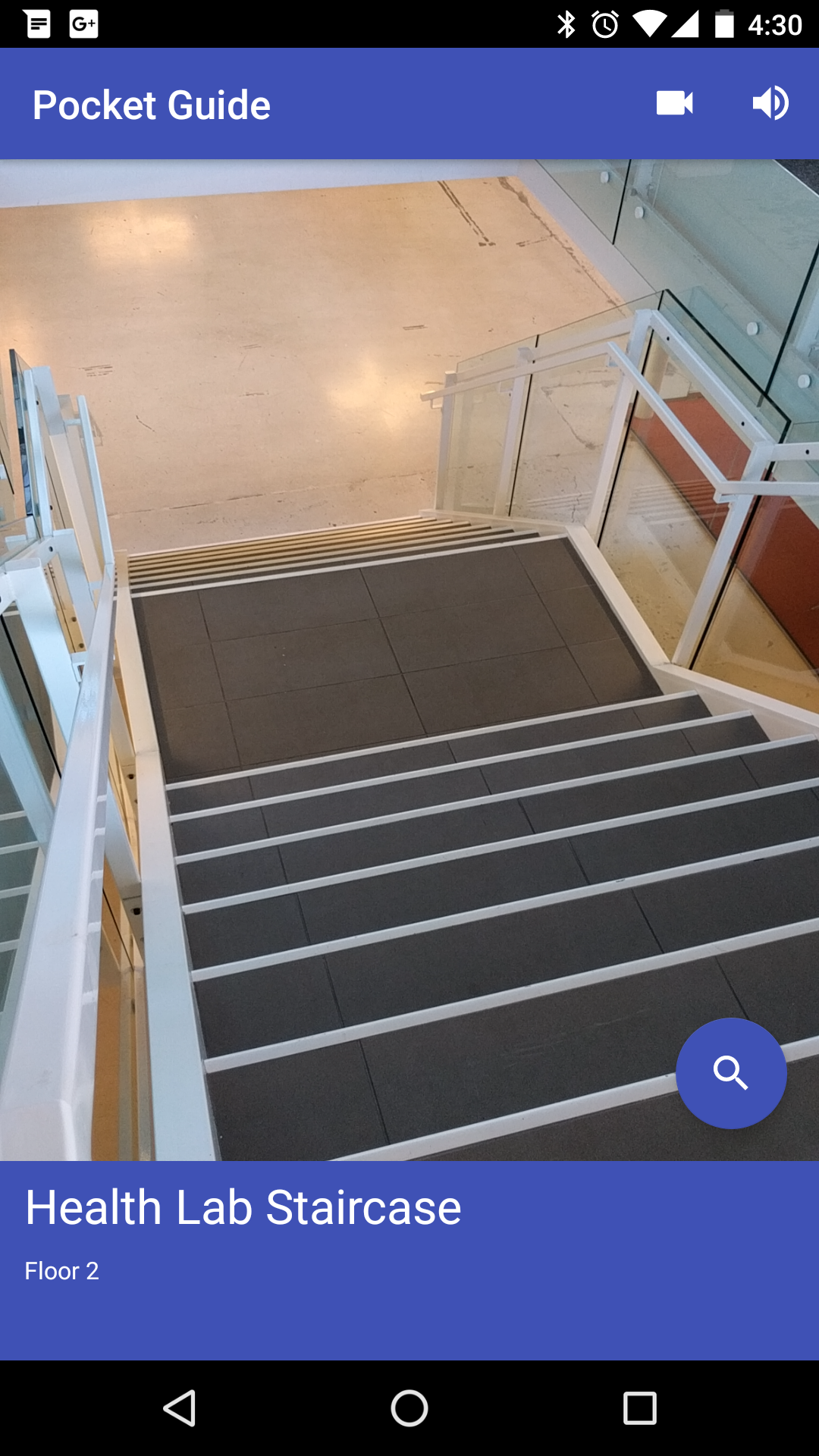
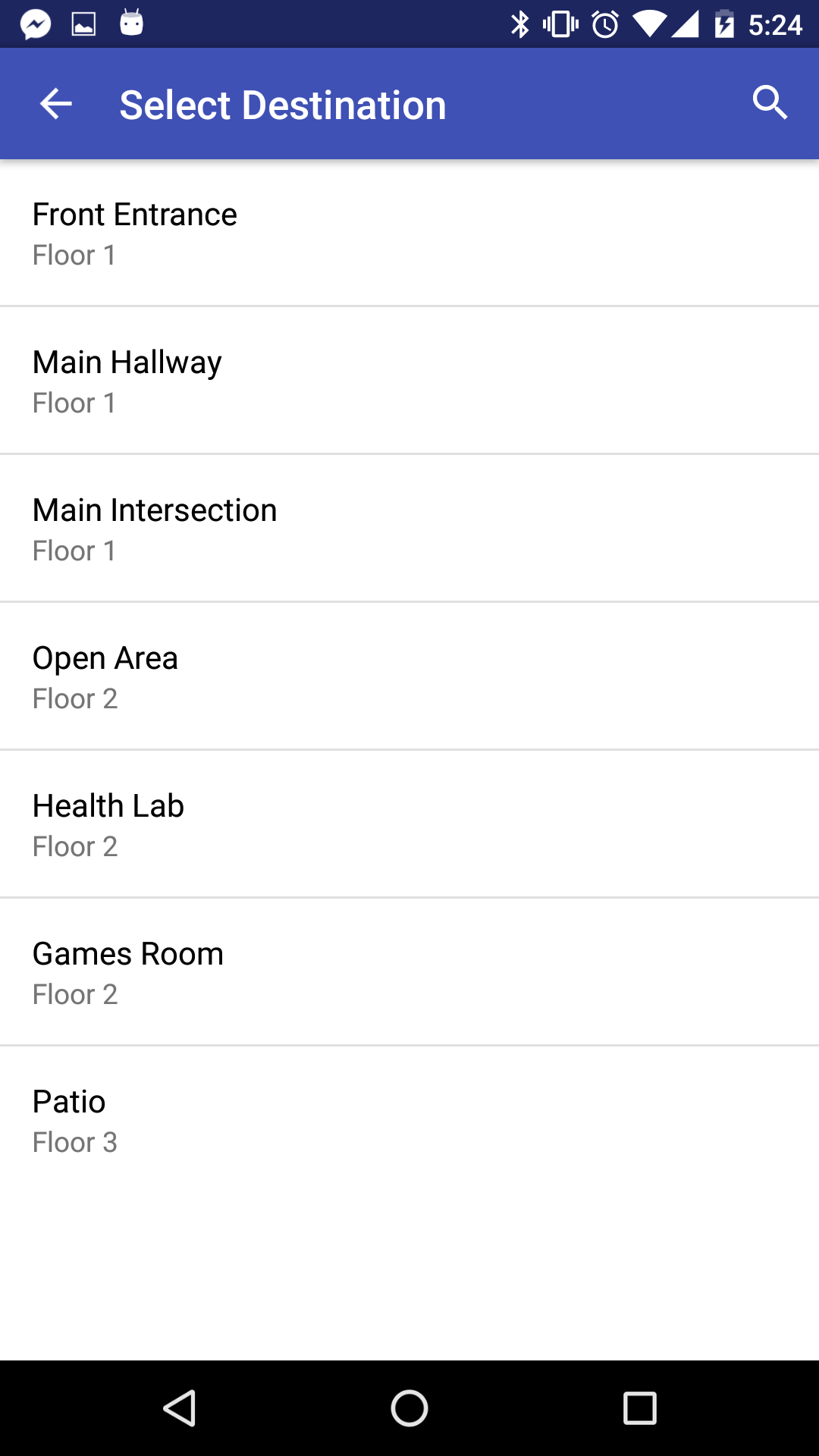
Shows the user their current floor and location.
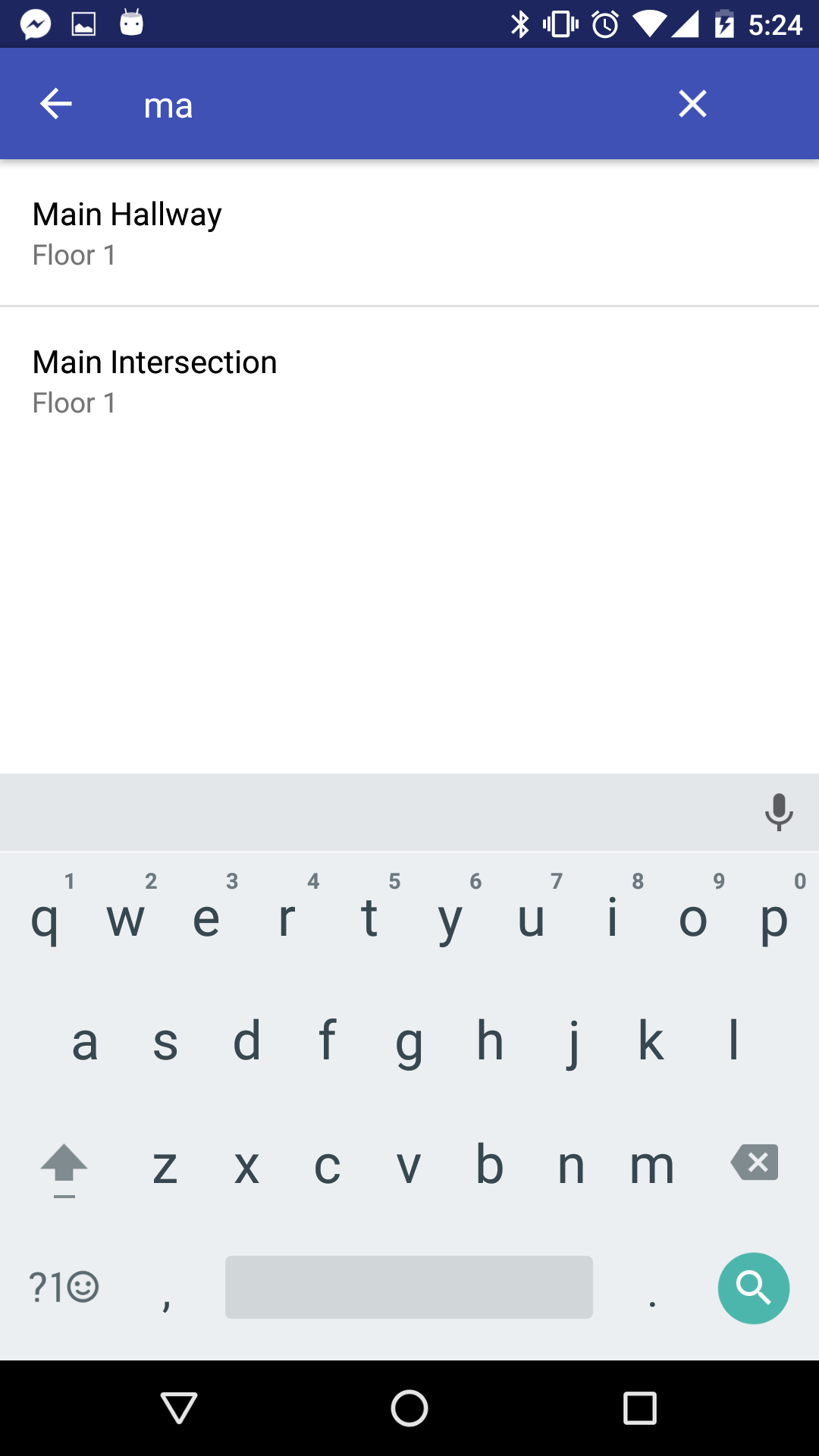
Allows the user to search for a place to navigate to.
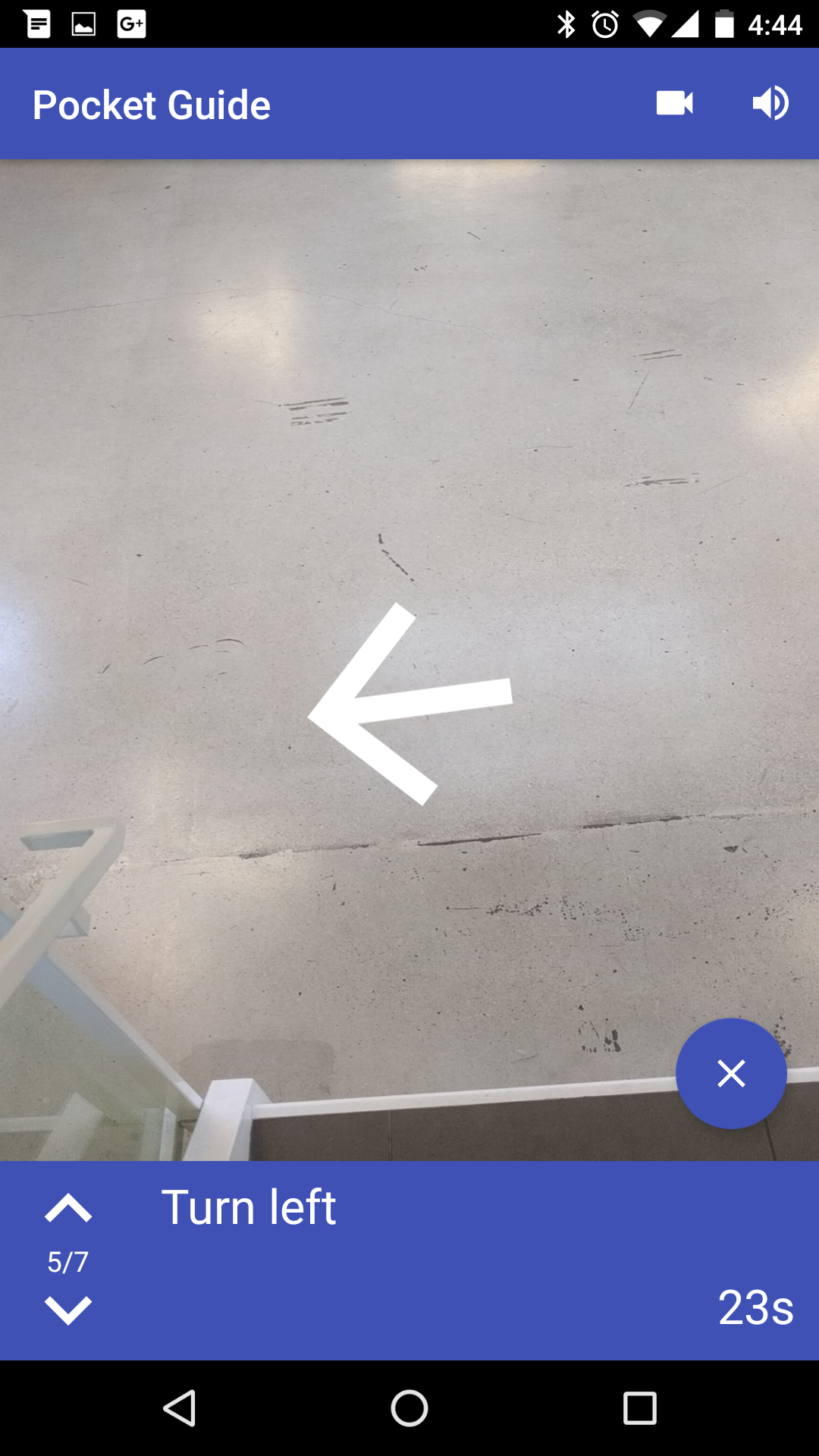
Provides turn-by-turn instructions to guide the user to their destination; uses text and audio instructions, on-screen arrows, and device vibrations.
See the beacons package; the ApplicationBeaconManager class manages and tracks beacons over time.
Each beacon broadcasts Bluetooth signals at 950ms intervals according to the iBeacon standard (https://developer.apple.com/ibeacon/, http://developer.estimote.com/ibeacon/). The application receives these signals and decides what to do based on the IDs and signal strength received.
Estimote Android SDK Documentation
Given the signal strength received from a beacon, the Estimote SDK provides an API that calculates the estimated distance to that beacon. The application uses a weighted average to better approximate the current distance to that beacon, with the most recent measurement having the greatest weight.
In discovery mode, the nearest estimated beacon is said to be the user's current location.
In navigation mode, the instructions change when the device is estimated to be within 3m of a beacon where the path changes.
Trilateration can be attempted, but is not accurate or reliable due to the beacons' weak signal strength, fluctuating measurements, and interference from floors, objects, and people.
See the map package; the Map class defines and manages the mapping data, which is based on a 3D grid system (x, y, and z axes).
- Define floors of the building
- z-position on the grid
- Correspond to Estimote beacons
- Belong to a floor
- x-y position on the grid
- ID numbers (UUID, major, minor)
Anchor Beacons - Placed at key intersection points between areas (e.g. doors, entrances/exits, stairs, elevators).
Support Beacons - Placed at other points.
- Define areas of the building
- Have a type (e.g. room, hallway, stairs, elevator)
- Can span multiple floors
- Must be defined so that the user can move between any two of its beacons in a straight line (necessary for the pathfinding algorithm)
- May be a destination the user can navigate to
All units are in metres and seconds.
See the pathfinding package; the Pathfinder and SPFA classes perform the shortest-path algorithm, while the NavigationStep, Path, and Step classes manage the navigation information.
The application uses SPFA and the mapping data to calculate the shortest path to the destination by time.
The map's graph is constructed using relationships between beacons and zones. Two beacons are connected in the graph if they share a common zone (can be moved between in a straight line). The connection weight is the travel time between the two beacons, calculated using the straight-line distance and average movement speed.
While not visible in the final application, debugging tools were used in development of this application.
See @+id/debug_view in content_main.xml and onCreate() in MainActivity.java to enable the debugging view that displays information on the main screen.
See @+id/action_debug in menu_main.xml to enable the information button on the main screen, which switches to a dedicated debugging screen when tapped.
Bruno Almeida: https://github.com/brunofalmeida
Gabriel Yeung: https://github.com/gabrielcyeung
Jacob Kelly: https://github.com/jacobjinkelly